Jones- ALL Powerpoints
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
powerpoints 1-5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Which of the following is not a part of the upper airway?
a. nasal turbinates
b. pharynx
c. larynx
d. trachea
d
What is the primary function of the upper respiratory system?
conduct air from outside into our body
non-exchanging airways
The trachea has a thick layer of _______________ that helps maintain open airways when we exhale.
cartilage
What is the primary functional unit of the respiratory system?
alveolar sacs
The tissue of the ________________ have less mucus, a thinner epithelium, smooth muscle, and no cartilage.
a. trachea
b. bronchioles
c. alveolus
b
The alveolus has type I and type II cells. What are the functions of each?
Type 1- structural
Type 2- produce surfactant
How does the mucous escalator work?
allows debris to be trapped in mucus and driven upward towards the mouth for expelling
cilia beat to move the mucus upward
What is the difference between the alveolar sac and the alveolus?
alveolar sac- refers to the entire structure containing many alveolus
bundle of grapes
alveolus- one singular “grape”
Alveoli slightly participate in debris removal through _____________________________.
alveolar macrophages
The lungs are inside a fluid-filled sac within the chest called the ___________________.
pleaural sac
What is the difference between the visceral and parietal pleura?
visceral- attached to the lungs
parietal- attached to the chest wall
What is found in the space between the visceral and parietal pleura?
intrapleural fluid
What are the many functions of the respiratory system?
gas exchange
pH regulation
speech
defense mechanisms
hormone activation
intrathoracic pressure
clot dissolution
How is the respiratory system effected in a pt. with chronic bronchitis?
mucous cells are increased and that inhibits cilia function
During inspiration, do the internal or external intercostal muscles contract?
external
During forced expiration, do the internal or external intercostal muscles contract?
internal
Does the diaphragm contract or relax when we’re breathing in?
contract
At rest, lung tissue pulls ____ and the chest wall pulls ______.
At rest, lung tissue pulls in and the chest wall pulls out.
FRC refers to what?
air in the lungs at rest
What do the following abbreviations mean?
Palv
PIP
PTP
Palv= alveolar pressure
PIP= intrapleural pressure
PTP= transpulmonary pressure
PTP= P? - P?
PTP= Palv - PIP
At rest, what are the pressures in each of the following? (Consider Patm= 0)
Palv=
PIP=
PTP=
Palv= 0
PIP= -4
PTP= +4
During inhalation, does the alveolar pressure increase or decrease?
decrease
Palv goes from 0 to -2
What is a pneumothorax?
hole in the chest wall
hole makes it so a pressure gradient can’t be generated= lung collapses
What 3 things effect resistance to airflow?
diameter of the bronchioles
compliance
surface tension
Bronchodilation deals with what part of the autonomic nervous system and what receptors?
sympathetic and b2 receptors
Bronchiole constriction deals with what part of the autonomic nervous system and what receptors?
parasympathetic and muscarinic receptors
How does asthma increase resistance?
decreases radius of the bronchioles
What term refers to the ability for our lungs to stretch and expand?
compliance NOT elasticity
What is the difference in compliance curves between inspiration and expiration?
Hysteresis
Stiffer lungs are _______ compliant and will not fill with as much air.
less
What helps reduce surface tension in smaller alveoli?
surfactant
How does surfactant effect compliance? (increase or decrease)
increases compliance
What is the name of the condition in which a pt. has low surfactant?
respiratory distress syndrome
What is the process of moving air into and out of the lungs?
ventilation
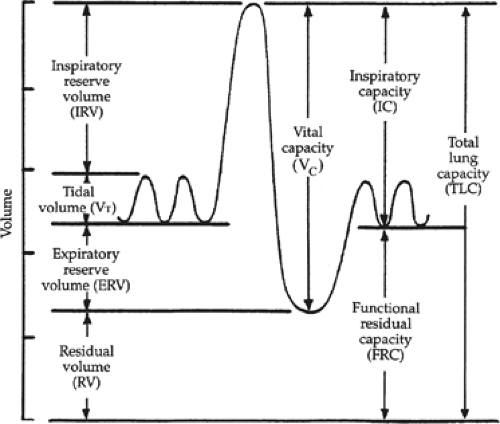
Which term on the graph describes the extra volume of air that can be inspired forcefully over and beyond normal tidal volume?
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV
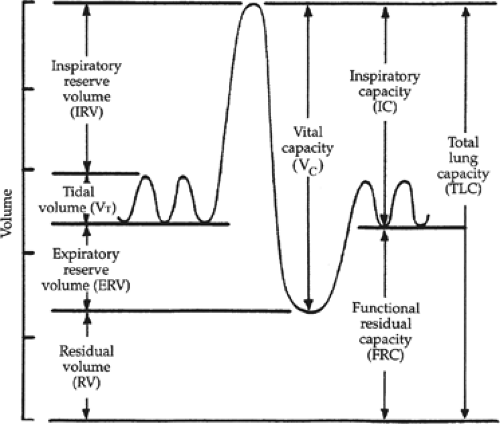
What term is the volume of air inspired or expired with each normal/quiet breath?
Tidal Volume (TV)
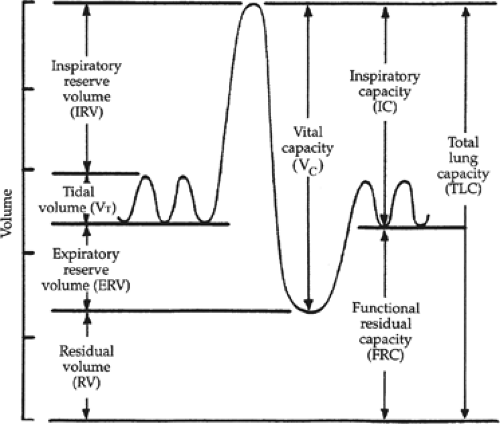
What term describes the volume of air remaining in the lungs after the most forceful expiration or the volume in the lungs after maximum expiration?
Residual Volume (RV)
What is the combination of the tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume?
Inspiratory Capacity
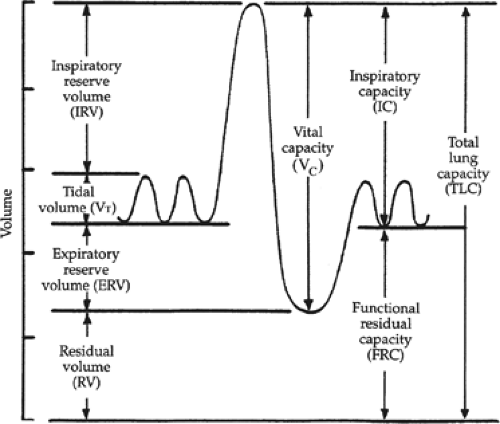
What is the volume of air in the lungs at rest?
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
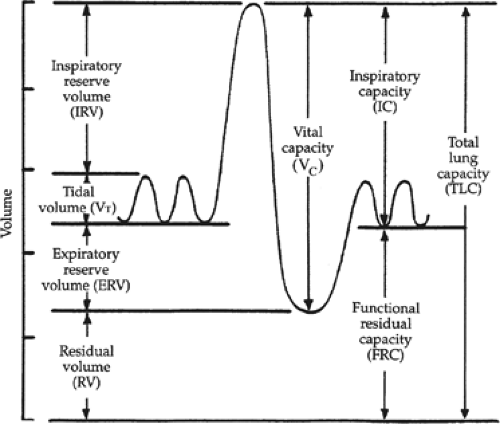
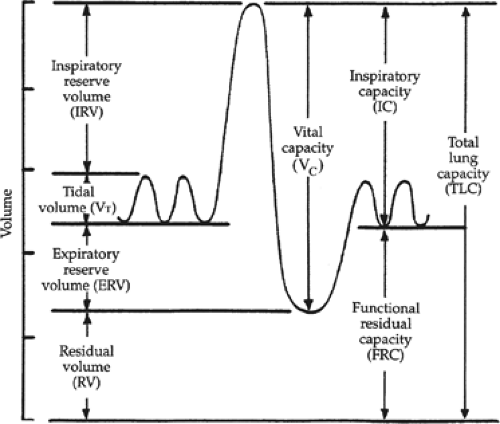
What term is used to describe the max we can inhale and exhale?
vital capacity
What is the combination of the Vital capacity and residual volume?
Total Lung Capacity
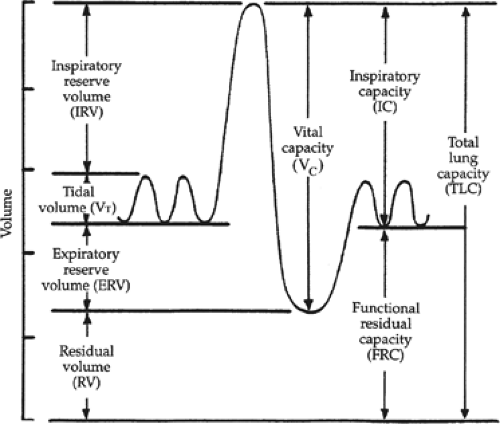
What term is used to describe the volume of breathed air that never reaches gas exchange areas?
dead space
What volume of the tidal volume is anatomical dead space?
a. 100 ml
b. 150 ml
c. 200 ml
d. 250 ml
b
In addition to anatomical dead space, we can also have dead space due to what?
non-functioning alveoli (physiologic dead space)
poor blood flow
poorly ventilated
What is the equation for calculating total dead space (VD)? (given gas pressures)

What term refers to the amount of total air inhaled and exhaled in one minute?
Minute Ventilation
What is the equation for alveolar ventilation?
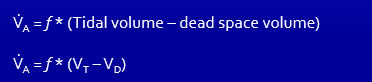
What is the percent of carbon dioxide and oxygen in our atmospheric pressure?
O2= 21%
CO2= 0.04% or 0%
If our atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg, how much of that is oxygen and much is carbon dioxide?
O2- 160 mmHg
CO2- 0 mmHg
What is inspired air? How does this effect the partial pressure of O2?
air that gets water added to it
Must account for the water by subtracting 47 from the atmospheric pressure
Instead of 160 mmHg, now 150 mmHg
What is the partial pressure of O2 and CO2 in the alveoli?
O2- 100 mmHg
CO2- 40 mmHg
Compared to normal, what happens to the partial pressures of O2 and CO2 in the alveoli when we hypoventilate?
SATA
a. O2 increases
b. O2 decreases
c. CO2 increases
d. CO2 decreases
b, c
True or False: When we hyperventilate, the amount of CO2 in the alveoli decreases compared to normal.
True
In what region of the lung would you expect the highest amount of blood flow?
a. apex/ top of the lung (zone 1)
b. middle (zone 2)
c. base (zone 3)
d. none of the above
c
What region of the lung has the lowest ventilation?
a. apex/ top of the lung (zone 1)
b. middle (zone 2)
c. base (zone 3)
d. none of the above
a
The V/Q ratio looks at the ratio of what to what?
ventilation to blood flow
Where in the lung would I expect each of the following:
a V/Q ratio >1
a V/Q ratio =1
a V/Q ratio <1
a V/Q ratio >1
apex/top of the lung
a V/Q ratio =1
middle of lung
a V/Q ratio <1
base of the lung
The partial pressure of CO2 and O2 in the alveoli matches which of the following:
a. veins
b. tissues
c. arteries
d. all of the above
c
If the partial pressure of O2 in the veins was 40 mmHg and the partial pressure of CO2 in the veins was 46 mmHg, what would be the pressure of each in the tissues?
VEINS MATCH TISSUE
O2=40 mmHg
CO2= 46 mmHg
Is carbon dioxide or water more soluble in blood?
CO2 is
exactly why we see more CO2 dissolved in the blood versus O2
The amount of O2 dissolved in the blood is 0.3 ml O2/ 100 mL of blood, which is not enough to sustain life. How do we overcome this problem?
use Hemoglobin to bind oxygen
True or False: The amount of Hb in our blood effects the pressure of oxygen in the blood.
FALSE- Hg DOES NOT CHANGE PRESSURE
What determines how much oxygen binds to hemoglobin?
amount dissolved in the blood
With what type of shift do I see decreased O2 affinity and more unloading?
RIGHT
With what type of shift do I see increased affinity and less unloading?
LEFT
Which of the following does not effect oxygen saturation?
a. pH
b. temperature
c. anemia
d. Red blood cell 2,3 BPG
c
What type of shift would occur in the following situations:
↑ temp= _______ shift
↓ temp= _______ shift
↑ temp= right shift
↓ temp= left shift
What type of shift would occur in the following situations:
↑ pH= ________ shift
↓ pH= ________ shift
↑ pH= left shift
More basic
↓ pH= right shift
More acidic
What is the Bohr effect? What type of shift do we see?
Bohr effect describes how CO2 effects oxygen’s affinity to Hb
basically at the tissues where CO2 is high we see a right shift
Fetal hemoglobin has a _______________ affinity for O2 compared to maternal hemoglobin. This causes what kind of shift?
higher- causes a left shift
What is the Haldane effect?
Describes how oxygen concentrations effect Hb’s affinity for CO2
basically where O2 is high aka lungs, we see increased CO2 and H+ unloading
An increase in Red Blood cell 2,3 BPG concentration causes what?
right shift
Carbon Dioxide is mainly transported by converting it into _____________.
bicarbonate
After CO2 is converted to Bicarb in the RBC, bicarb is exchanged for ______ and then is in the plasma.
Cl-
How is CO2 converted into bicarbonate?
CO2 and H20 are combined using carbonic anhydrase to turn it into bicarb and H+
During quiet inspiration and expiraton, what muscles are contracting?
quiet insp- diaphragm and external intercostals
quiet exp- NONE
Which of the following medullary regions controls quiet inspiration?
a. Pre-Botzinger complex
b. DRG
c. VRG
d. Pons
b
The VRG deals with active breathing and controls which of the following:
a. inspiration
b. expiration
c. both
c
What complex is known as the “pacemaker” in the medulla and drives DRG firing?
pre-botzinger
What is the difference between the pneumatic and apneustic centers of the pons?
pneumatic- switch off the DRg for smooth inspiratory and expiratory transition
apneustic- inspiratory neurons of the VRG and DRG from turning off