Topic 12- Magnetism and the Motor Effect
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
The Law of Magnetism
two like poles repel each other
two unlike poles attract each other
magnetic materials
iron
steel
cobalt
nickel
magnetic materials will always be ___ to magnets (regardless of north or south pole)
attracted
how to tests whether a material is a magnet
bring close to a known magnet
if it can be repelled than it is a magnet
if it can only be attracted it is a magnetic material
Permanent magnets
made out of permanent magnetic materials
produces its own magnetic field
will not lose its magnetism
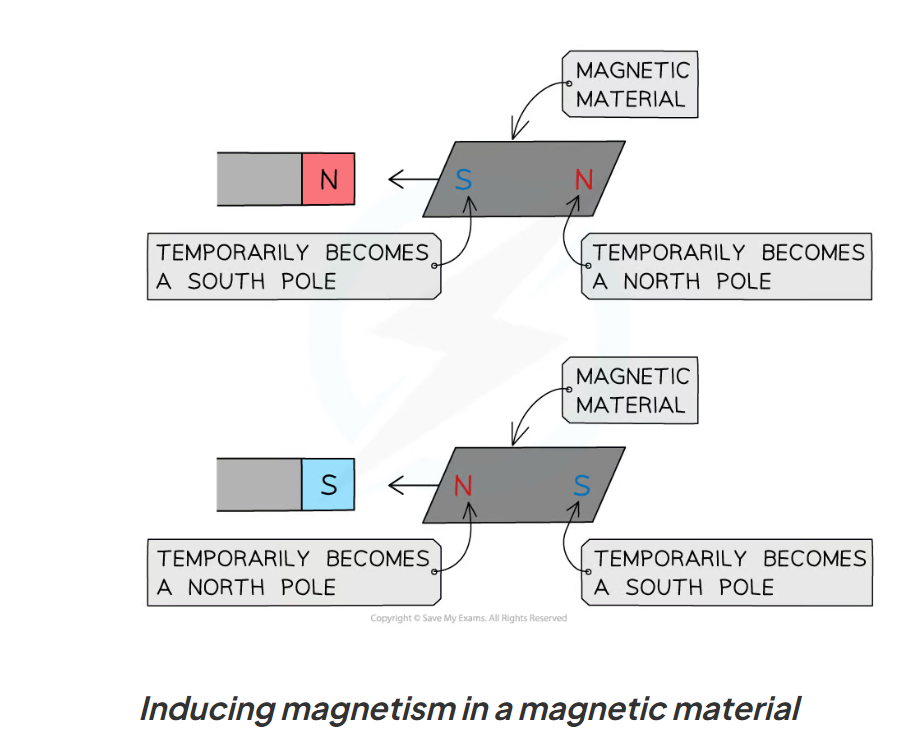
induced magnet
magnetic material temporarily turned into a magnet in another magnetic field
one of end of the material becomes a north/south pole
the end of the magnetic material closest to the magnet will have the opposite pole to the closet pole of the magnet
when the magnetic field is removed from the field it will lose its magnetism quickly
magnetic field
the region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or on a magnetic material.
magnetic fields are also known as…
B fields
measure of magnetic field strength
magnetic flux density
symbol B
unit Tesla
magnetic field lines always go…
from North to South
magnetic field lines show the direction of a…
north-seeking pole
where are uniform magnetic fields found?
the space between two opposite poles
uniform magnetic field (definition)
a magnetic field that has the same strength and direction at all points
(shown by equal spacing between field lines)
magnetic field is strongest…
at the poles
what happens as distance from a magnet increases
magnetic flux density (and therefore field strength) decreases
how to investigate shape and direction of magnetic field
plotting compasses
arrow points towards south pole
place a bar magnet on a piece of paper
plot direction of compass and draw points
connect the dots
repeat to create several field lines
evidence that the core of the earth is magnetic
in the absence of a magnet, a magnetic compass will always point towards geographic North Pole (actually the magnetic South), showing that the core’s magnetic field is similar to that of a bar magnet.
the shape of the magnetic field around a current-carrying wire is…
in concentric circles, indicating there are no poles
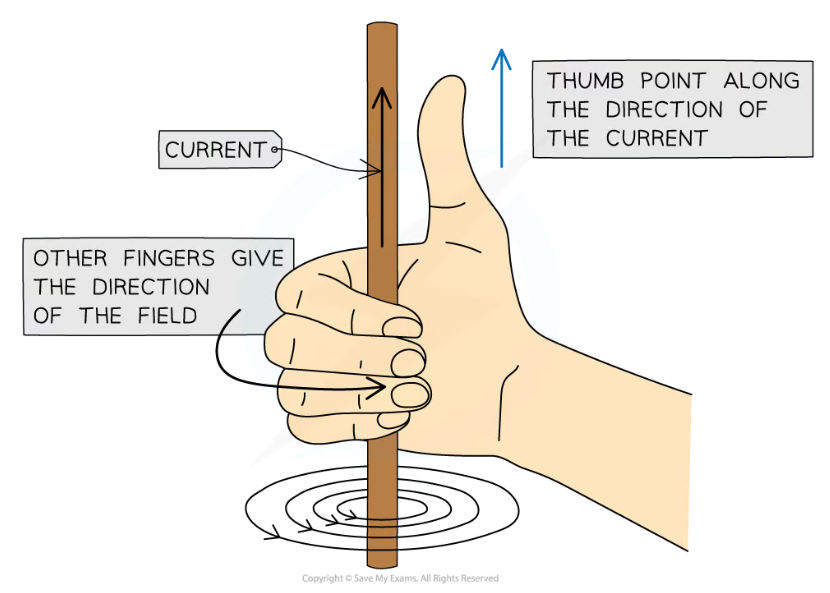
how to work out the direction of a magnetic field around a wire?
right hand thumb rule
factors affecting strength of field around a wire
size of current → bigger = stronger
distance from wire → further = weaker
as you get further from a wire, the field lines get…
further apart (exaggerate if asked to draw in exam), showing the field strength getting weaker
path of field lines when a current carrying wire is in a coil
they go through and around the coil, strongest on the inside
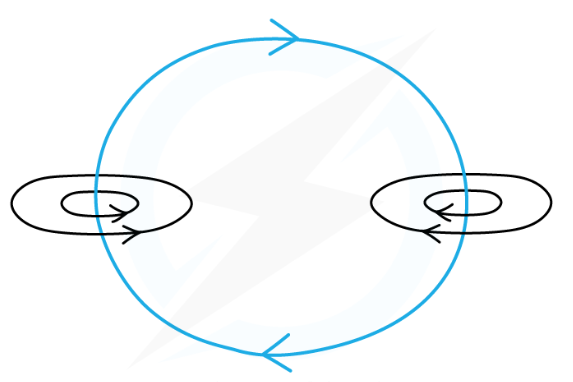
how does a solenoid increase the strength of the magnetic field of a coil
fields from individual ‘turns’ combine through the centre of a solenoid to produce a very strong, almost uniform field
outside the solenoid, they cancel to give a weaker field.

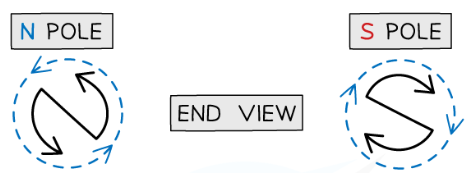
how to work out the poles of a solenoid
N = current travels anticlockwise
S = current travels clockwise
how to increase the magnetic field strength of a solenoid
bigger current
iron core
more turns in the coil
motor effect (def)
a wire with a current flowing through it is placed in another magnetic field it experiences a force. Caused by the interaction of 2 magnetic fields. An equal and opposite force acts on the magnet.
how to increase magnetic forces
stronger mag field with a stronger magnet
increase current to produce stronger mag field around wire
place wire at 90° to direction of magnet’s field, so most field lines are cut (if parallel there will be no force)
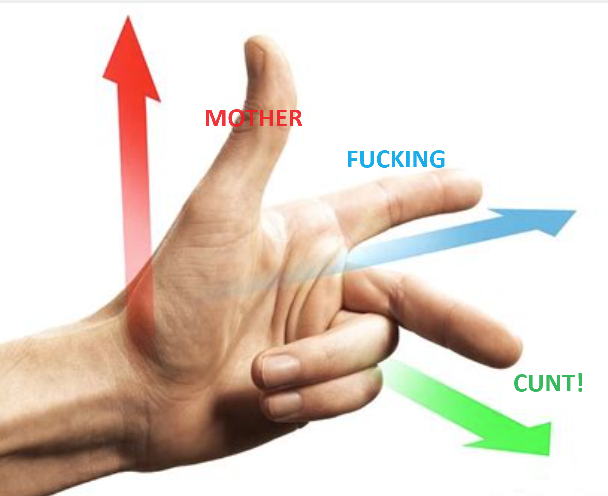
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
MOTHER FUCKING CUNT
(Motion, force, current)
(thumb, forefinger, middle finger)
Equation for calculating force on a current-carrying conductor (motor effect)
F = BIL
Force = Magnetic Flux Density (field strength) x Current x Length of conductor within the magnetic field
force in Newtons N
current in amps A
magnetic flux density in tesla N/Am
length in metres m
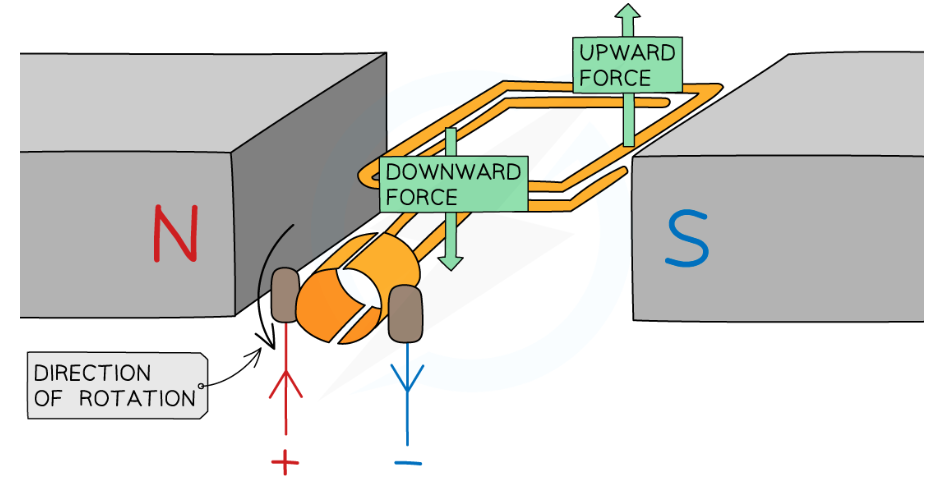
how is the motor effect used in electric motors?
a coil of wire which is free to rotate positioned in a uniform magnetic field
when the current flows at 90° to the direction of the mag field, the current creates a magnetic field around the coil, which interacts with the uniform mag field produced by magnets
force is exerted on the coil (direction determined by Fleming’s LHR). current flows in opposite directions either side of coil, so one side pushed up and one down
split ring commutator swaps the sliding contacts as the coil rotates, reversing the current every half turn.
this reverses the direction of the force exerted on each end of the coil, so it keeps rotating in the same direction