ap psychology unit 1 mcq study guide
1/79
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1. Which neurotransmitter is primarily involved in regulating mood
and appetite?
A) Dopamine
B) Serotonin
C) Acetylcholine
D) GABA
B
2. What is the primary function of the cerebellum?
A) Regulates vital functions
B) Coordinates movement and balance
C) Processes sensory information
D) Facilitates thought and perception
B
3. Which part of the brain plays a key role in forming new
memories?
A) Hippocampus
B) Amygdala
C) Cerebral cortex
D) Basal ganglia
A
4. What is the function of dopamine in the brain?
A) Regulates mood and appetite
B) Involved in reward and motivation
C) Regulates movement
D) Facilitates sleep
B
5. Which brain structure is responsible for regulating basic functions
like breathing and heart rate?
A) Hindbrain
B) Midbrain
C) Forebrain
D) Cerebral cortex
A
6. What is the role of the amygdala in emotional processing?
A) Regulates fear and anxiety
B) Involved in reward and motivation
C) Facilitates memory formation
D) Regulates mood
A
7. Which neurotransmitter is an inhibitory neurotransmitter,
promoting a calming effect?
A) GABA
B) Glutamate
C) Dopamine
D) Serotonin
A
8. What is the primary function of the cerebral cortex?
A) Regulates movement
B) Processes sensory information
C) Facilitates thought, perception, and memory
D) Regulates vital functions
C
9. Which brain structure is involved in regulating sleep and
dreaming?
A) Pons
B) Medulla
C) Cerebellum
D) Hippocampus
A
10. What is the function of acetylcholine in the brain?
A) Regulates mood and appetite
B) Involved in muscle contraction and memory formation
C) Regulates movement
D) Facilitates sleep
B
11. Which part of the brain is responsible for processing visual
information?
A) Occipital lobe
B) Temporal lobe
C) Parietal lobe
D) Frontal lobe
A
12. What is the role of the hippocampus in memory formation?
A) To store short-term memories
B) To consolidate long-term memories
C) To retrieve memories
D) To forget irrelevant information
B
13. Which neurotransmitter is involved in regulating movement?
A) Dopamine
B) Serotonin
C) Acetylcholine
D) GABA
A
14. What is the primary function of the brainstem?
A) To regulate vital functions
B) To facilitate sensory perception
C) To control movement
D) To regulate emotions
A
15. Which brain structure is involved in emotional processing?
A) Amygdala
B) Hippocampus
C) Cerebral cortex
D) Brainstem
A
16. What is the function of glutamate in the brain?
A) Inhibitory neurotransmitter
B) Excitatory neurotransmitter
C) Regulates mood and appetite
D) Involved in muscle contraction
B
17. Which part of the brain is responsible for regulating body
temperature?
A) Hypothalamus
B) Thalamus
C) Cerebral cortex
D) Brainstem
A
18. What is neuroplasticity?
A) The brain's ability to adapt and change
B) The process of detecting sensory stimuli
C) The interpretation of sensory information
D) The storage of sensory information in memory
A
19. Which neurotransmitter is involved in reward and motivation?
A) Dopamine
B) Serotonin
C) Acetylcholine
D) GABA
A
20. What is the primary function of the basal ganglia?
A) Regulates movement
B) Facilitates thought and perception
C) Processes sensory information
D) Regulates vital functions
A
21. Which brain structure is involved in regulating hunger and thirst?
A) Hypothalamus
B) Thalamus
C) Cerebral cortex
D) Brainstem
A
22. What is the role of the cerebral cortex in motor control?
A) To regulate reflexes
B) To facilitate voluntary movements
C) To control involuntary movements
D) To regulate posture
B
23. Which neurotransmitter is involved in regulating sleep and
wakefulness?
A) Serotonin
B) Melatonin
C) Dopamine
D) Acetylcholine
B
24. What is the primary function of the limbic system?
A) To regulate emotions and motivation
B) To facilitate sensory perception
C) To control movement
D) To regulate bodily functions
A
25. Which part of the brain is responsible for processing auditory
information?
A) Temporal lobe
B) Occipital lobe
C) Parietal lobe
D) Frontal lobe
A
26. What stage of sleep is characterized by vivid dreams and
increased brain activity?
A) NREM sleep
B) REM sleep
C) Stage 1 sleep
D) Stage 3 sleep
B
27. How many sleep cycles do people typically experience per night?
A) 2-3
B) 4-6
C) 7-8
D) 9-10
B
28. What is the primary consequence of sleep deprivation?
A) Improved cognitive function
B) Increased risk of chronic diseases
C) Enhanced creativity
D) Better mood regulation
B
29. Which stage of sleep is characterized by decreasing
consciousness and increasing relaxation?
A) REM sleep
B) NREM sleep
C) Stage 1 sleep
D) Stage 3 sleep
B
30. What is the typical duration of a sleep cycle?
A) 30 minutes
B) 60 minutes
C) 90 minutes
D) 120 minutes
C
31. What is the primary function of REM sleep?
A) Physical recovery
B) Memory consolidation
C) Emotional regulation
D) Cognitive function
B
32. What is the consequence of chronic sleep deprivation?
A) Improved physical health
B) Increased risk of mental health disorders
C) Enhanced cognitive function
D) Better mood regulation
B
33. Which sleep disorder is characterized by sudden attacks of
sleep?
A) Insomnia
B) Narcolepsy
C) Sleep apnea
D) Restless leg syndrome
B
34. What is the primary benefit of NREM sleep?
A) Physical recovery
B) Memory consolidation
C) Emotional regulation
D) Cognitive function
A
35. How does sleep deprivation affect cognitive function?
A) Improves focus and attention
B) Impairs problem-solving skills
C) Enhances creativity
D) Increases productivity
B
36. What is the role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in sleep
regulation?
A) Regulates sleep-wake cycle
B) Regulates appetite
C) Regulates body temperature
D) Regulates emotional response
A
37. Which stage of sleep is critical for physical recovery?
A) REM sleep
B) NREM sleep
C) Stage 1 sleep
D) Stage 3 sleep
B
38. What is the consequence of sleep deprivation on mood?
A) Improved mood
B) Increased irritability
C) Enhanced emotional regulation
D) Reduced stress
B
39. Which sleep disorder is characterized by difficulty falling asleep?
A) Insomnia
B) Narcolepsy
C) Sleep apnea
D) Restless leg syndrome
A
40. What is the primary function of sleep?
A) To rest the body
B) To process and consolidate memories
C) To regulate emotions
D) To facilitate learning
B
41. How does sleep affect memory consolidation?
A) Impairs memory consolidation
B) Enhances memory consolidation
C) Has no effect on memory consolidation
D) Only affects short-term memory
B
42. Which stage of sleep is associated with increased heart rate and
blood pressure?
A) REM sleep
B) NREM sleep
C) Stage 1 sleep
D) Stage 3 sleep
A
43. What is the consequence of sleep deprivation on the immune
system?
A) Weakened immune system
B) Strengthened immune system
C) No effect on the immune system
D) Only affects the immune system in older adults
A
44. Which sleep disorder is characterized by pauses in breathing
during sleep?
A) Insomnia
B) Narcolepsy
C) Sleep apnea
D) Restless leg syndrome
C
45. What is the primary benefit of REM sleep for emotional
regulation?
A) Reduces stress and anxiety
B) Increases emotional reactivity
C) Enhances emotional regulation
D) Has no effect on emotional regulation
C
46. How does sleep deprivation affect reaction time?
A) Improves reaction time
B) Slows reaction time
C) Has no effect on reaction time
D) Only affects reaction time in older adults
B
47. Which sleep stage is associated with increased brain activity and
vivid dreams?
A) REM sleep
B) NREM sleep
C) Stage 1 sleep
D) Stage 3 sleep
A
48. What is the primary function of NREM sleep for physical
recovery?
A) Repairs and regenerates tissues
B) Consolidates memories
C) Regulates emotions
D) Facilitates learning
A
49. How does sleep affect glucose regulation?
A) Impairs glucose regulation
B) Enhances glucose regulation
C) Has no effect on glucose regulation
D) Only affects glucose regulation in people with diabetes
A
50. Which sleep disorder is characterized by uncomfortable
sensations in the legs during sleep?
A) Insomnia
B) Narcolepsy
C) Sleep apnea
D) Restless leg syndrome
D
51. What is the minimum intensity of a stimulus that can be
detected?
A) Absolute threshold
B) Difference threshold
C) Sensory threshold
D) Perceptual threshold
A
52. Which sensory system is responsible for detecting light and color?
A) Visual system
B) Auditory system
C) Tactile system
D) Olfactory system
A
53. What is the process of interpreting sensory information?
A) Sensation
B) Perception
C) Attention
D) Memory
B
54. Which part of the eye is responsible for detecting light and
transmitting signals to the brain?
A) Retina
B) Cornea
C) Lens
D) Optic nerve
A
55. What is the minimum amount of change required to notice a
difference in a stimulus?
A) Absolute threshold
B) Difference threshold
C) Sensory threshold
D) Perceptual threshold
B
56. Information from the body’s somatic nervous system is relayed
to the spinal cord and brain by ___________.
(A) Afferent Neurons
(B) Efferent Neurons
(C) Interneurons
(D) Glial Cells
A
57. What is the role of the brain in perception?
A) To detect sensory stimuli
B) To interpret sensory information
C) To filter out irrelevant information
D) To store sensory information in memory
B
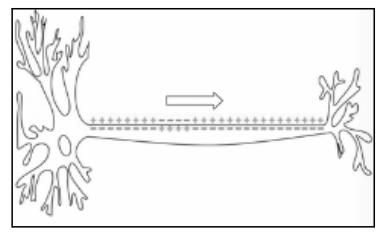
58. Which neural process is shown above?
(A) Action Potential
(B) Reuptake
(C) Synaptic Transmission
(D) Synaptic Pruning
A
59. What is the process of detecting sensory stimuli?
A) Sensation
B) Perception
C) Attention
D) Memory
A
60. Which sensory system is responsible for detecting touch and
pressure?
A) Visual system
B) Auditory system
C) Tactile system
D) Olfactory system
C
61. What is the function of the optic nerve in the visual system?
A) To detect light and color
B) To transmit visual information to the brain
C) To focus light on the retina
D) To regulate pupil size
B
62. Which of the following structures of the brain has been linked
with the regulation of hunger and thirst?
(A) Hippocampus
B) Hypothalamus
C) Thalamus
D) Pons
B
63. What is the role of attention in perception?
A) To filter out irrelevant information
B) To enhance sensory processing
C) To store sensory information in memory
D) To detect sensory stimuli
A
64. Which part of the brain is responsible for processing visual
information?
A) Occipital lobe
B) Temporal lobe
C) Parietal lobe
D) Frontal lobe
A
65. What is the function of the auditory nerve in the auditory
system?
A) To detect sound waves
B) To transmit auditory information to the brain
C) To localize sound sources
D) To regulate hearing thresholds
B
66. Which sensory system is responsible for detecting movement
and balance?
A) Visual system
B) Auditory system
C) Vestibular system
D) Tactile system
C
67. What is the process of recognizing and interpreting sensory
information?
A) Sensation
B) Perception
C) Attention
D) Memory
B
68. Which part of the brain is responsible for processing auditory
information?
A) Temporal lobe
B) Occipital lobe
C) Parietal lobe
D) Frontal lobe
A
69. What is the function of the olfactory bulb in the olfactory
system?
A) To detect odor molecules
B) To transmit olfactory information to the brain
C) To process olfactory information
D) To regulate olfactory thresholds
B
70. Which sensory system is responsible for detecting taste?
A) Gustatory system
B) Olfactory system
C) Visual system
D) Auditory system
A
71. What is the role of the somatosensory cortex in processing
sensory information?
A) To process visual information
B) To process auditory information
C) To process touch and pressure information
D) To process olfactory information
C
72. Which part of the eye is responsible for focusing light on the
retina?
A) Lens
B) Cornea
C) Iris
D) Pupil
A
73. What is the function of the vestibular system in balance and
equilibrium?
A) To detect movement and balance
B) To regulate posture and movement
C) To process visual information
D) To detect sound waves
A
74. Which sensory system is responsible for detecting pain?
A) Nociceptive system
B) Tactile system
C) Visual system
D) Auditory system
A
75. What is the process of adapting to a sensory stimulus?
A) Sensory adaptation
B) Sensory detection
C) Sensory perception
D) Sensory processing
A
76. Satoru has problems coordinating her movement and keeping
her balance. Which part of her brain is NOT functioning properly?
A) Hippocampus
B) Amygdala
C) Cerebellum
D) Cerebrum
E) Frontal Lobe
C
77. Minnie is a dancer. She has been dancing for years, but one
evening at a late-night rehearsal, her tired partner accidentally
dropped her on her head. Now, Minnie has problems dancing. She
knows the correct steps she must make, but she feels as if her legs
and arms are moving as if directed by someone else. What area of
her brain was damaged by her fall?
A) Wernicke’s Area
B) Hippocampus
C) Broca’s Area
D) Pons
E) Cerebellum
E
78. What is one major difference between the sympathetic and
parasympathetic nervous system?
A) The sympathetic nervous system increases physiological arousal,
while the parasympathetic nervous system returns the body to a
calmer and relaxed state
B) The sympathetic nervous system is a subdivision of the somatic
nervous system, while the parasympathetic nervous system is a
subdivision of the autonomic nervous system
C) The sympathetic nervous system plays a role in traumatic events,
while the parasympathetic nervous system only plays a role in
digestion
D) The parasympathetic nervous system is used more often
that the sympathetic nervous system
E) The expression of genetic predispositions and brain
physiology are both influenced by environmental factors,
therefore nature and nurture are interrelated
A
79. Tanjiro was preparing to study for his psychology exam
when the first alarm went off. His heart raced and his
breathing sped up. Which part of the nervous system
activated Jackson’s stress response?
(A) Parasympathetic
(B) Sympathetic
(C) Somatic
(D) Limbic System
(E) Endorphins
B
80. Which of the following reflects the order and direction
of a neural impulse within a cell?
A) Dendrite to Cell Body to Axon
B) Cell Body to Dendrite to Axon
C) Dendrite to Axon to Cell Body
D) Axon to Cell Body to Dendrite
E) Axon to Dendrite to Cell Body
A