central nervous system
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
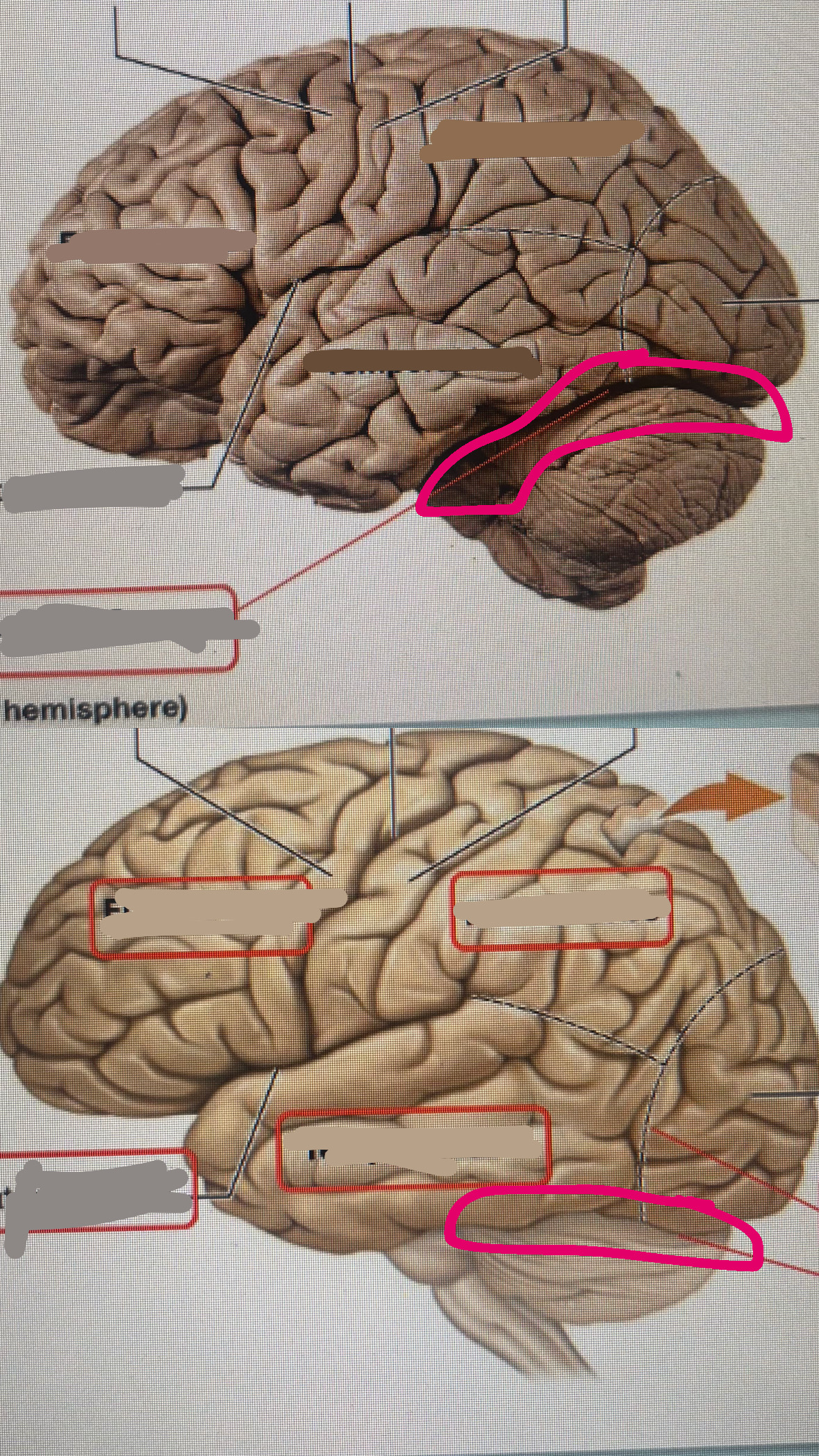
temporal lobe
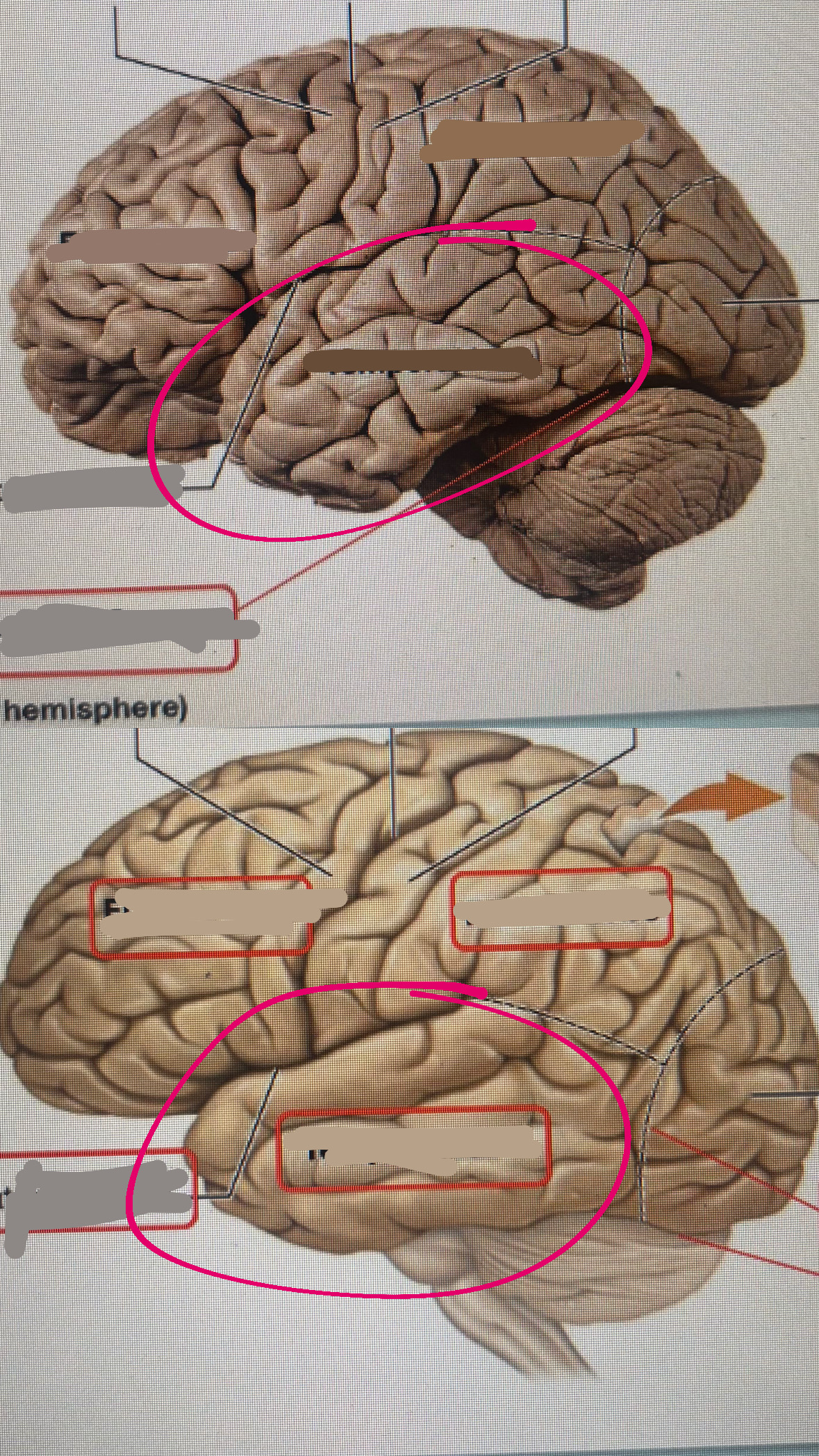
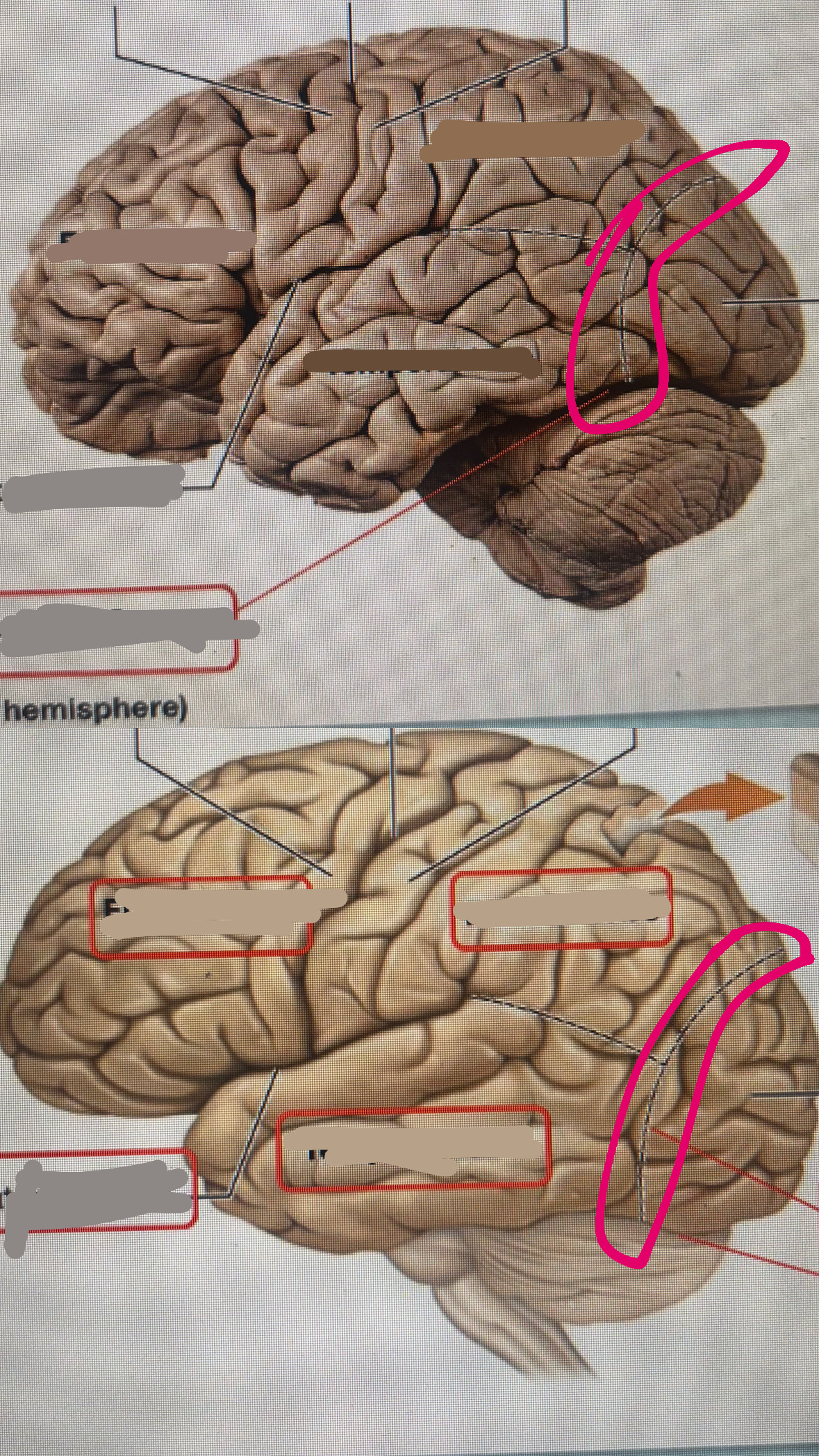
lateral fissure
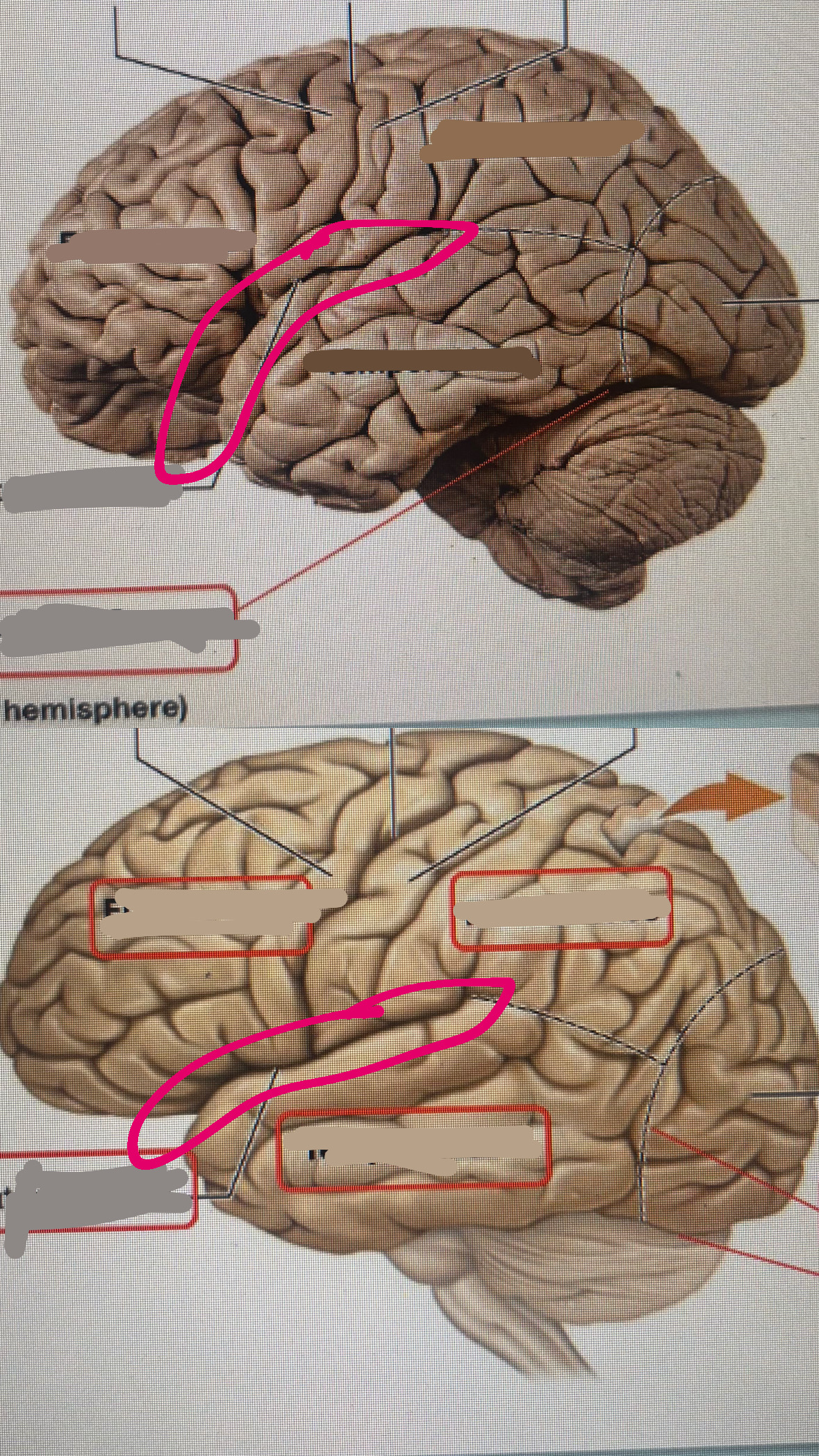
frontal lobe
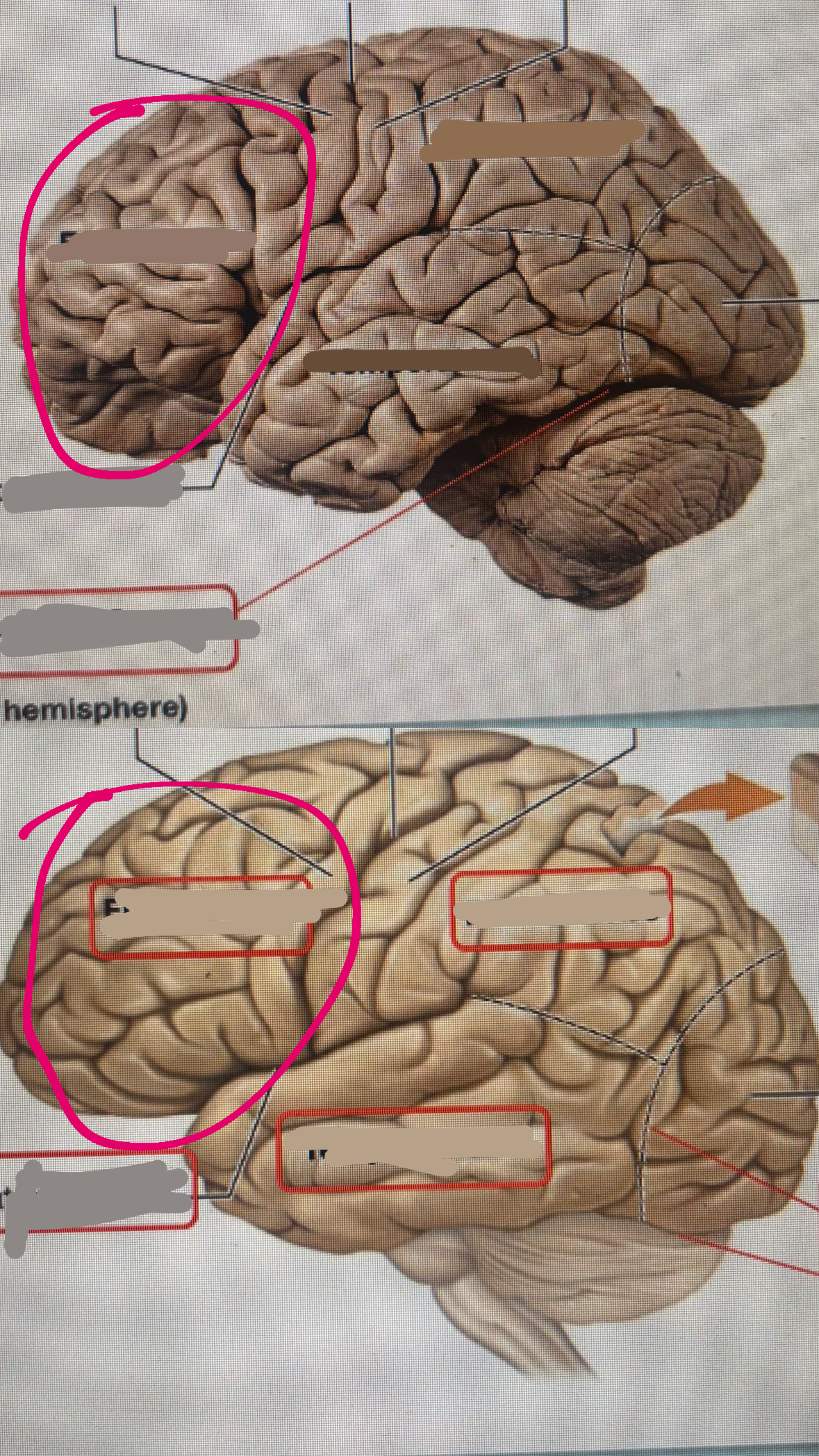
precentral gyrus
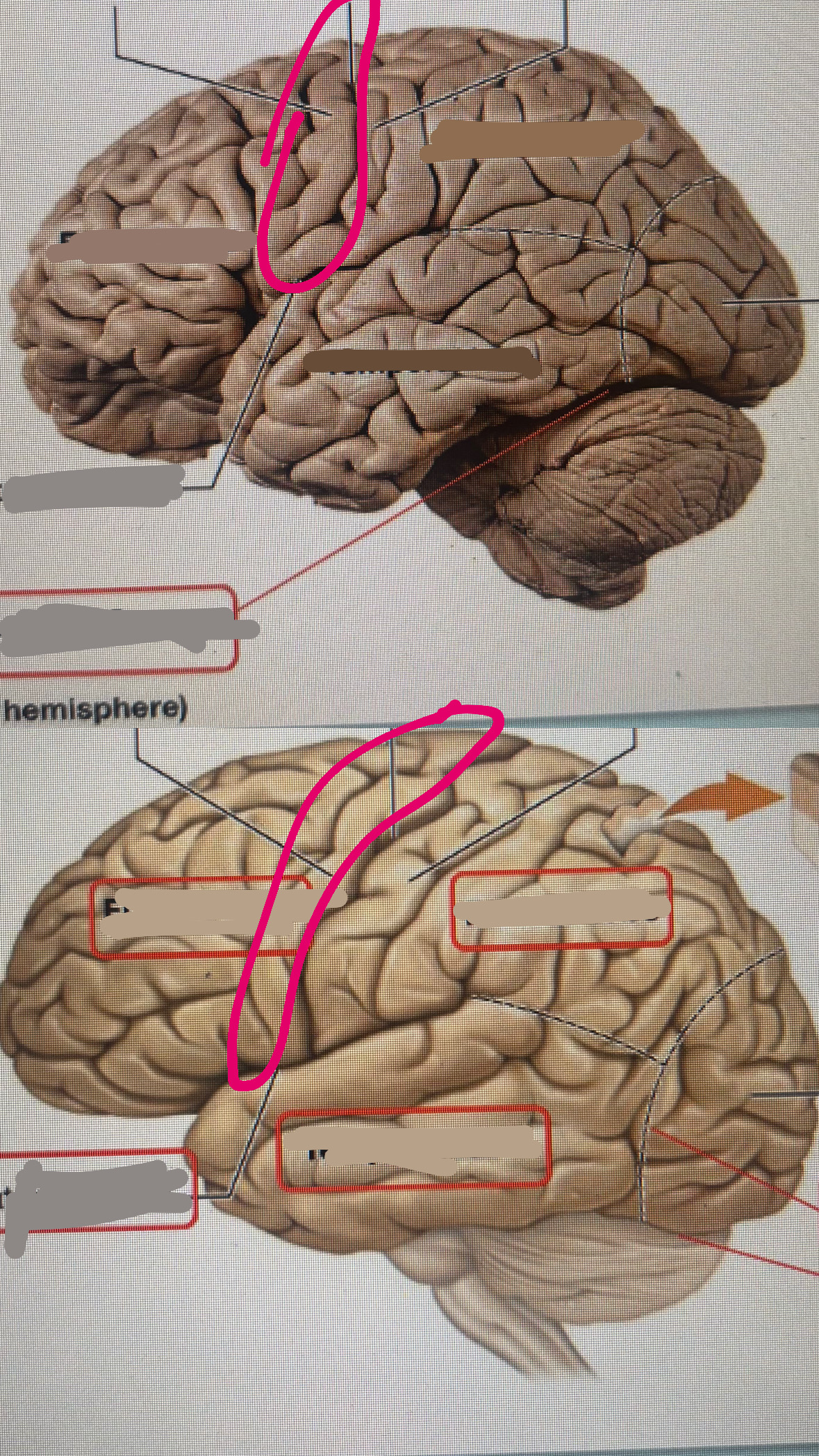
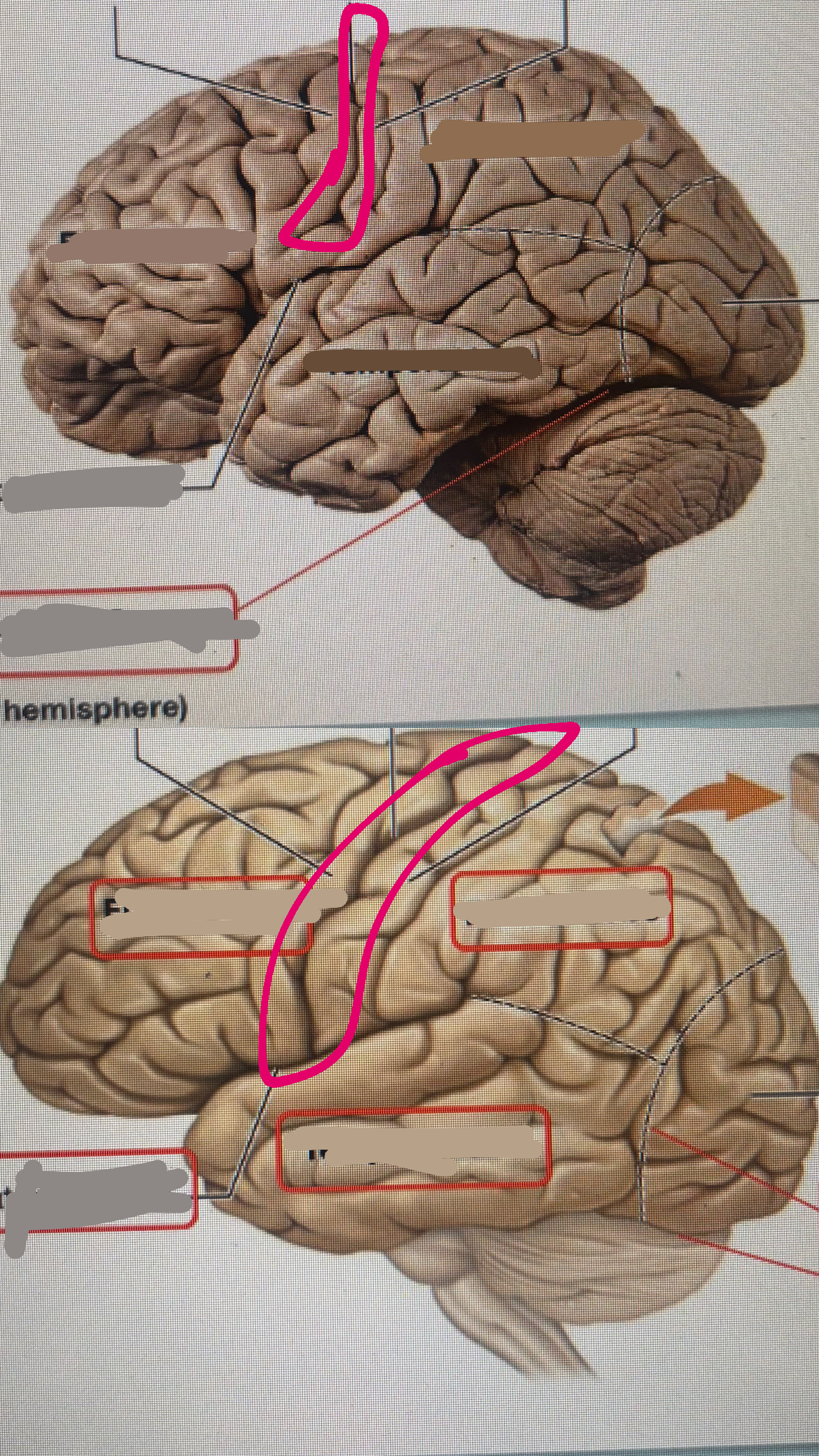
central sulcus
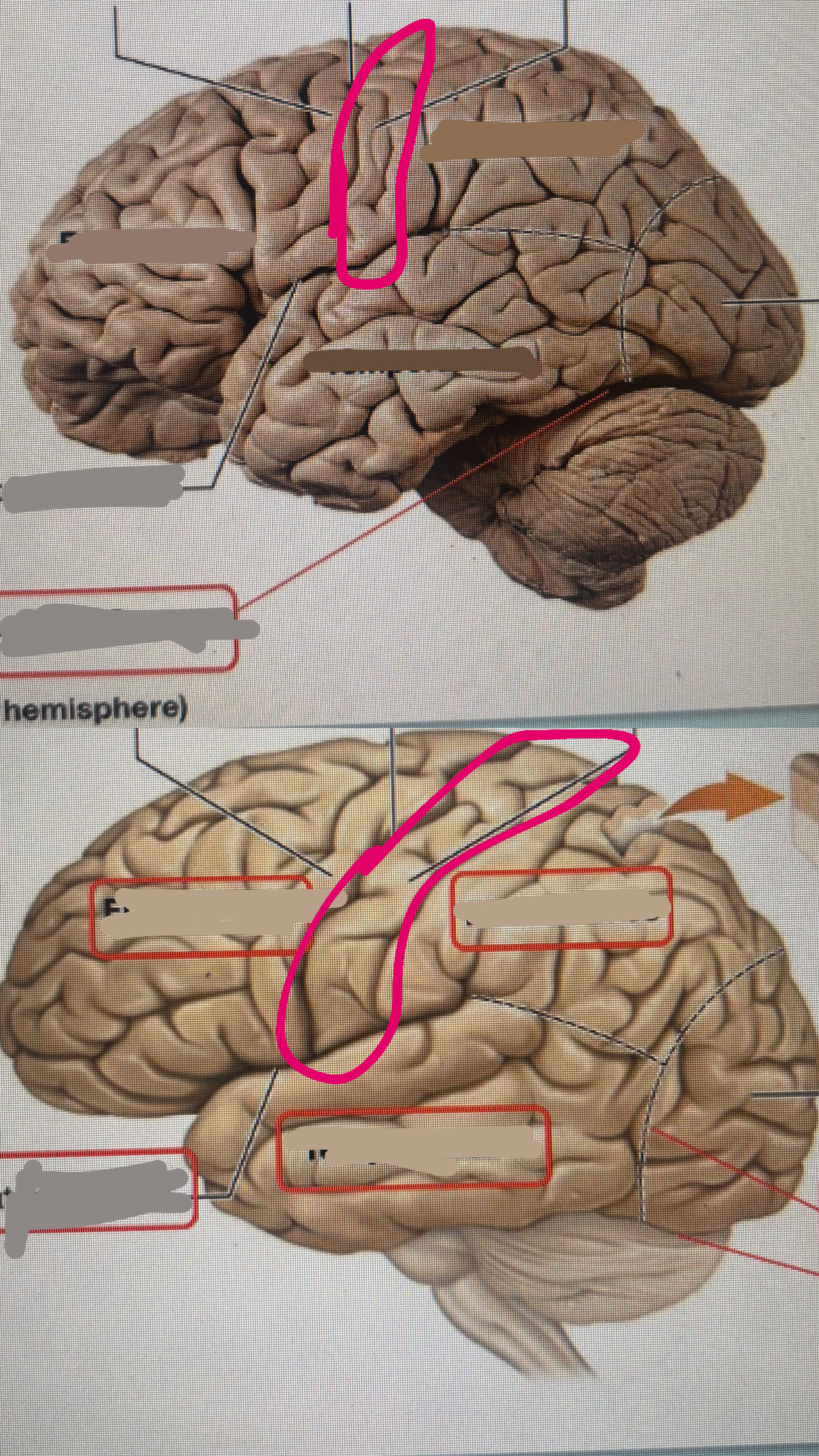
postcentral gyrus
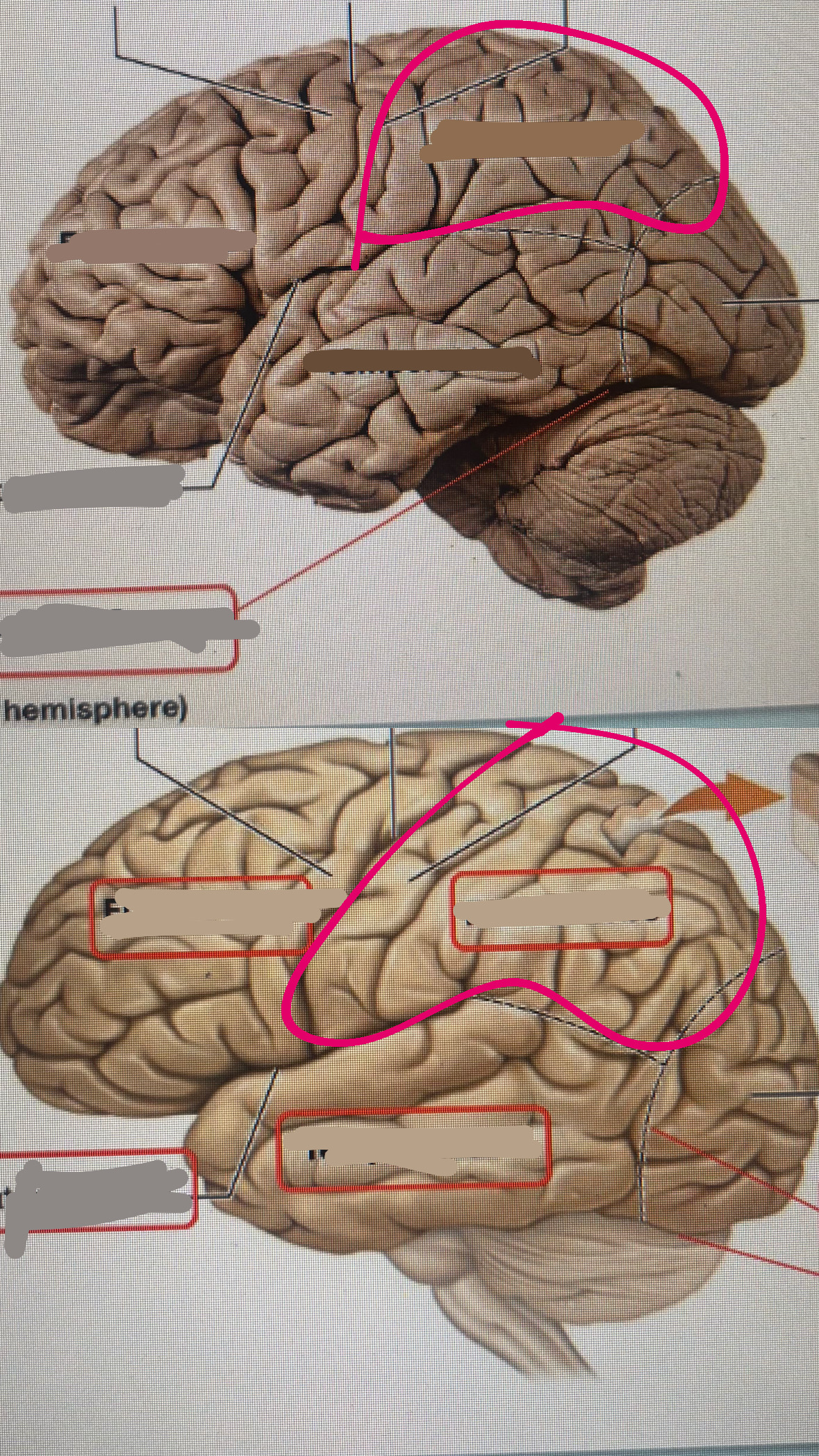
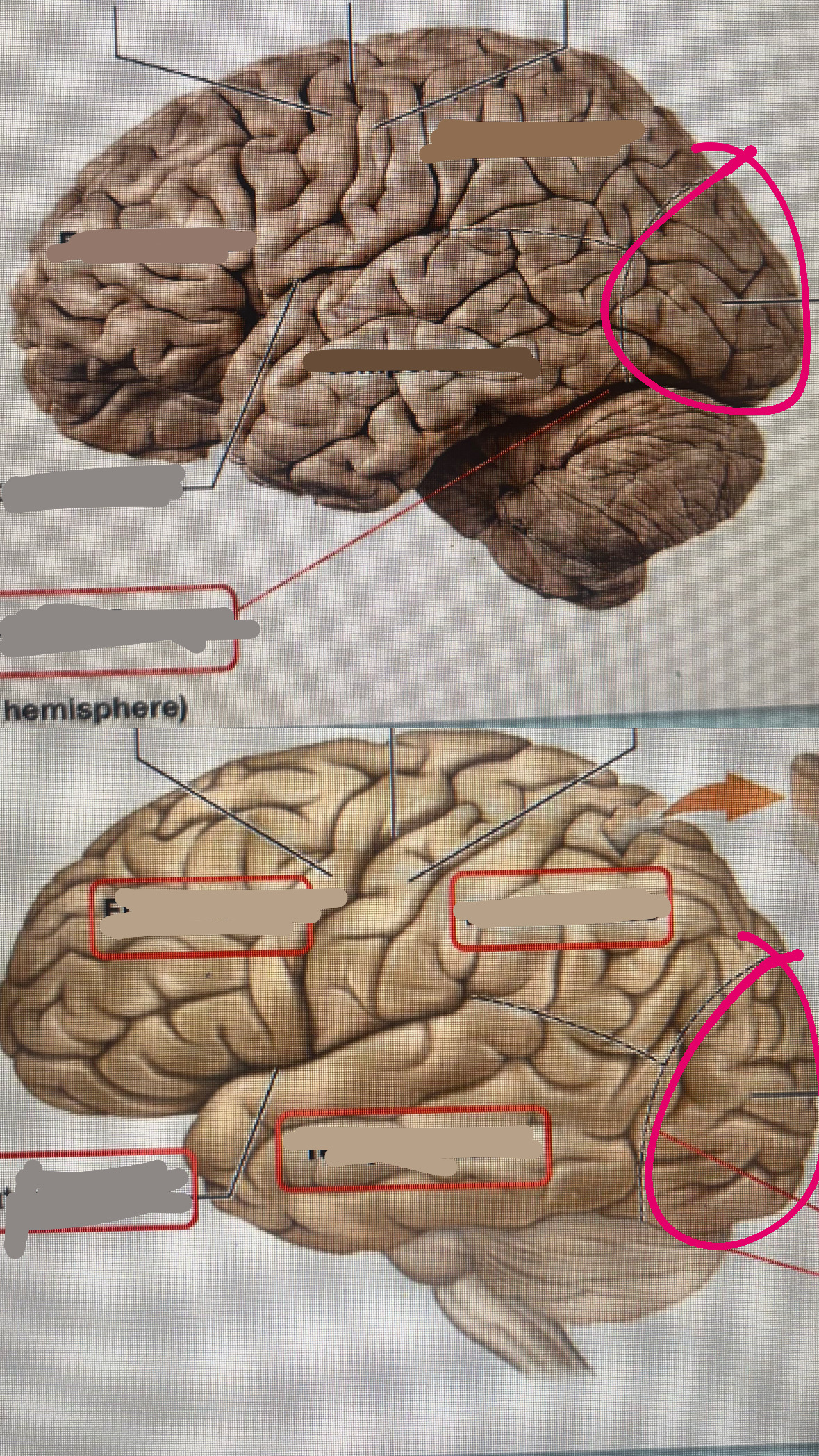
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
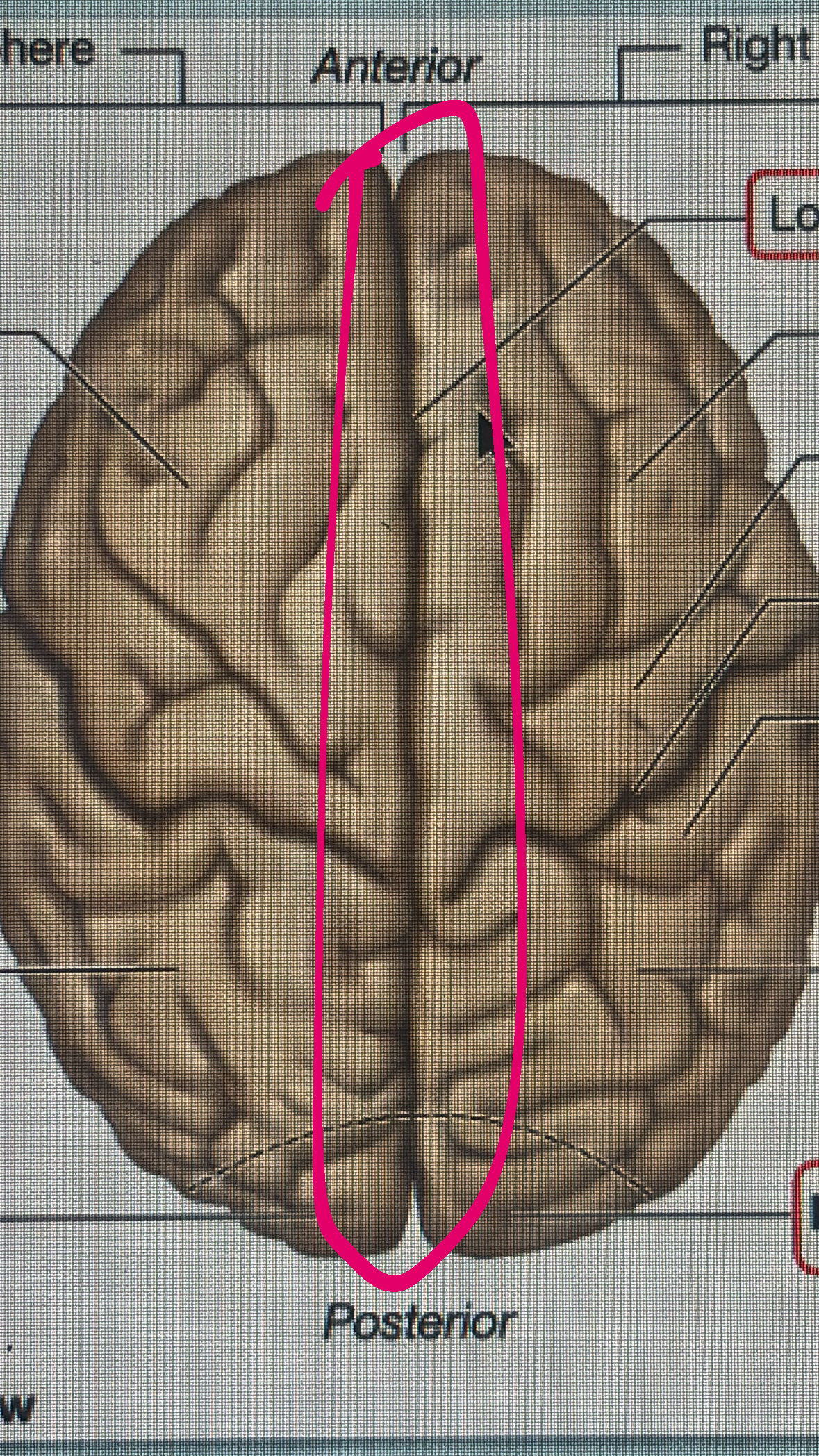
transverse cerebral fissure
parieto occipital sulcus
sulcus

gyrus
longitudinal fissure
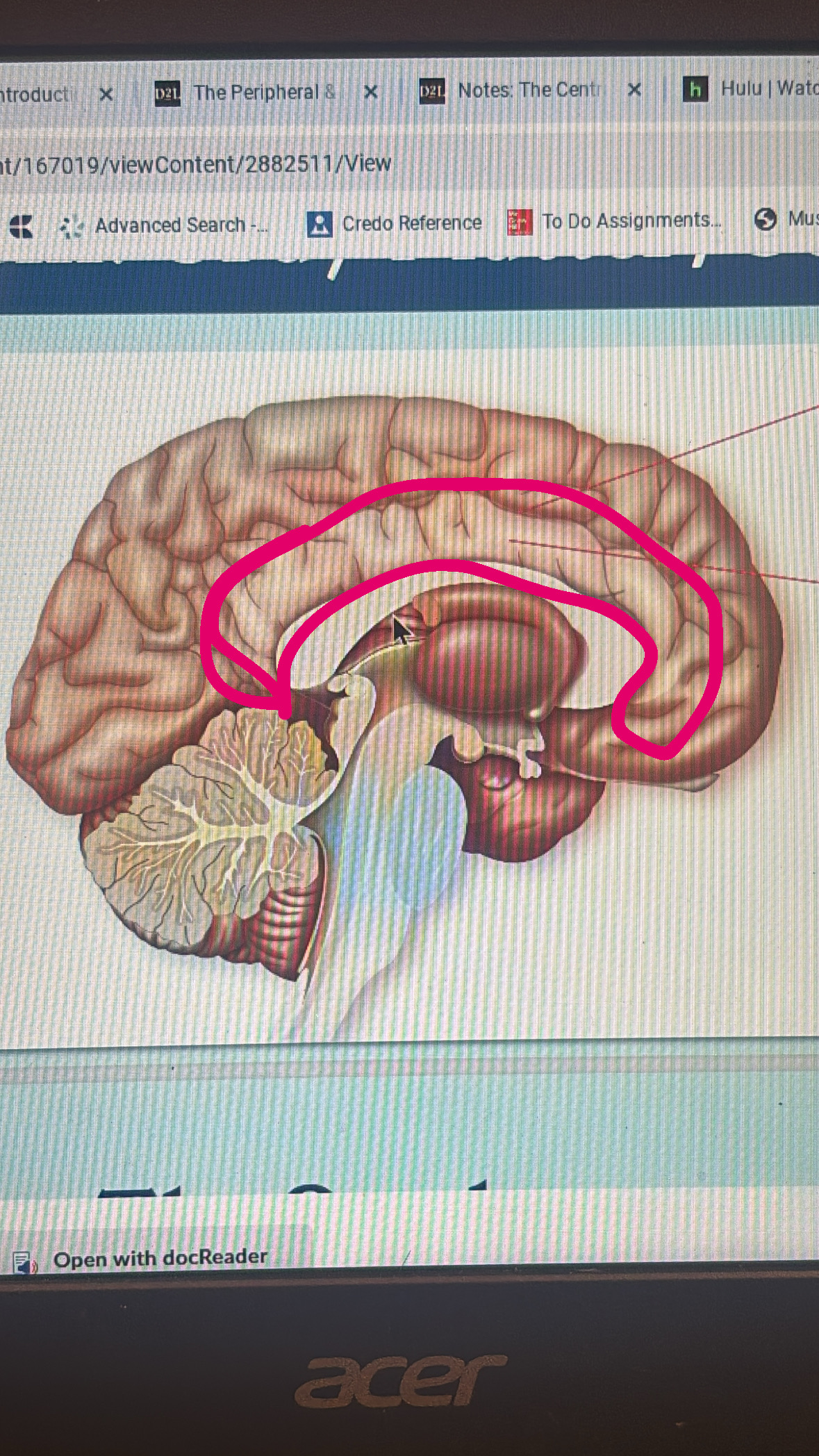
cingulate sulcus
line that separates the cingulate gyrus
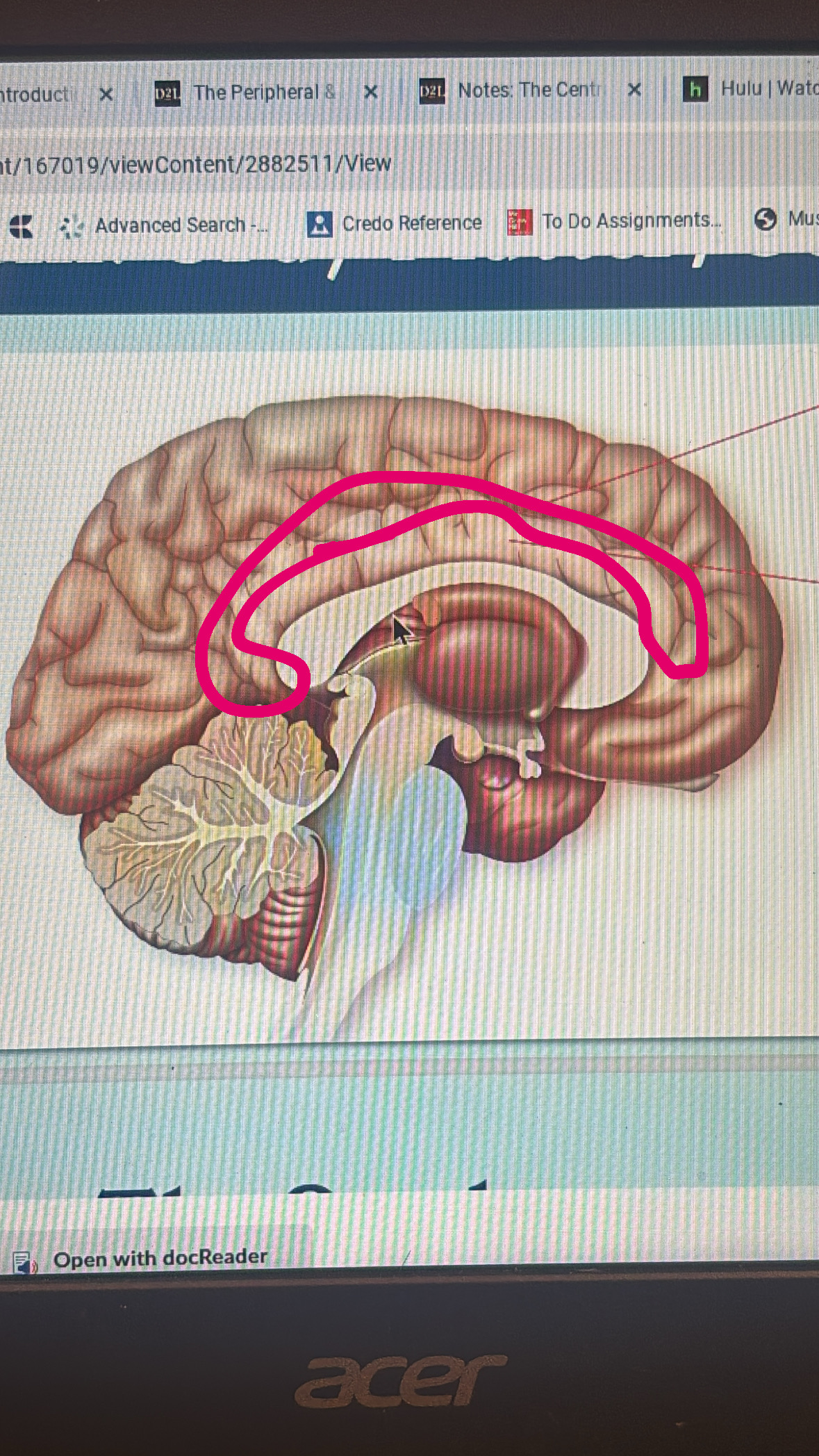
cingulate gyrus
deep line
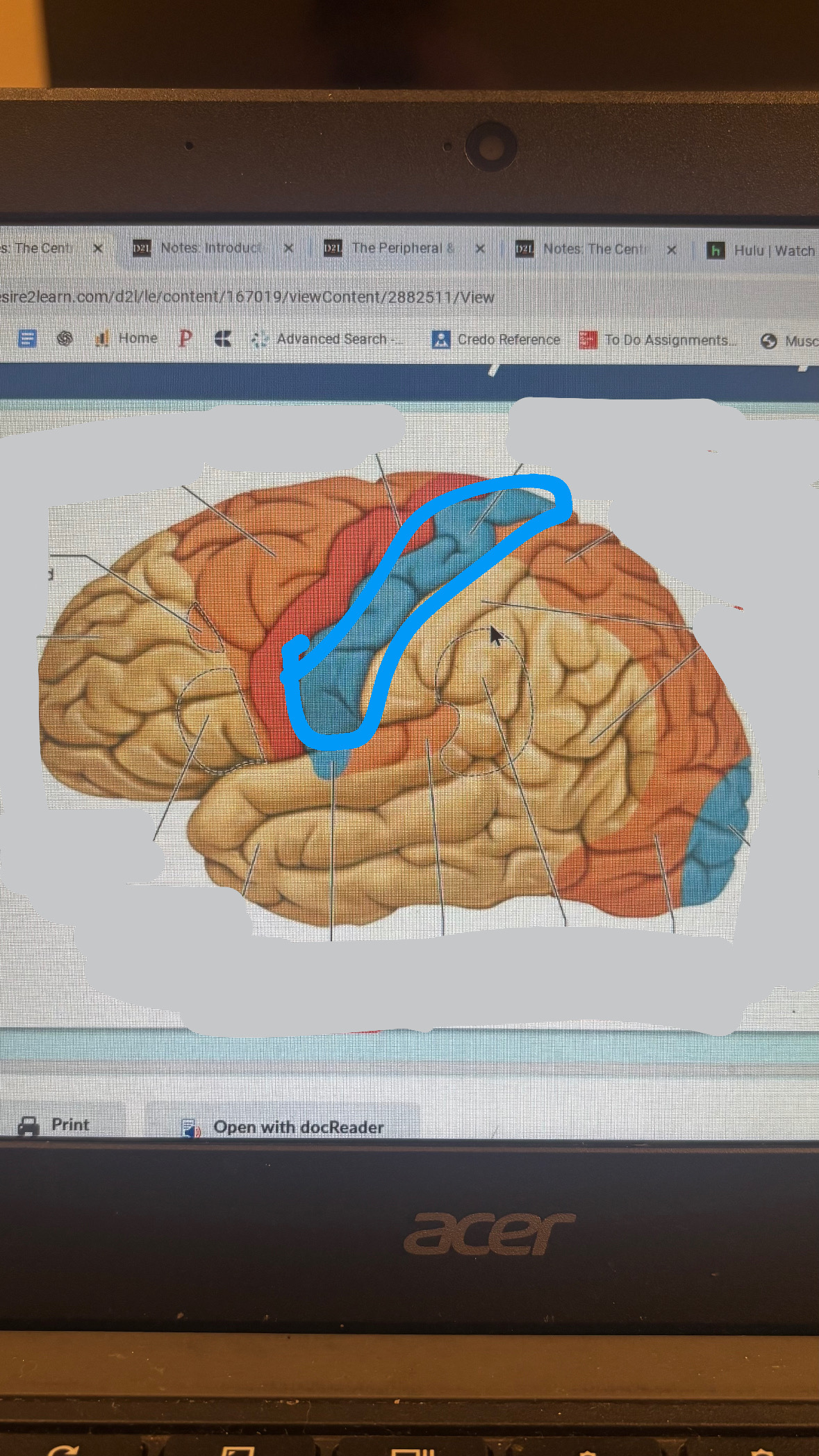
primary somatosensory cortex
S1
pertain to temperature and touch sensation
primary visual cortex
visual input
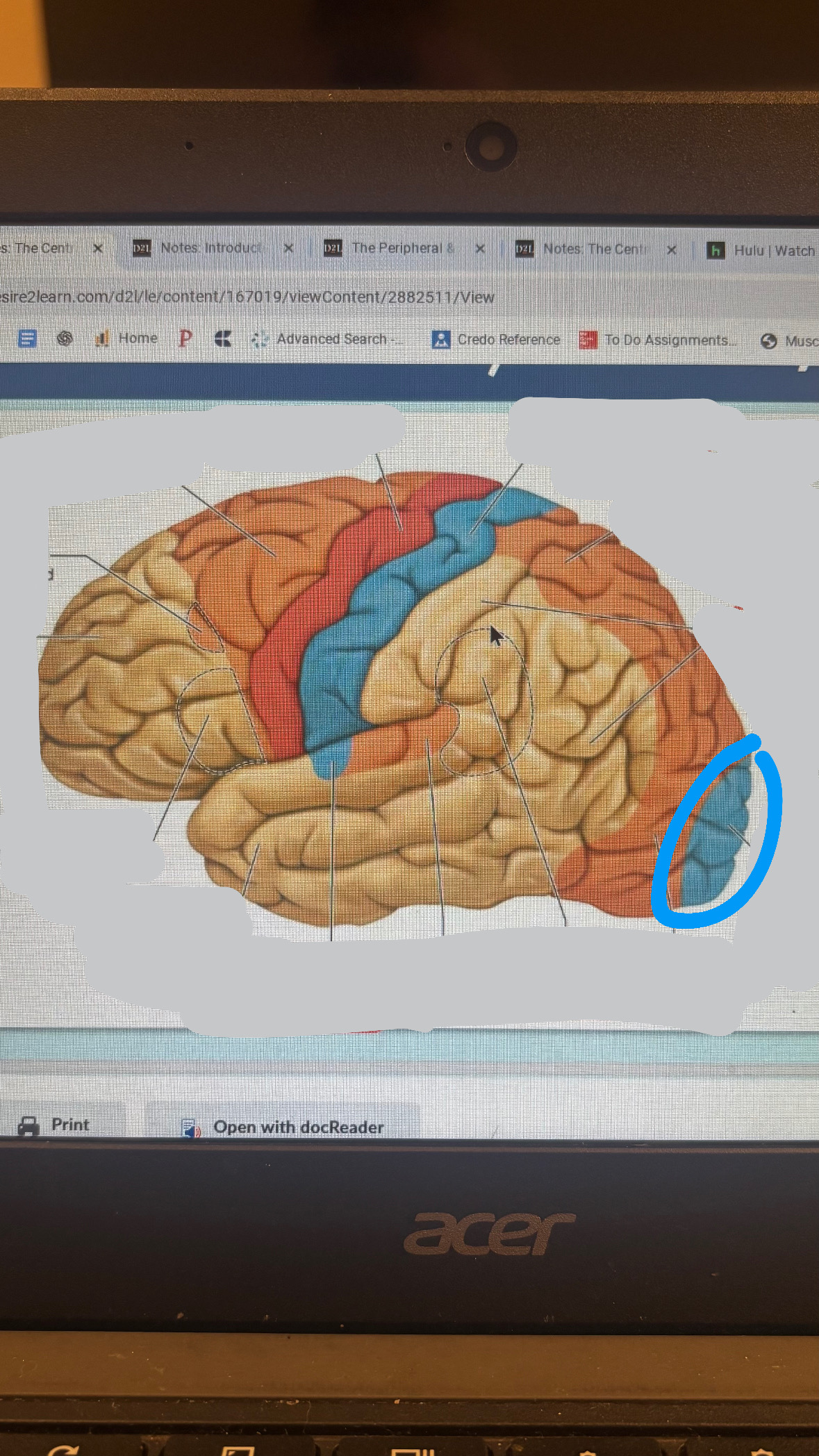
primary auditory cortex
sound sensation
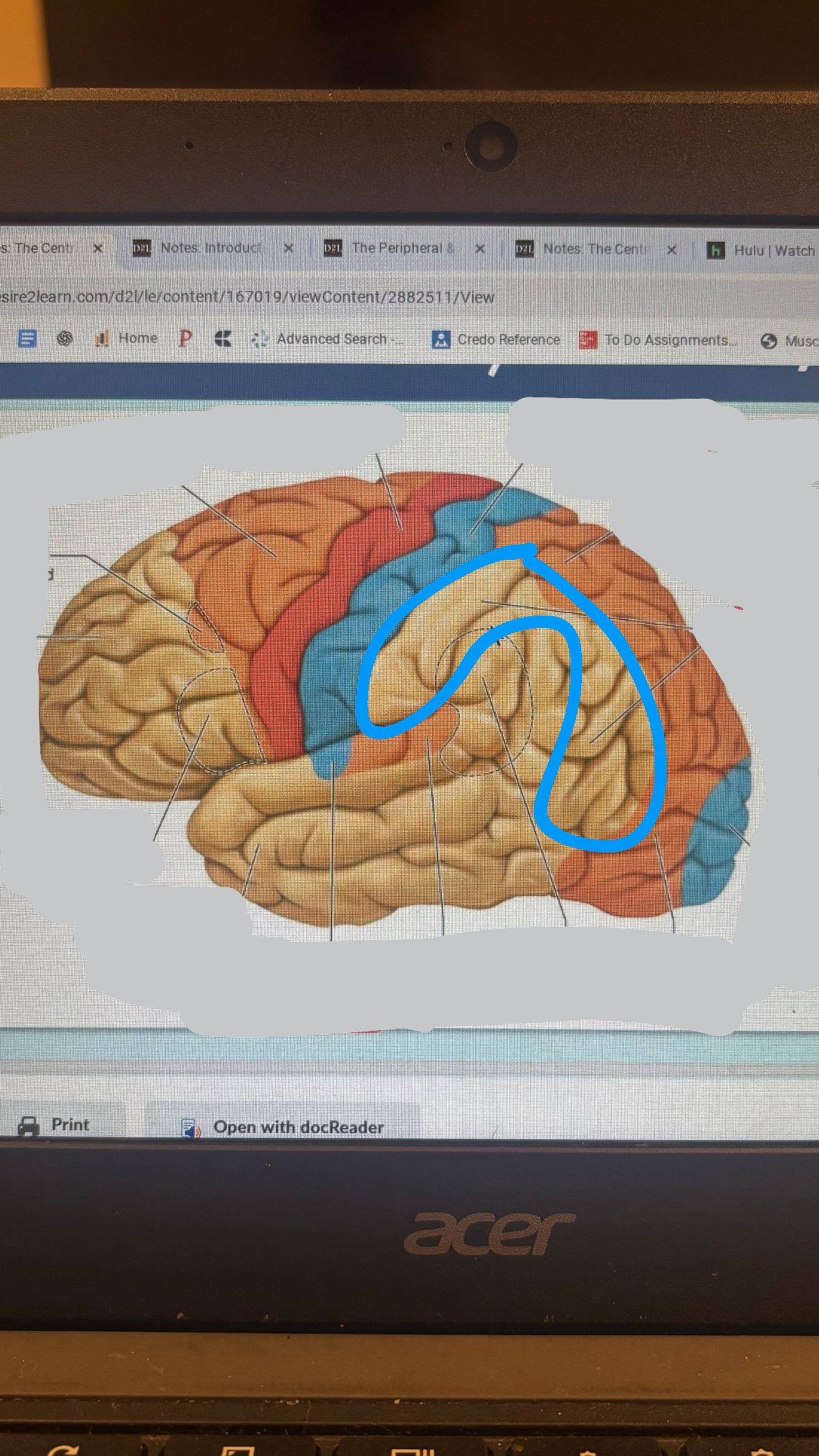
primary sensory cortices
primary somatosensory cortex
primary visual cortex
primary auditory cortex
parietal association cortex
wide variety of sensory integration tasks
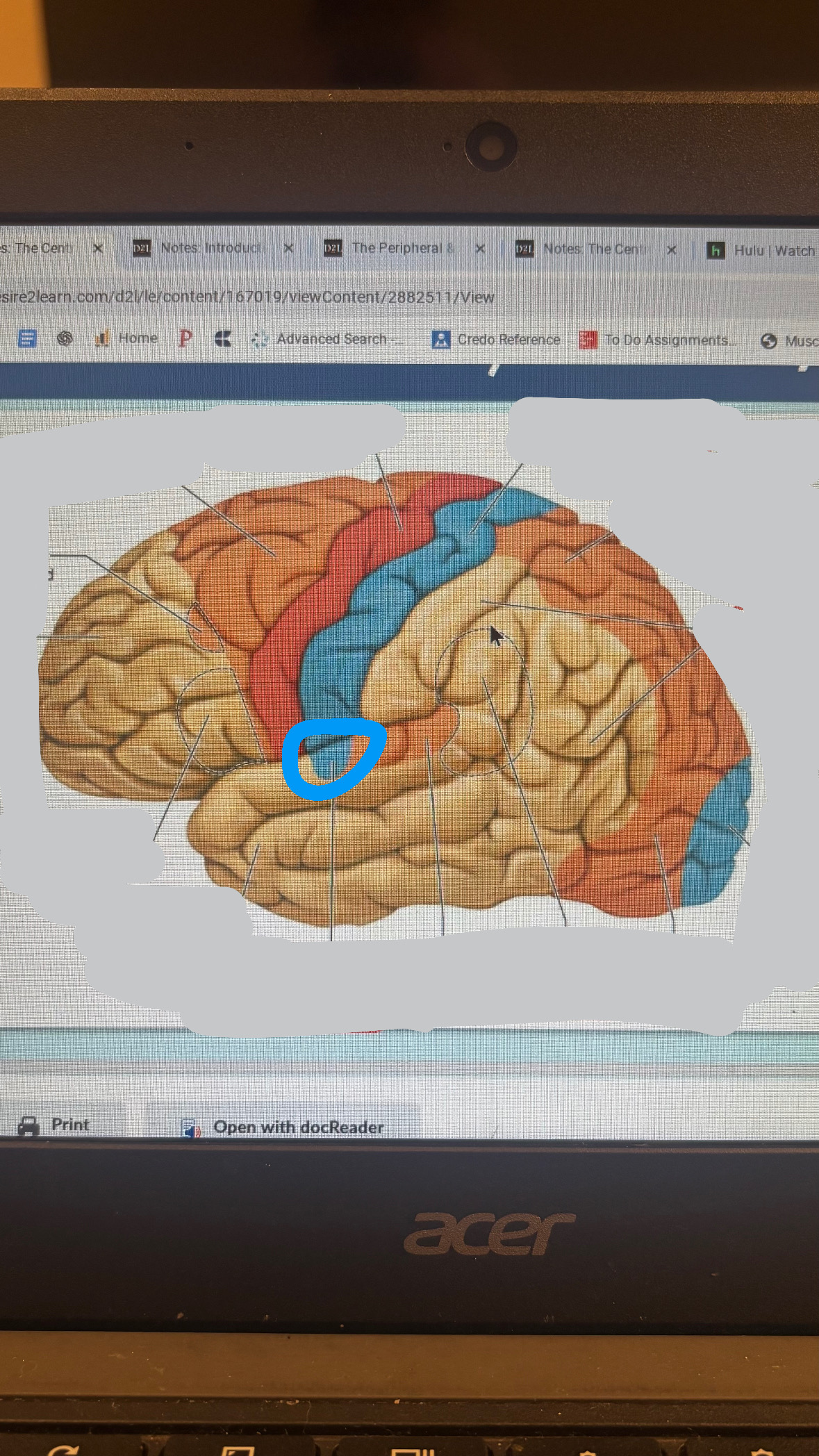
wernicke’s area
area for understanding language
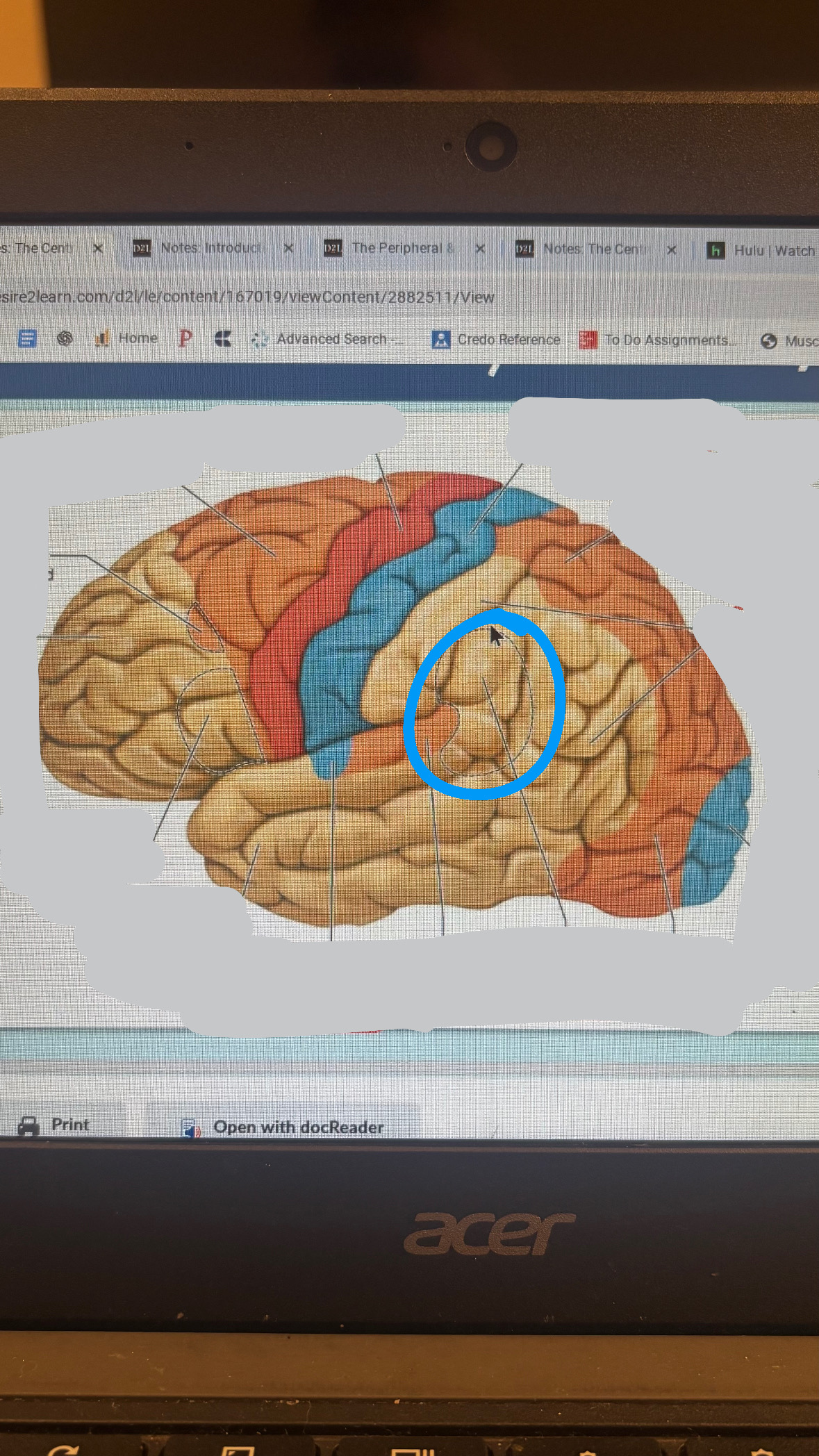
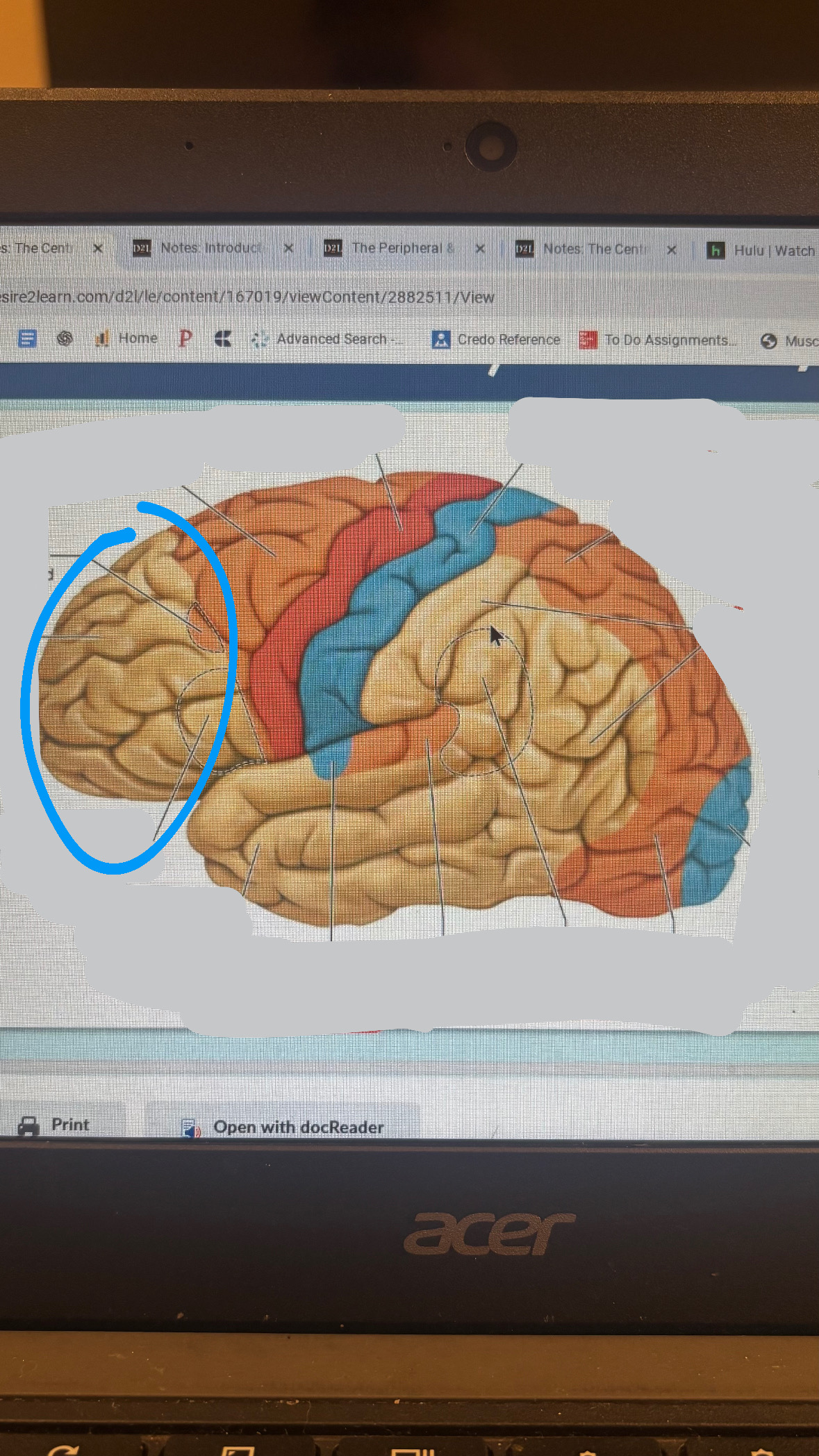
temporal association cortex
wide variety of sensory integration tasks
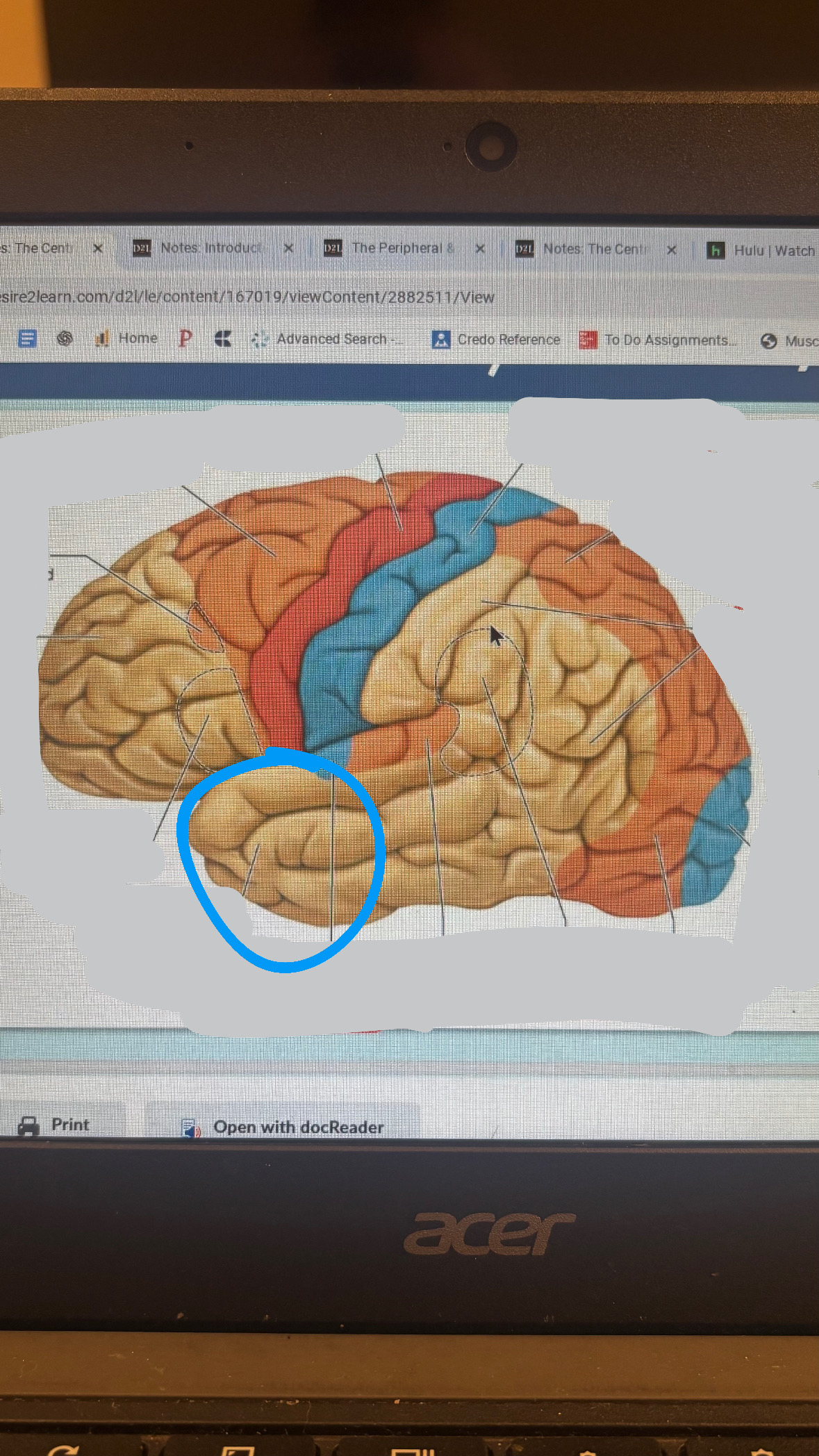
broca’s area
area for producing speech sounds and language (planning, ordering, granmar, syntax)
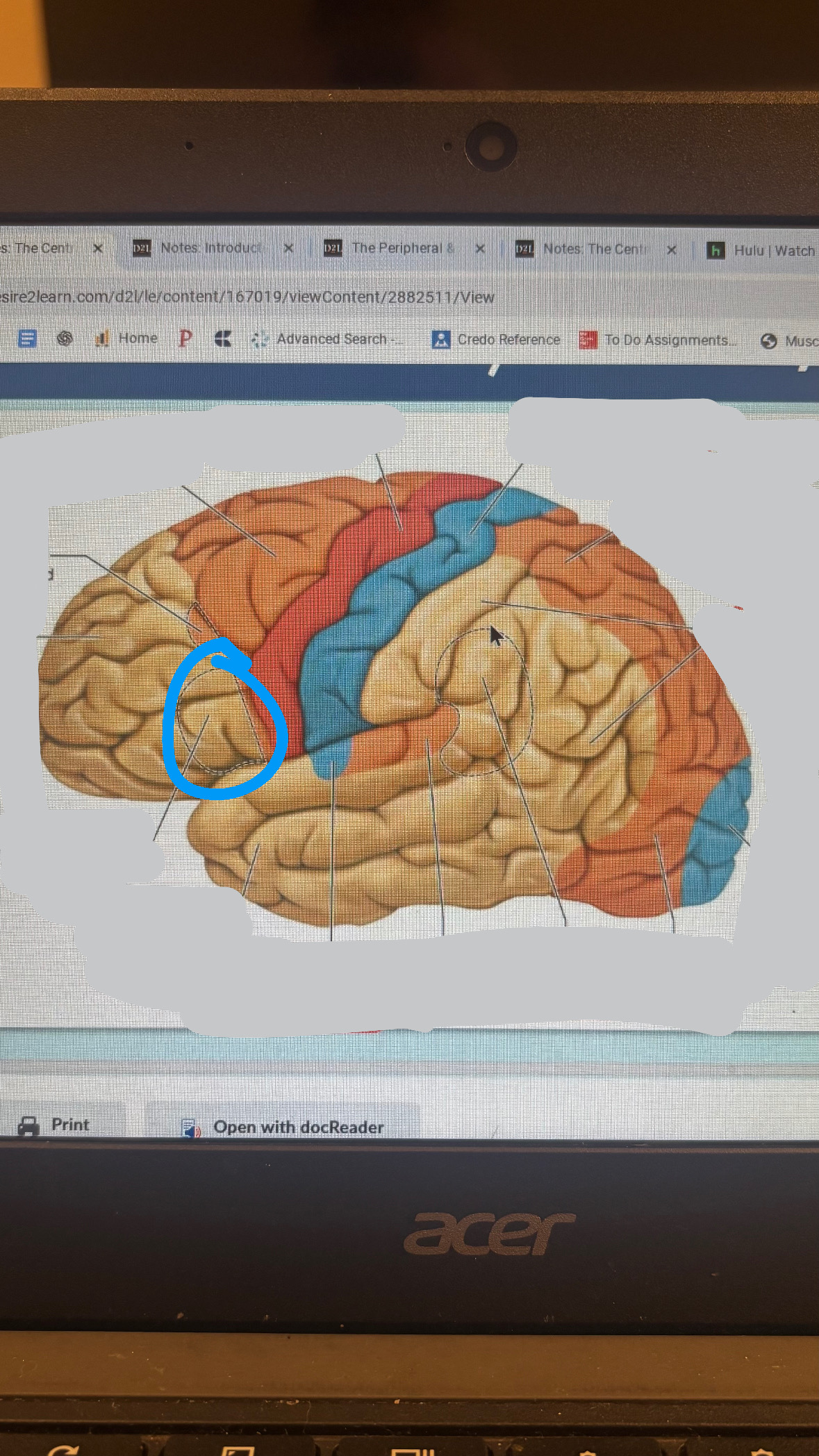
prefrontal cortex
planning, personality, higher cognitive function
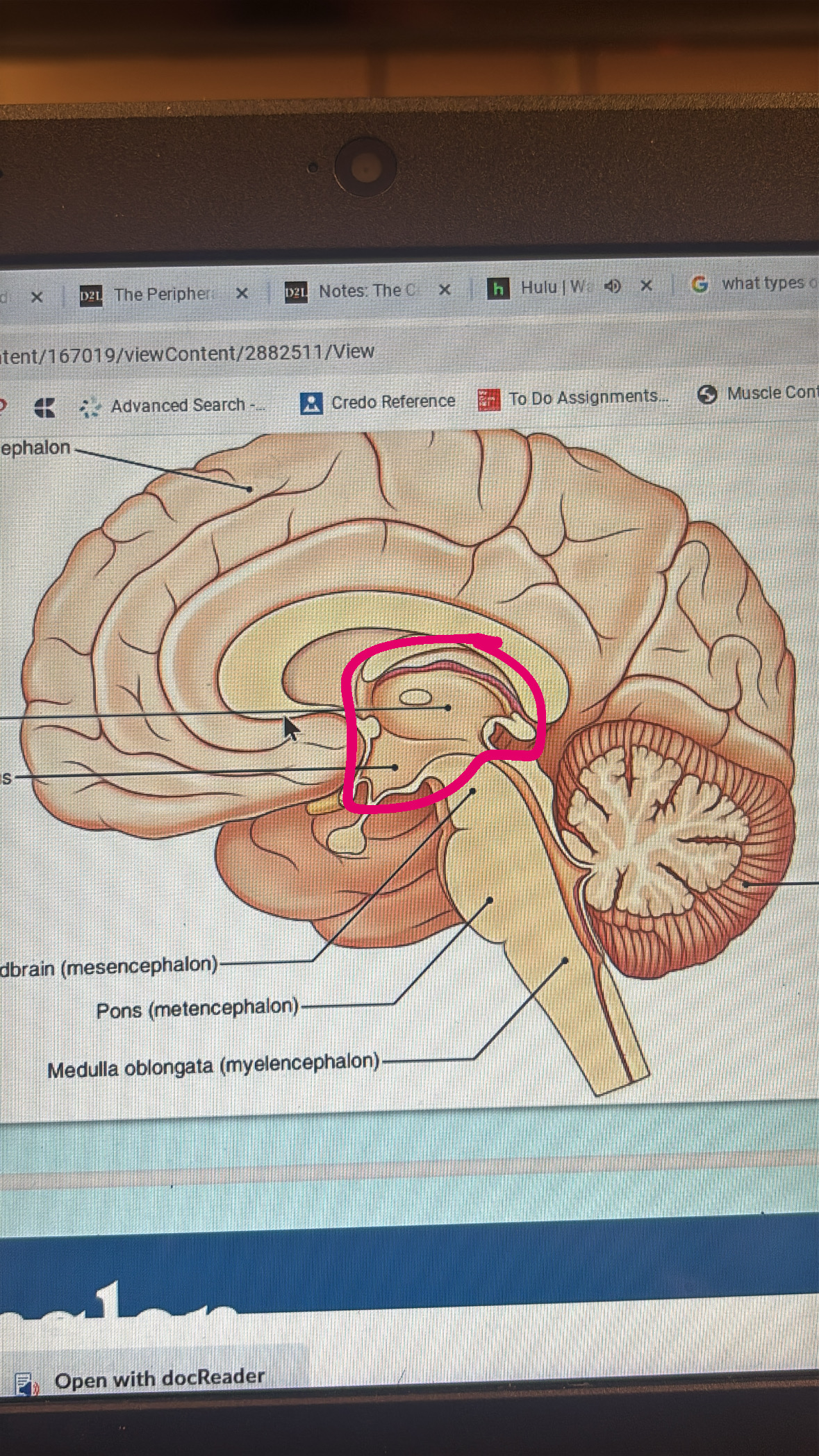
diencephalon
all of thalamus hypothalamus and pineal gland
thalamus
regulated an activity of the cerebral cortex by controlling the type of info that reaches the cortex
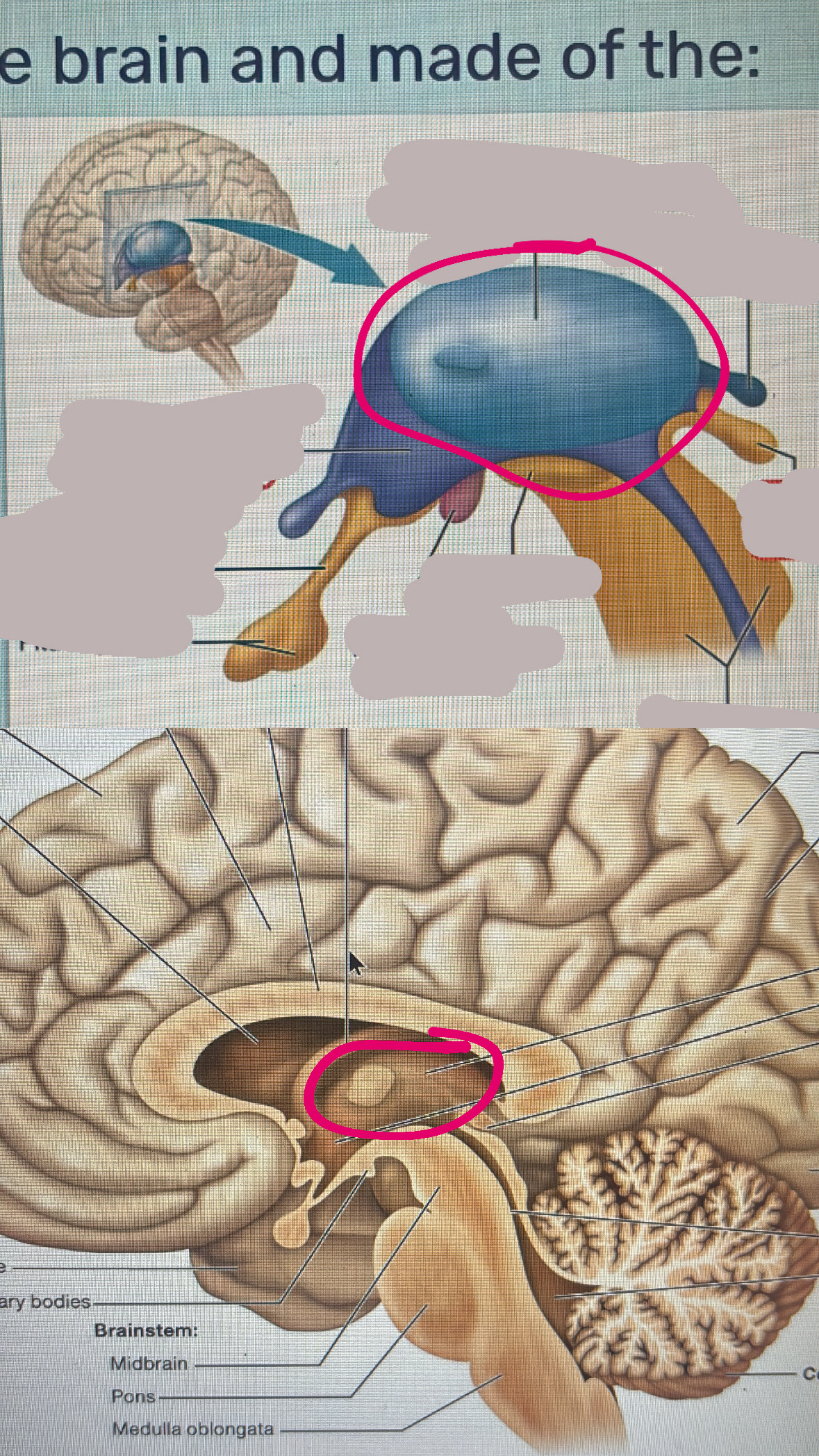
hypothalamus
regulation of sleep/wake cycle
thirst and hunger
body temp
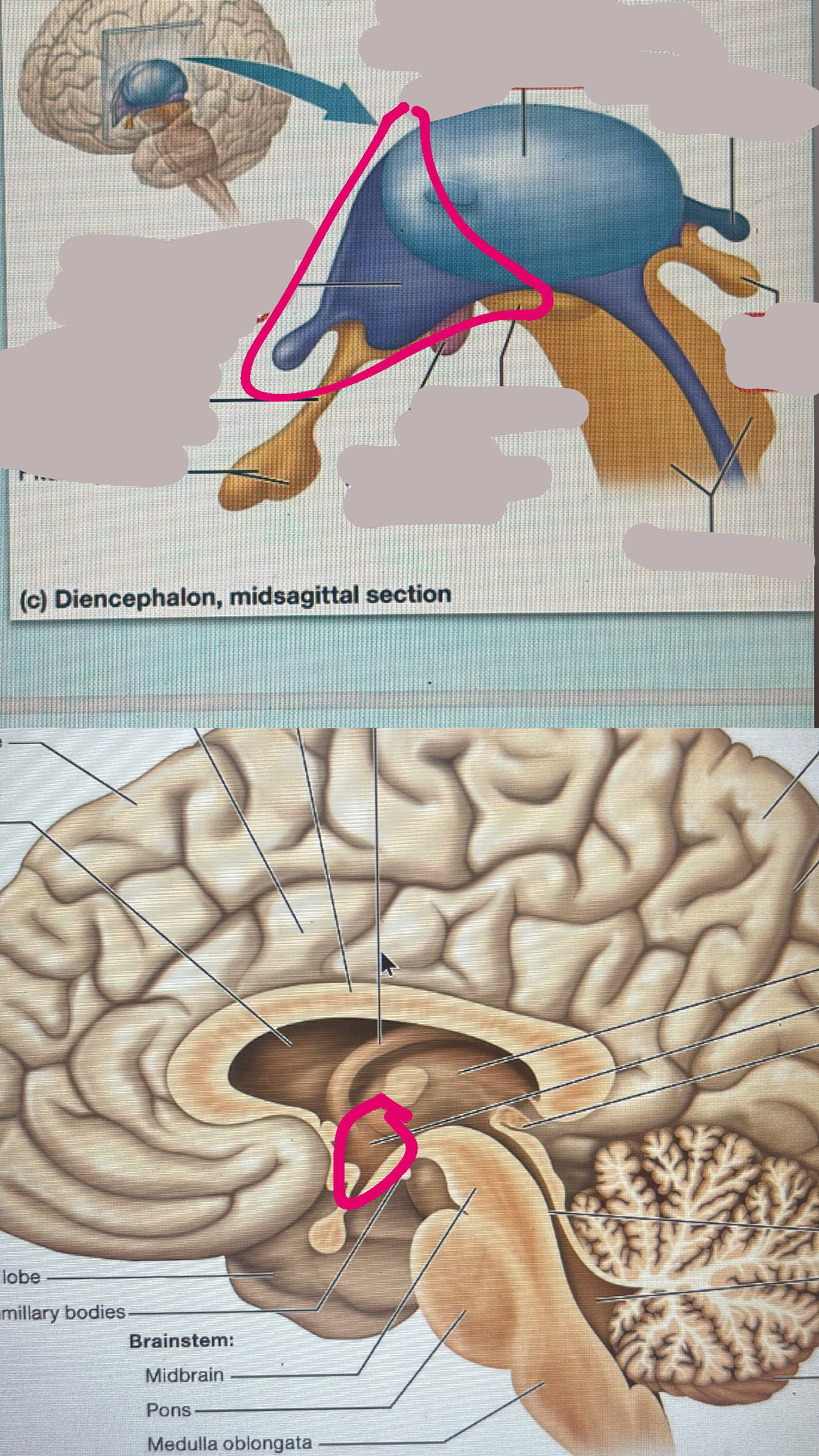
infundibulum
pituitary glad is connected to it
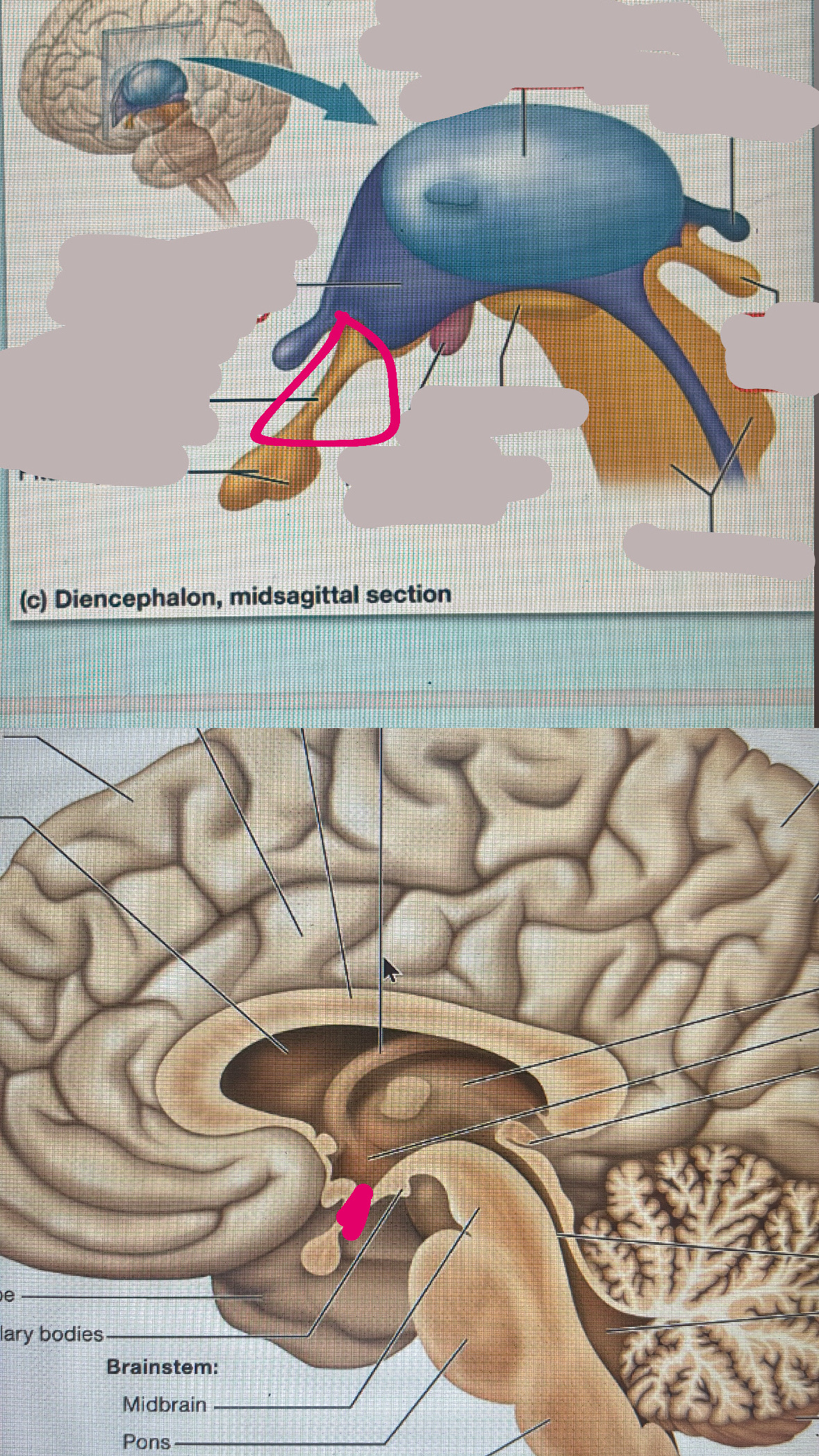
pineal gland
is contained in the epithalamus which regulates sleep with melatonin
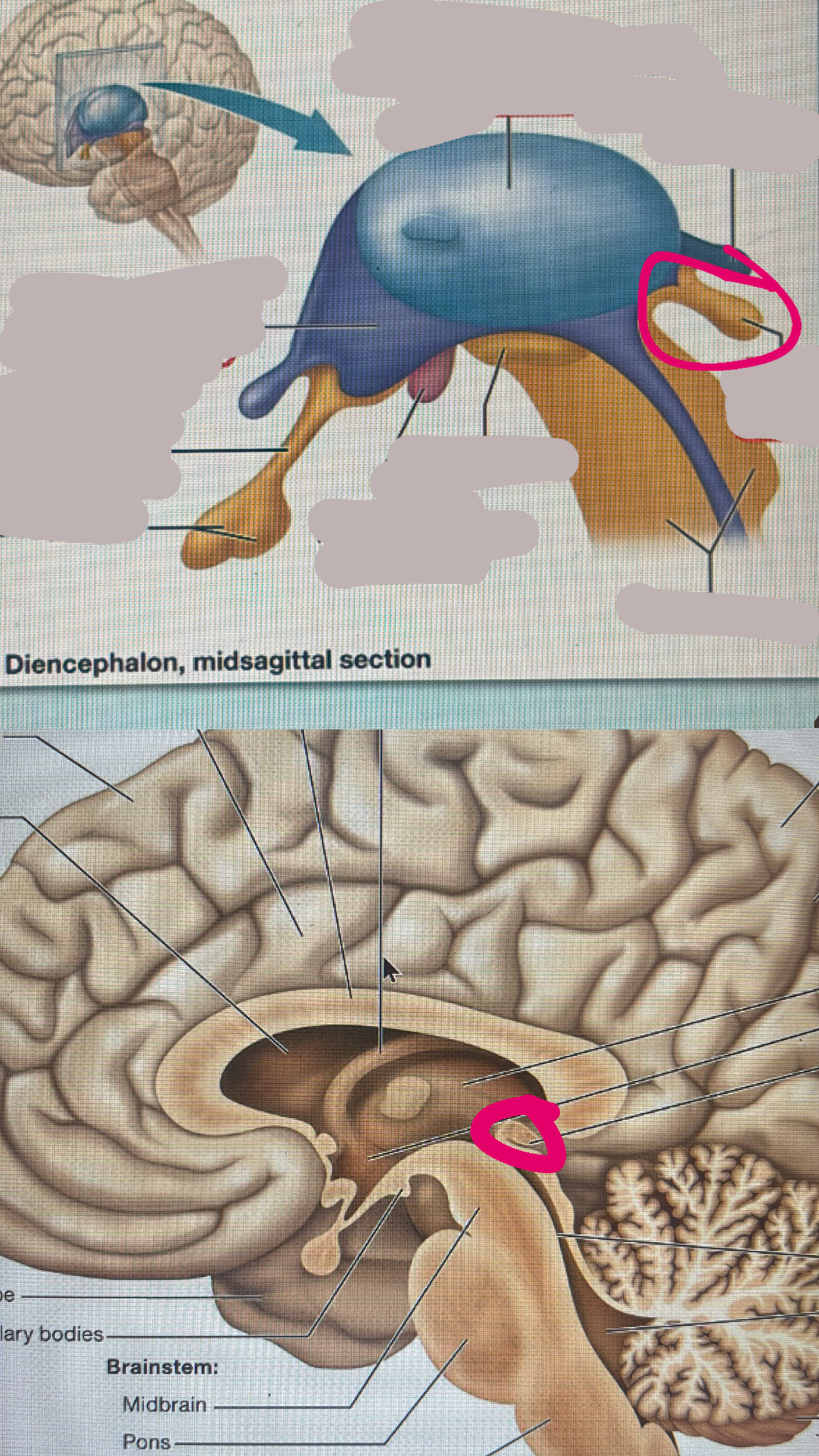
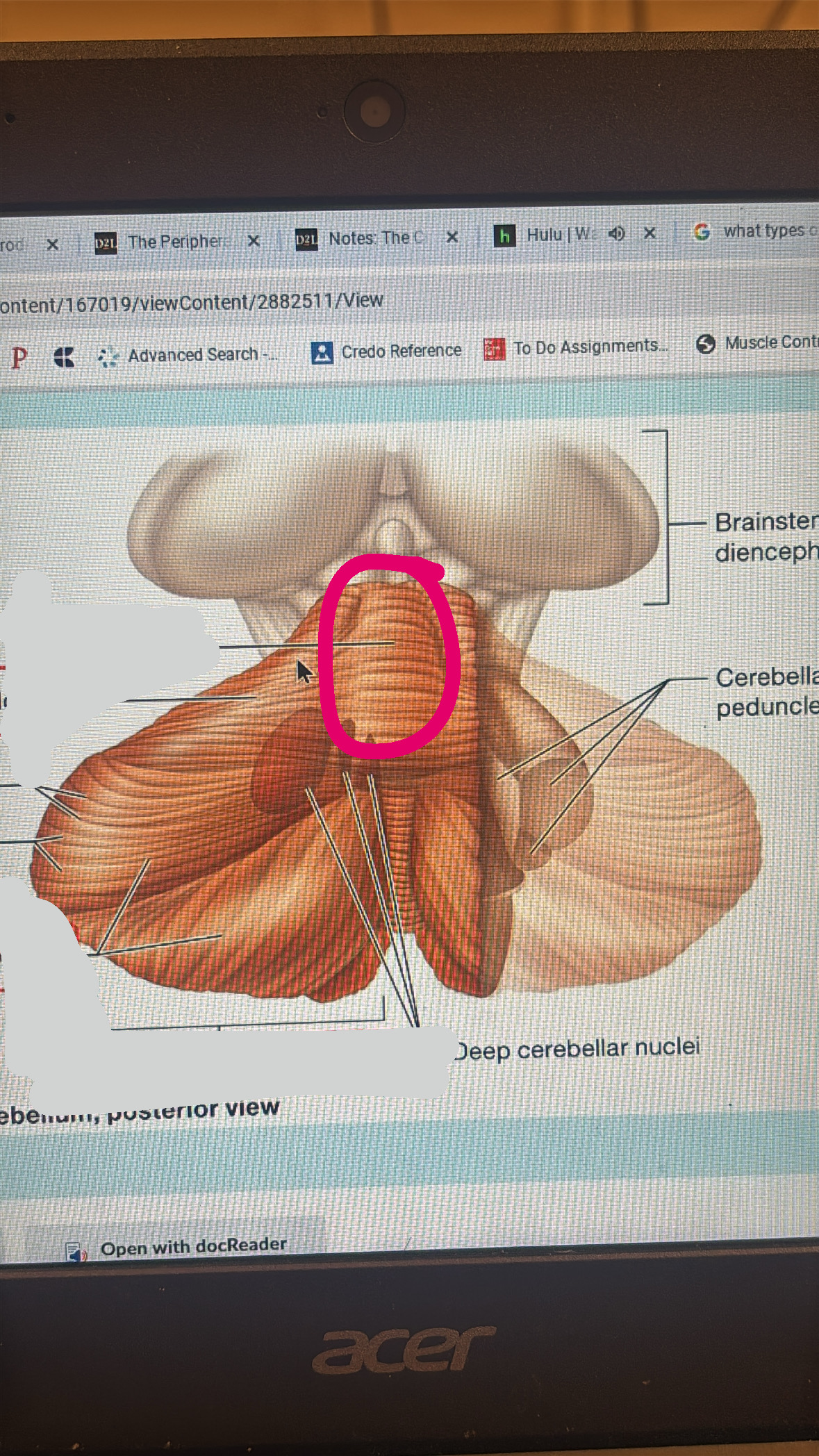
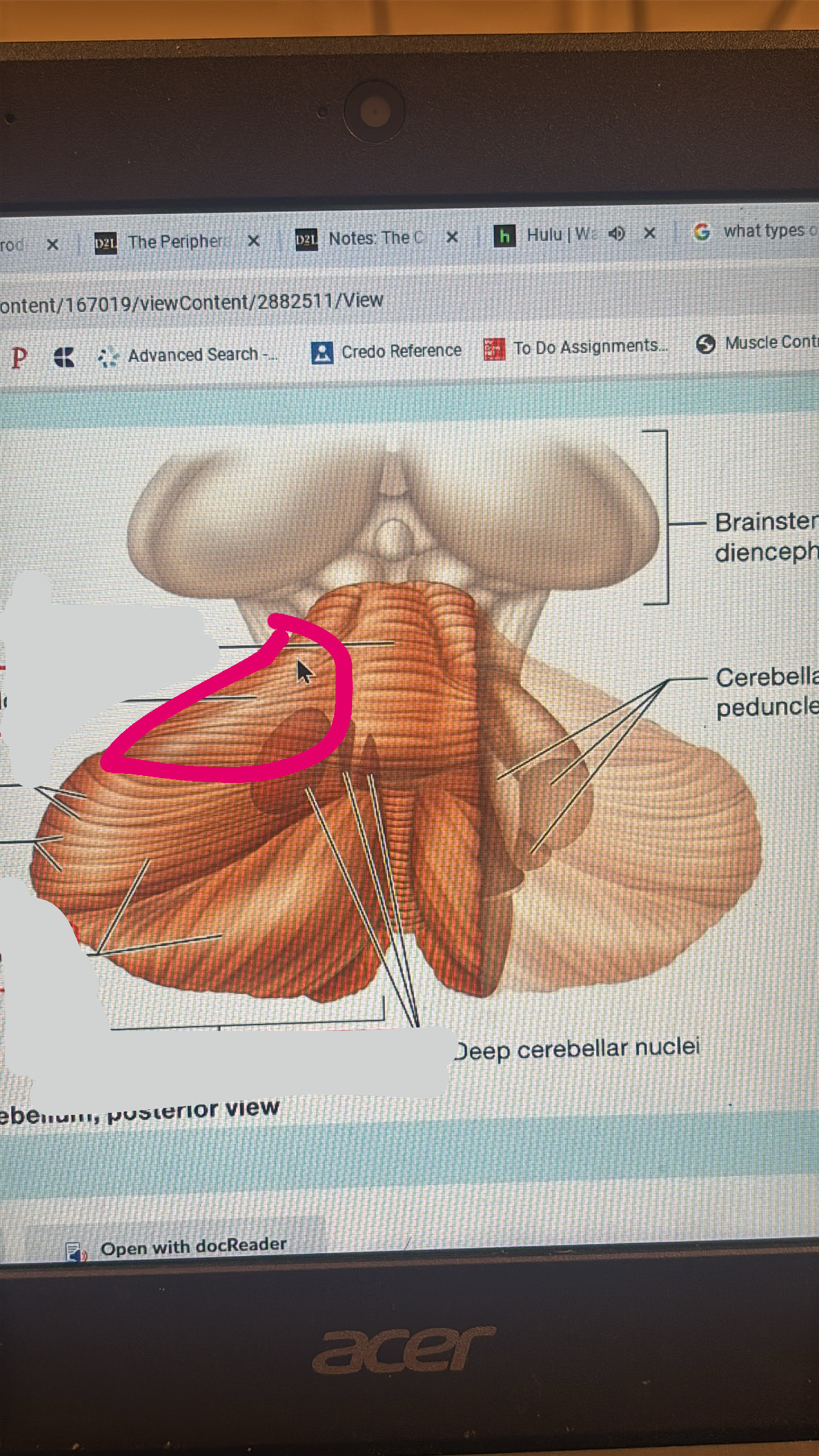
cerebellum
functions with other brain structures to coordinate ongoing voluntary movement to reduce motor error
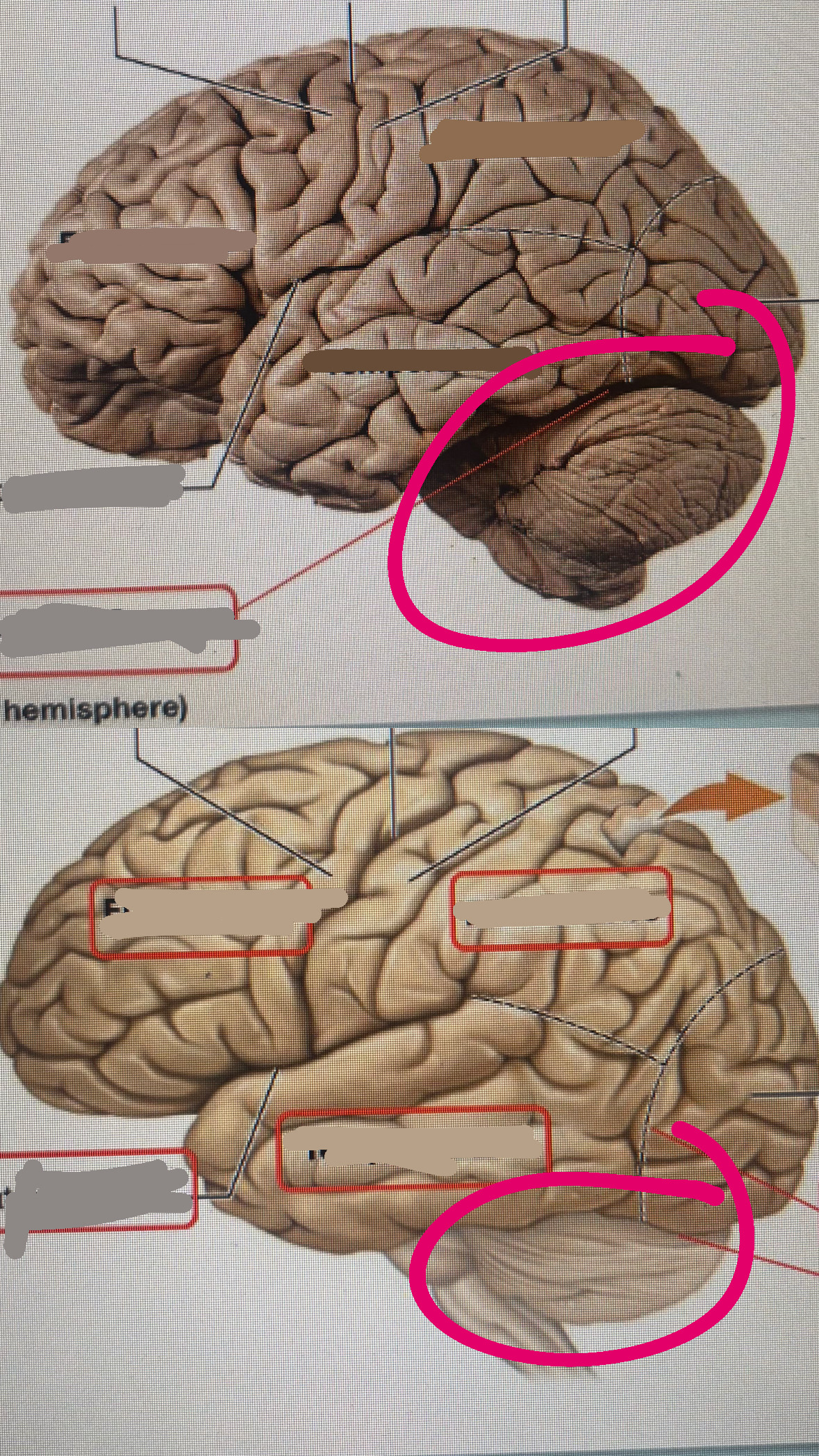
vermis
anterior lobe
posterior lobe
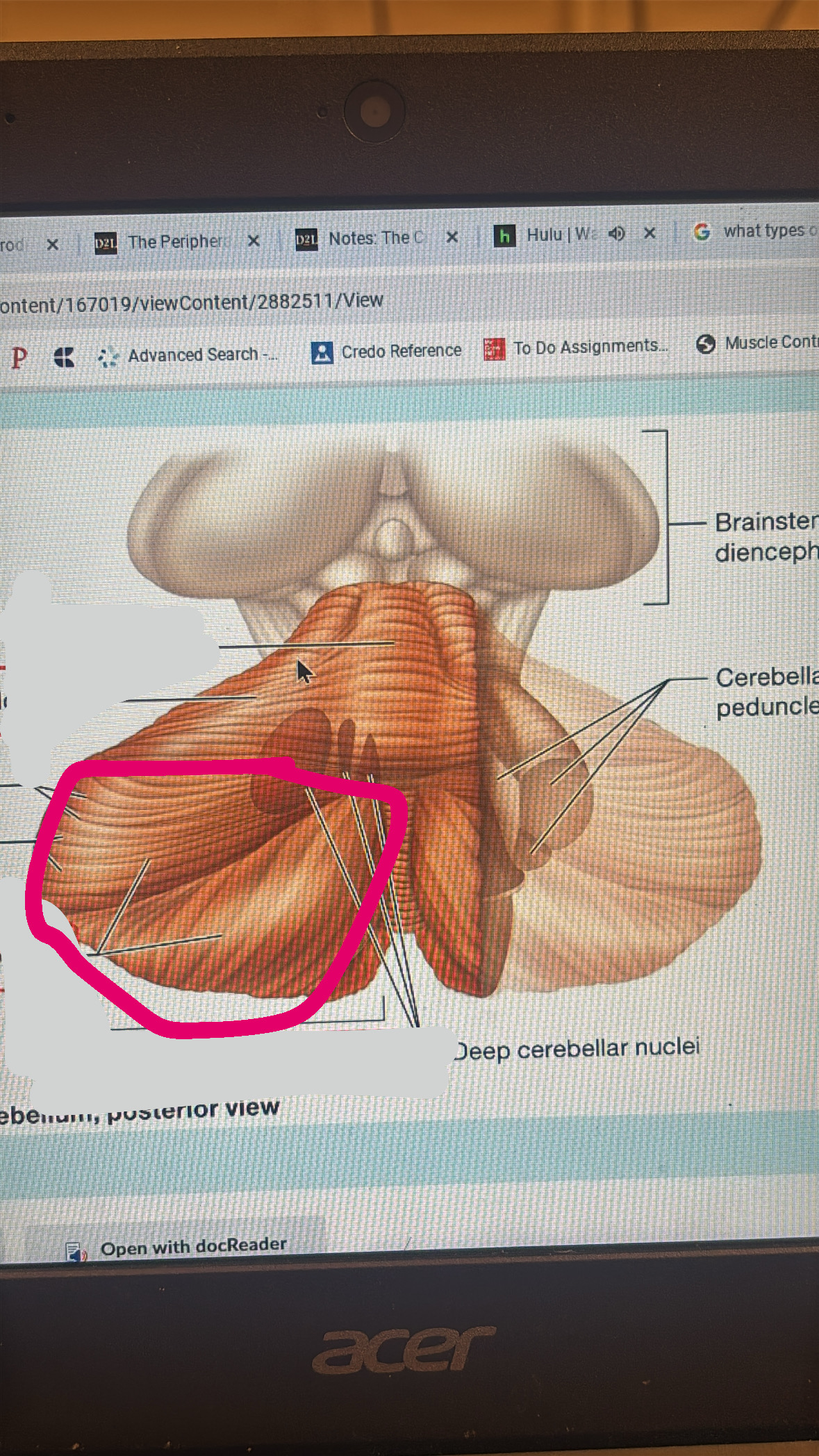
cerebellar hemisphere
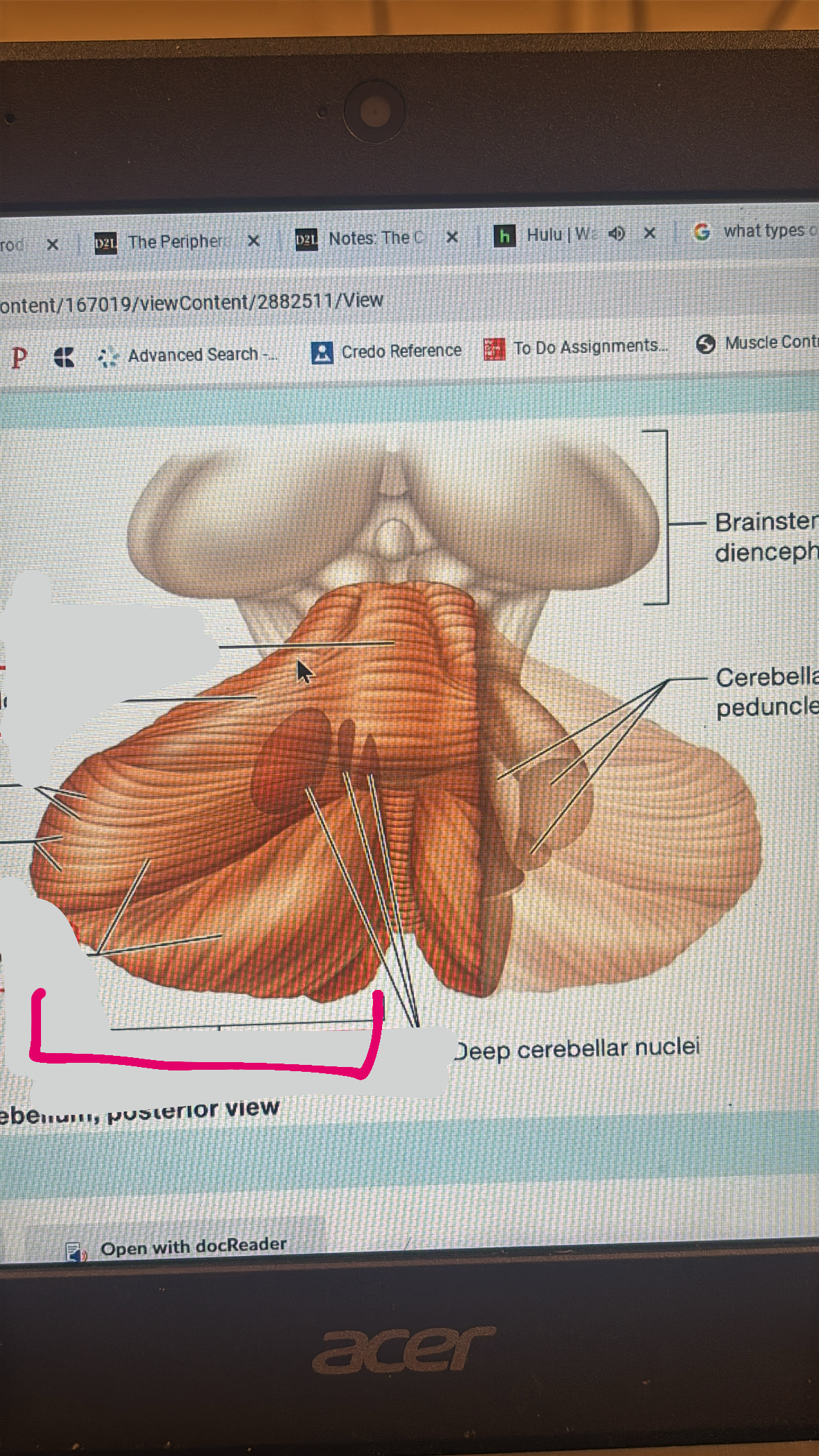
cerebellar cortex
the grey matter in the cerebellum
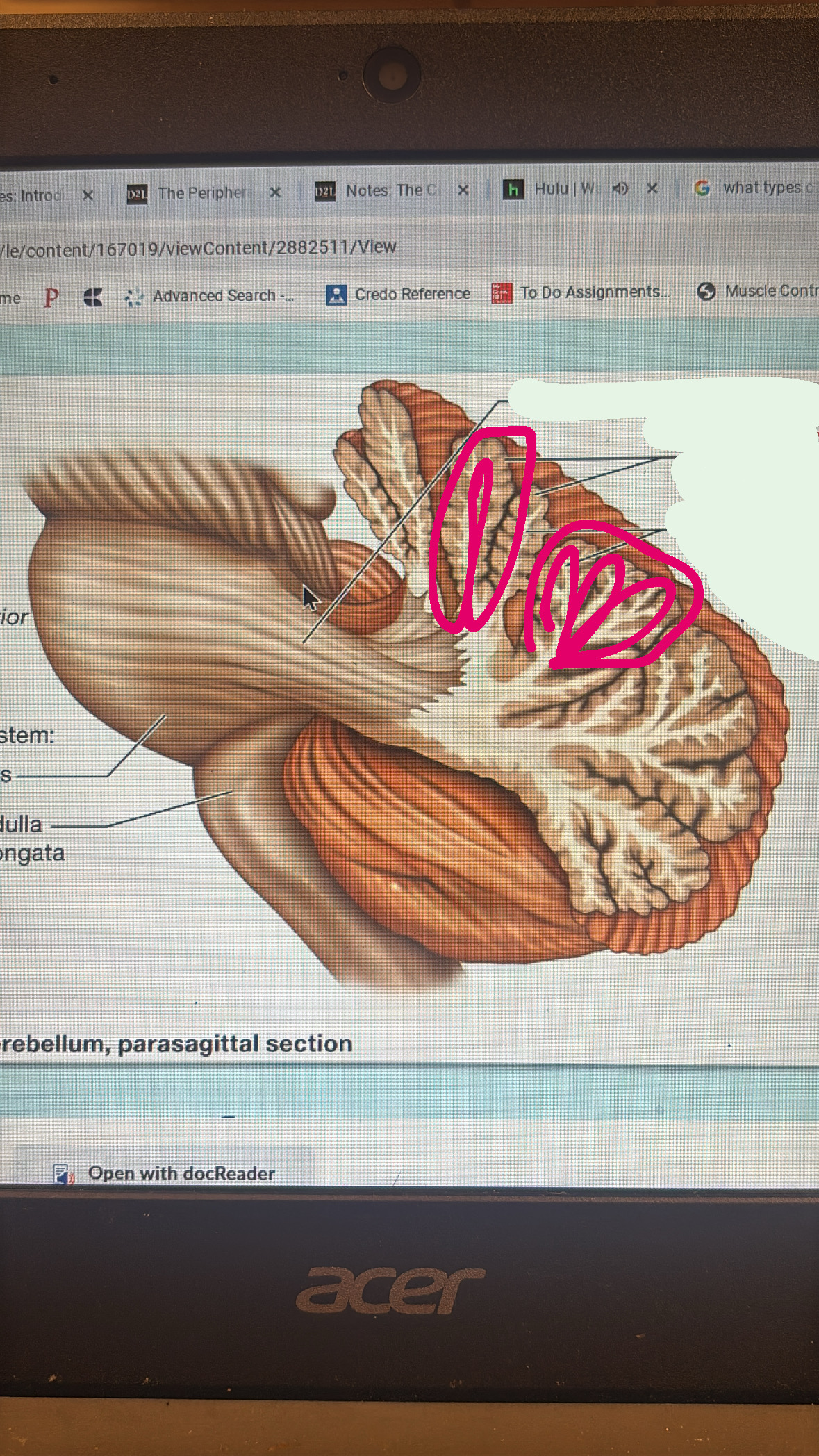
arbor vitae
white matter in cerebellum (tree of life)
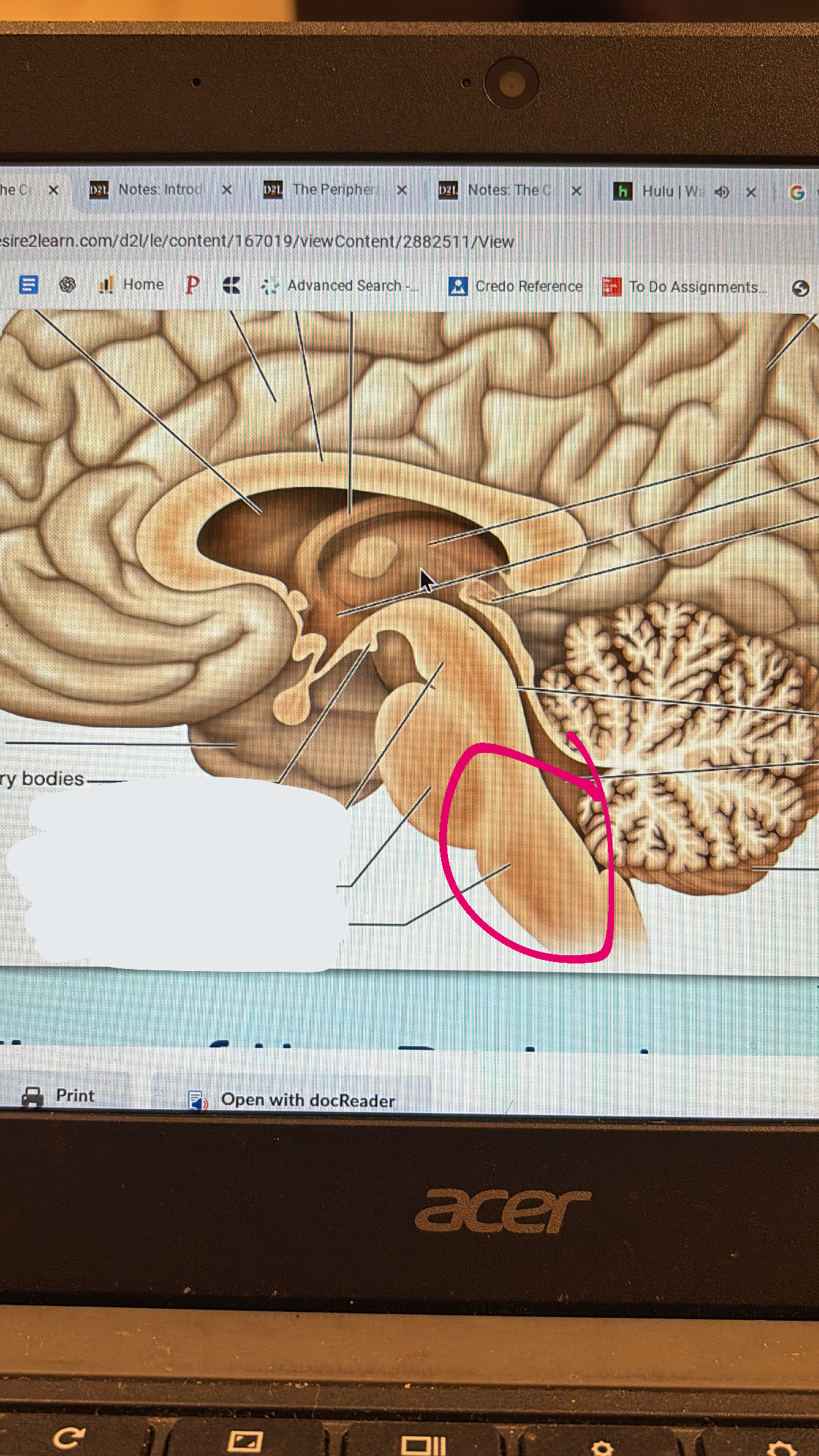
midbrain
top part of the brain stem
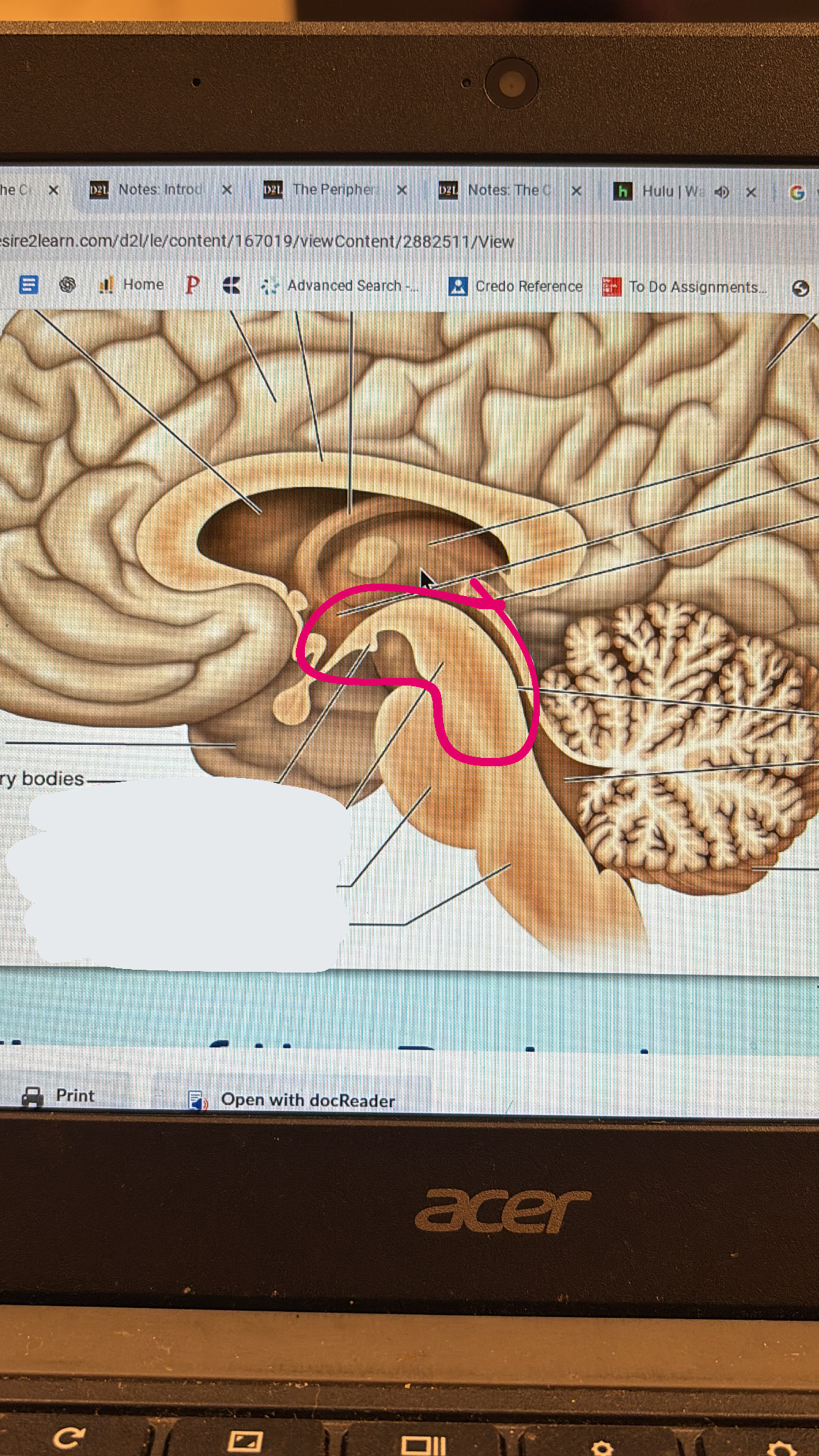
pons
meaty middle part of the brain stem
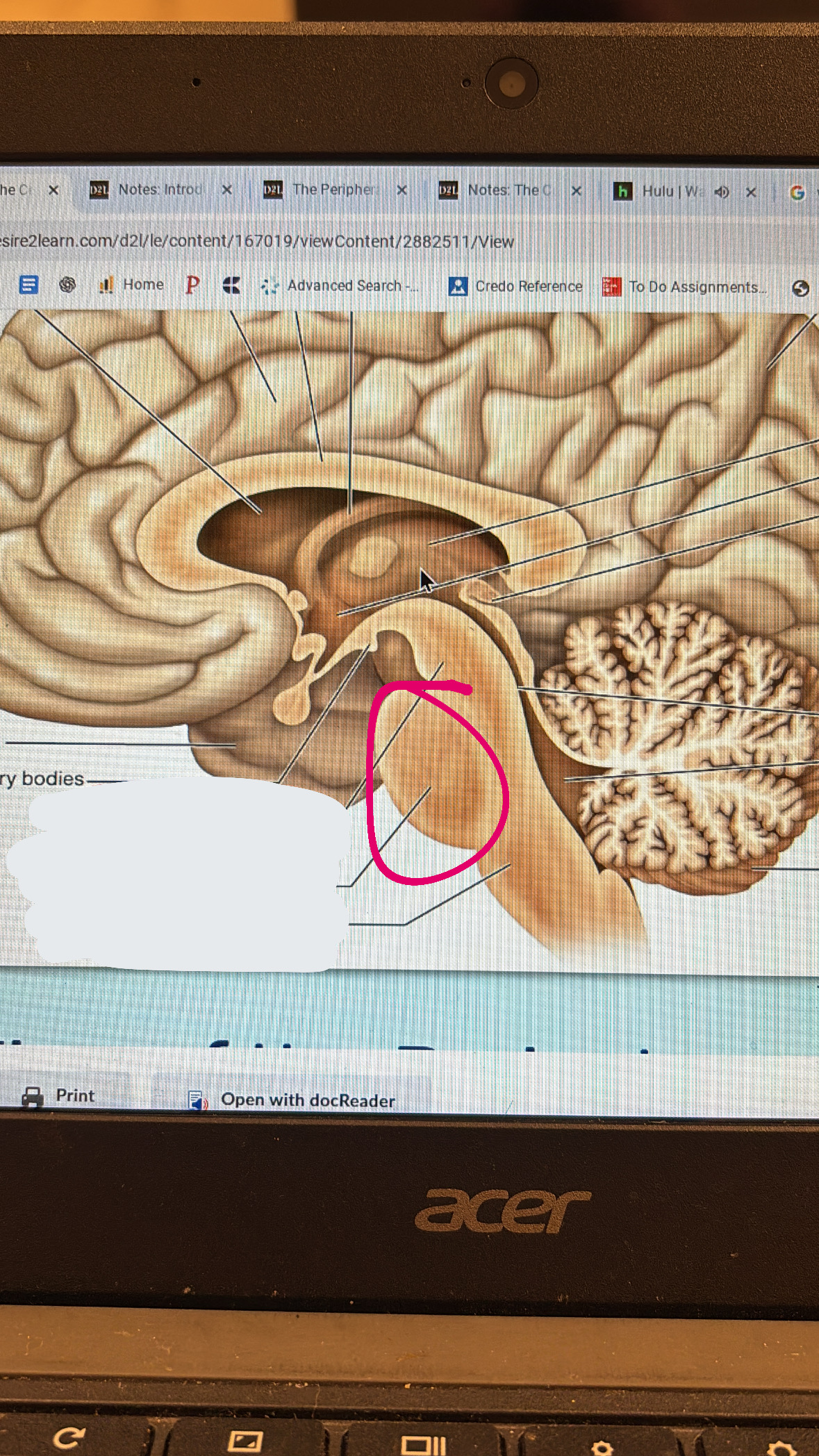
medulla oblongata
lowest part of the brain stem
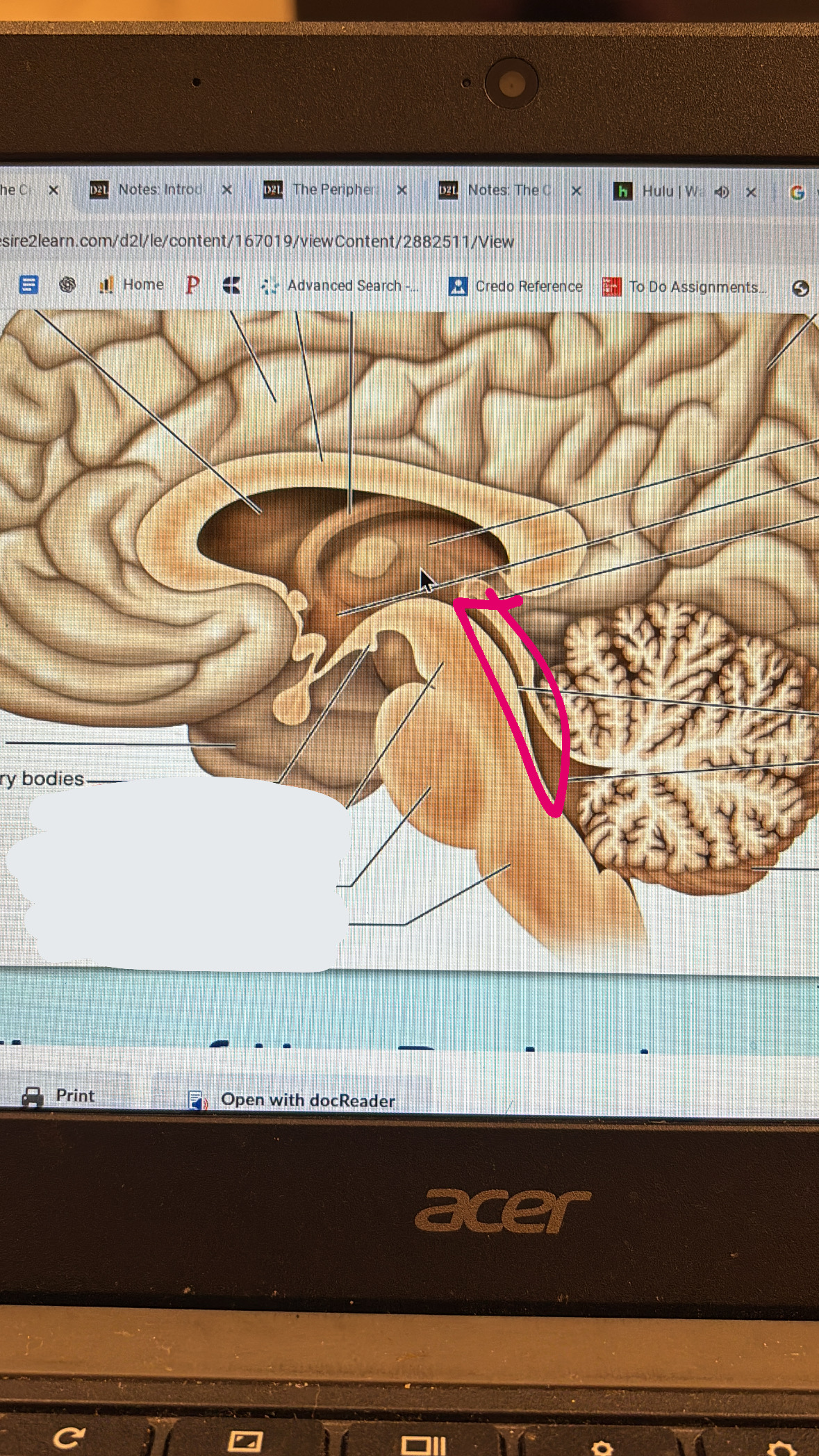
cerebral aqueduct
little tube thing separating the cerebellum and the brain stem
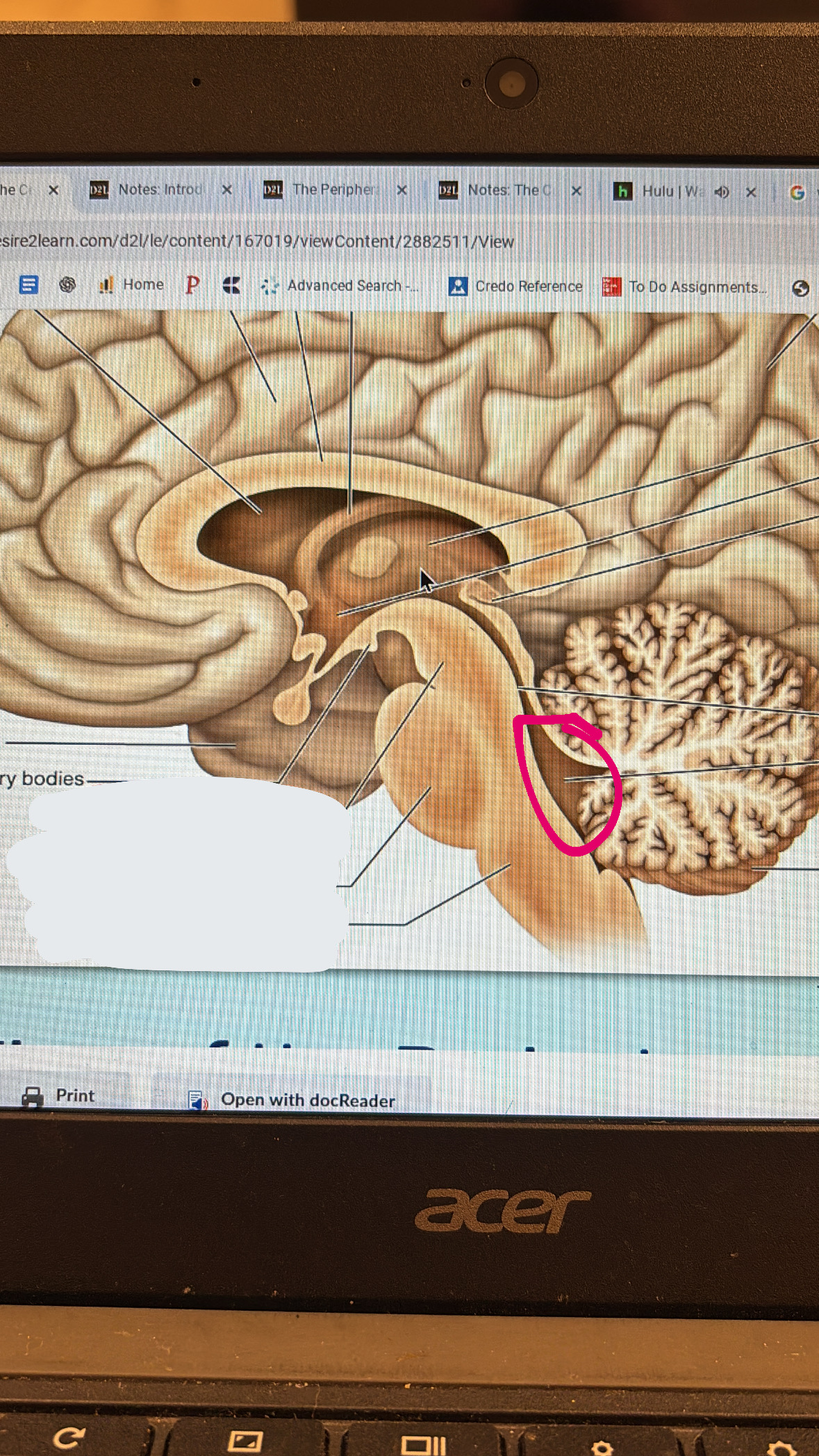
fourth ventricle
bigger space between the cerebellum and the brain stem
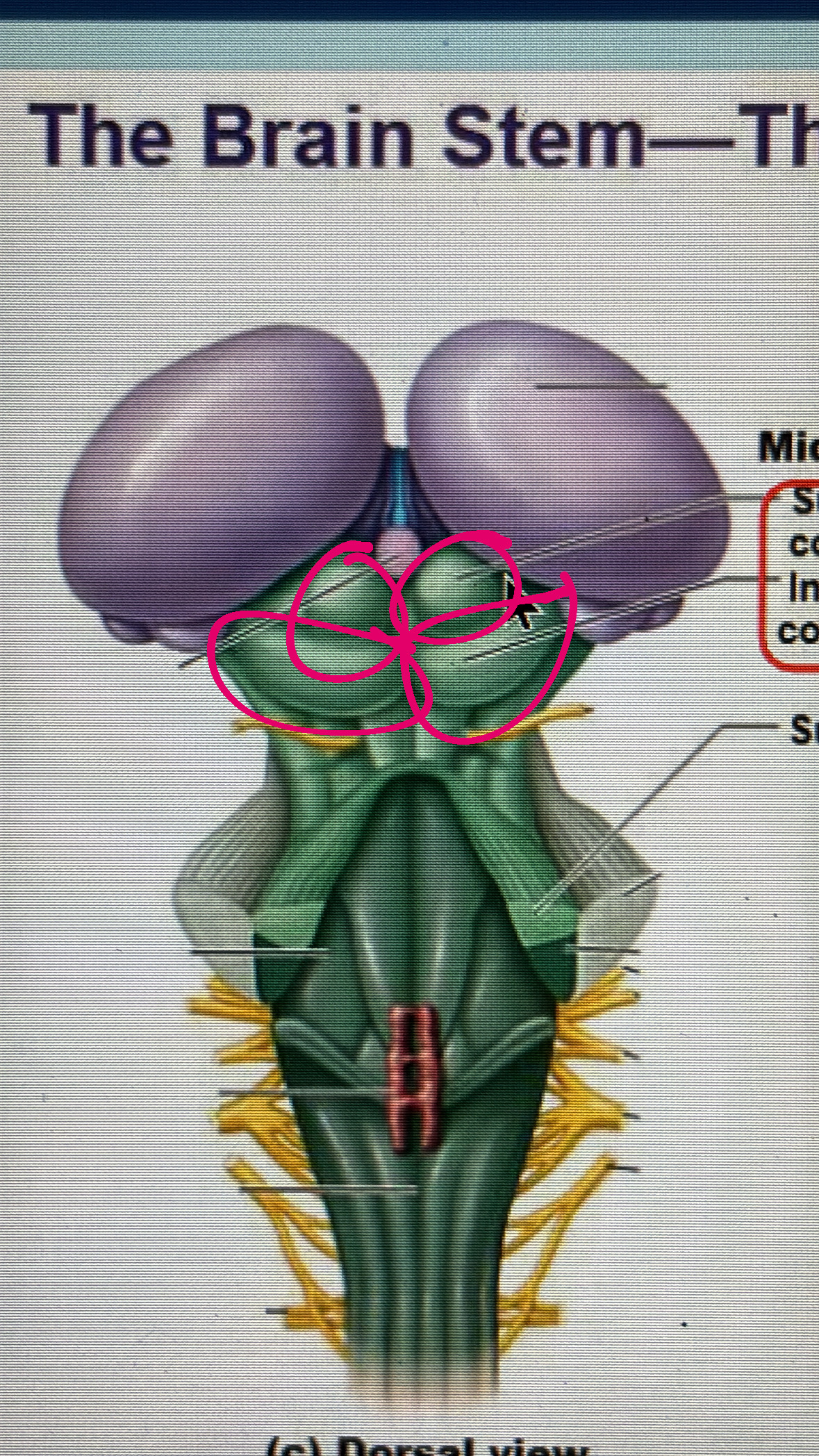
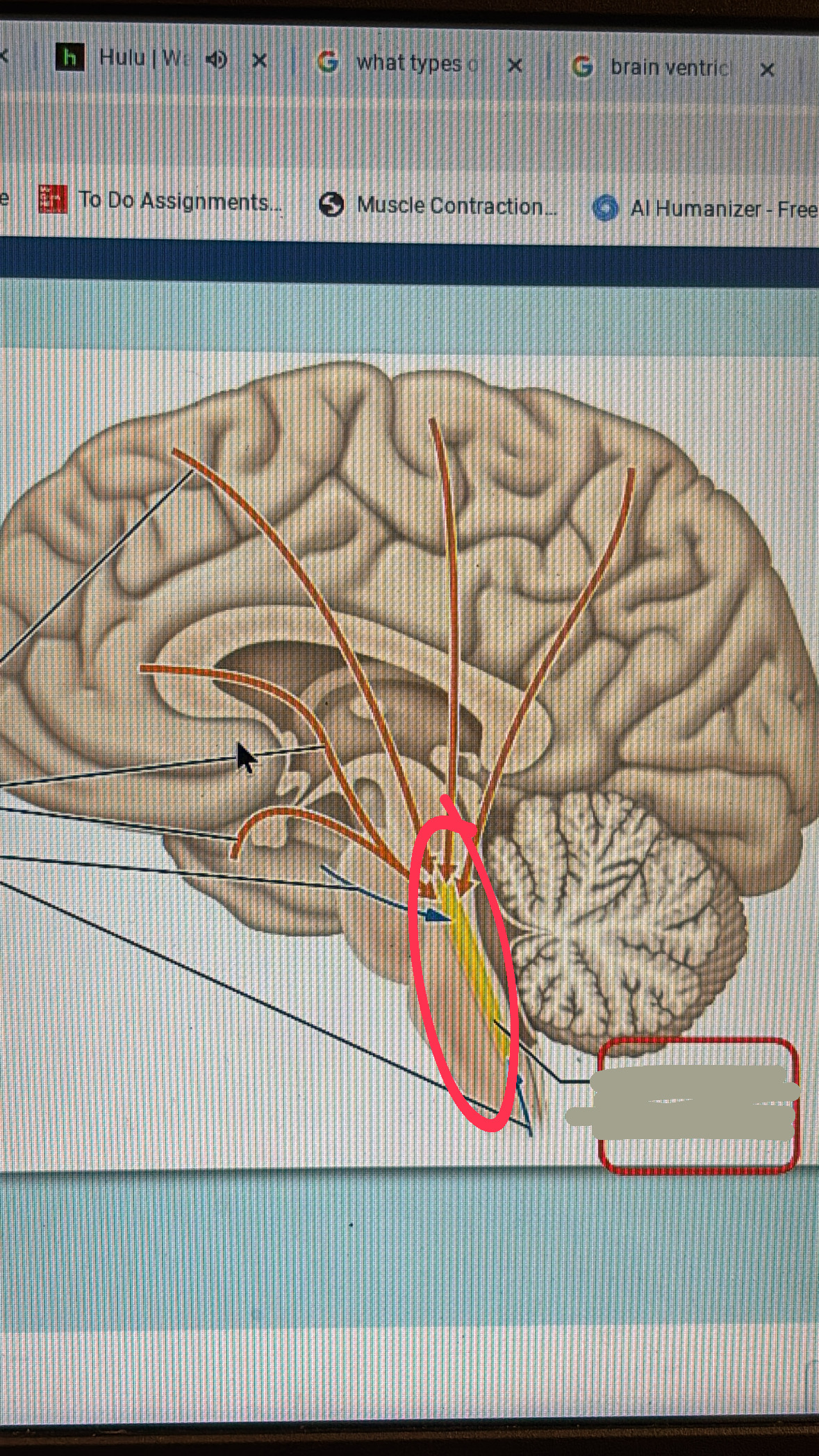
crus cerebri
2 of these make the midbrain
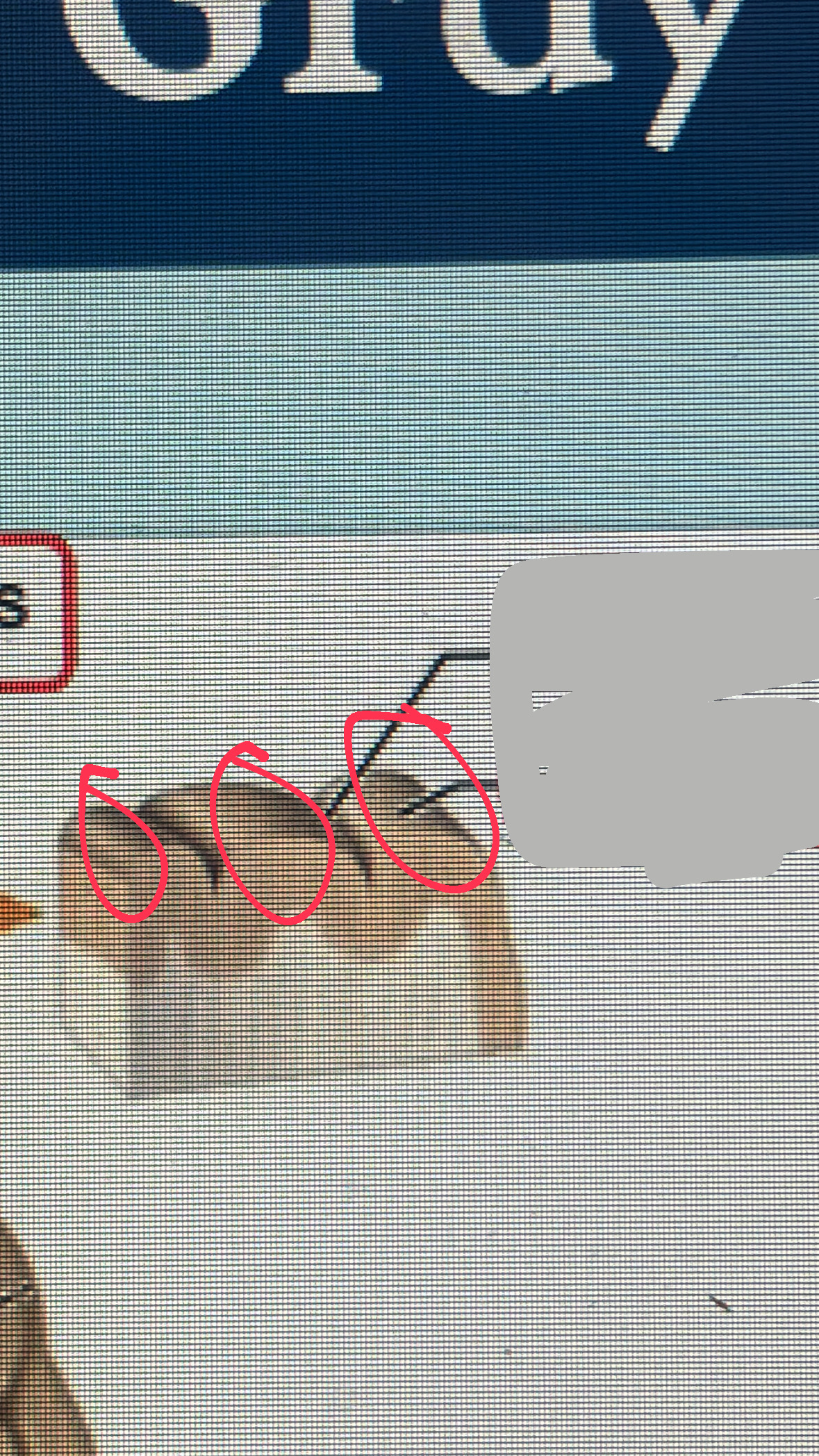
corpora quadrigemina
includes the superior and the inferior COLLICULUS
reticular formation
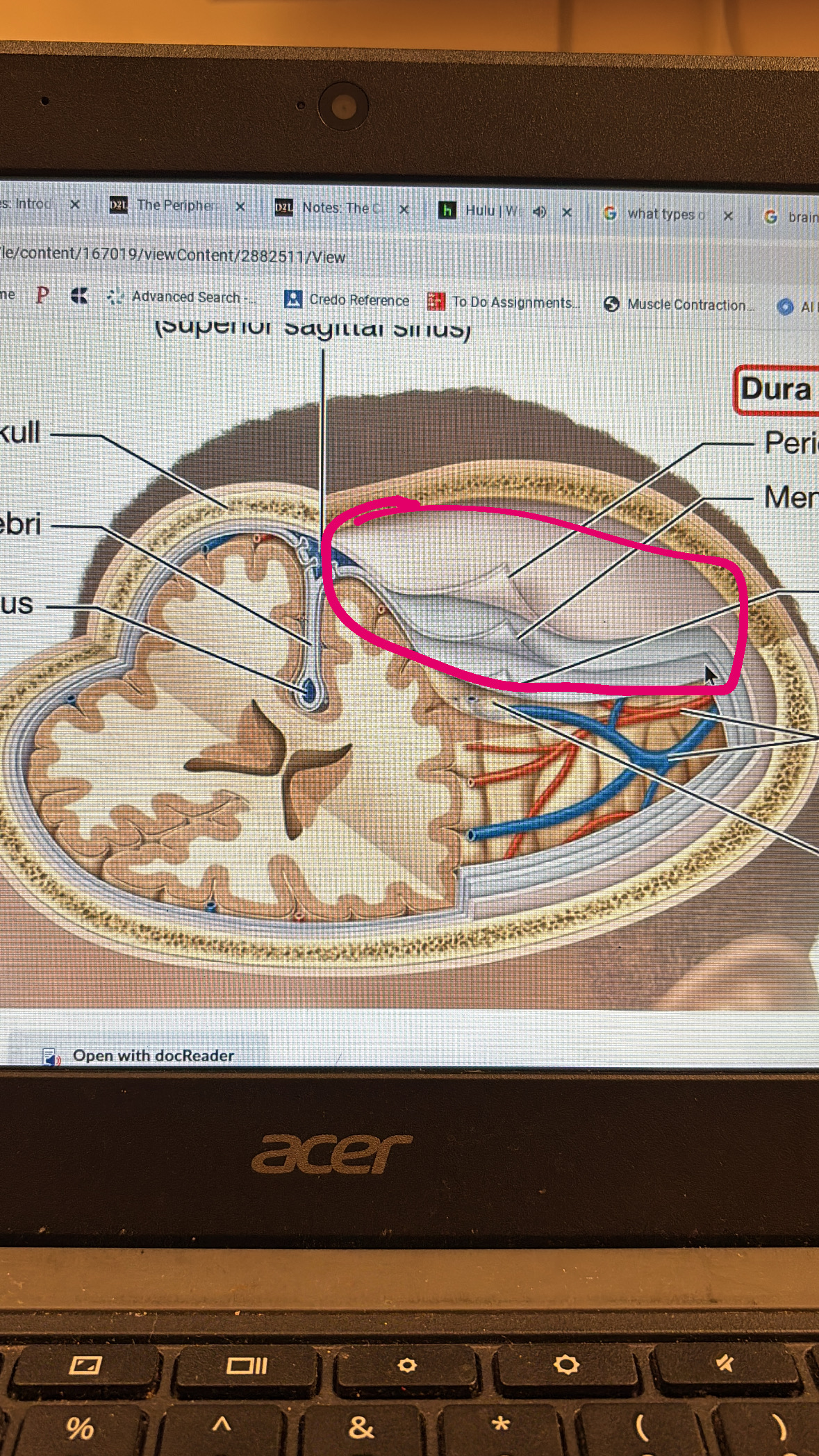
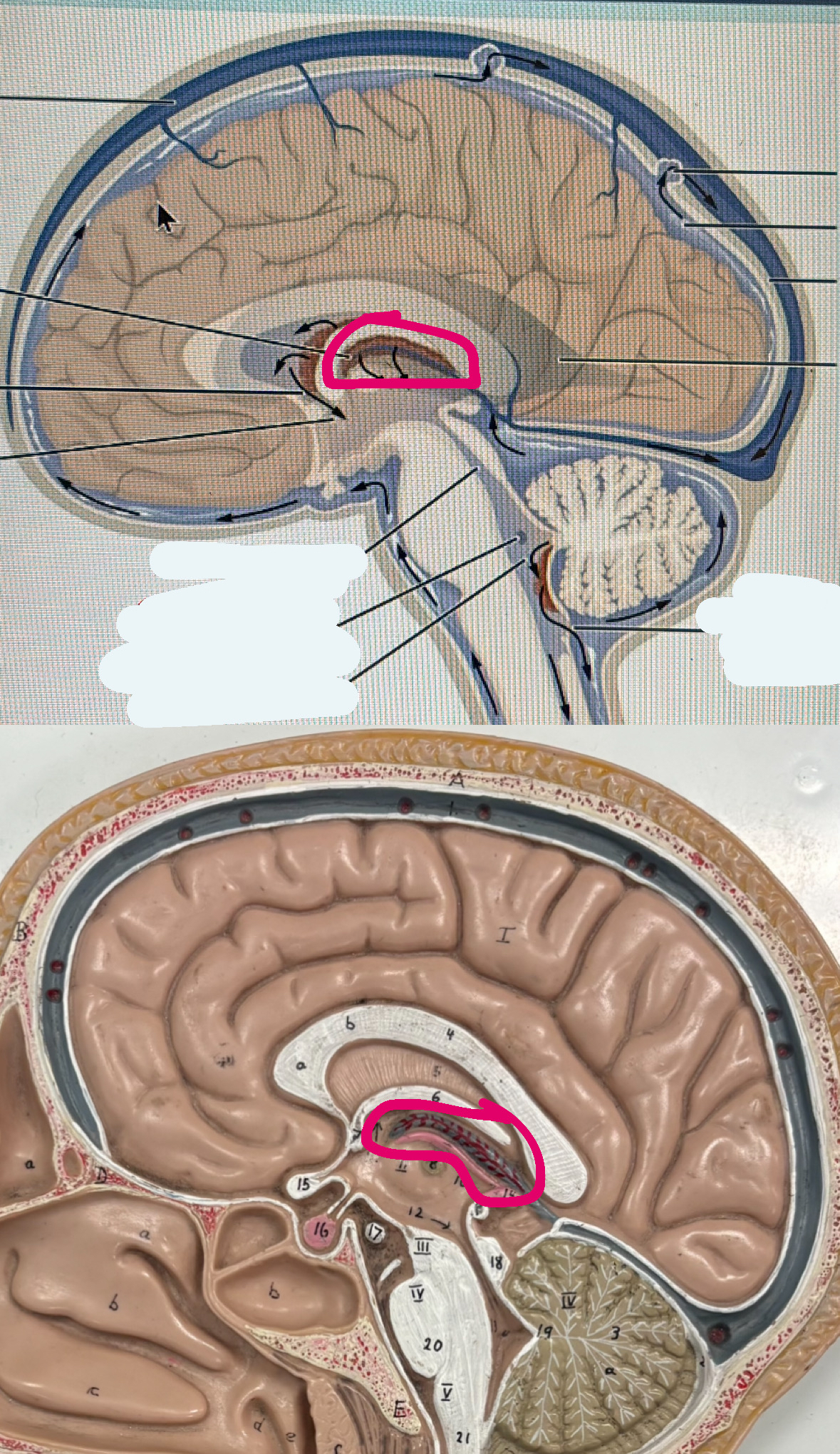
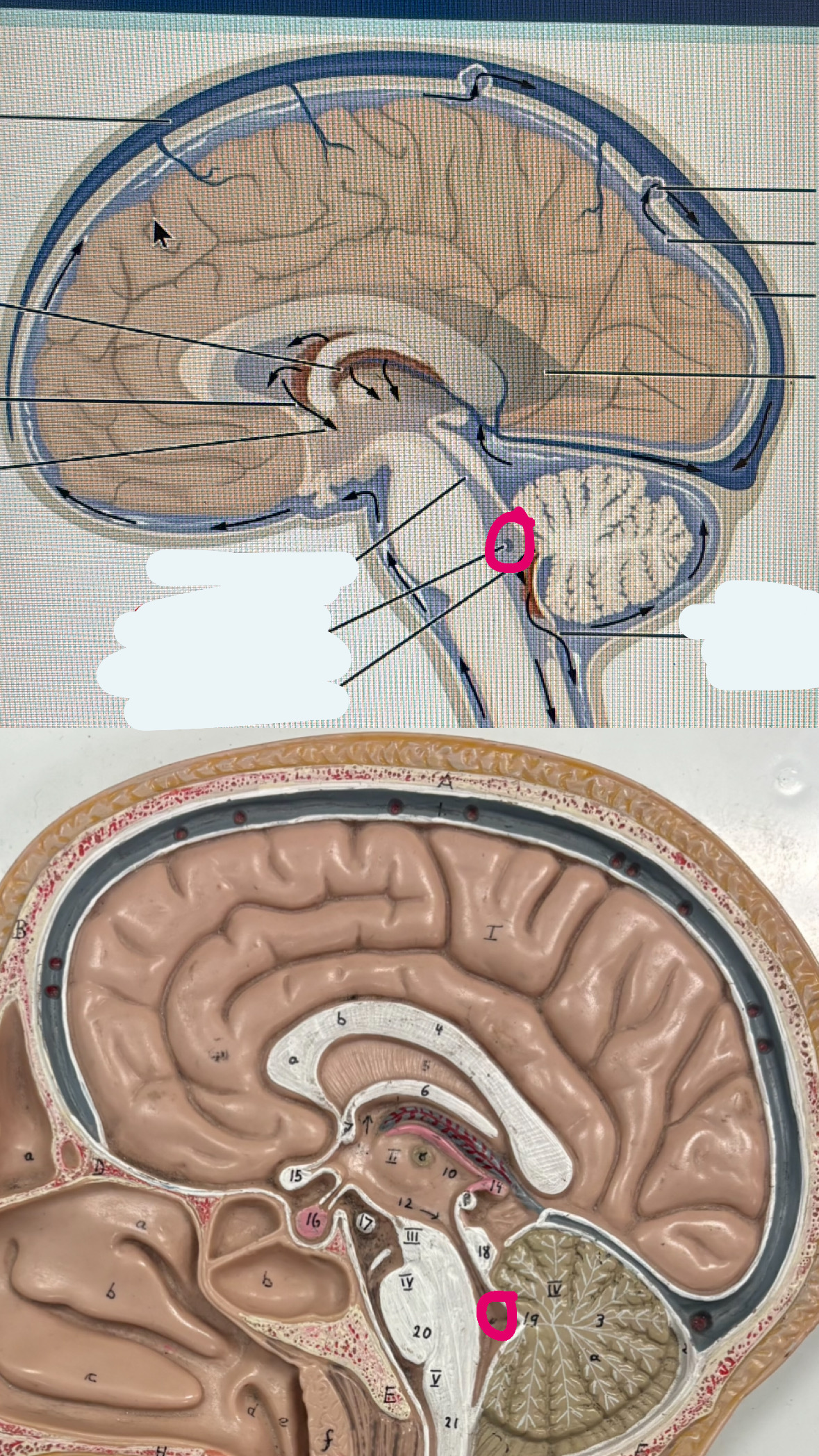
dura mater
top two layers protecting the brain
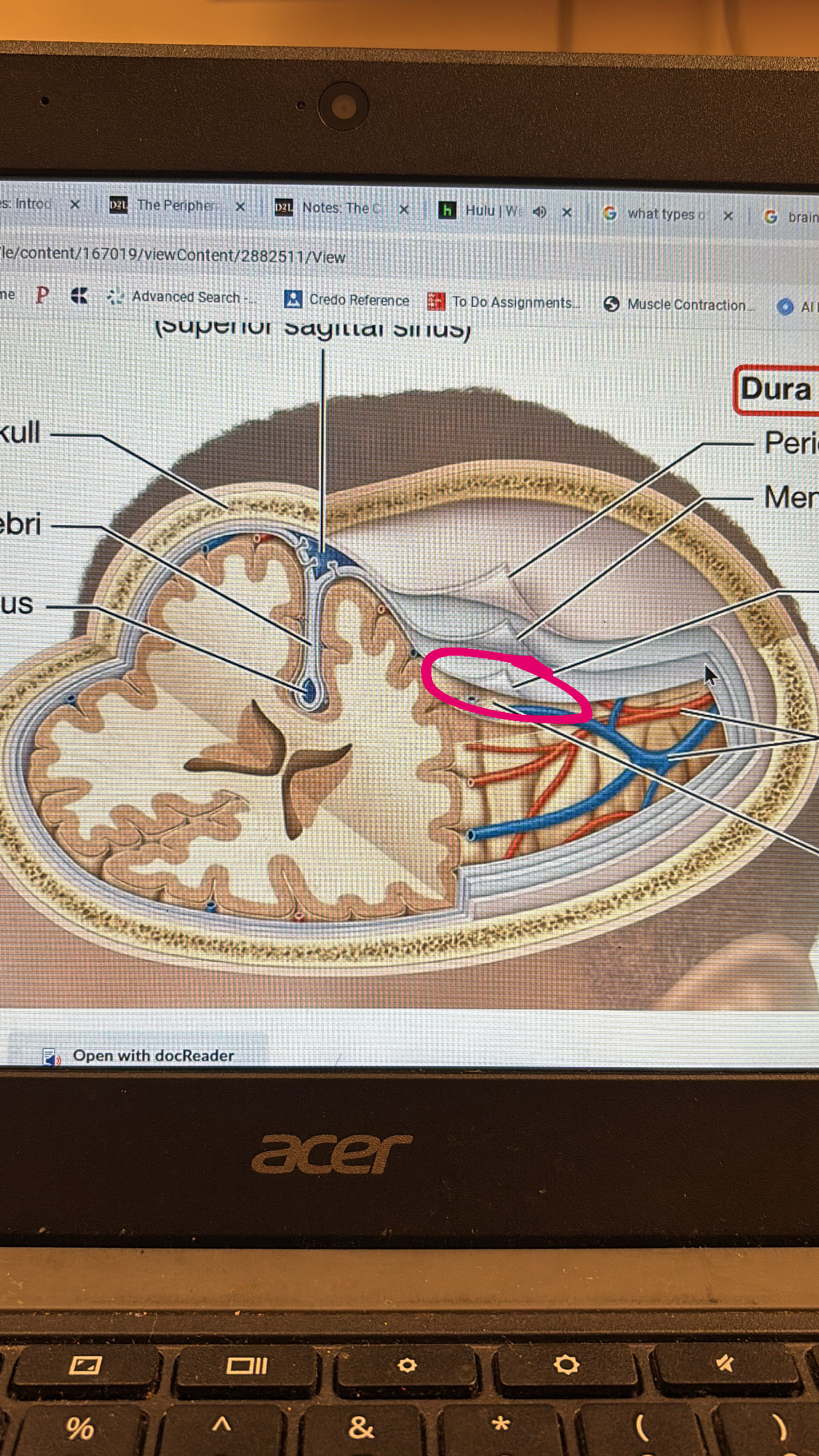
arachnoid mater
third layer protecting the plan
pia mater
4th clear layer protecting the brain
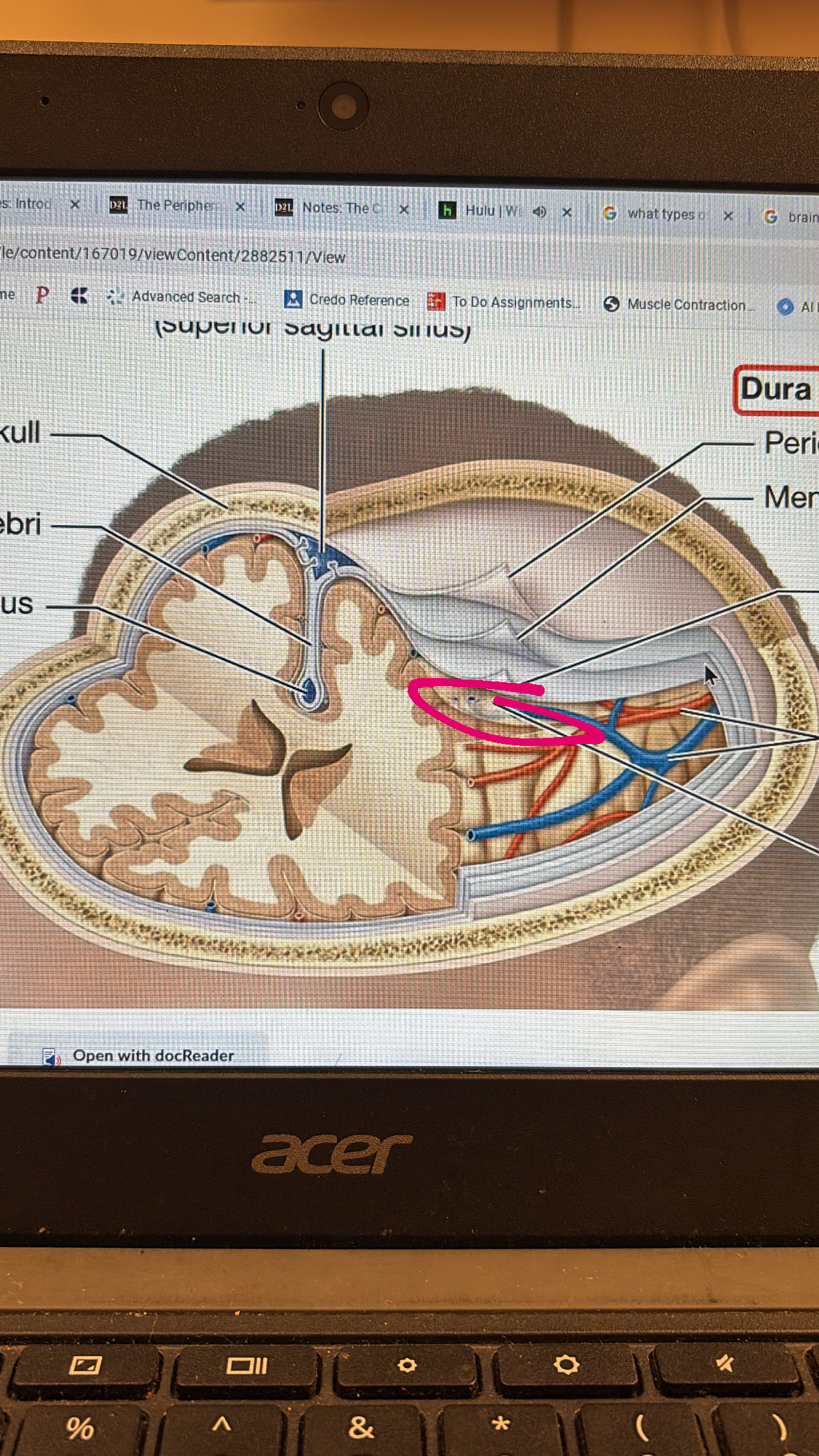
subarachnoid space
space with hair like things below the arachnoid mater but above the pia mater
first and second ventricles
lateral ventricles
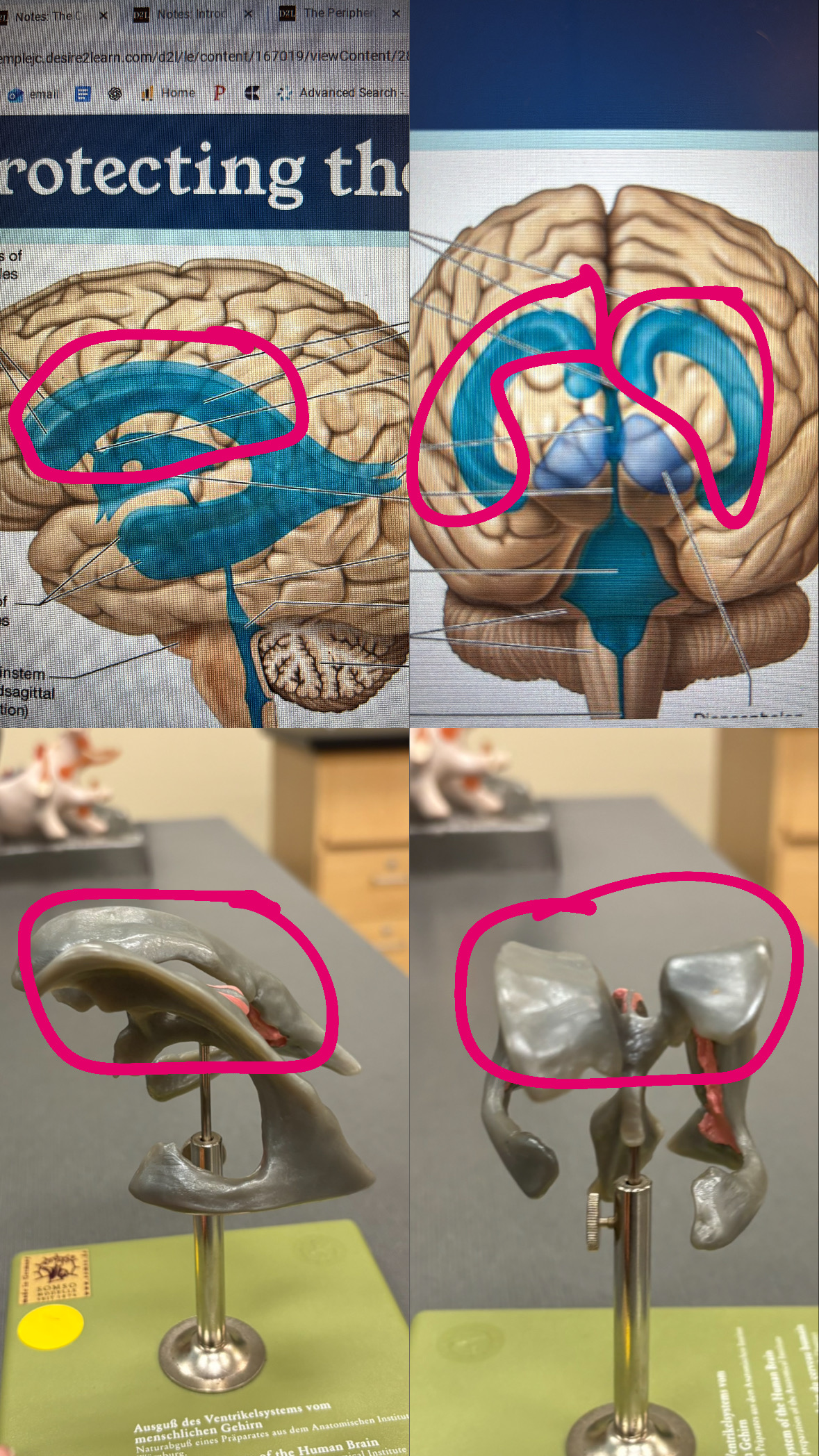
interventricular foramen
connects the lateral venteicles to the third ventricle
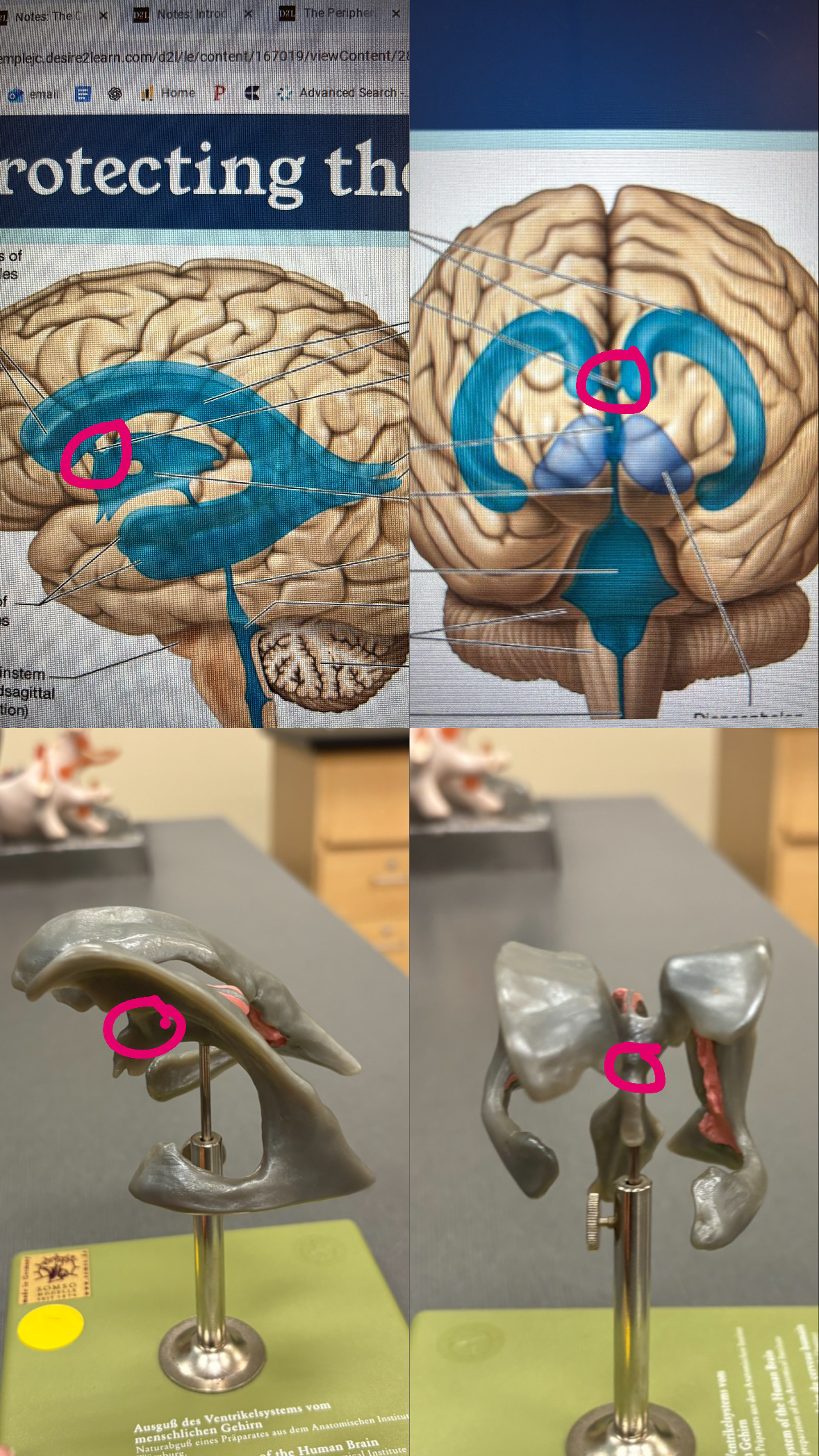
third ventricle
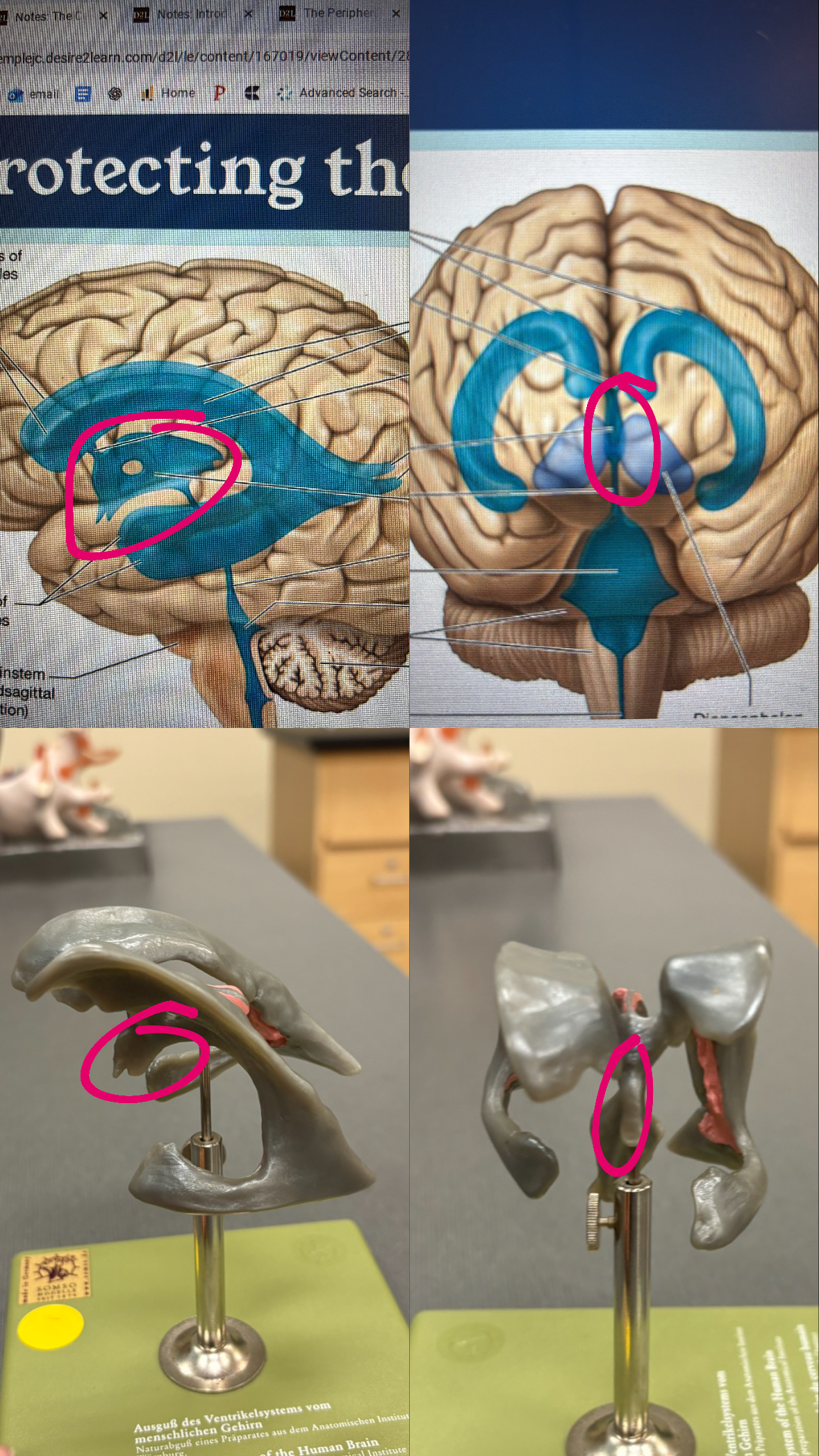
cerebral aqueduct
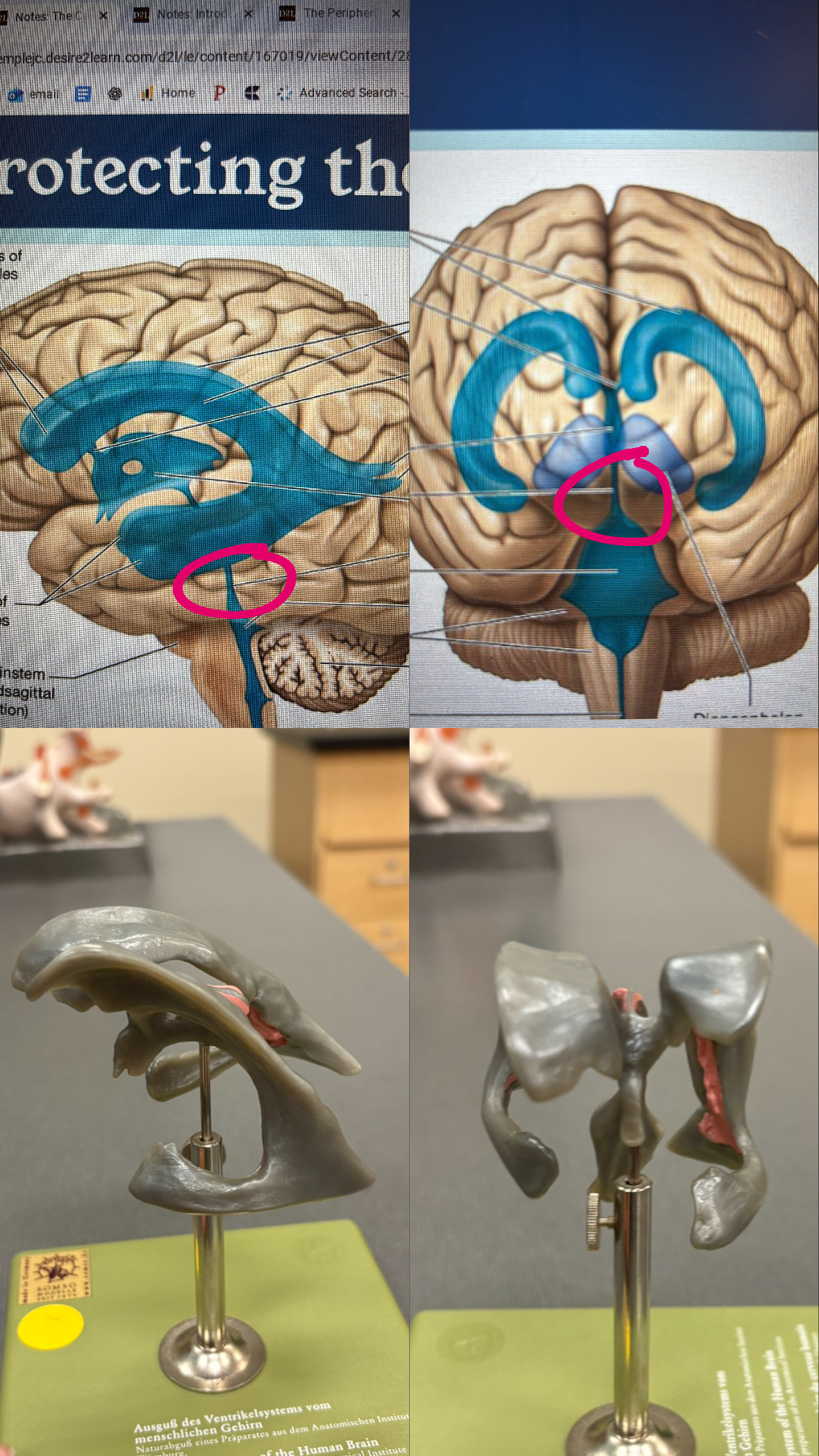
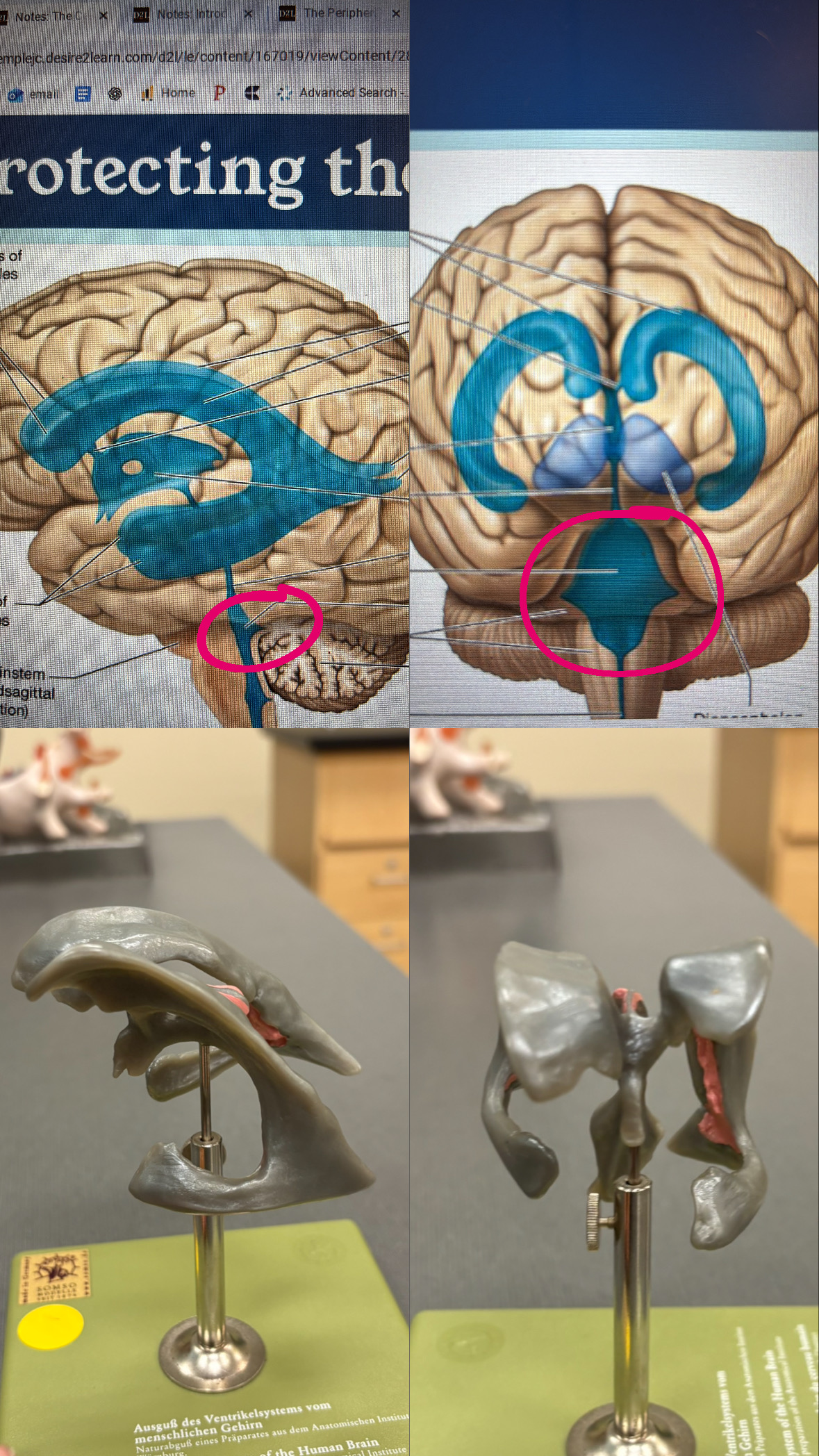
fourth ventricle
choroid plexus
the meaty worm
lateral aperture
the hole in the “fourth ventricle” space between the cerebellum and the brain stem
median aperture
little bone space below the cerebellum
blood brain barrier
prevents substances from traveling back and forth between the blood and the brain extracellular fluid
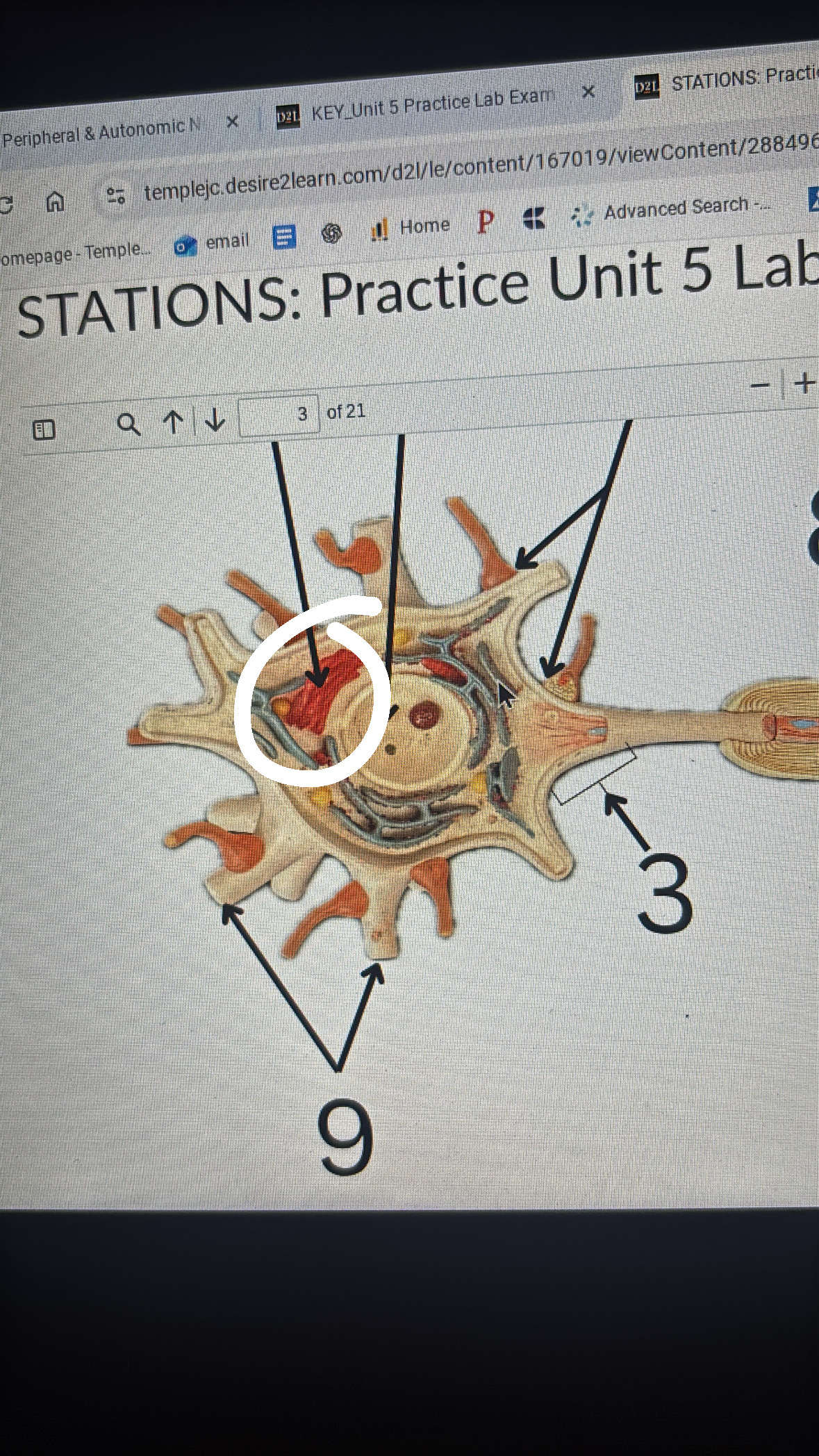
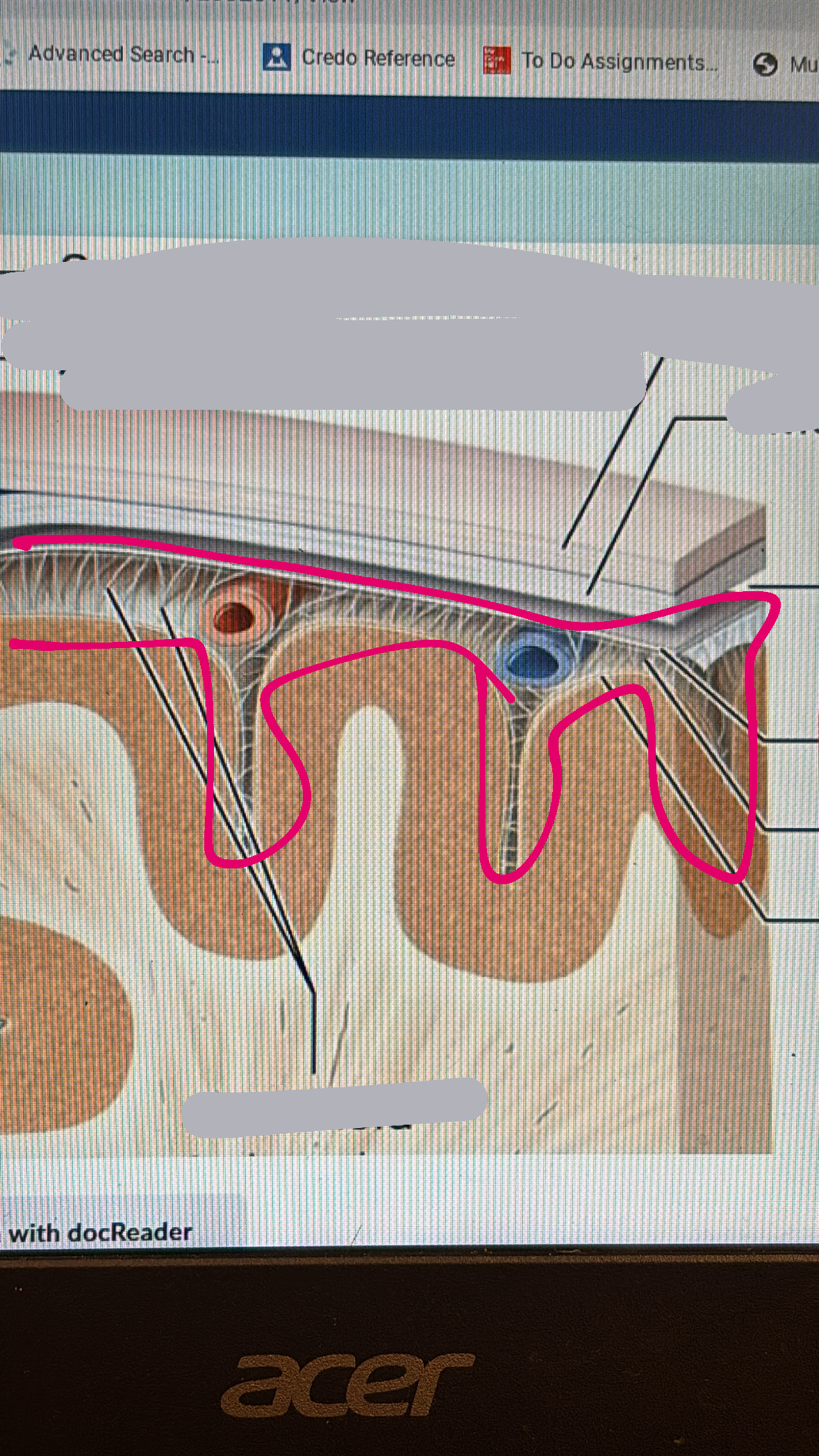
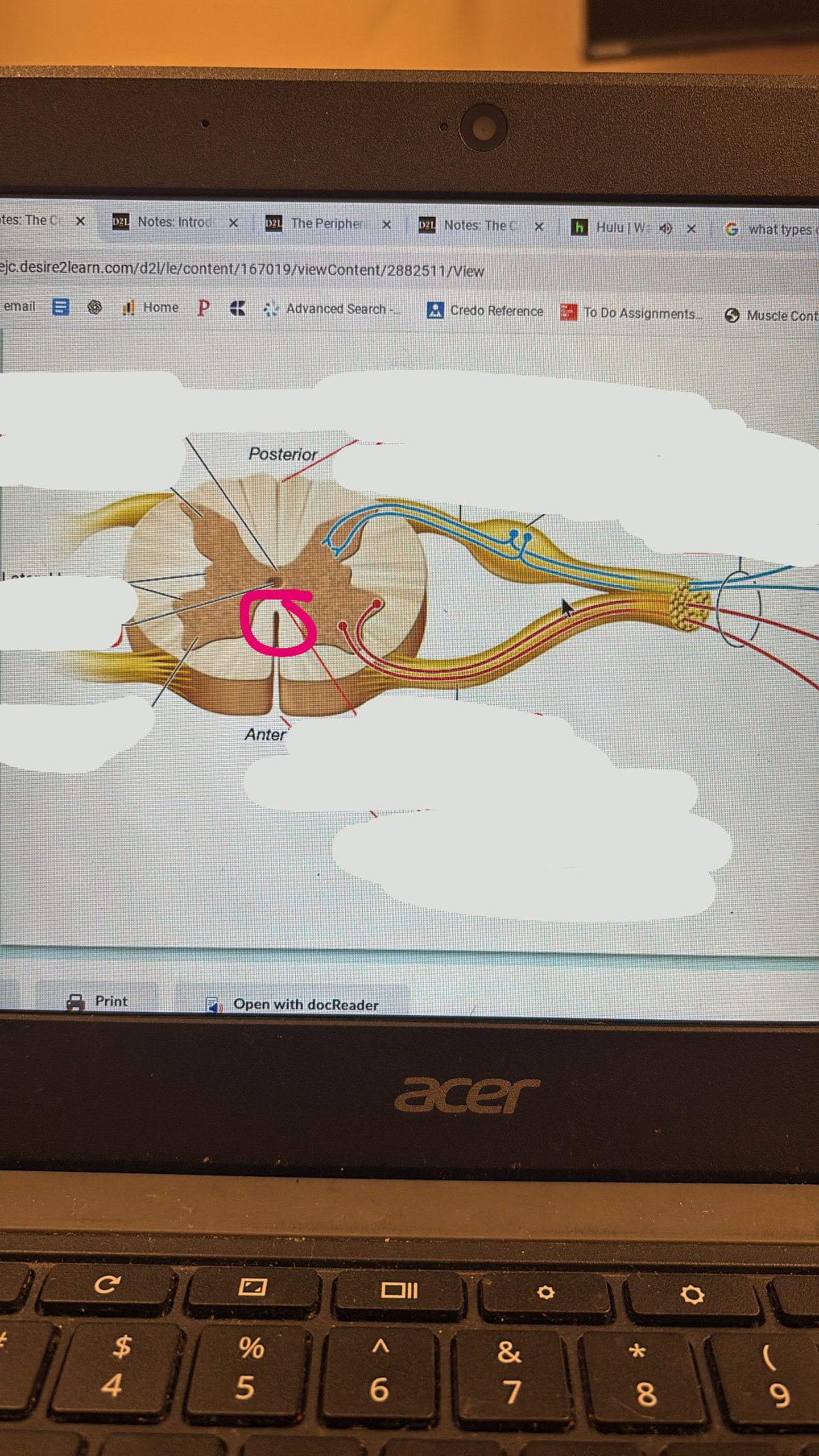
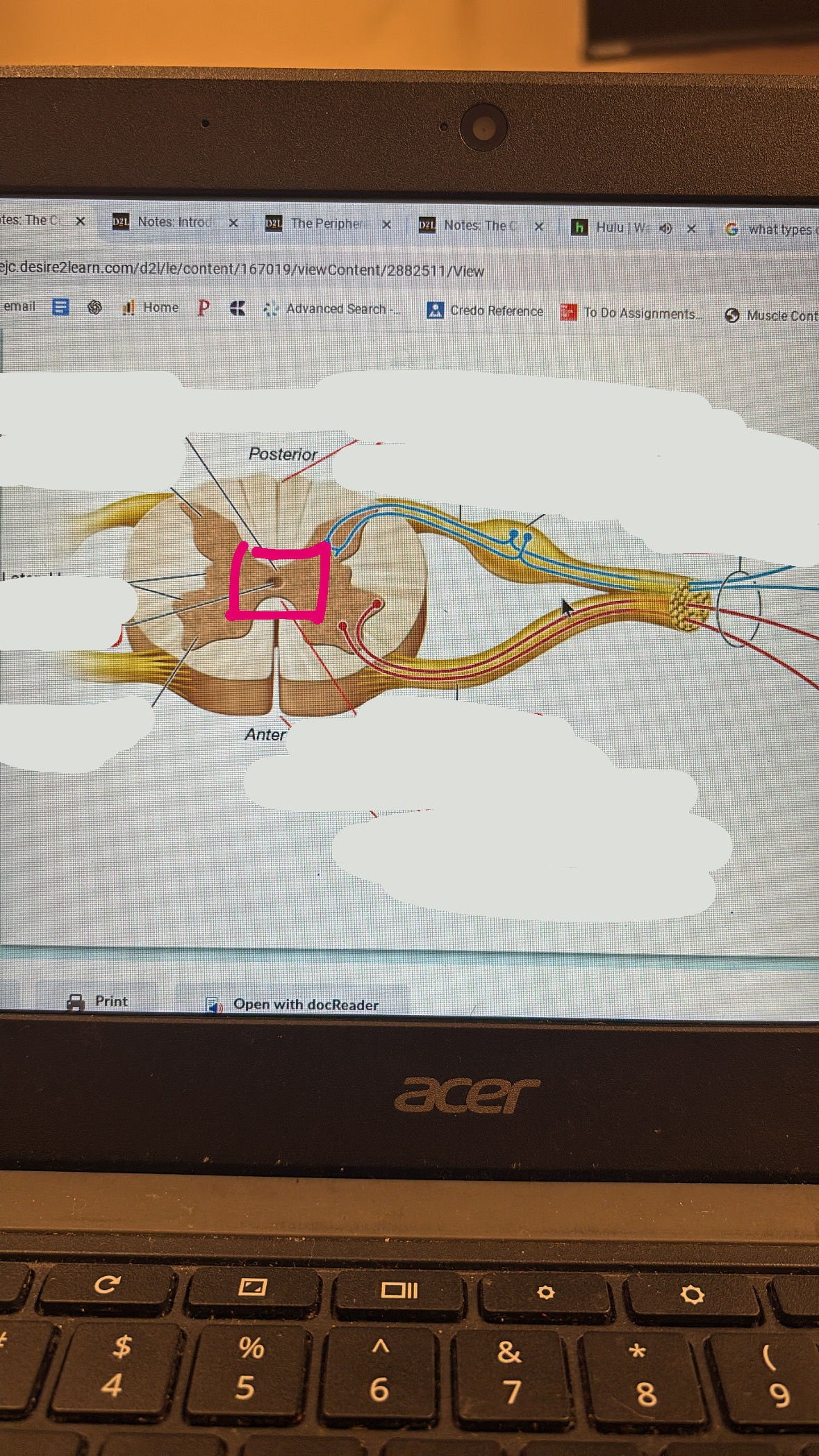
posterior median sulcus
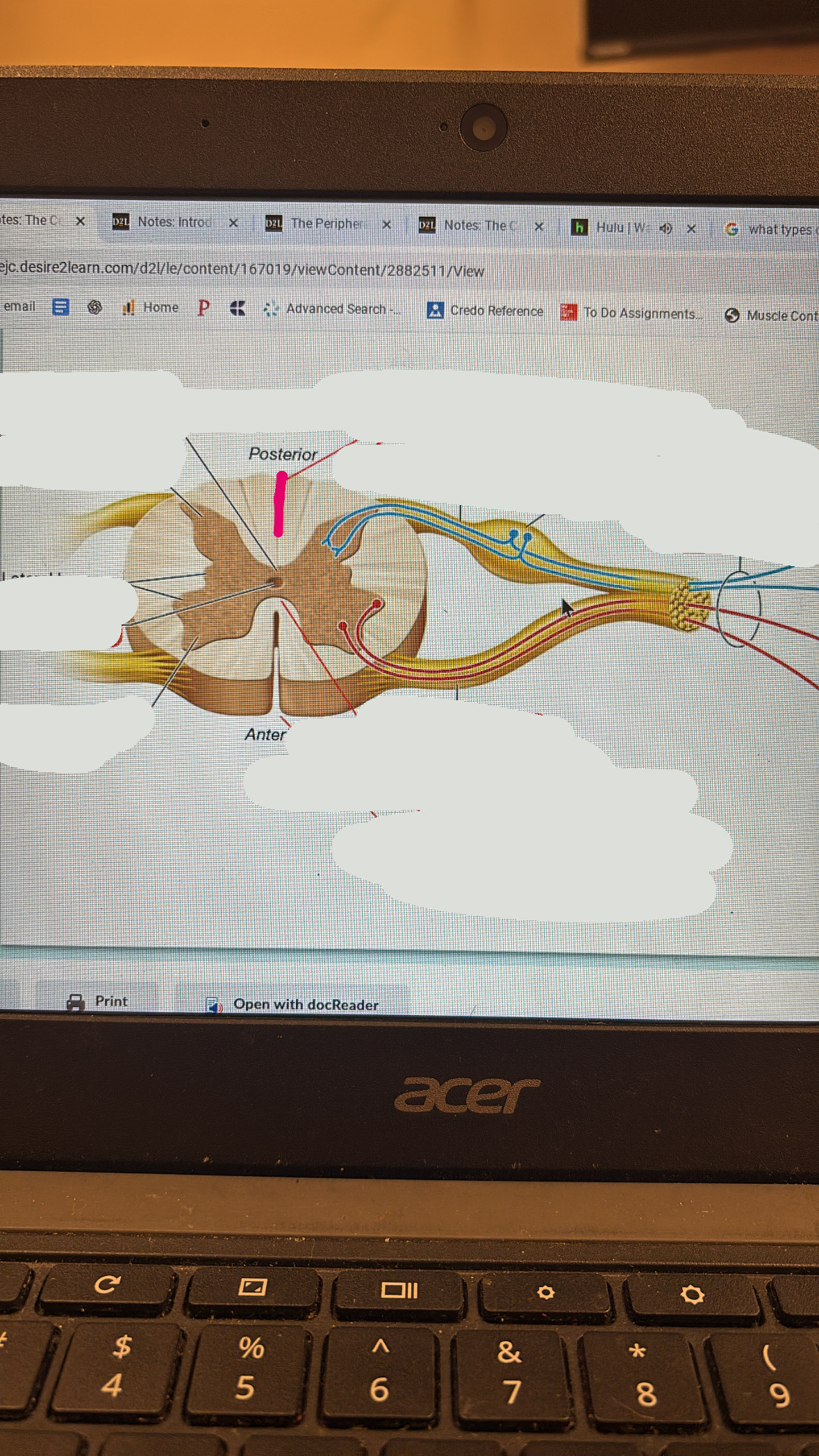
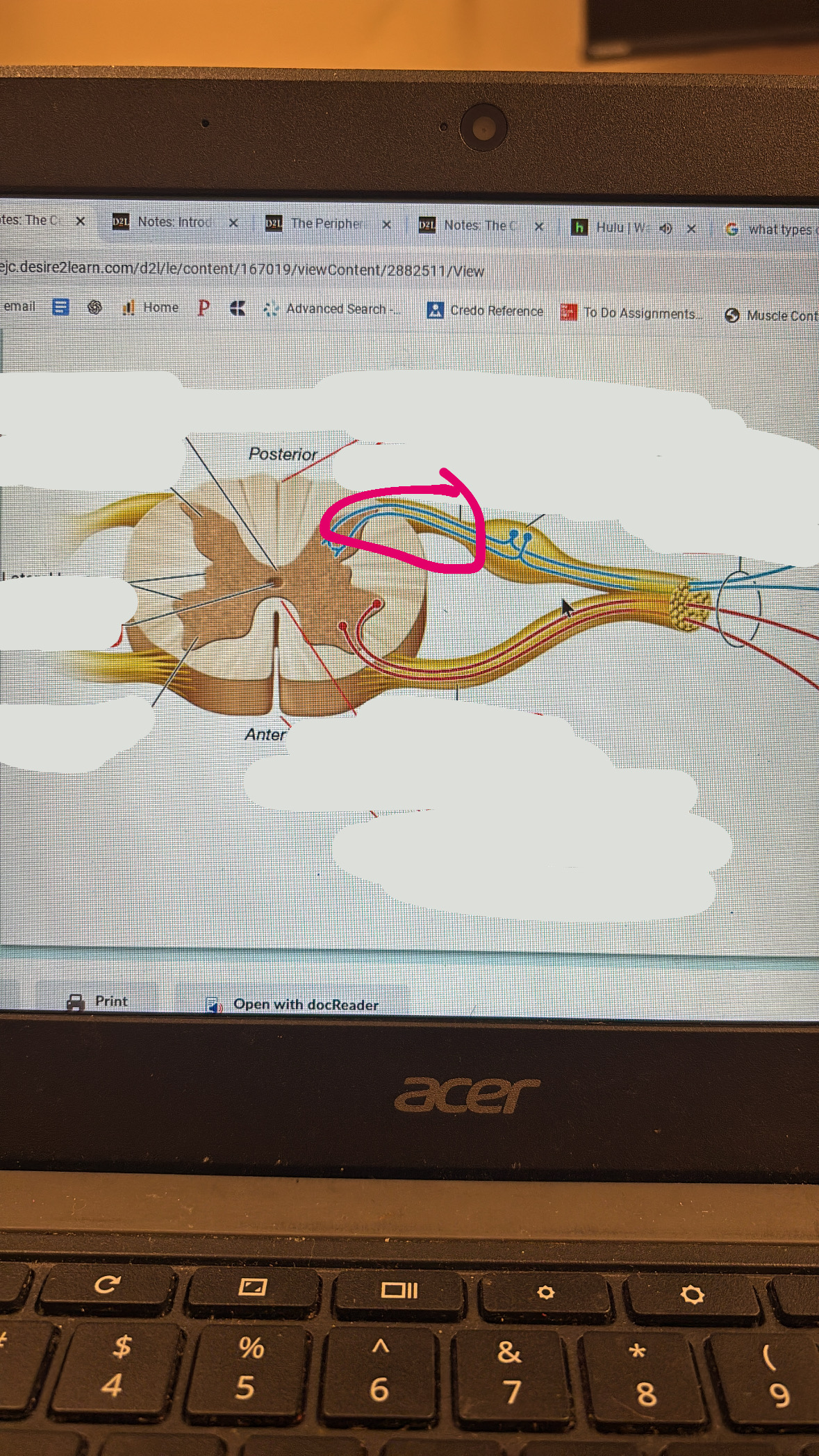
posterior root
sensory
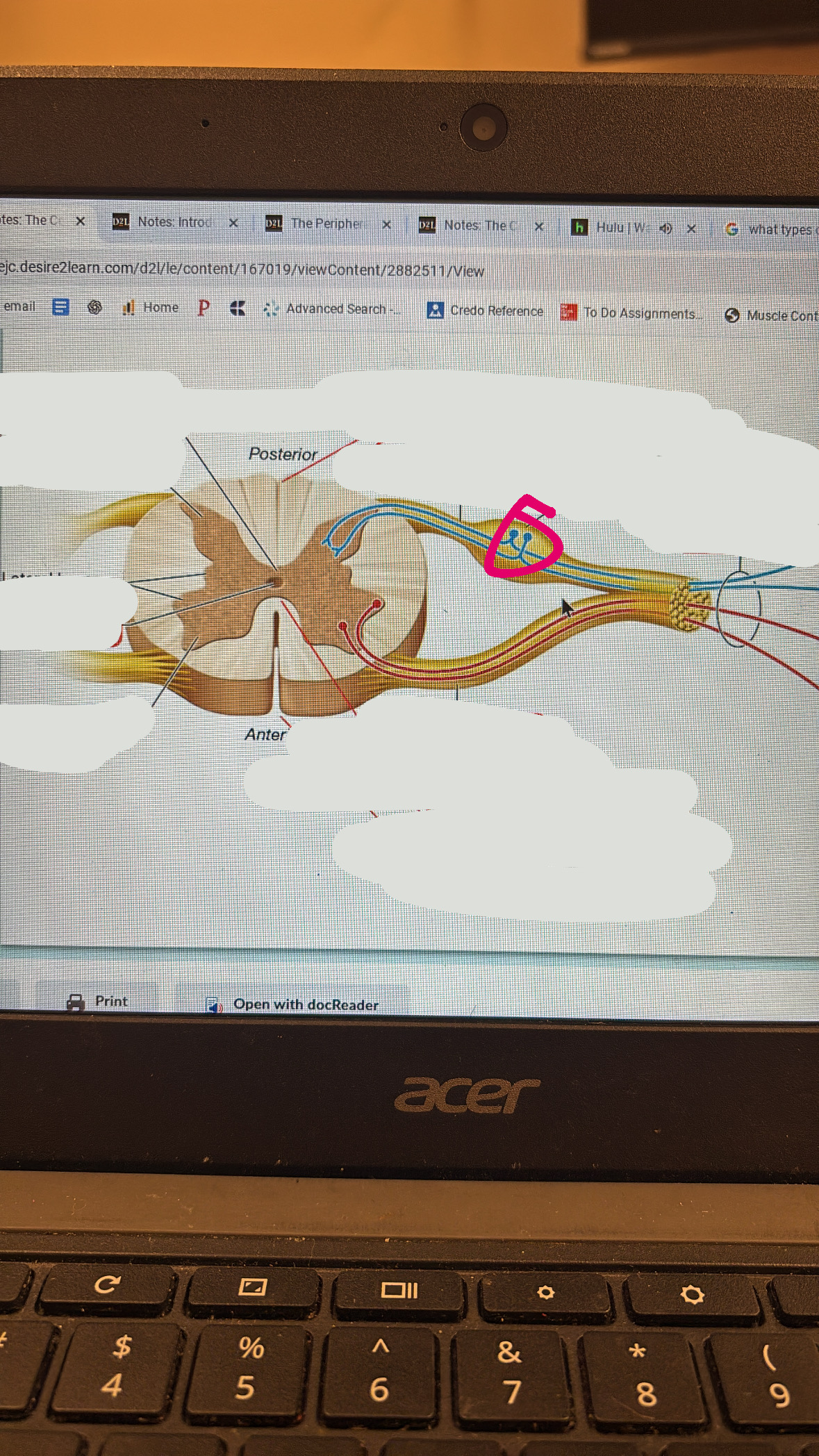
posterior root ganglion
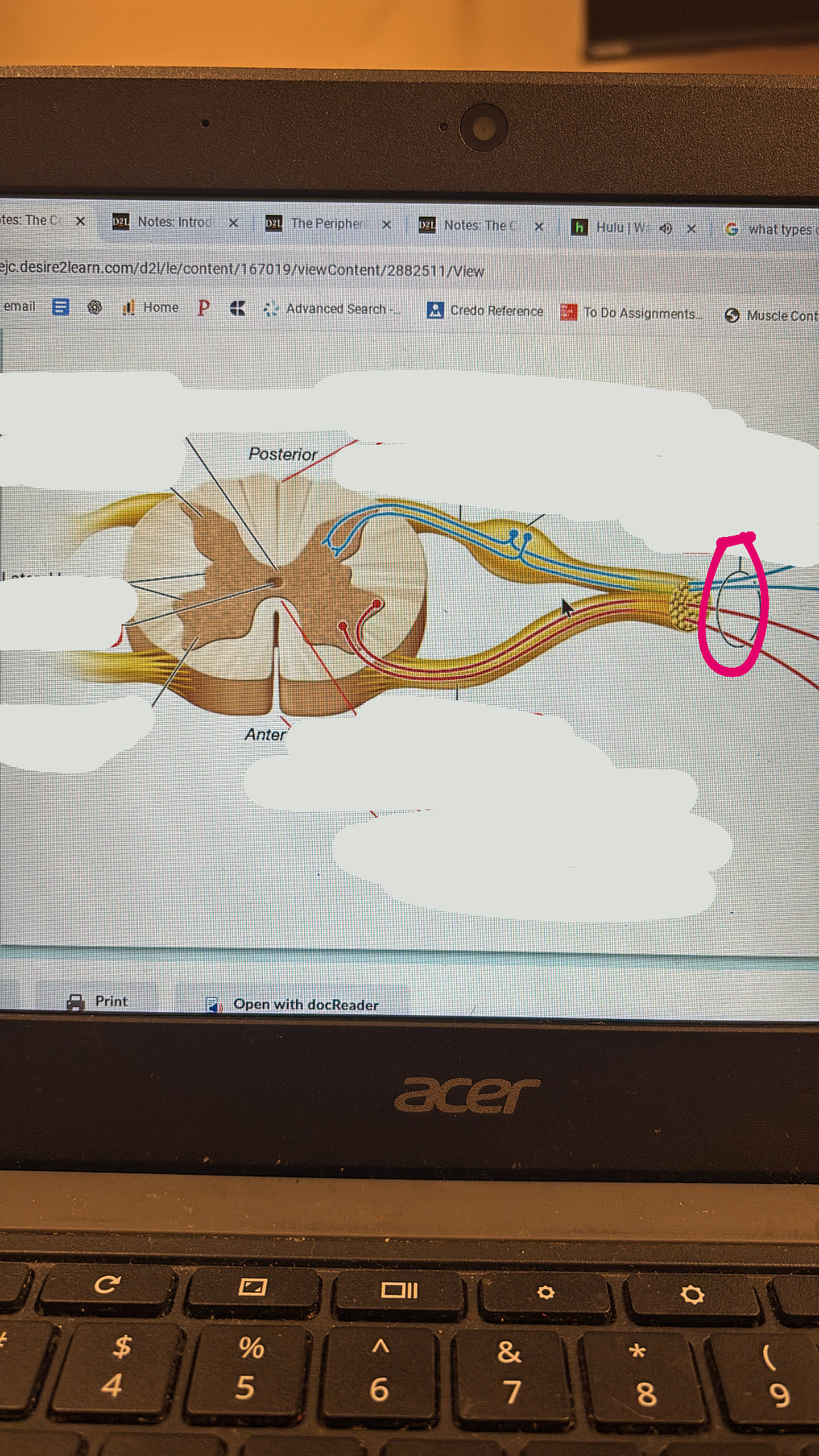
spinal nerve
anterior root
motor
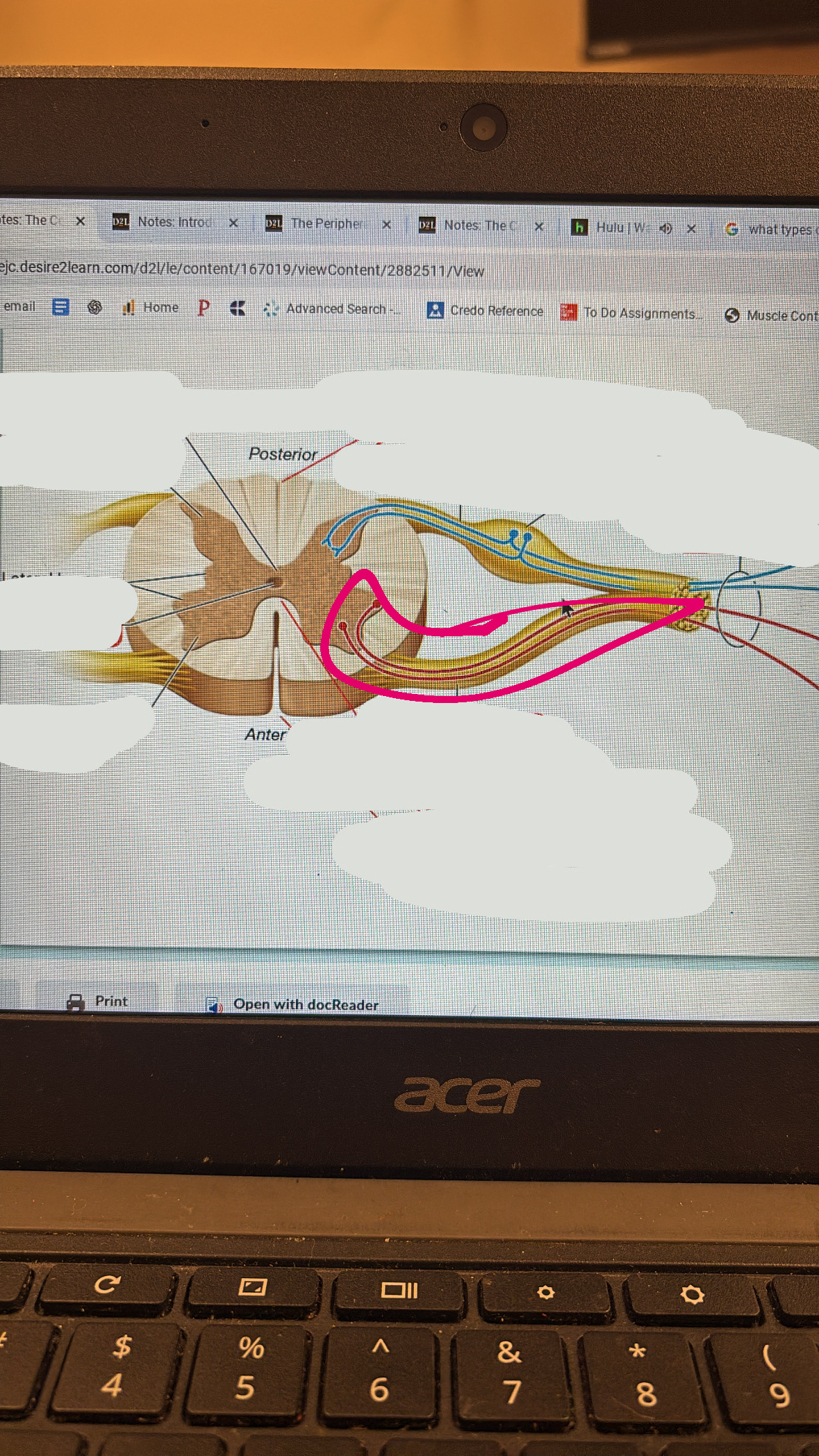
white commissure
white matter in spinal cord
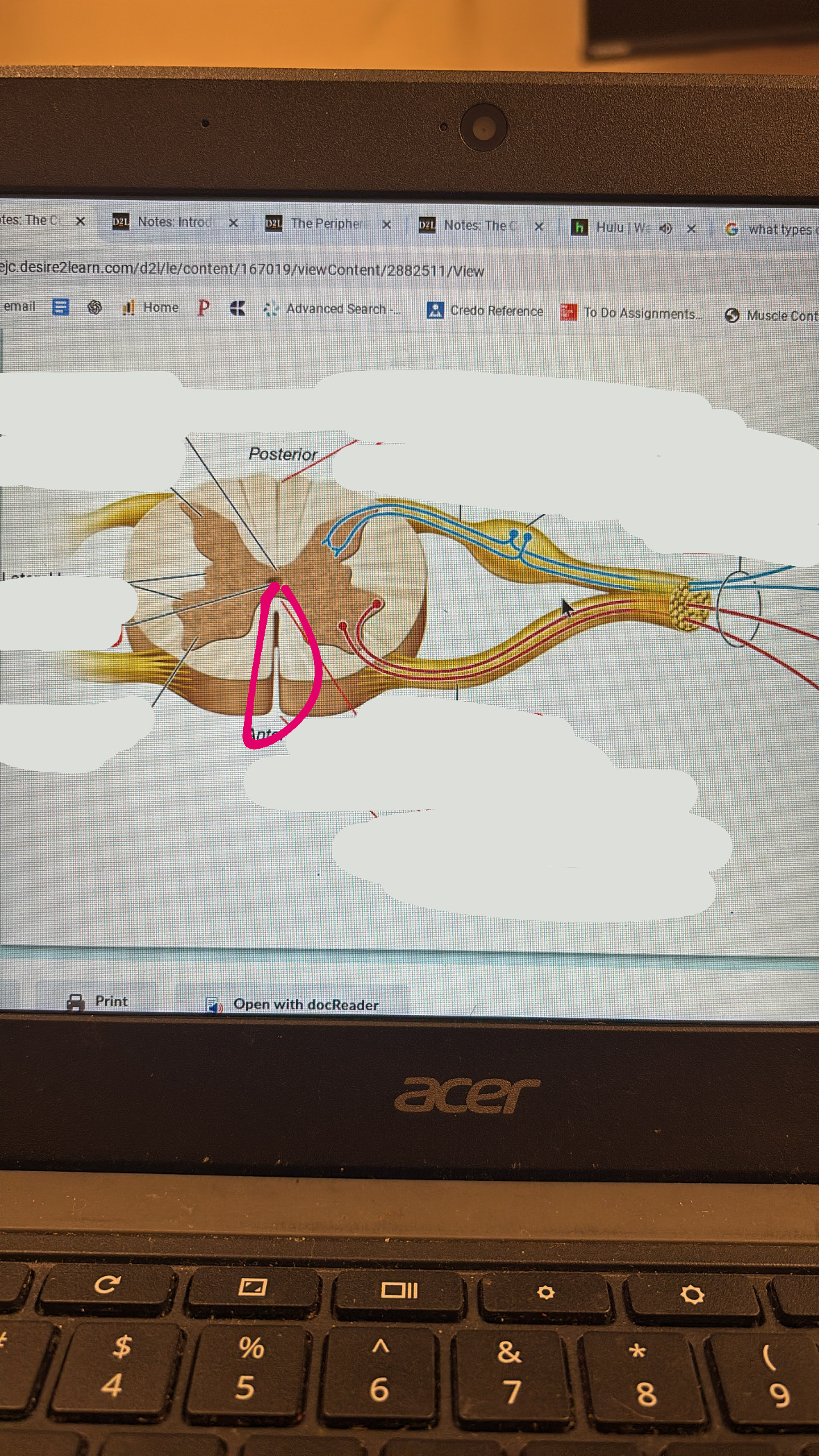
anterior median fissure
anterior horn
central canal
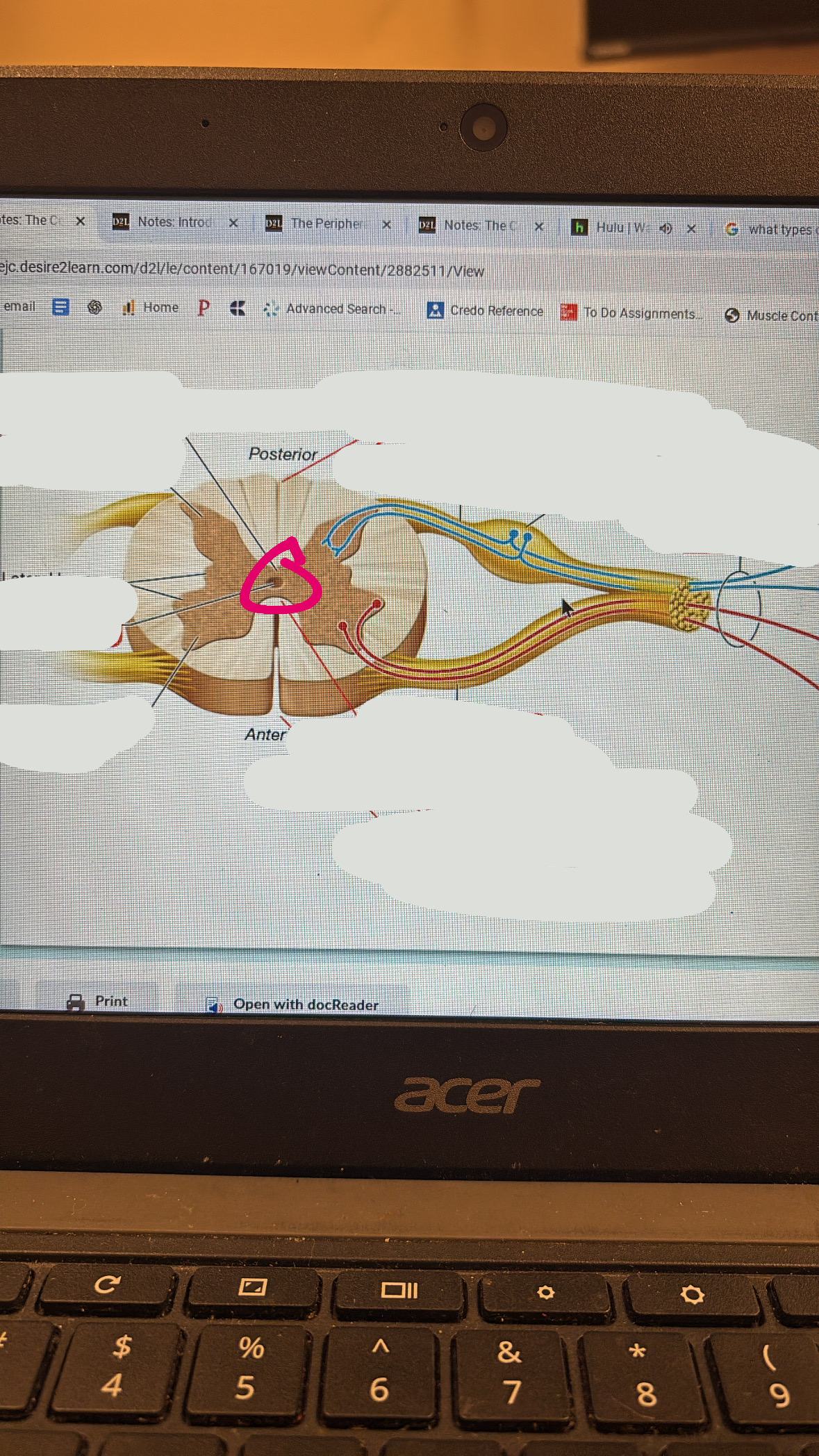
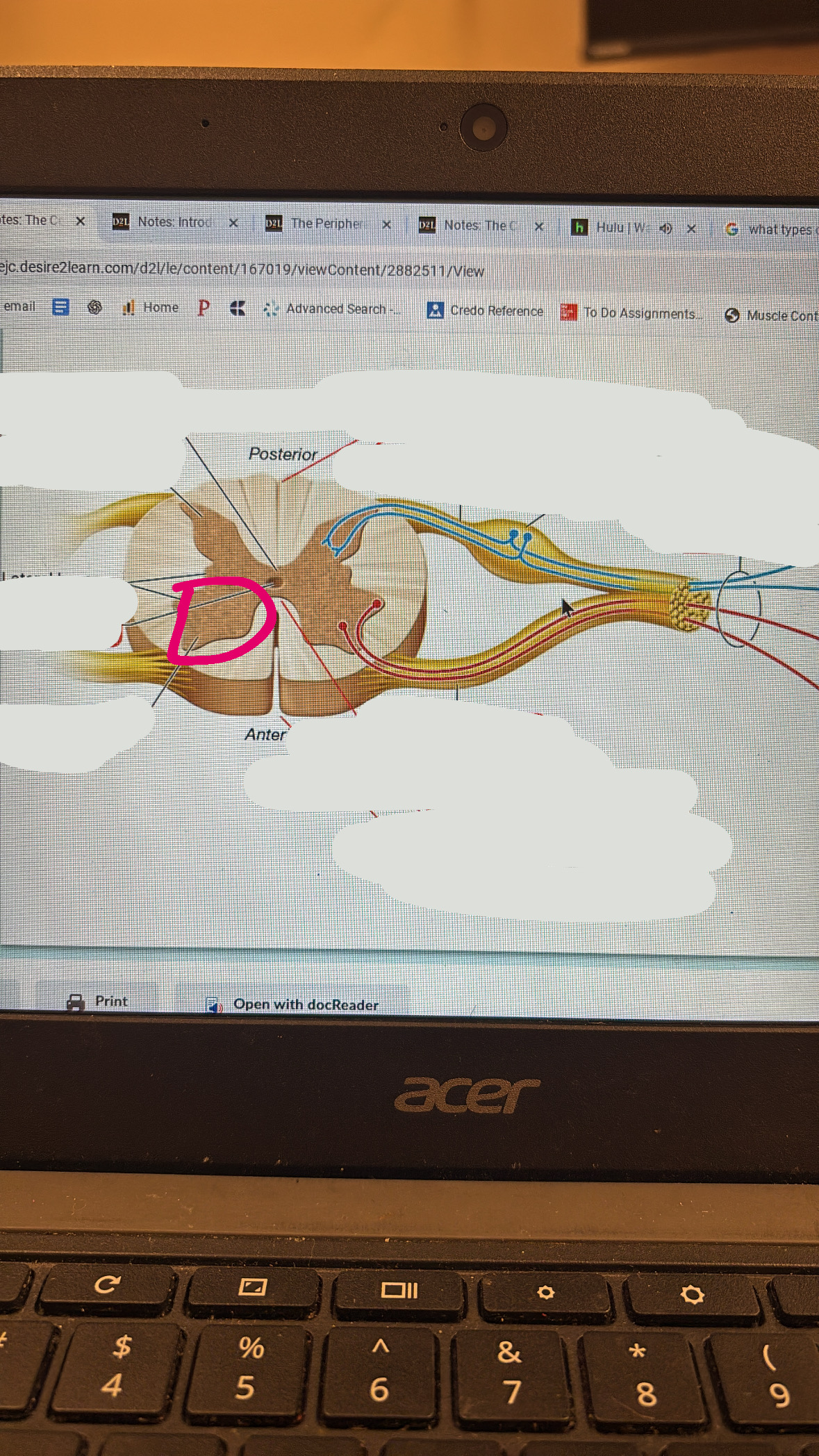
posterior horn
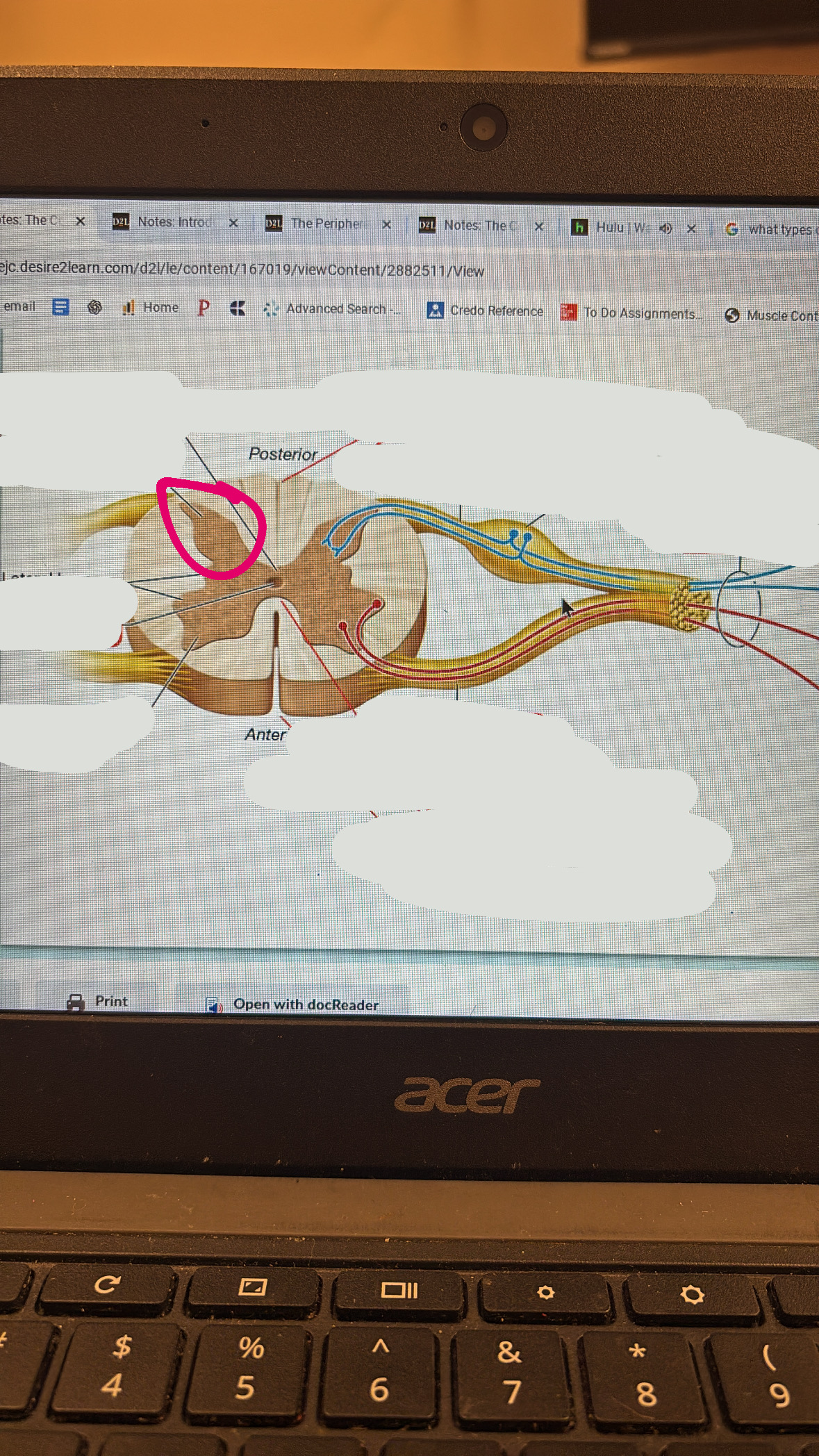
gray commissure
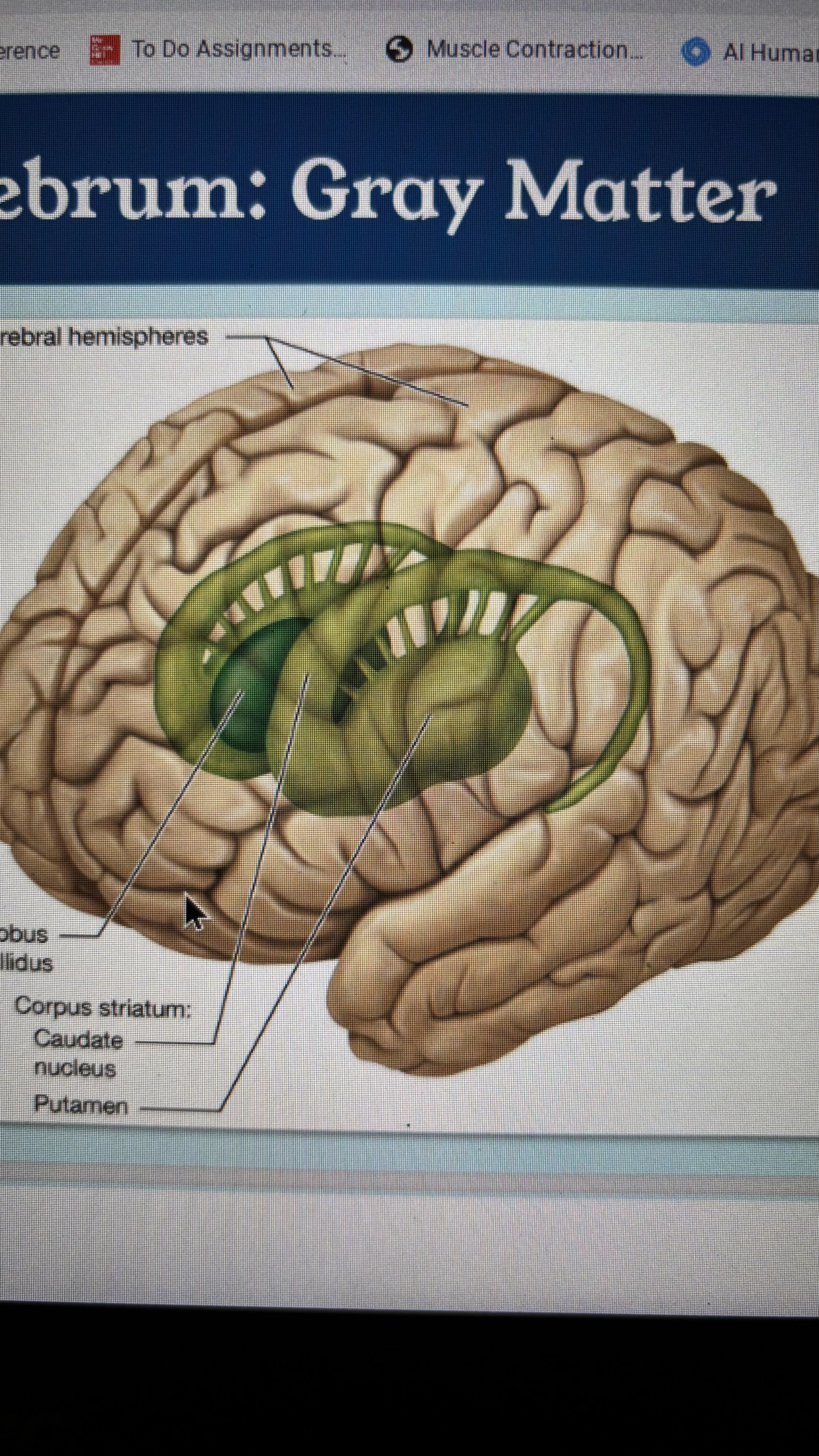
basal nuclei
located within the cerebral hemisphere on each side of the diencephalon
inhibit involuntary movement
initiate voluntary movement
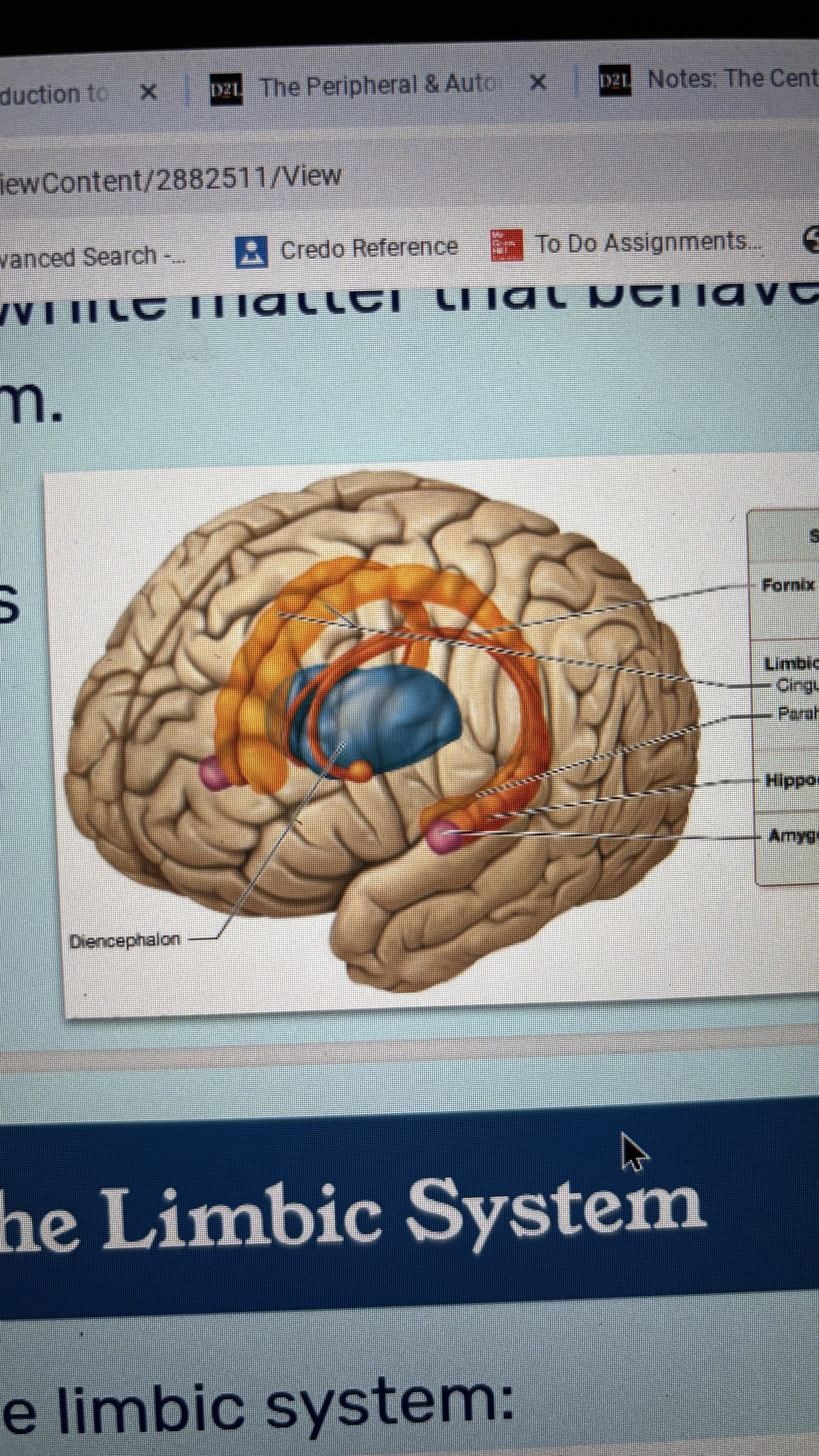
limbic system
composed of gray matter nuclei and connecting white matter that behaves as a functional system
limbic lobe
hippocampus
amygdala
fornix
corpus collosum
golgi apparatus
modify and store protein and lipids