Genetics E1- Patterns of Inheritance
1/28
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Which pattern of inheritance?
manifests in heterozygous state
vertical pattern affects multiple generations
confirmed w/ male to male transmission
Autosomal Dominant
What are examples of autosomal dominant conditions?
Neurofibromatosis type 1, huntingtons, marfans
With an autosomal dominant condition, what are the chances that the offspring would have the affected phenotype if an affected person mates with an unaffected person?
50%
What term refers to the difference in clinical manifestations between individuals in autosomal dominant disorders? (some have mild dz, some have severe)
Variable expressivity
What occurs when some individuals with a disease causing genotype do not develop the disease phenotype at all?
Reduced penetrance
What term describes an individual who carries the disease gene but shows no clinical features of the condition?
Non-penetrance
What is the proportion of people with a specific genotype who manifest a particular clinical characteristic or phenotype, expressed as a percentage?
Penetrance
What kind of pedigree pattern is observed with autosomal recessive inheritance?
Horizontal; only 1 generation affected; M=F
With an autosomal recessive condition, what are the chances that the offspring would be affected if both parents are asymptomatic, heterozygous carriers?
25% chance of being affected, 25% chance of inheriting neither mutant allele, and 50% chance of being an asx carrier
With an autosomal recessive condition, what are the chances that the offspring would be affected if one parent is affected and one parent is a carrier?
50% will be affected, 50% will be carriers
With an autosomal recessive condition, what are the chances that the offspring would be affected if both parents are affected?
100% will be affected
With an autosomal recessive condition, what are the chances that the offspring would be affected if one parent is affected and one is an unaffected non carrier?
100% will be asymptomatic carriers
What term refers to a recessive trait that mimics dominant transmission?
Pseudodominance
When does pseudodominance occur?
One parent is affected / homozygous recessive (aa) & one parent is asx carrier / heterozygous (Aa) → 50% offspring affected, 50% asx carriers
What term refers to mating between persons biologically related as second cousins or greater, which therefore increases the likelihood of having 2 copies of a harmful allele?
Consanguinity
What type of inheritance?
carried on X chromosome
usually manifests only in males
transmitted from carrier females to their sons → affected males transmit to carrier daughters
X-linked recessive inheritance
If a male with an X-linked recessive condition has offspring, who would be at risk for inheriting the same condition?
Male grandchildren through carrier daughters
What is an example of an X-linked recessive condition?
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
What type of inheritance?
heterozygous females & males w/ variant allele on their single X chromosome manifest the disease
no father to son transmission
F > M
X-linked dominant inheritance
What are examples of X-linked dominant conditions?
Rett syndrome, x-linked hypophosphatemia (vitamin D resistant rickets)
With an X-linked dominant condition, which offspring would be affected if the father has the condition?
100% of daughters, 0% of sons
With an X-linked dominant condition, which offspring would be a affected if the mother has the condition?
50% of daughters, 50% of sons
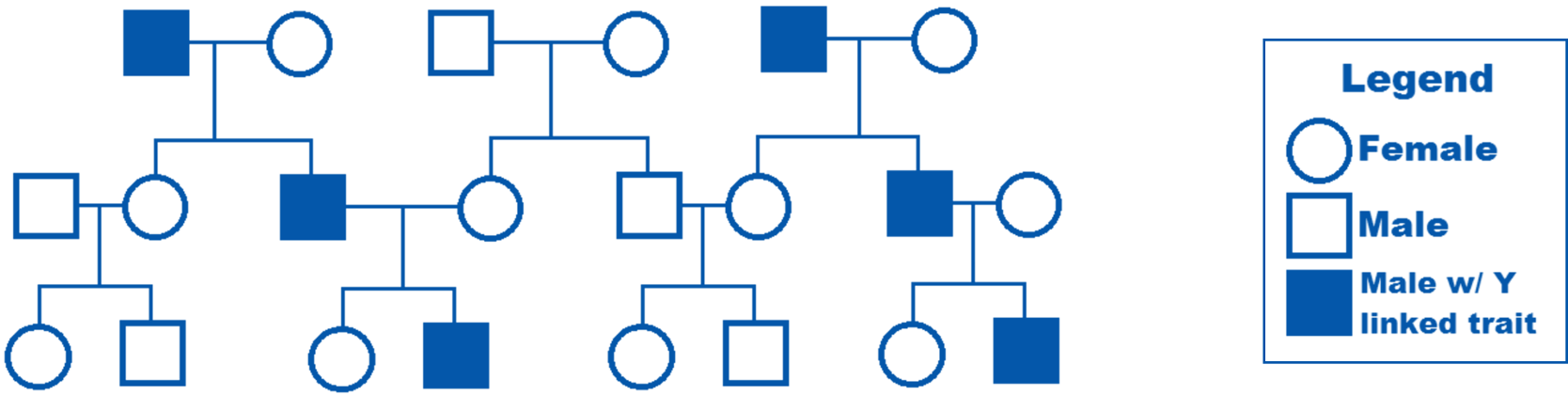
What type of inheritance?
only males affected
affected males must transmit to their sons
H-Y histocompatibility antigen
Y-linked inheritance / Holandric inheritance
How is mitochondrial DNA inherited?
Exclusively transmitted through the maternal line (mitochondria comes exclusively from the egg during conception)
Which has a higher rate of spontaneous variation, mitochondrial DNA or nuclear DNA?
Mitochondrial DNA
What is homoplasmy?
mtDNA is identical across different mitochondria (MC)
What is heteroplasmy?
2 populations of mtDNA exist due to a variant in the mtDNA of an individual
What type of inheritance consists of disorders that demonstrate familial clustering but don’t have a recognized pattern of mendelian inheritance?
Ex: DM, cancer, CAD, mental health diseases
Multifactorial inheritance
What are genome-wide association studies?
Models showing certain disease states are caused by multiple “bad” genes & adverse environmental factors (T2DM, schizophrenia, RA, etc)