Psych 255
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Brain
Produces behavior and what is affected by behavior
Behavior
An observable phenomenon produced by the nervous system that has both a cause and a function
three controversies
Nature vs nurture
Perspective on Brain and Behaviour
The evolution of evolution
Nature vs Nurture
both
Perspective on Brain and Behaviour
mentslism
Dualism
Materialism
Phones Gage
Mentalism-Aristotle
An explanation of behavior as a function of the nonmaterial mind
Dualism-Descartes
A nonmaterial mind and the material body contribute to behavior
Dualism-Rene Descartes
Mind regulates behavior by directing the flow of ventricular fluid to appropriate muscles (pineal body and ventricles)
Materialism
Behavior can be explained as a function of the nervous system without explanatory recourse to the mind
Phineas Gage
If you physical change the brain it will change who you are
The evolution of evolution
Evolution and Natural selection
Natural Selection (Darwin)
Organisms that have advantageous traits for the environment that they live in will be able to survive and procreate, thus passing on their advantageous traits to the next generation
Implications of natural selections
brains/ neurone are related
behaviours are related
complexity in brain and behaviour evolved gradually, in response toenvironmental demands & experience
How are traits selected naturally
Genetic variation —> Adaptive trait —> increases chances of survival —> trait passed on to offspring
Why study the brain and behavior?
Many behavioral disord
Dorsal
Up, above, or superior
Ventral
Down, Below, inferior
Lateral
Left, side
Medial
Right, Middle
Anterior
Front, rostral
Posterior
Behind, Tail, Caudal
Horizontal planes
Anterior to Posterior
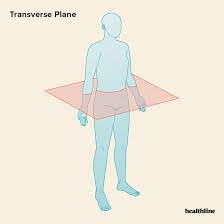
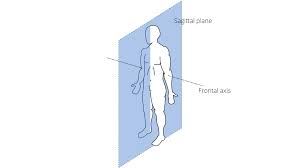
Sagittal planes
Lateral to Medial
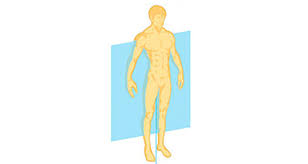
Coronal plane
Dorsal to Ventral
Contralateral
left motor cortex works the right hand) vise versa
Ipsilateral
right olfactory bulb works the right olfactory cortex) vise versa
Efferent
outgoing
Afferent
incoming
Create a sensory reality (first primary function)
Our sense organs receive information and send it to our brain and our brian interprets it and provides information to us about the world.
Integrate and store information (second primary function)
We hear something (take in information) we integrated in to understand it and we store it for X amount of time
Produce behavioral response (third primary function)
What we do after we hear the noise. We get up and check it out, we ignore it
Nervous system
Is made up of the brian, spinal cord, and nerves (cranial nerves and spinal nerves)
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal Cord (receives , processes, interprets, stores and responds to sensory information)
Spinal Cord
Spinal Reflex
Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic NS and Autonomic NS (affect nerves and effect nerves)
somatic NS
12 pairs of Cranial nerves
Sensory fibers
Dorsal side of spinal cord
Motor fibers
Ventral side of spinal cord
Sympathetic Nervous System
Initiates “fight or flight”response
Parasympathetic system
Allows body to “rest and digest
Meninges
dura mater
arachnoid layer
pia mater
layers of the head
skull
Meninges (dura mater, arachnoid layer, pia ater)
subarachnoid space filled with CSF)
Major Fissures
Central fissure
longitudinal fissure
lateral fissures
internal features
white matter
gray matter
ventricle
white matter
areas of the nervous system rich in fat-sheathed neural axon
grab matter
areas of the nervous system predominately composed of cell bodies and blood vessels
ventricle
a cavity in the brain that produces and contains cerebrospinal fluid
Ventricular system
lateral ventricles
third ventricle
fourth ventricle
Corpus callous
band of fibres connecting the two cerebral hemispheres
the brainstem
hindbrain
midbrain
diencephalon
hindbrain
cerebellum
medulla oblongata
pons
reticular formation
cerebellum
motor coordinations
cognitive functions
midbrain
tectum
tegmenjtum
tectum
superior colliculi —> visual
inferior colliculi —> auditory
diencephalon
hypothalamus
thalamus
forbrain
neocortex
limic system
basal ganglia
basal ganglia
important for controlling voluntary movements
limbic system
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Cingulate cortex
Amygdala
emotion processing
hippocampus
involved in memory and spatial navigation
Cingulate Cortex
cognitive and emotional processing
occipital lobe
visual functions
parietal lobe
movement programming
temporal lobe
auditory function
frontal lobe
ensures behavior is appropriate for context
neocortical maps
cytoarchitectonics used to make cortical maps
NS creates movement and perception
The nervous system creates a perceptual reality for each of us.. And allows us to act within this reality
The NS is forever changing (plasticity)
The brain is physically changed by experience
Many of the bairns circuits are crossed
Most sensory inputs to the brain and motor outputs from the brain are crossed
Functions are produced by Neuronal Circuits
Neurons don't working in isolation– rather function are reproduced by circuits of neurons working together
Brain is symmetric and asymmetric
Structural asymmetry
Planum temporale
Structural symmetry
Primary sensory and motor cortices
Functional asymmetry
Language vs. music and prosody
Functional symmetry
Sensory and motor control
Hierarchical and parallel origination
Sensory and motor processing occurs at multiple levels of the CNS
Sensory and motor divisions
Peripheral nervous system
Spinal nerves
Cranial nerves
Central nervous system
Spinal cord all the way up to the cortex
Sensory input divided for object recognition and motor control
Sensory information is used for
These processes take place in parallel, in distinct neural regions
Function Localized and distributed
Basic functions are localized (controlled by a specific brian area)
Whereas complex functions are distributed (multiple localized areas play a role in the function)
Brain uses excitation and inhibition
Brain work is using both excitation and inhibition