Chapter 20 and 21 Orgo II
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:14 AM on 4/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
1
New cards
ester nomenclature
Esters are named as alkyl alkanoates. The alkyl group connected to the oxygen is named first, followed by the group attached to the carbonyl.
The acyl portion is named by substituting the suffix -ate
The acyl portion is named by substituting the suffix -ate
2
New cards
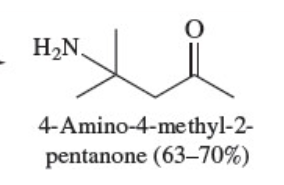
Amide nomenclature
When naming amides, replace the -ic acid or -oic acid of the corresponding carboxylic acid with -amide. Substituents, irrespective of whether they are attached to the acyl group or the amide nitrogen, are listed in alphabetical order. Substitution on nitrogen is indicated by the locant N-.
3
New cards
nitriles
substitutive IUPAC names for nitriles add the suffix -nitrile to the name of the parent hydrocarbon chain that includes the carbon of the cyano group
4
New cards
less stable to most stable
acyl chlorides, acid anhydrides , esters, amides
5
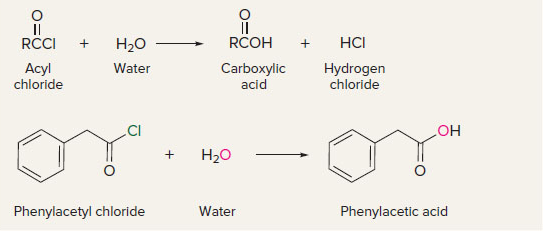
New cards
acyl chlorides to carboxylic acids
6
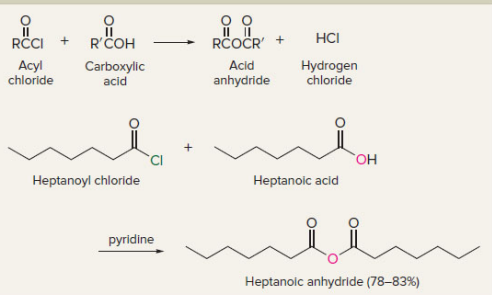
New cards
acyl chlorides to acid anhydrides
7
New cards
acyl chlorides to esters
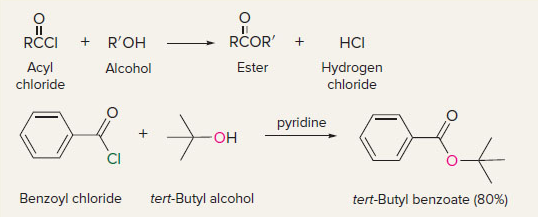
8
New cards
acyl chlorides to amides
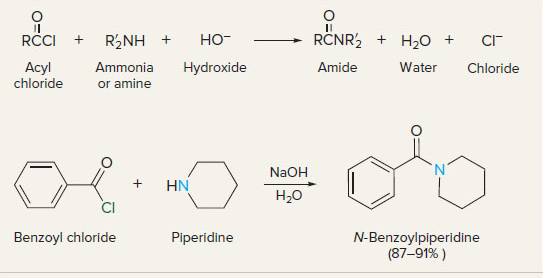
9
New cards
acid anhydrides to esters
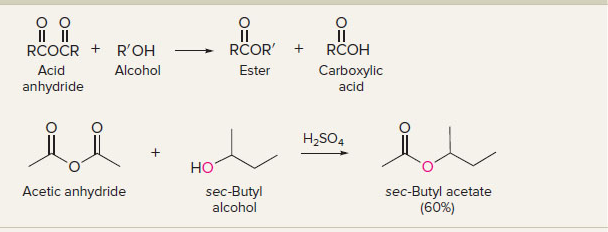
10
New cards
acid anhydrides to amides
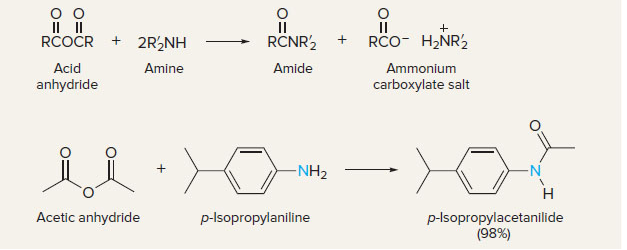
11
New cards
carboxylic acid to ester
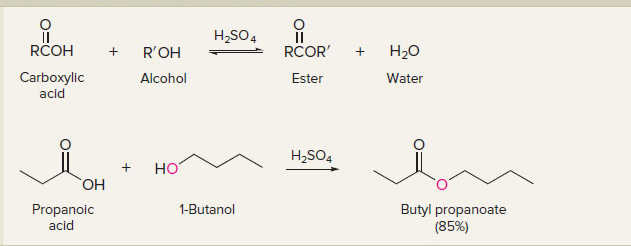
12
New cards
Baeyer-Villiger oxidation of ketones
oxygen goes to the more substituted side
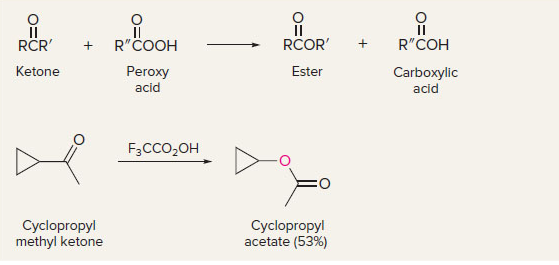
13
New cards
esters to amides
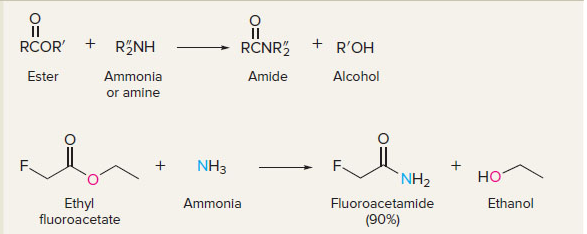
14
New cards
hydrolysis of esters
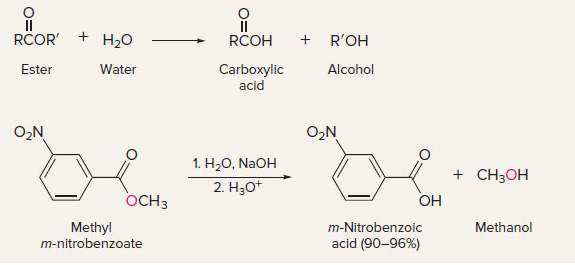
15
New cards
acid catalyzed hydrolysis of esters
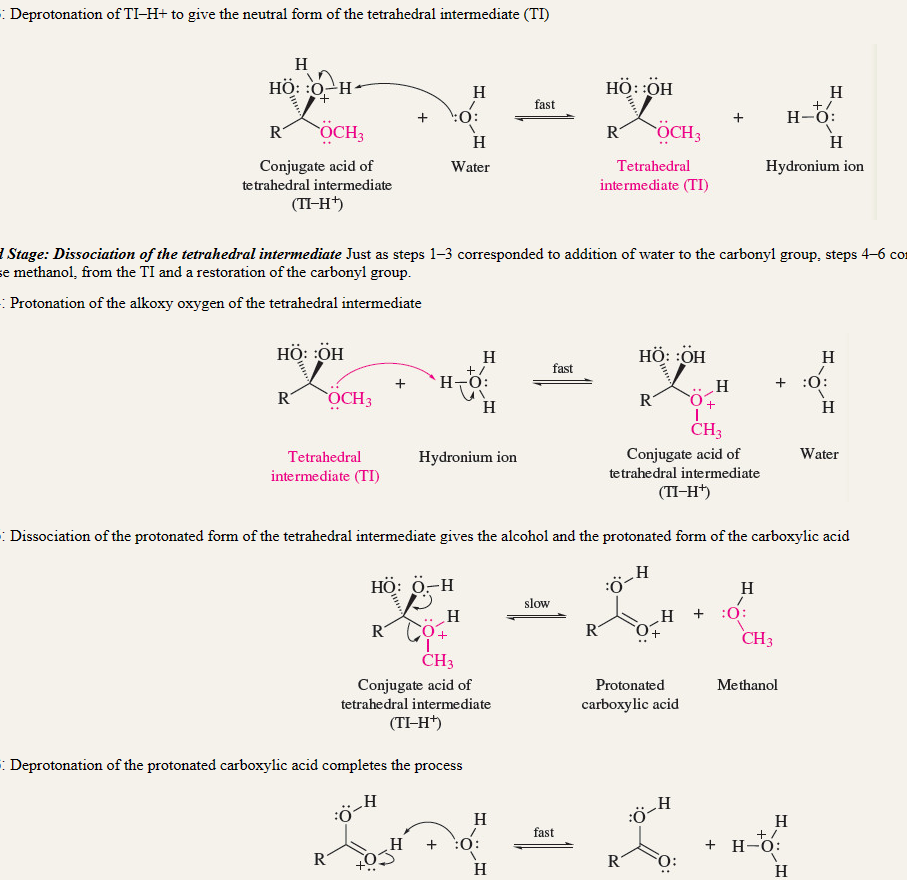
16
New cards
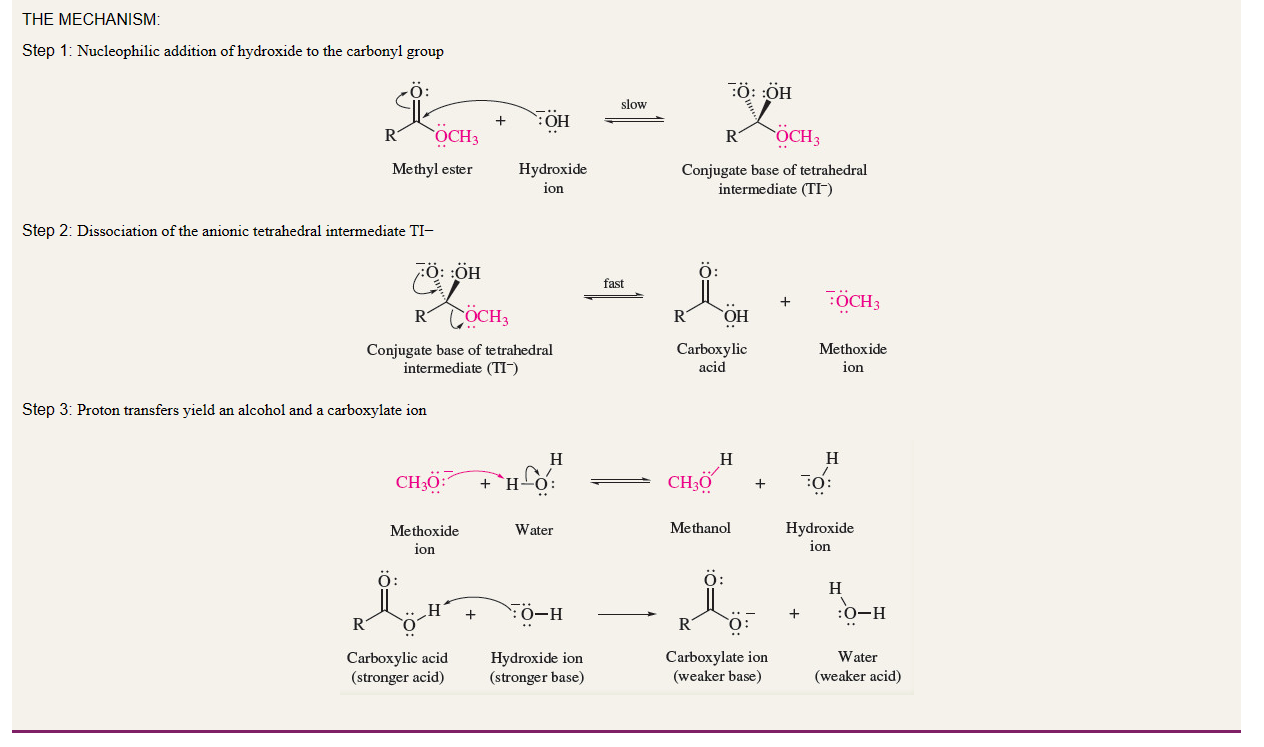
saponification
RETENTION OF CONFIGURATION
17
New cards
Reaction of Esters with Grignard and Organolithium Reagents and Lithium Aluminum Hydride
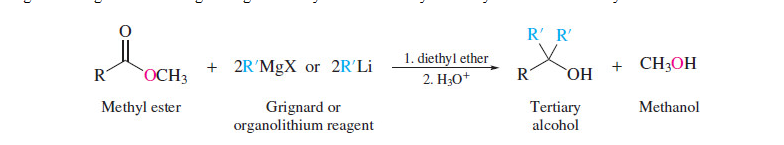
18
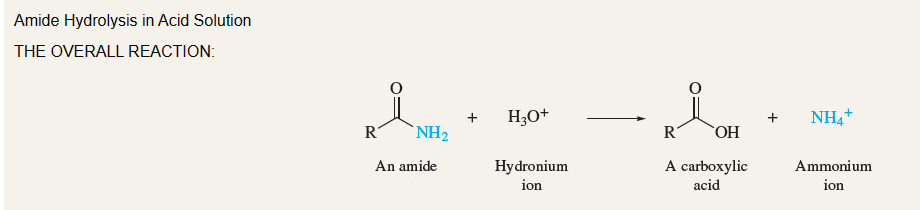
New cards
Amide Hydrolysis
Formation of (+) tetrahedral intermediate and then disassociation of NH3
19
New cards
Amide Hydrolysis in Basic Solution
products are carboxylate and ammonia
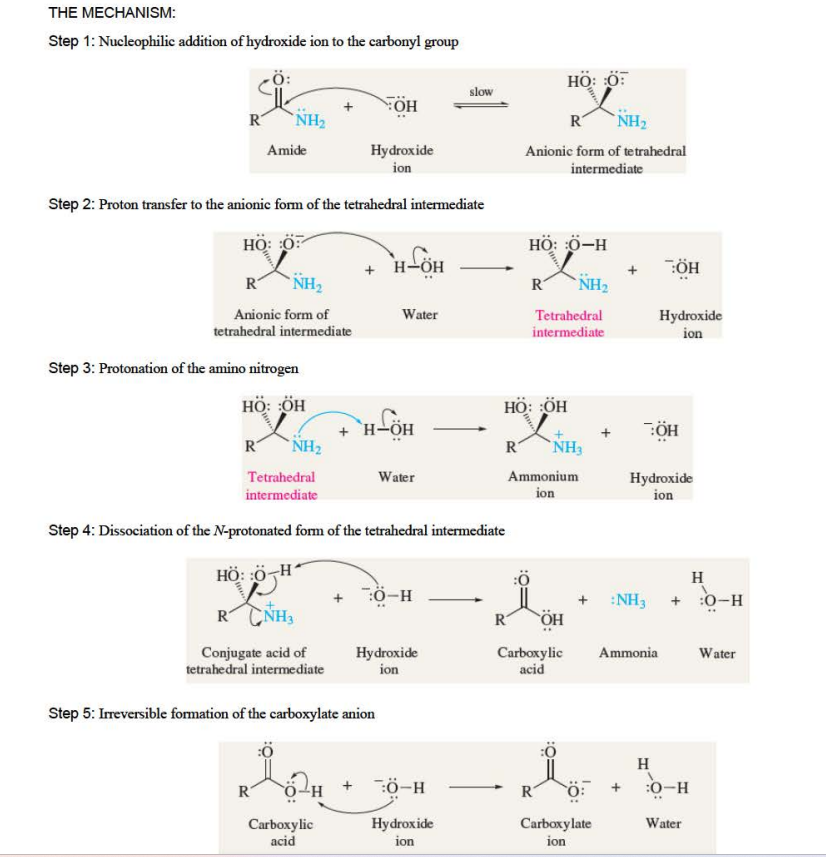
20
New cards
Nucleophilic substitution by cyanide ion
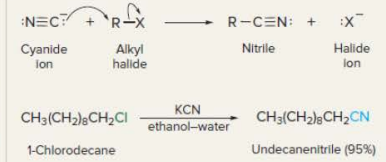
21
New cards
Cyanohydrin formation
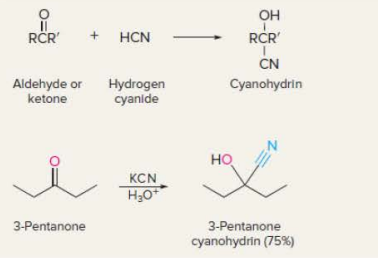
22
New cards
Nitrile Hydrolysis in Basic Solution
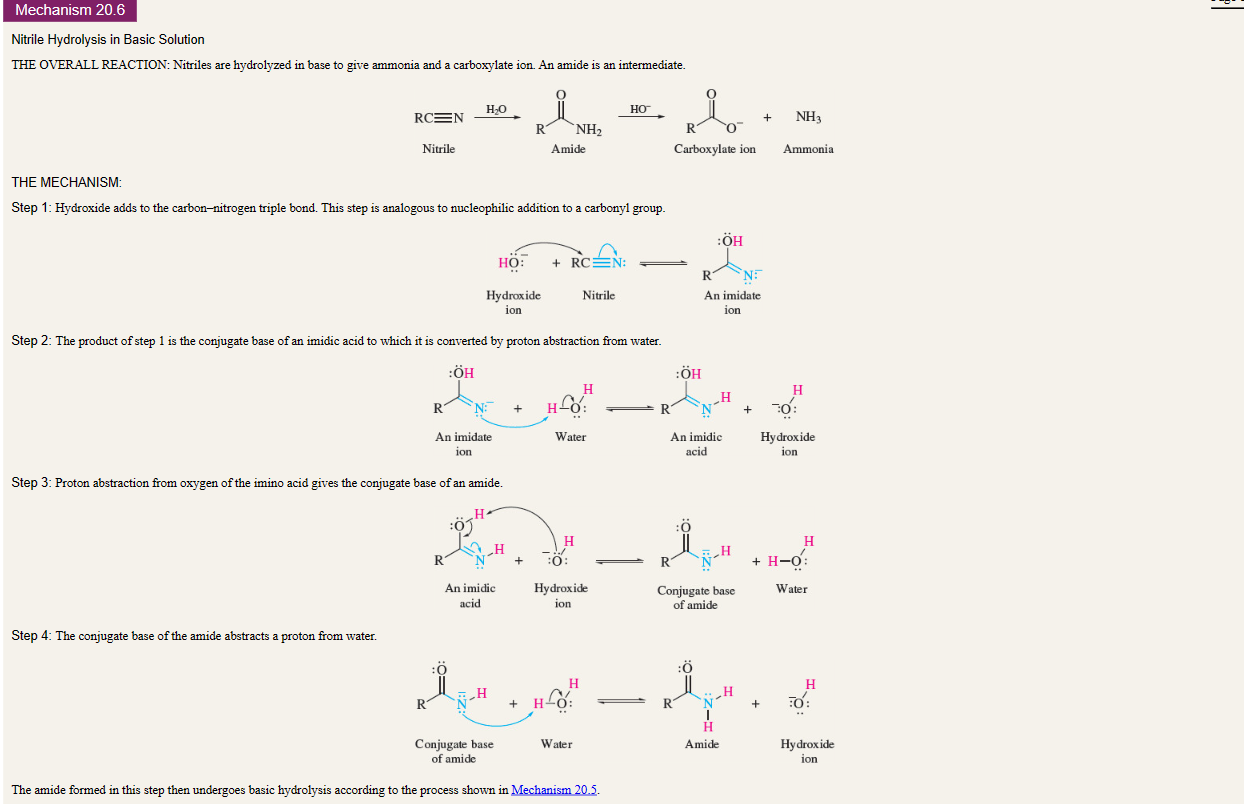
23
New cards
nitriles to ketones
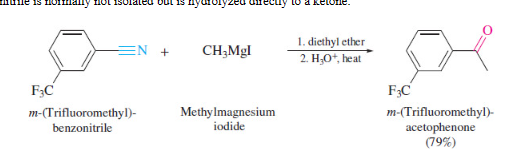
24
New cards

Write the structure for this name
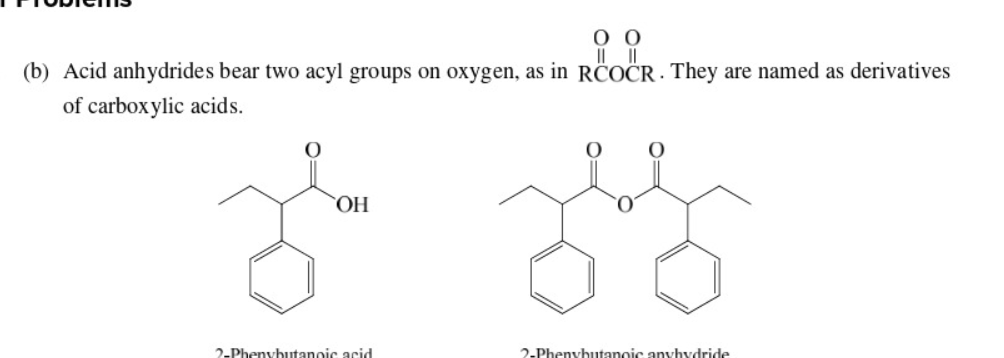
25
New cards

Write the structure for this name
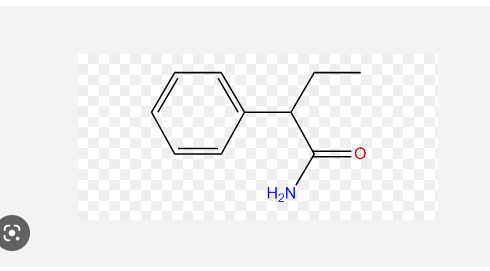
26
New cards

What does this yield?
\
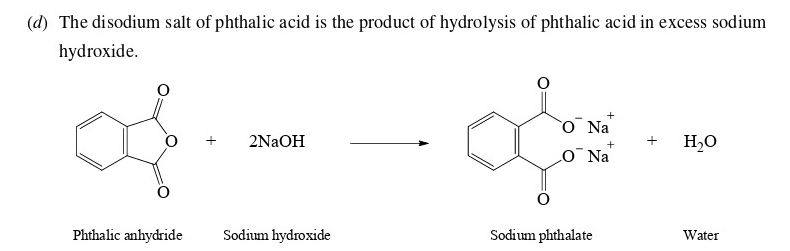
27
New cards
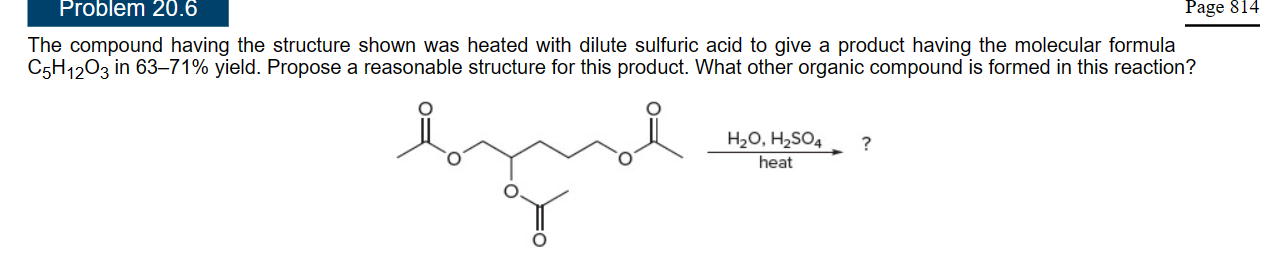
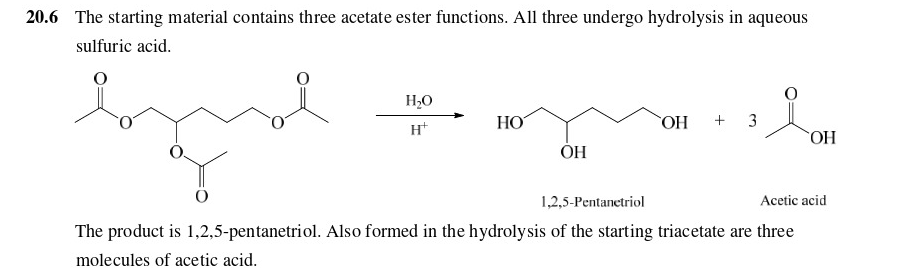
28
New cards
Mechanism of reaction between esters and amines
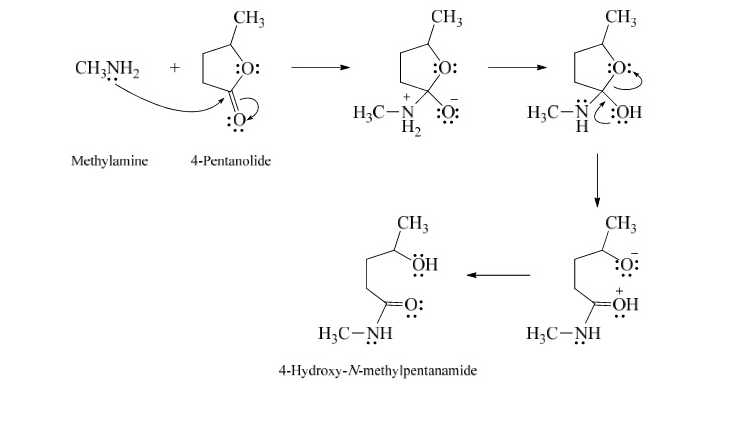
29
New cards

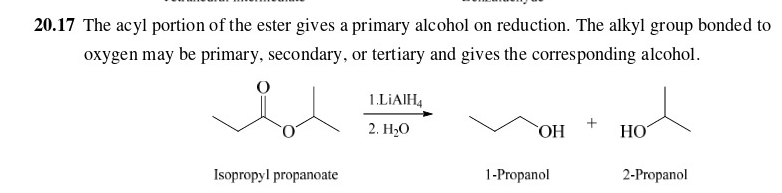
30
New cards
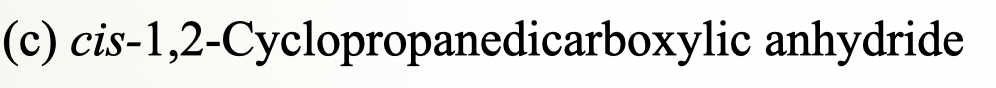
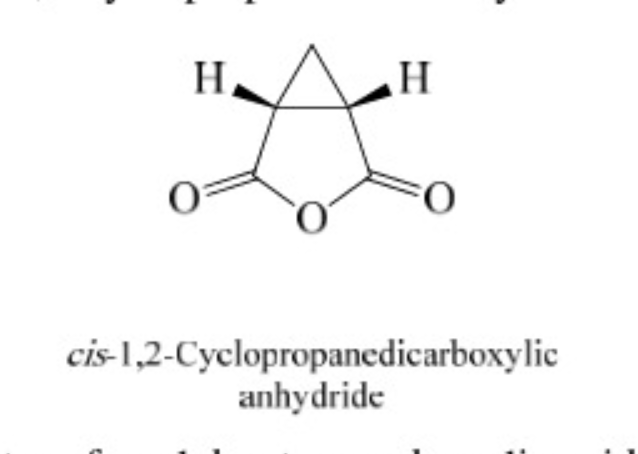
31
New cards
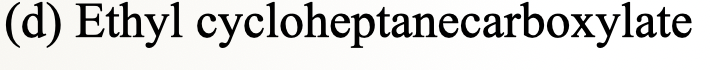
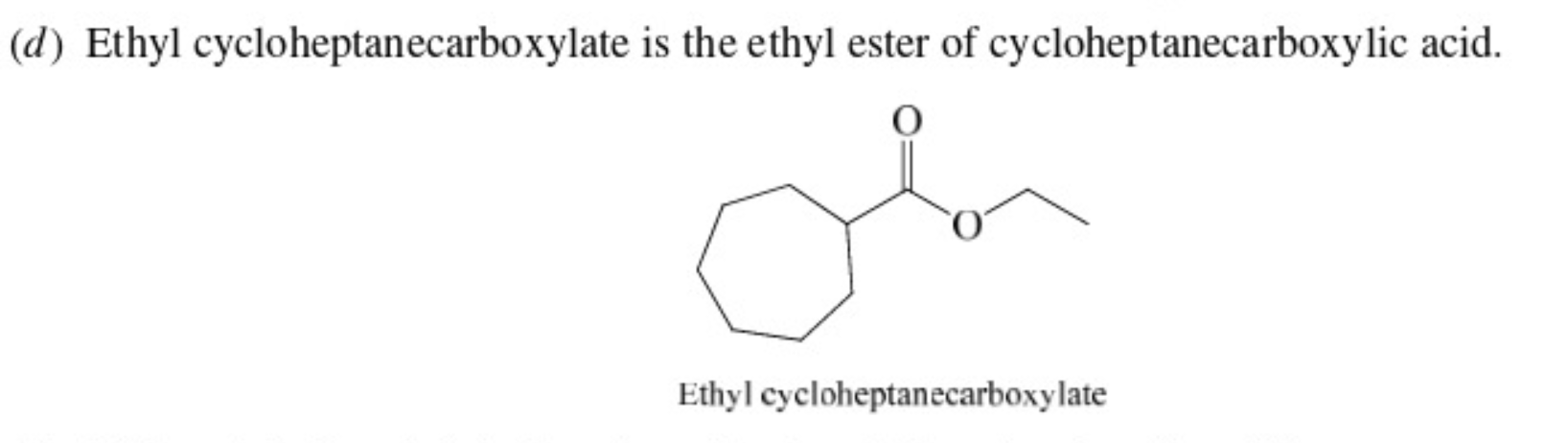
32
New cards
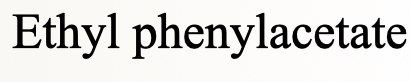
33
New cards

34
New cards

35
New cards
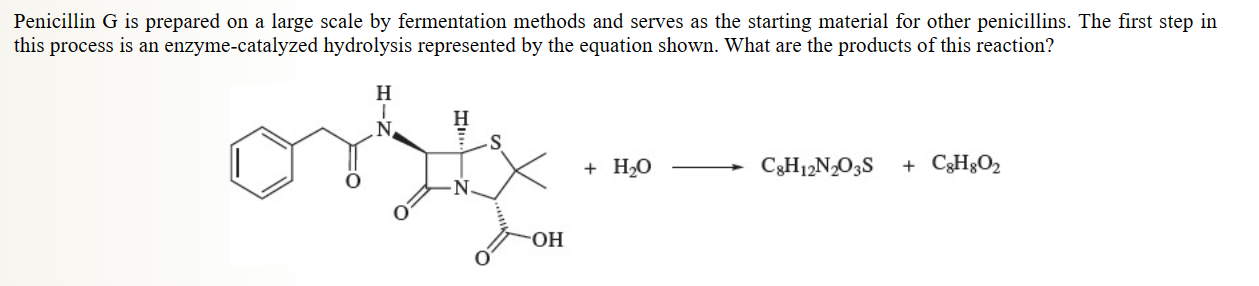
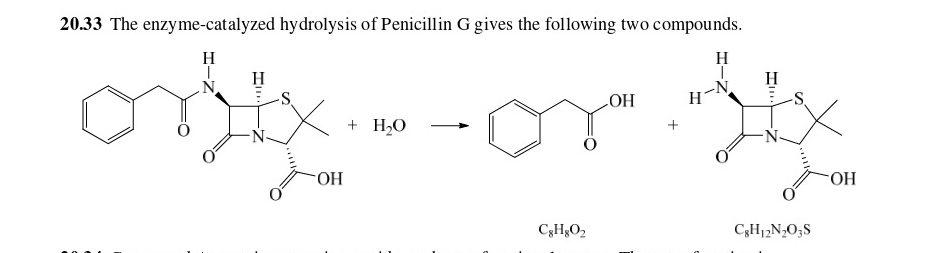
36
New cards
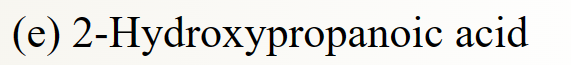
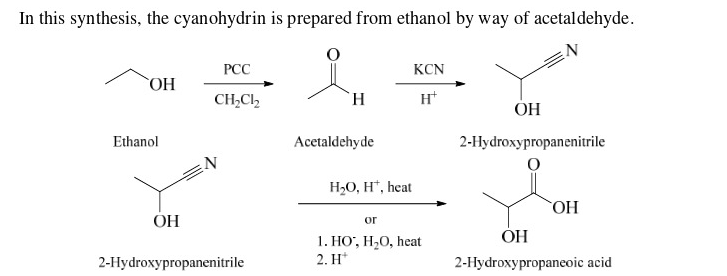
37
New cards

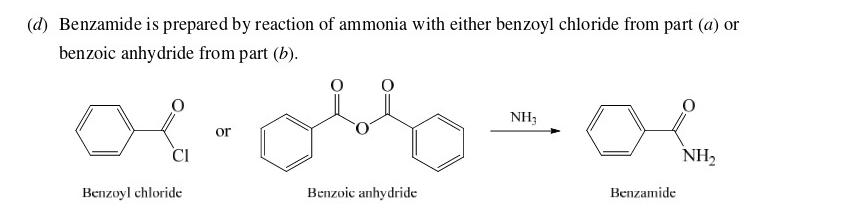
38
New cards
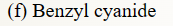
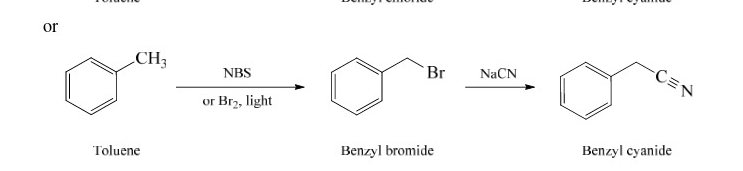
39
New cards
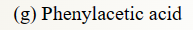
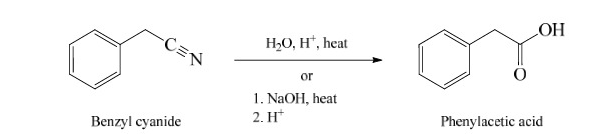
40
New cards
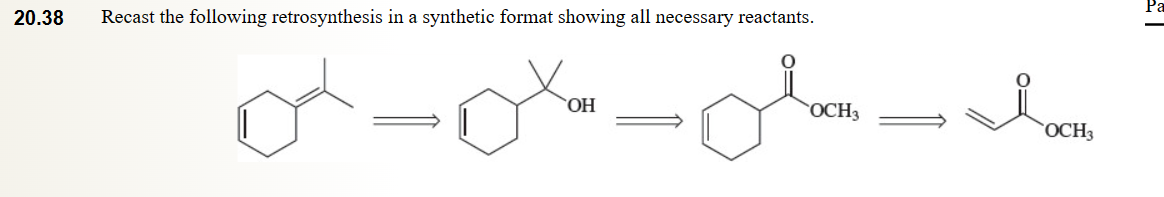
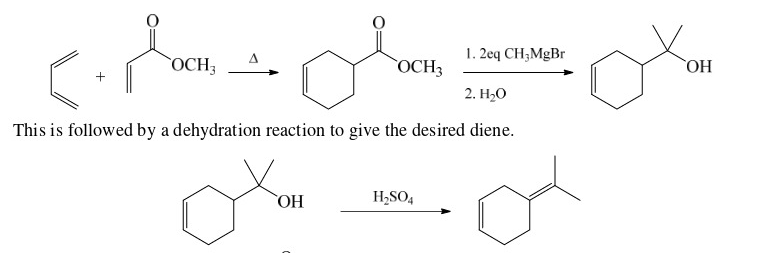
41
New cards
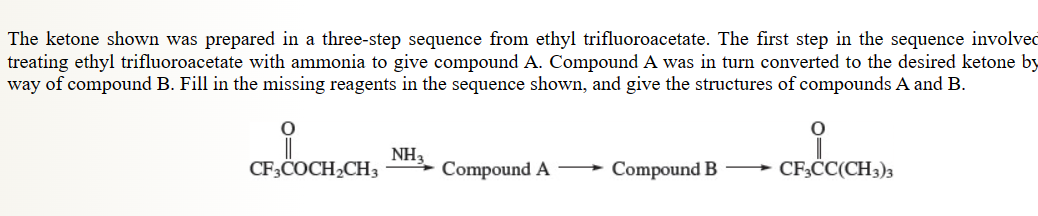
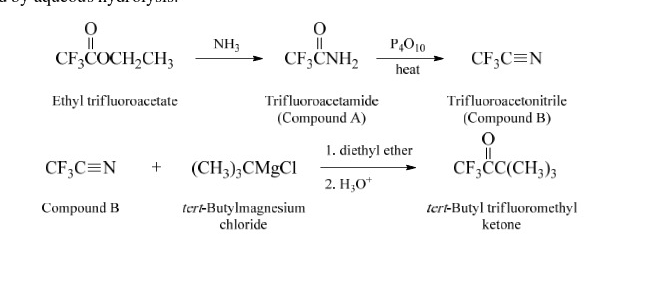
42
New cards

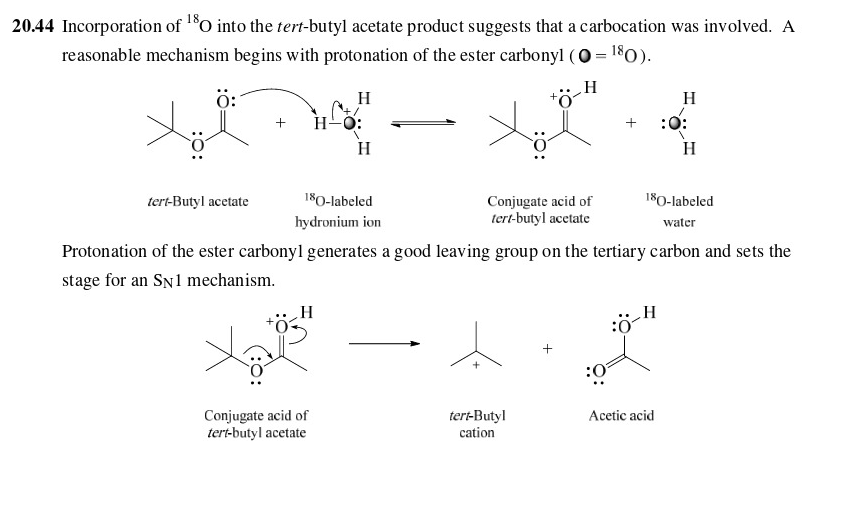
43
New cards
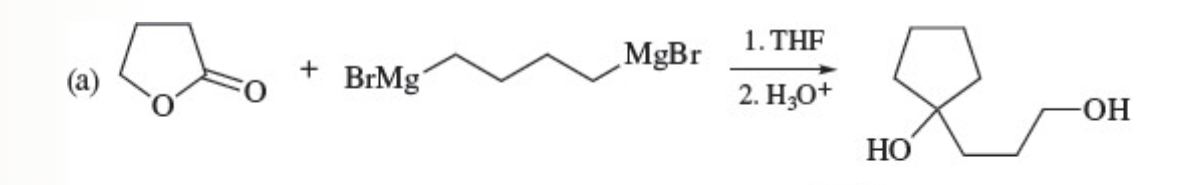
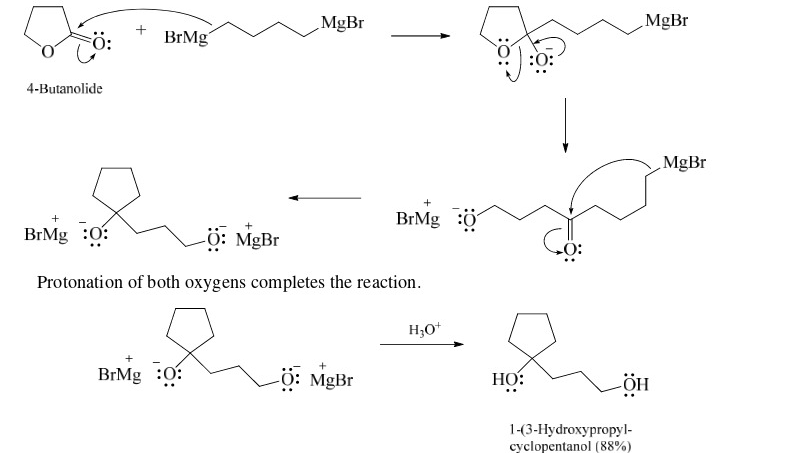
44
New cards
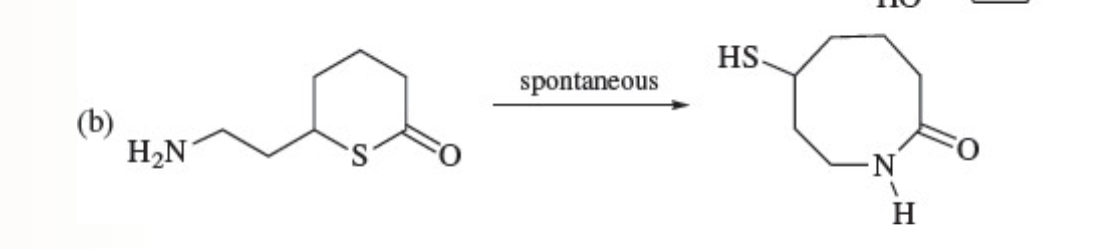
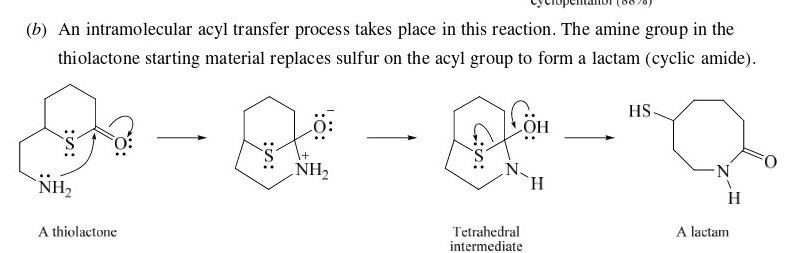
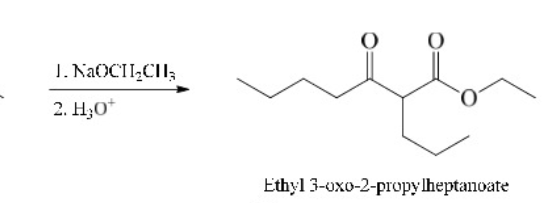
45
New cards
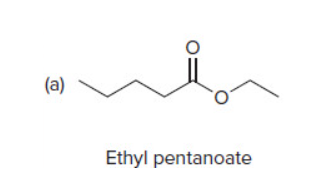
Claisen Condensation
46
New cards
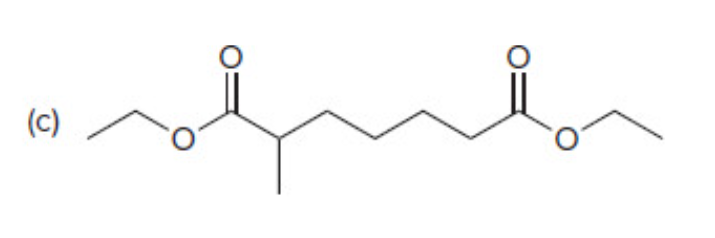
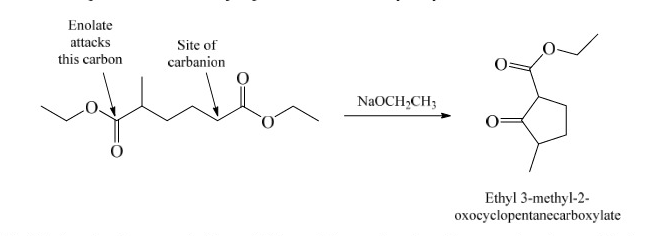
47
New cards
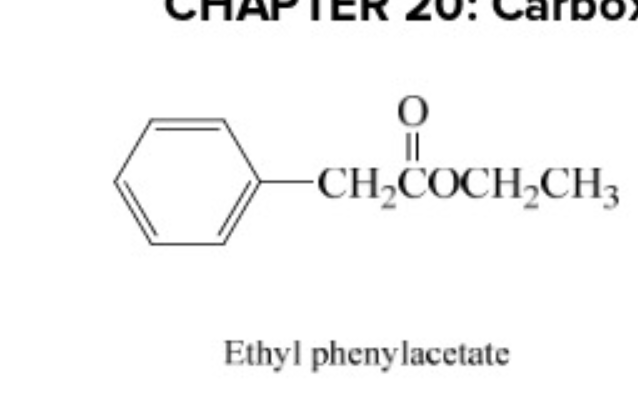
ethyl phenylacetate
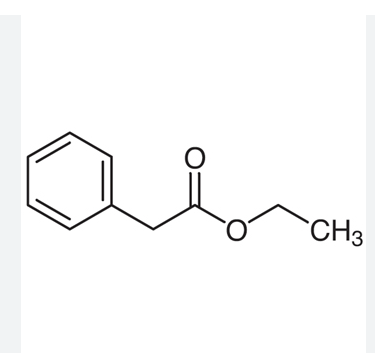
48
New cards
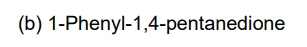
retrosynthesis of this compound
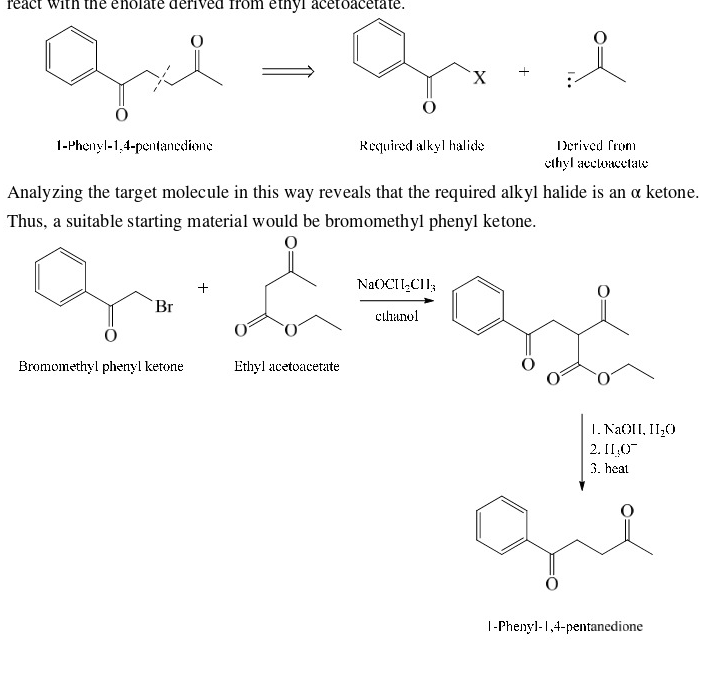
49
New cards
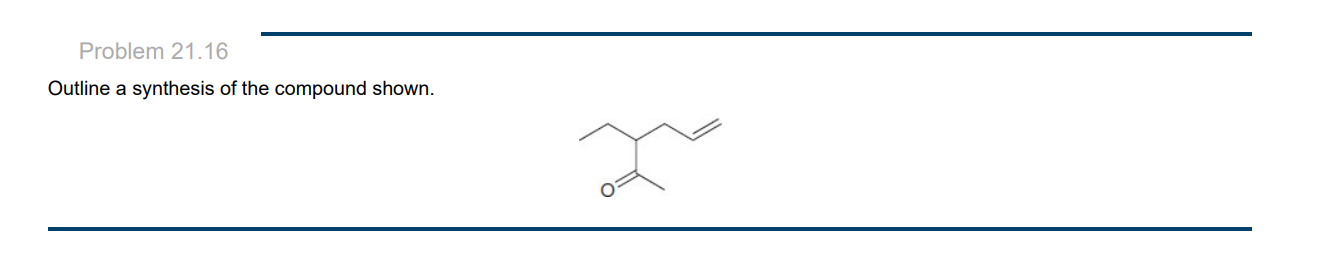
50
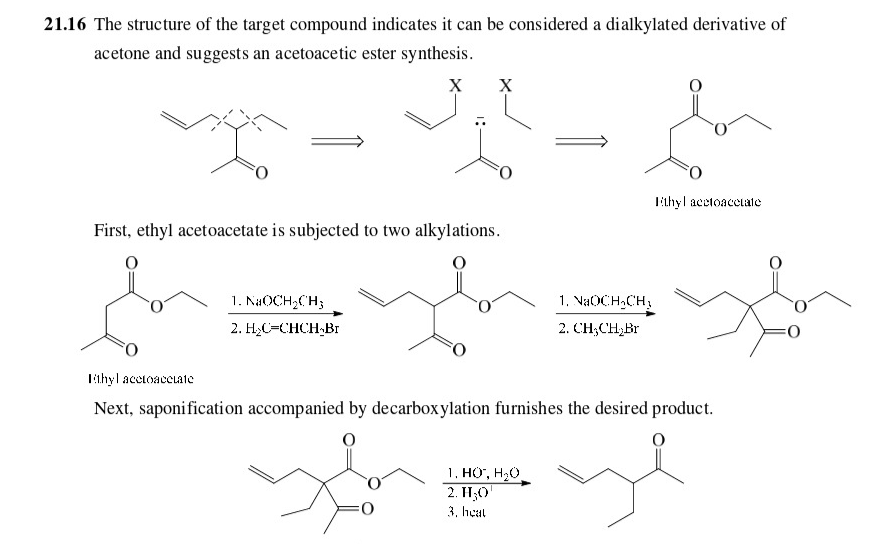
New cards
write the mechanism
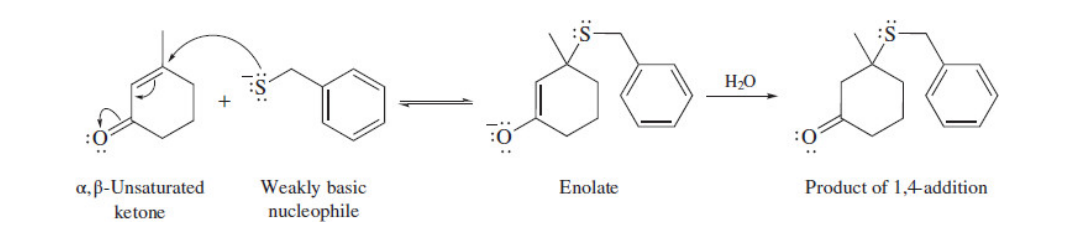
51
New cards
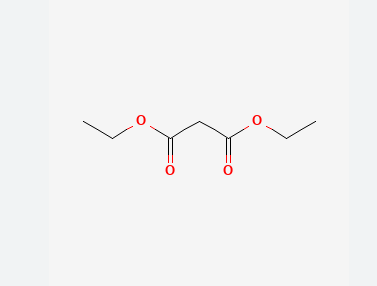
diethyl malonate
52
New cards
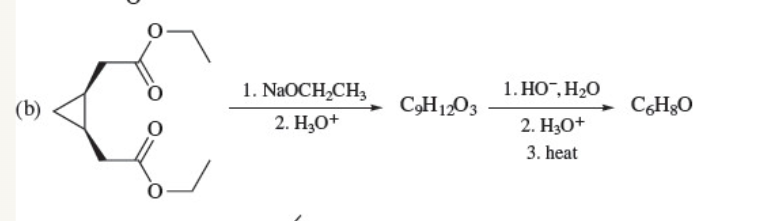
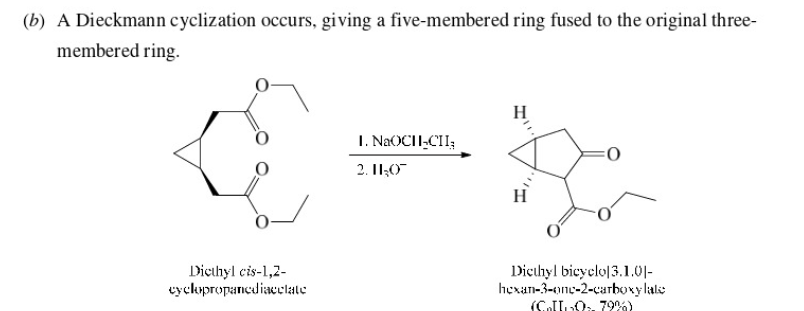
53
New cards
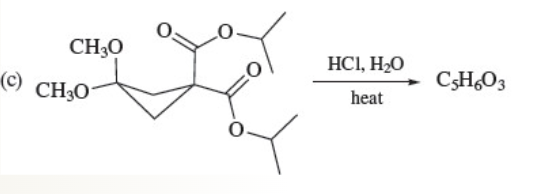
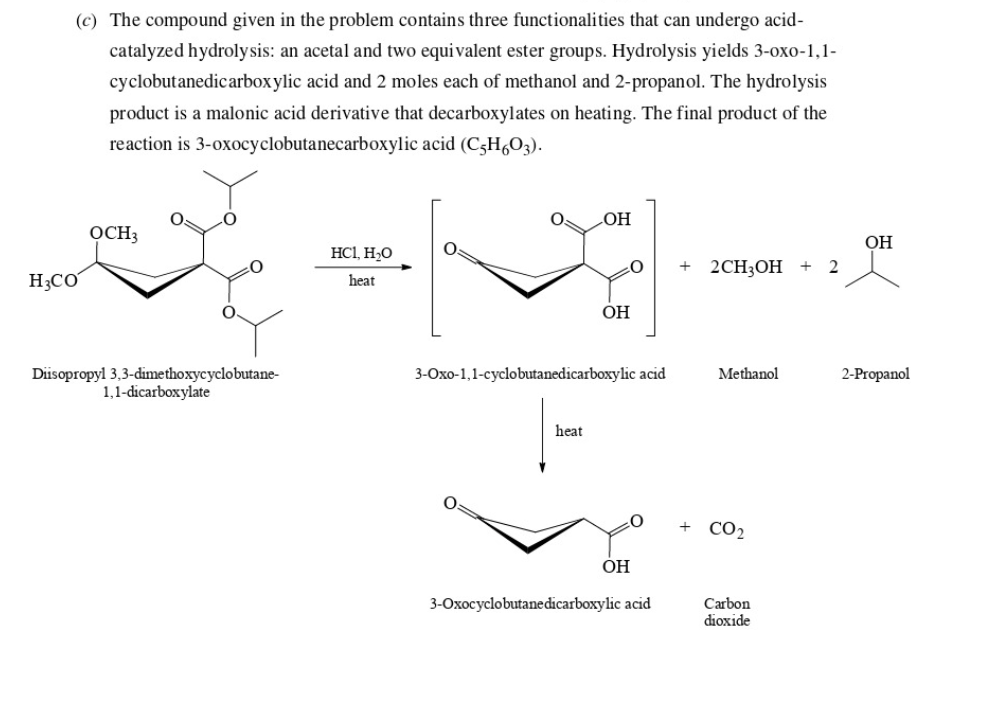
54
New cards
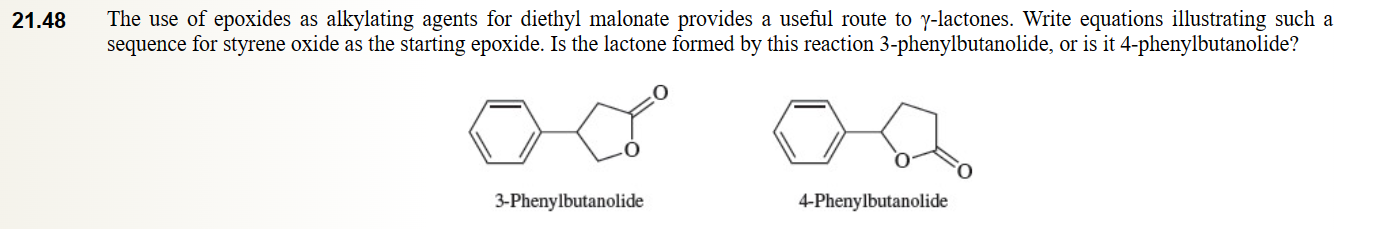
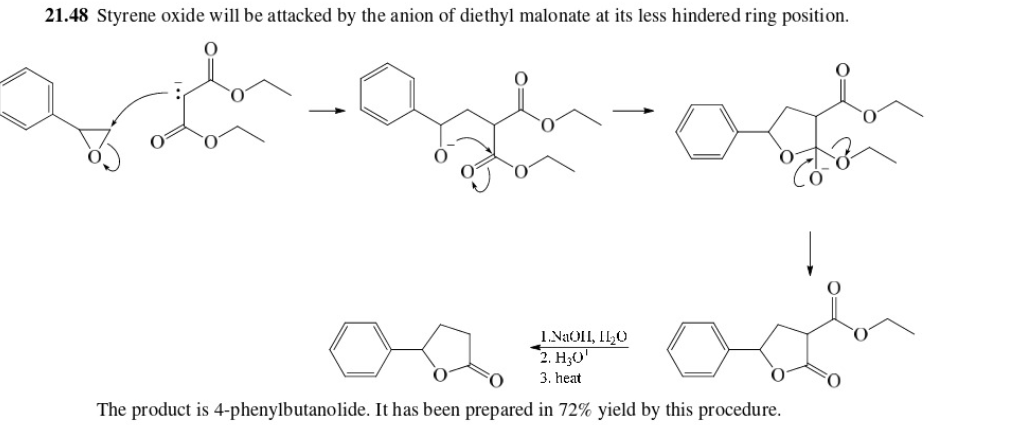
55
New cards
make 2-Bromo-3-pentanone from 3-pentanone
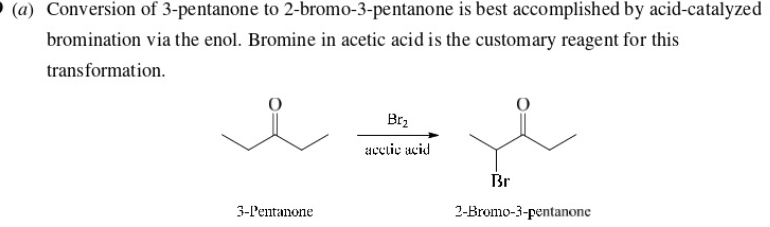
56
New cards
make 1-Penten-3-one from 3-pentanone
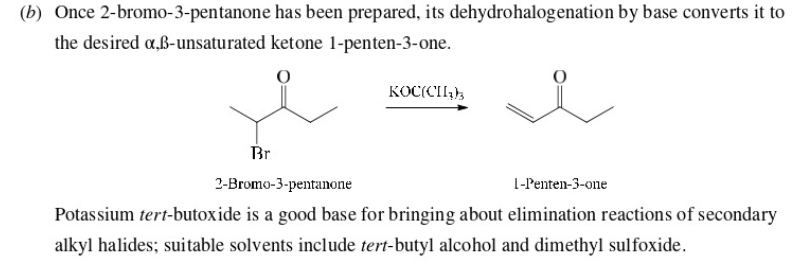
57
New cards
make 3-Hexanone from 3-pentanone
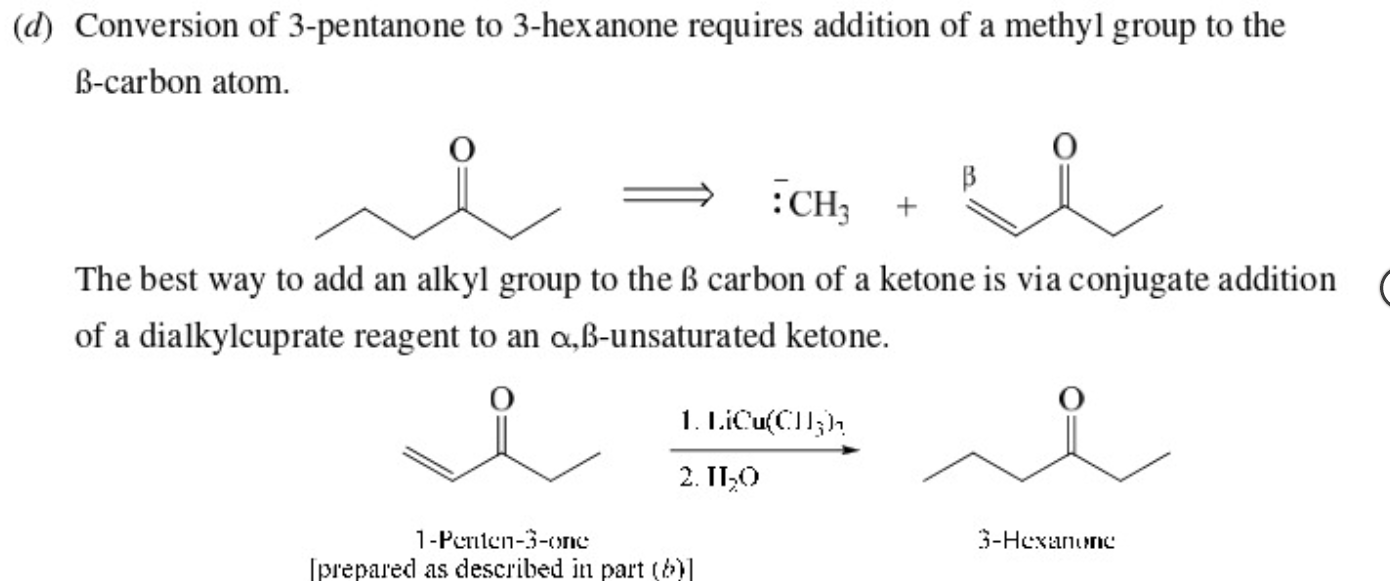
58
New cards
make 2-Methyl-l-phenyl-l-penten-3-one from 3-pentanone
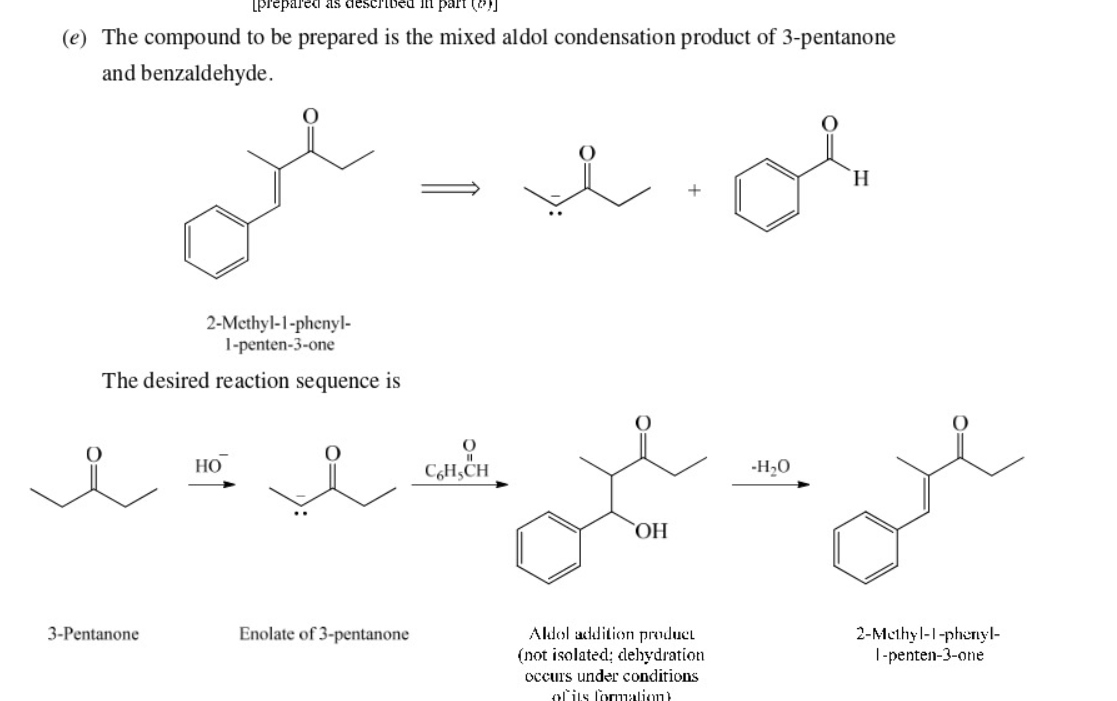
59
New cards
2-Allyl-1,3-propanediol from propene
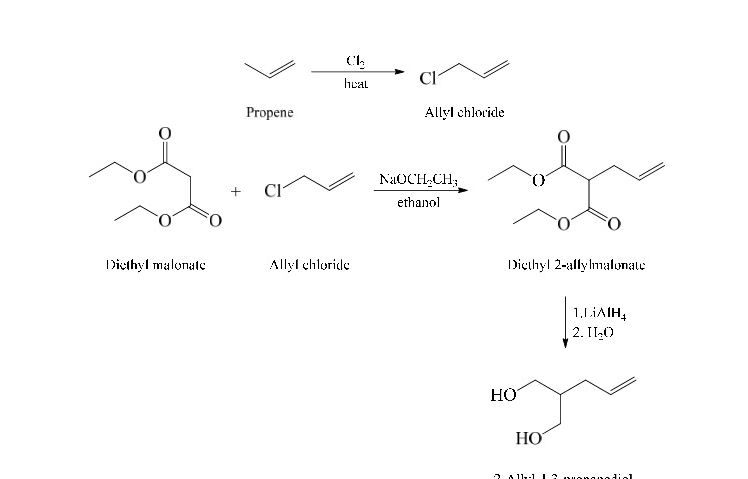
60
New cards
3-Phenylpropanoic acid from benzyl bromide
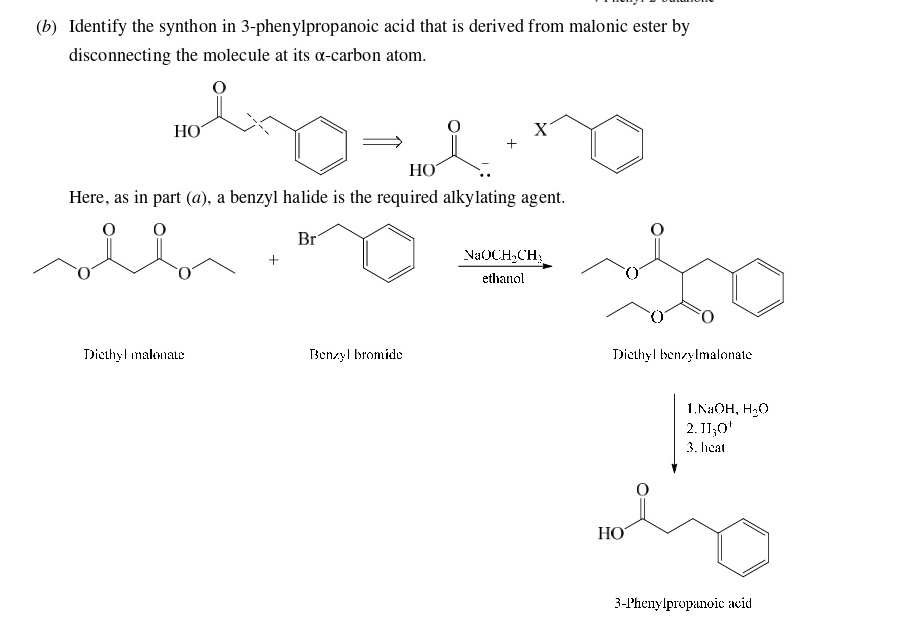
61
New cards
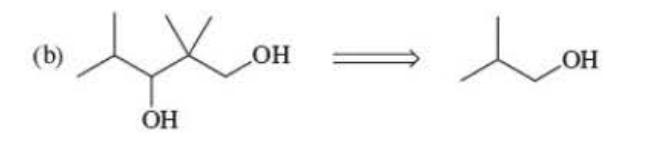
and use PCC to make the alcohol to a aldehyde
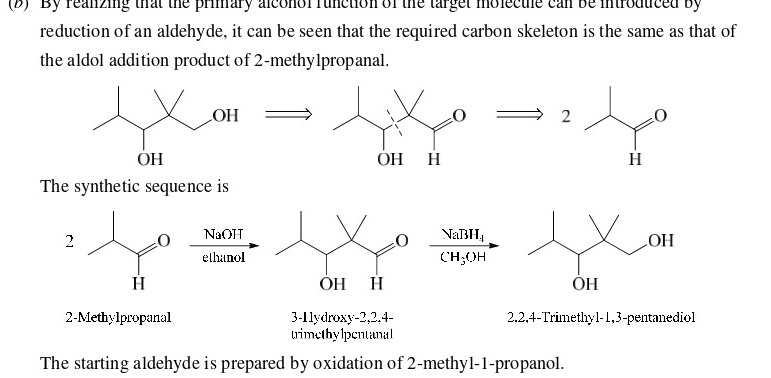
62
New cards
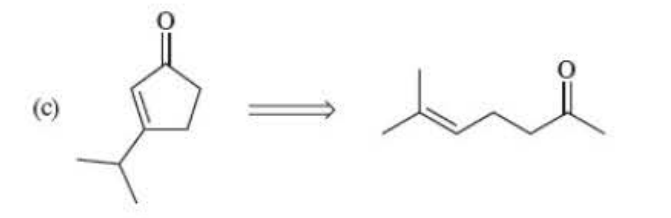
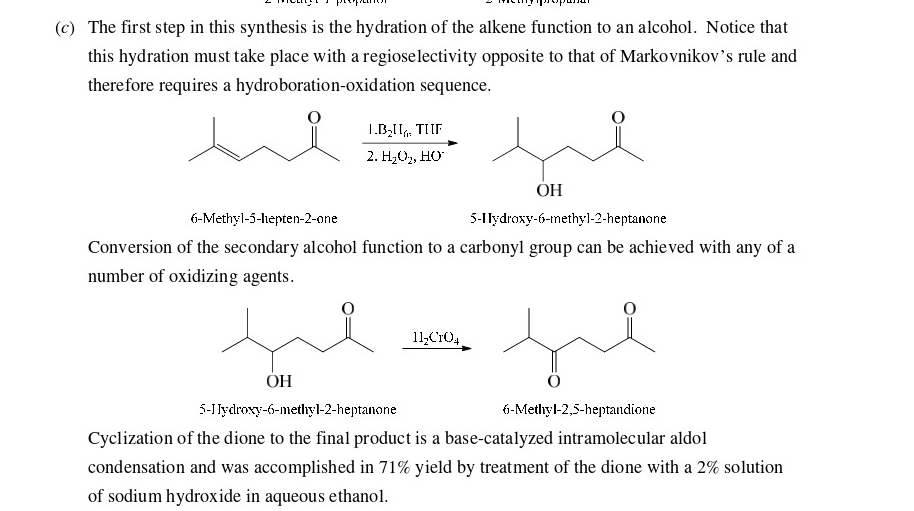
63
New cards
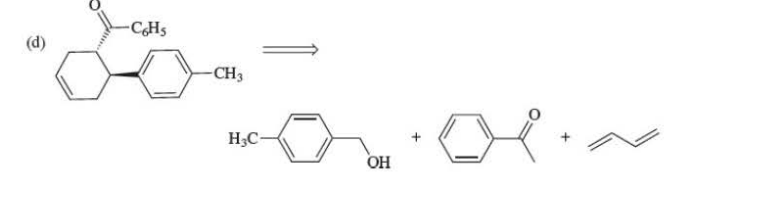
Make the alcohol to an aldehyde. Diels Alder is last
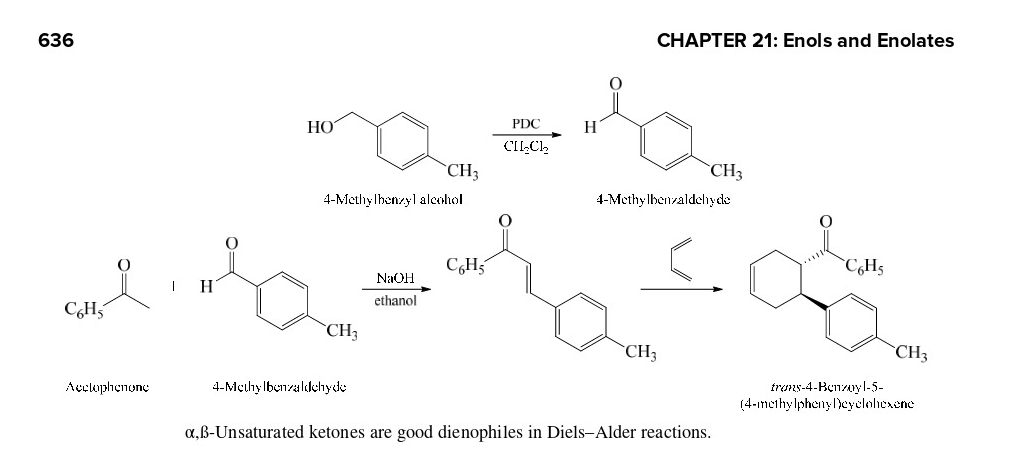
64
New cards
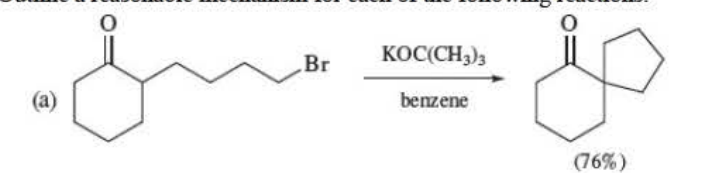
Outline a reasonable mechanism
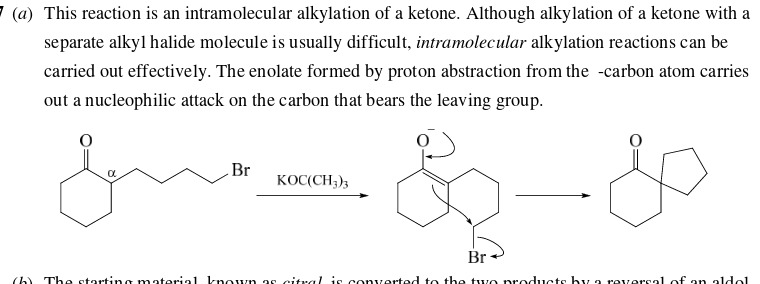
65
New cards
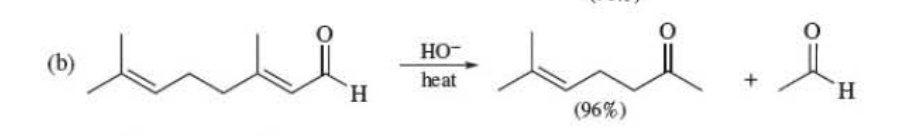
Outline a reasonable mechanism
First add the hydroxide, then reinstate the carbonyl by taking a hydrogen from water. Then the rest is the photo
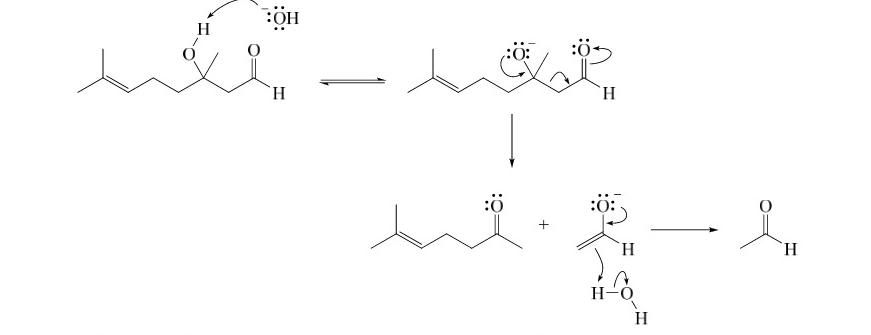
66
New cards
Outline a reasonable mechanism
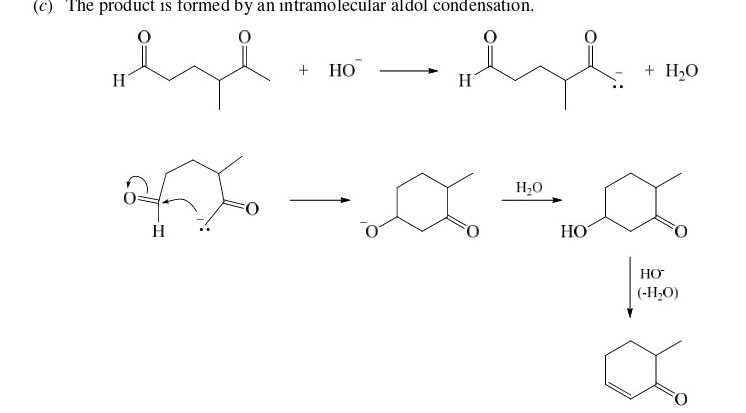
67
New cards
Enol
acid catalyzed
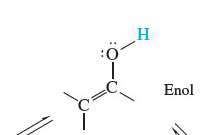
68
New cards
Enolate
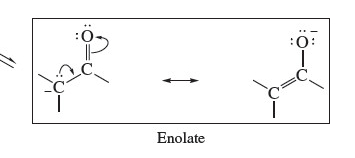
69
New cards
Aldol condensation mechanism
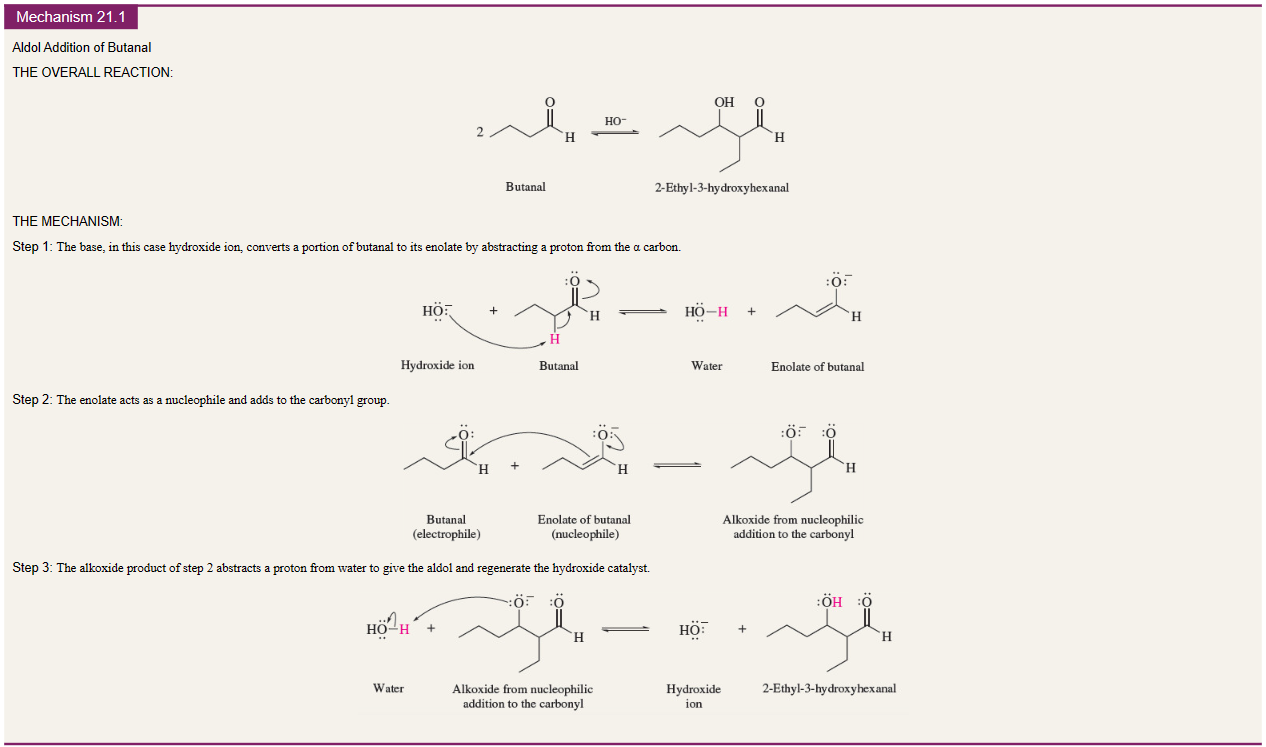
70
New cards
aldol condensation trick
replace the alpha hydrogen with the double bond of the electrophilic carbonyl
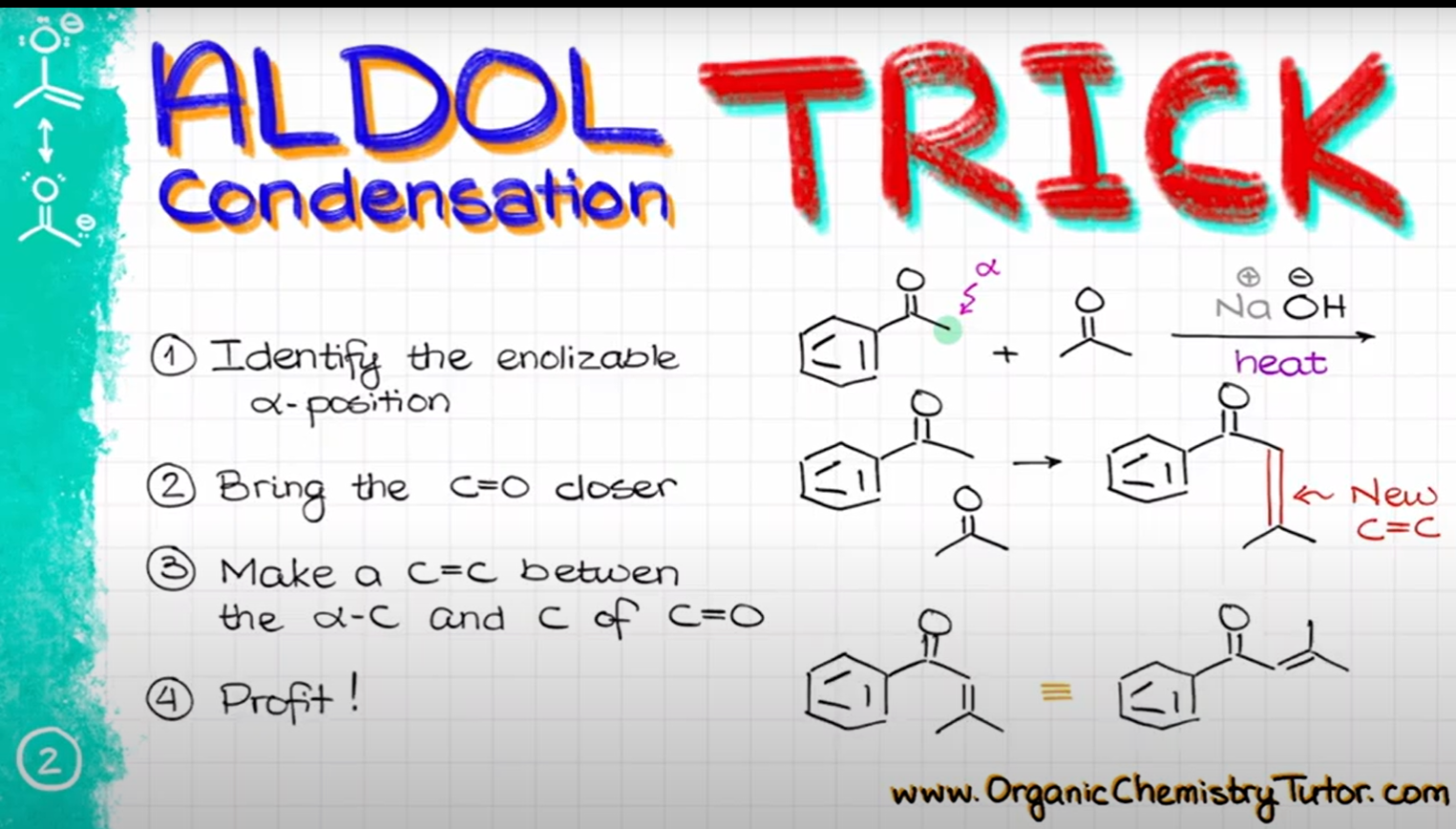
71
New cards
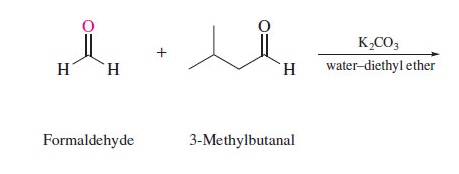
state the product
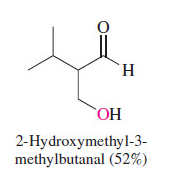
72
New cards
a strong base used to create enolates
LDA
73
New cards
Claisen Condensation
one ester is the source of both the acyl group and the enolate and the product is a β-keto ester (**must have at least 2 alpha hydrogens**)
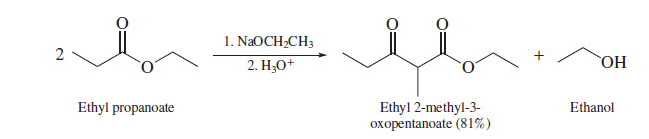
74
New cards
Claisen Condensation Mechanism
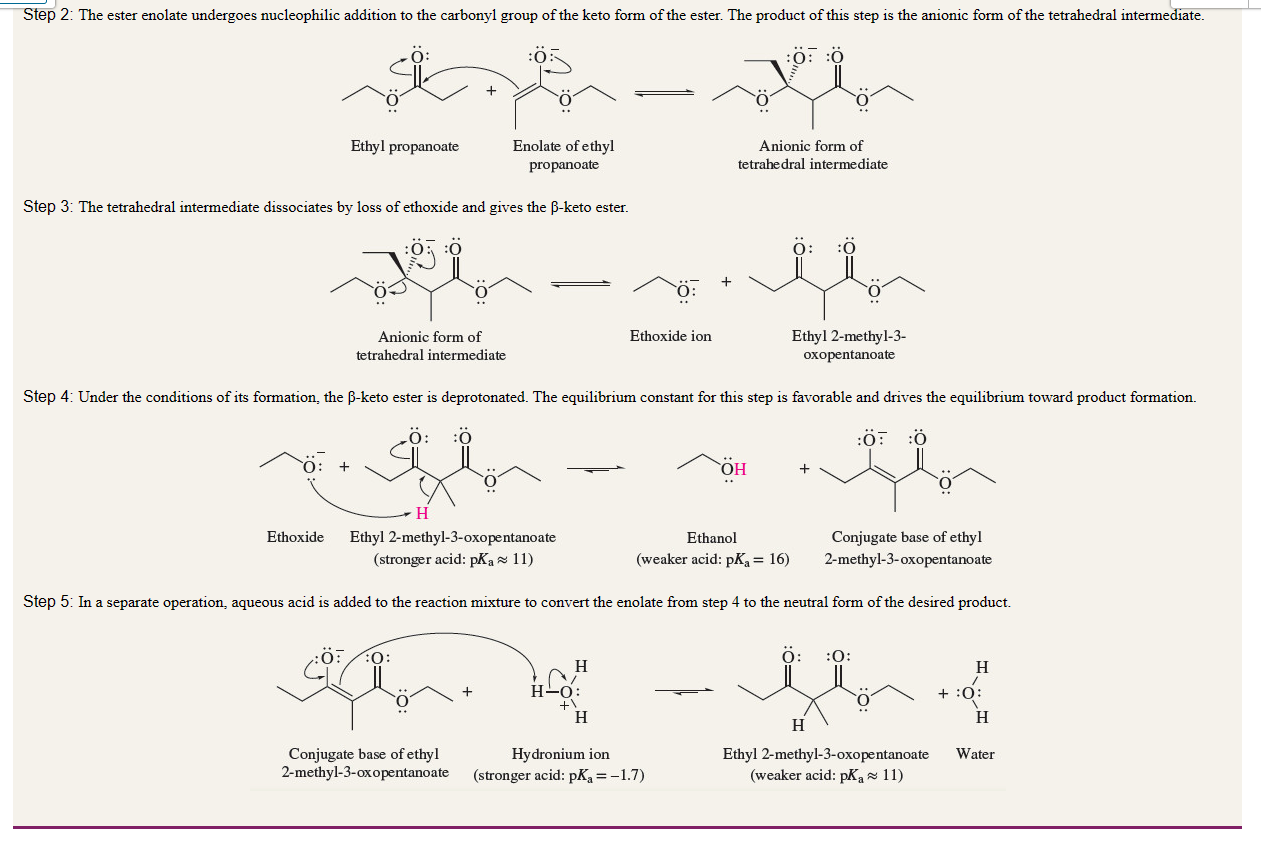
75
New cards
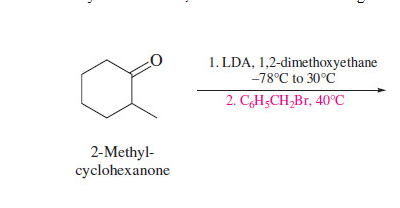
Alkylation of enolates
Simple aldehyde, ketone, and ester enolates are relatively basic, and their alkylation is limited to methyl and primary alkyl halides
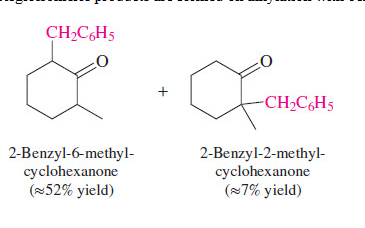
76
New cards
Alkylation of bicarbonyls, hydrolysis and decarboxylation
**Methyl, primary, and unhindered secondary alkyl halides are satisfactory alkylating agents**. Elimination (E2) is the only reaction with tertiary alkyl halides
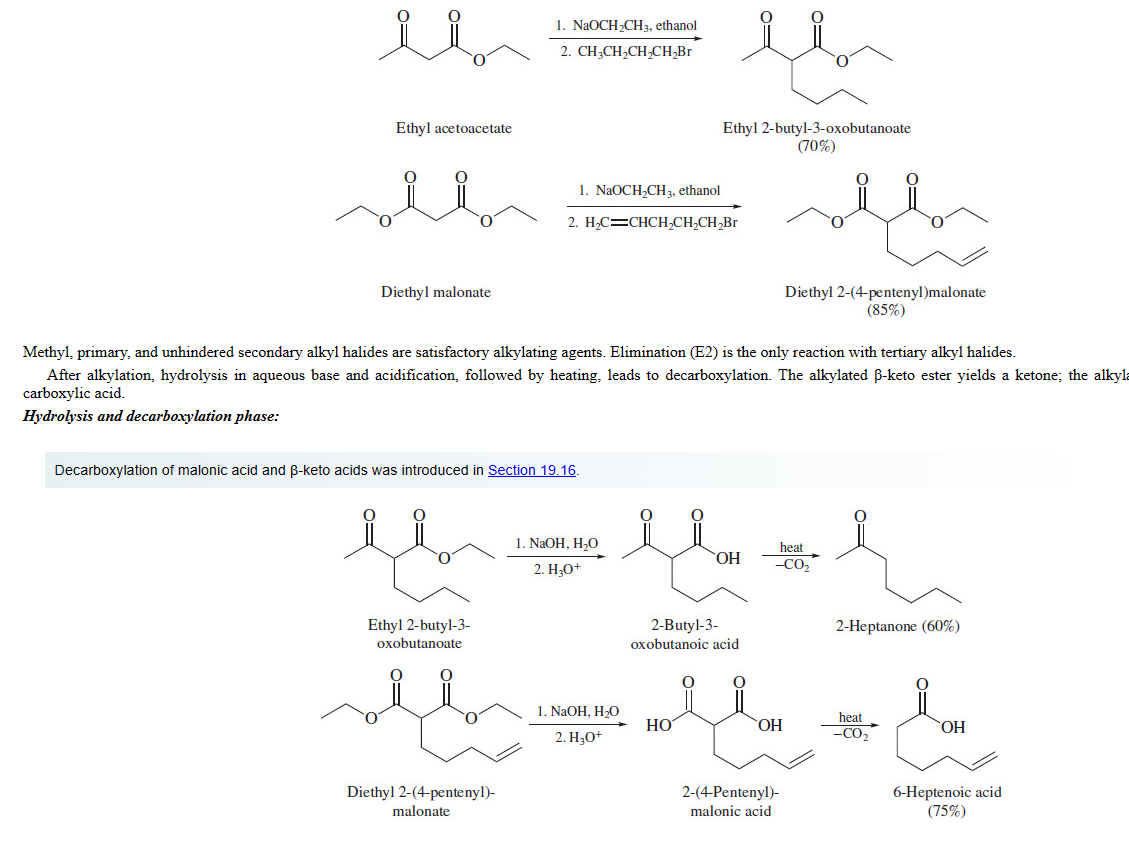
77
New cards
Acid catalyzed enolization mechanism
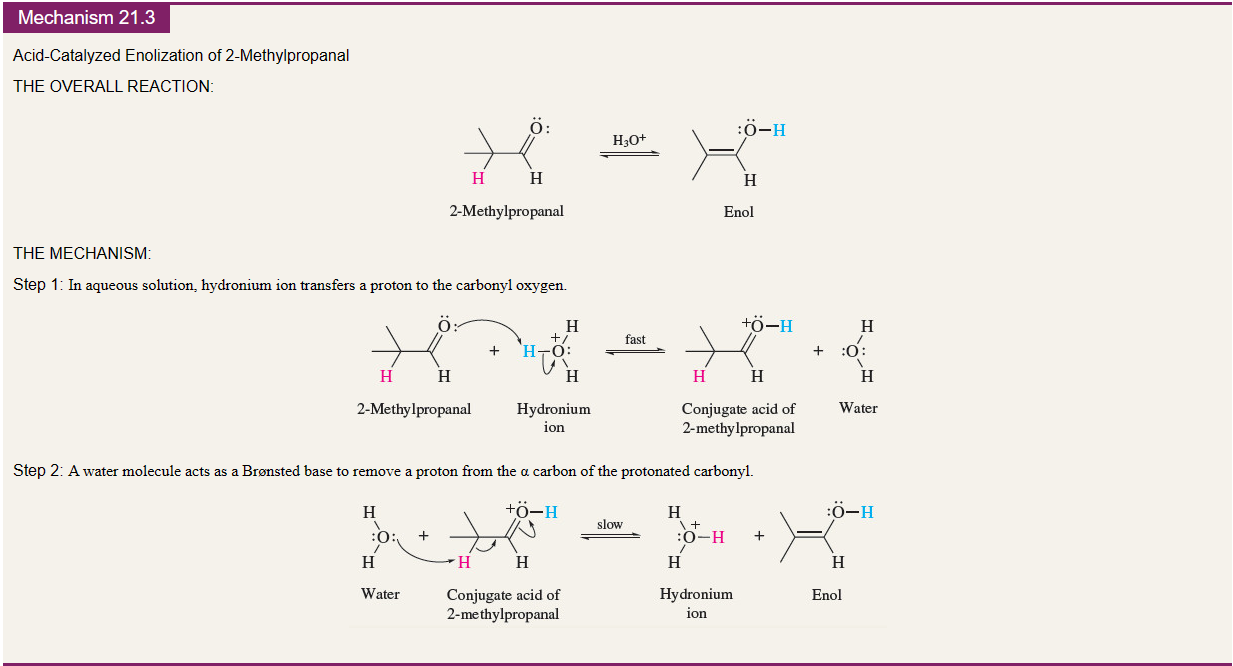
78
New cards
Halogenation of aldehydes and ketones
X2 and an acid (ie acetic acid)
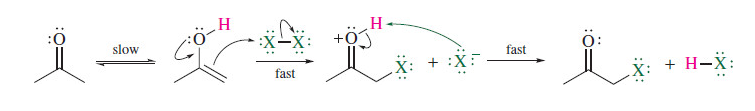
79
New cards
Haloform reaction
**Methyl ketones** undergo a novel C–C cleavage on treatment with excess halogen in the presence of base.
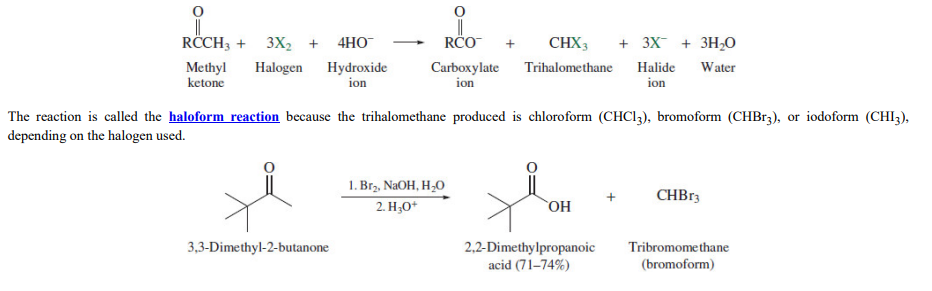
80
New cards
Haloform Reaction Mechanism
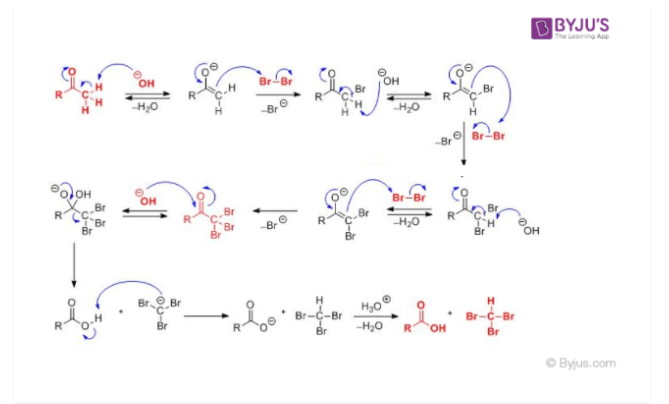
81
New cards
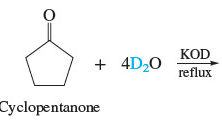
Substitution of deuterium for hydrogen at the α-carbon atom of an aldehyde or a ketone is a convenient way to introduce an **isotopic labe**l into a molecule and is readily carried out by treating the carbonyl compound with deuterium oxide (D2O) and base
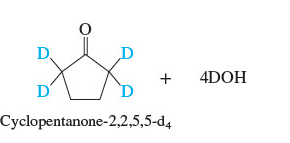
82
New cards
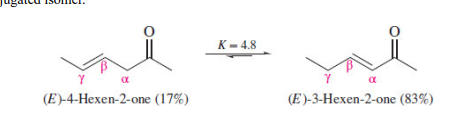
Which is more stable?
α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones are more stable than their nonconjugated isomers
83
New cards
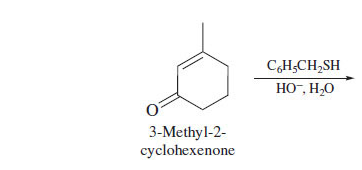
What is the product?
84
New cards
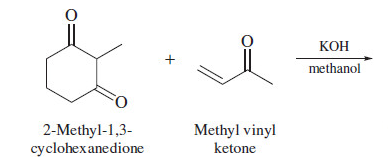
The Michael reaction is an alkylation in which unsaturated ketone serves the same kind of electrophilic role that alkyl halides do toward the enolate.
85
New cards
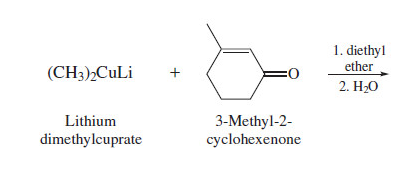
lithium dialkylcuprates and alpha-beta conjugated ketones
86
New cards
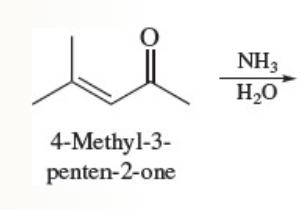
The beta carbon of an alpha, beta unsaturated carbonyl compound is electrophilic;
The nucleophile bonds to the beta carbon
The nucleophile bonds to the beta carbon