GCSE Physics paper 1
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Dalton’s model of the atom
small, indestructible sphere
all atoms in an element are the same
the atoms in one element are different from the atoms in all other elements
JJ Thomson’s model of the atom
he discovered electrons
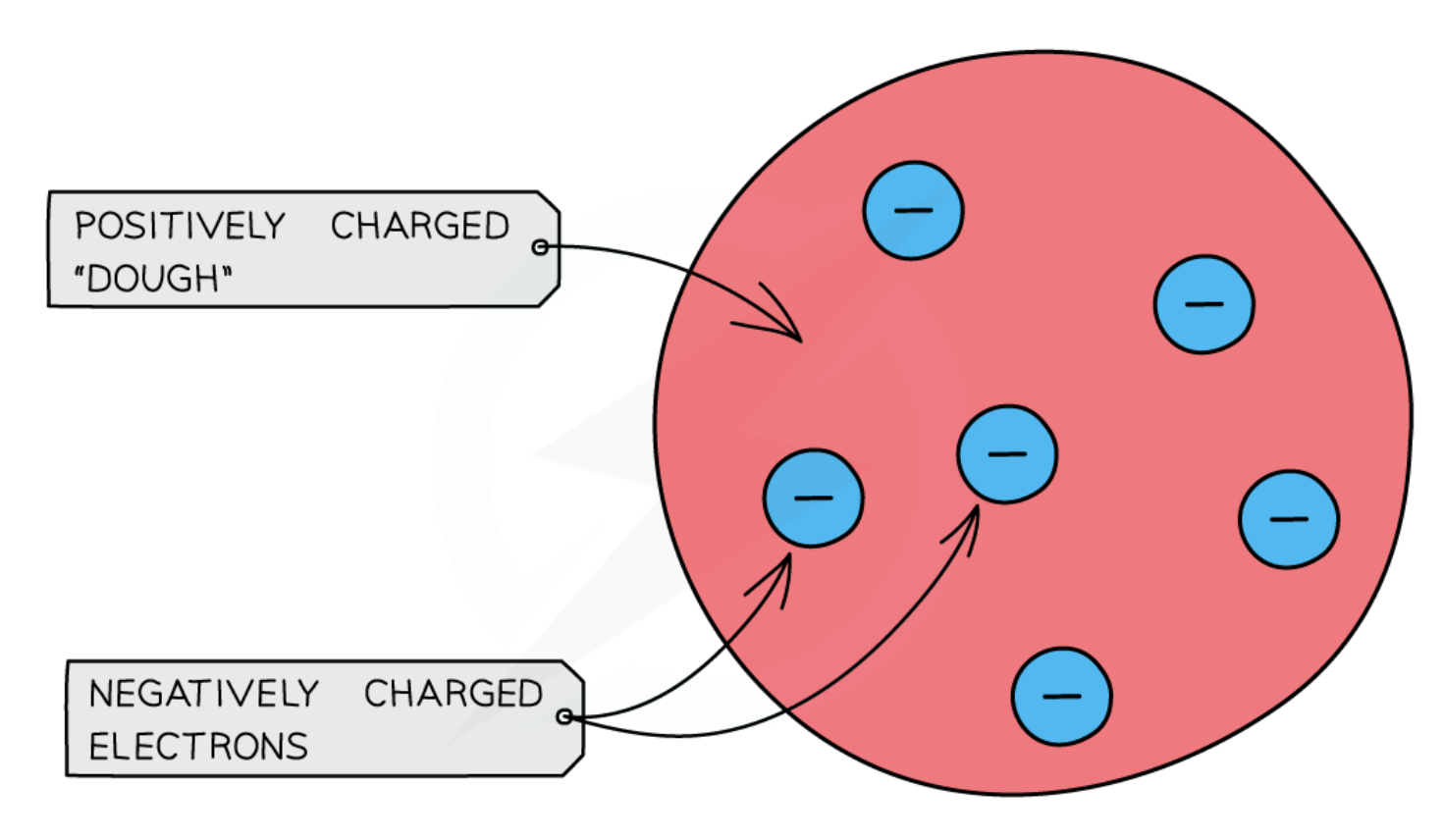
the plum pudding model
Ernest Rutherford’s model of the atom
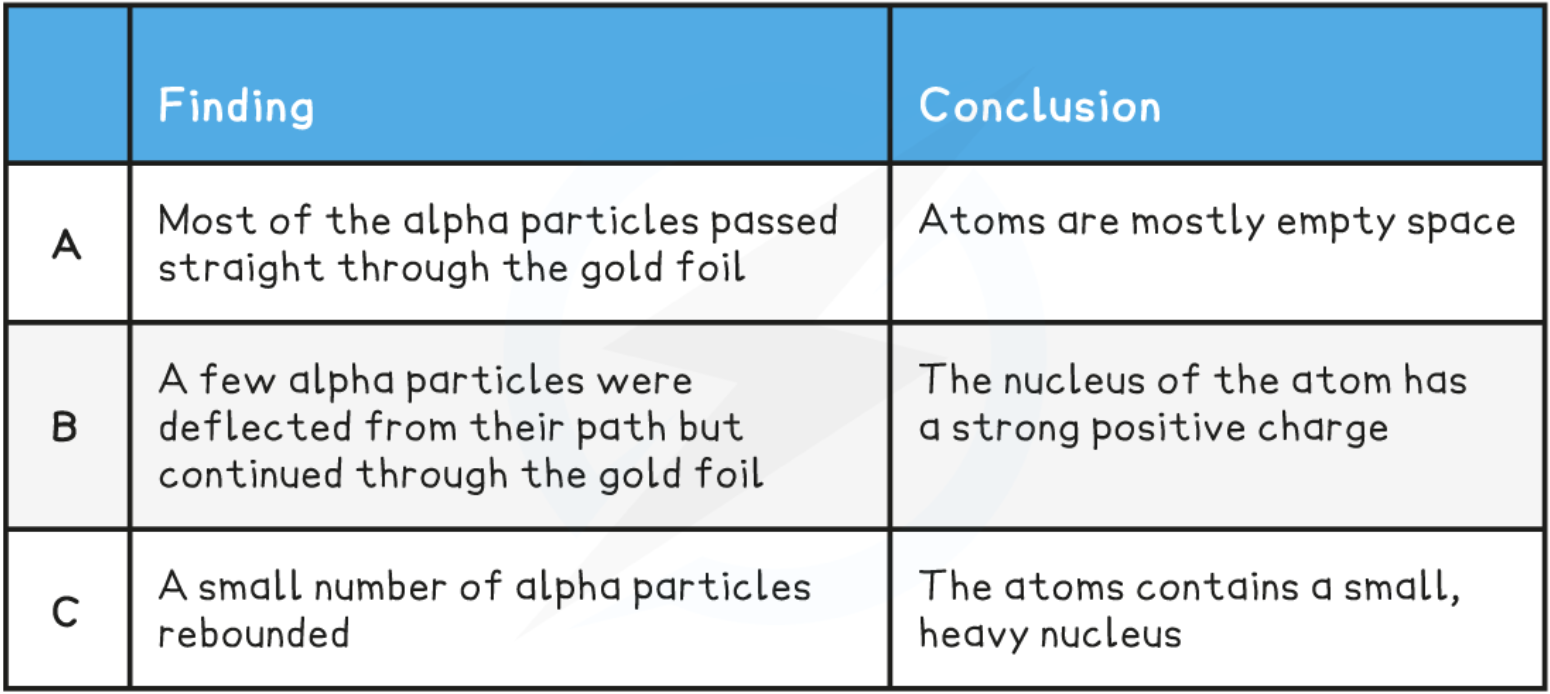
nearly all of the atom’s mass is concentrated in the centre
positively charged nucleus
negatively charged electrons orbit the nucleus
Rutherford, Geiger & Marsden’s experiment
alpha particles (+) fired at thin gold foil
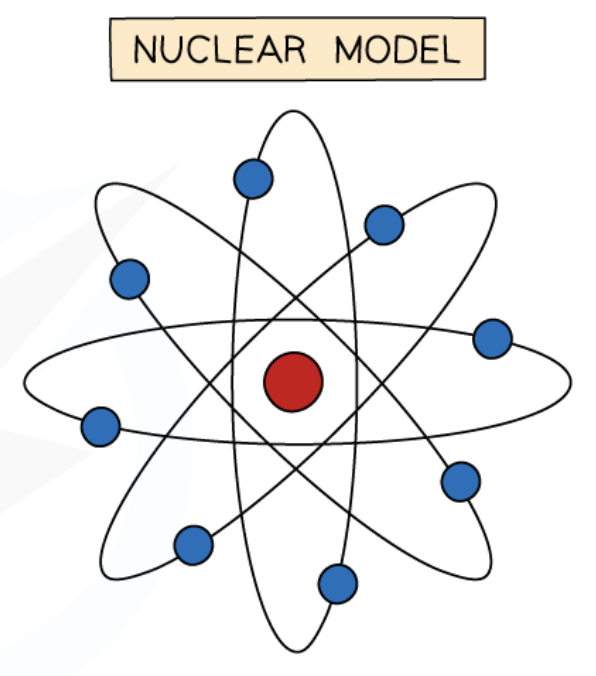
Niels Bohr’s model of the atom
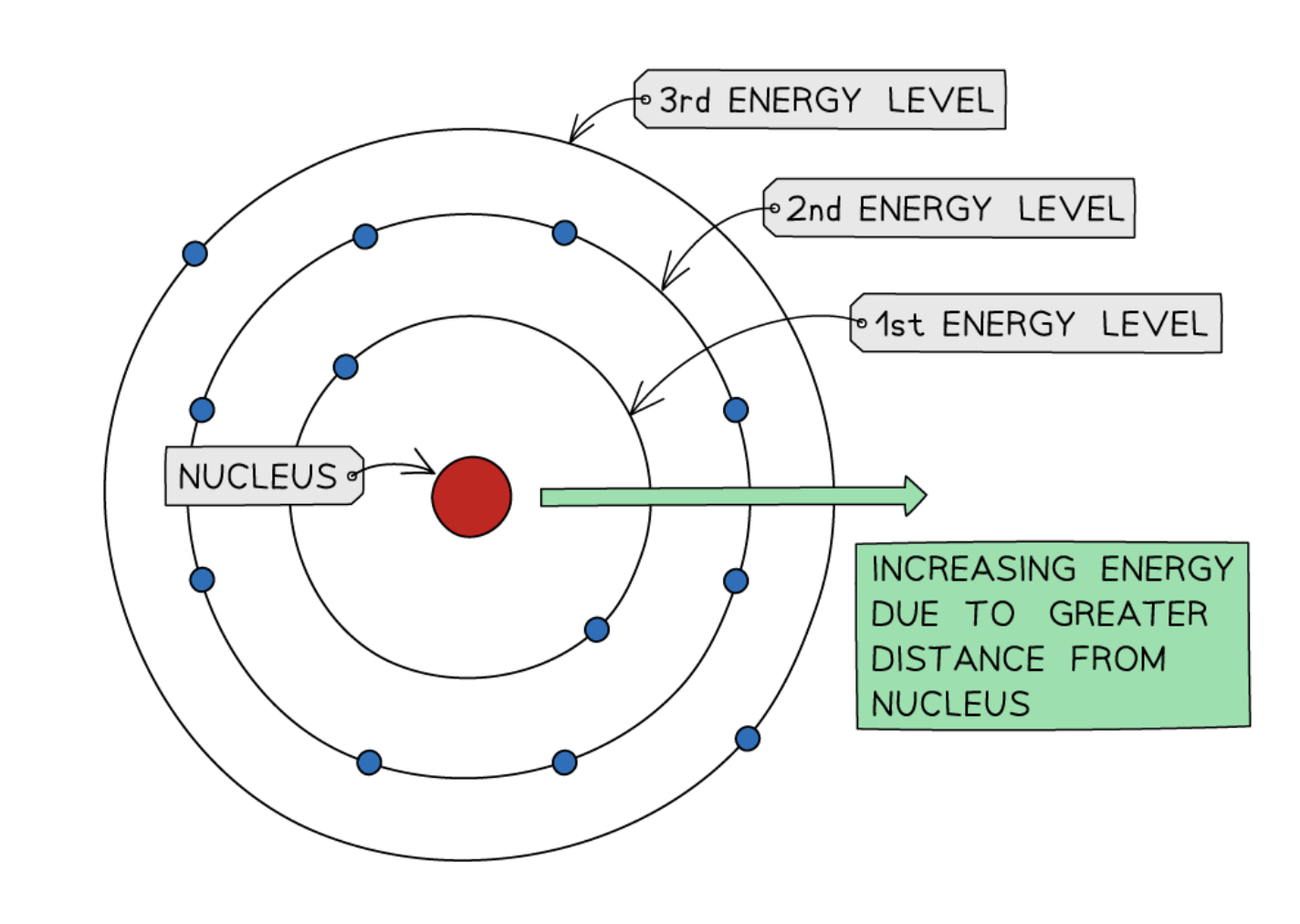
discovered that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels
better than Rutherford’s model, because the atom would collapse otherwise
Diameter of the atom
1 × 10⁻¹⁰ m
Density
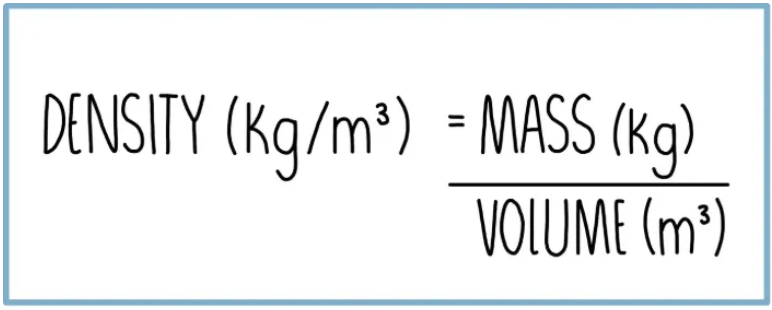
Conservation of mass
the principle that when a substance changes state, the number of molecules in that substance doesn’t change and neither does its mass.
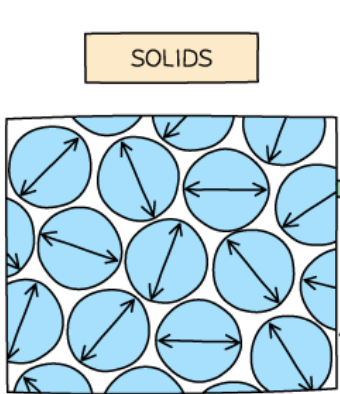
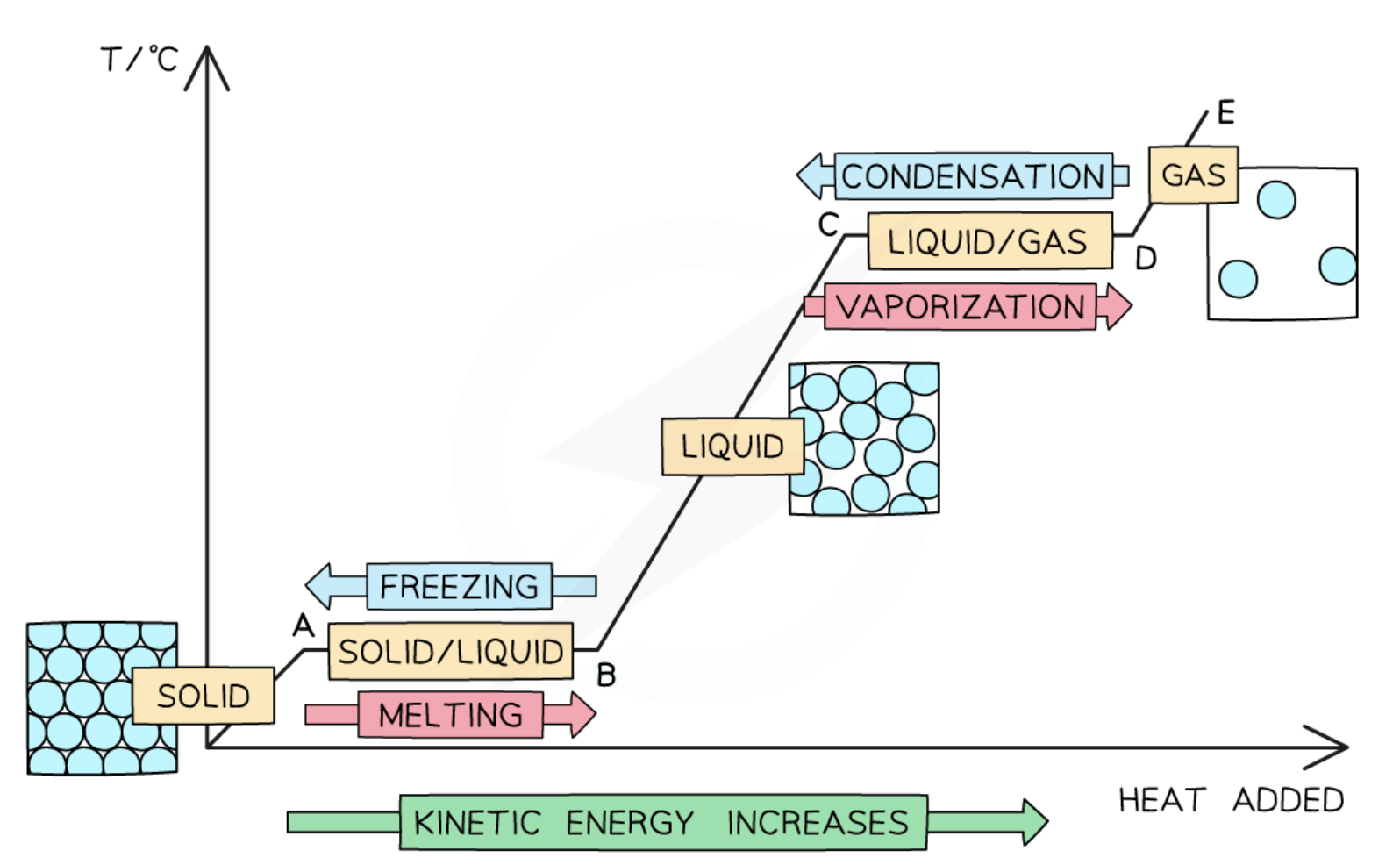
Particles in a solid
very close
arranged in a regular pattern
vibrate about fixed positions
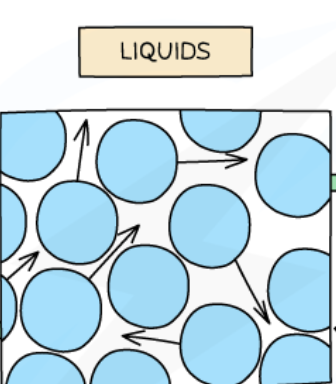
Particles in a liquid
close together
NOT in an arranged pattern
able to slide past each other
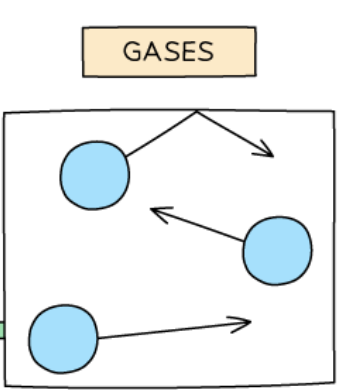
Particles in a liquid
very far apart
move randomly at high speeds
Heating curve
Specific heat capacity
the quantity of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1˚C.
Specific latent heat
the quantity of energy required to change the state of a substance with no change in temperature.