Genetic mutations
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Define gene mutations
Any change to the quantity of bases or base sequence in the DNA- results in a change in the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide (the primary structure).
Mutations can arise spontaneously during DNA replication.
What are the 2 main types of gene mutations?
Point mutation
Frame shift
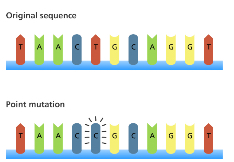
Describe point mutations
Just affects one nucleotide/base e.g. base substitutions:
A nucleotide in a DNA molecule is replaced with another nucleotide with a different base
3 outcomes:
The new triplet codes for a different amino acid
The polypeptide produced will differ by one amino acid
The effect will depend on the precise role/importance of that one amino acid
May result in a different shape and not function properly
The new triplet may still code for the same amino acid (due to degenerate code)
The new triplet happens to code for a stop codon- so stopping the production of the polypeptide chain
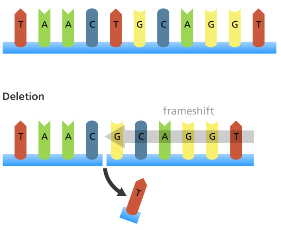
Describe base deletions (causes framshifts)
When a nucleotide is lost from the normal DNA sequence
All the subsequent bases are shifted to the left and so cause all the triplets after the deletion to be read differently
This can cause all the following amino acids to change
Frame shifts have a much larger effect on the protein than a point mutation
Define chromosome mutations
Changes in the structure or number of whole chromosomes
Can arise spontaneously
2 forms
What are the 2 forms of chromosome mutation?
Changes in whole sets of chromosomes (polyploidy)- when organisms have 3 or more sets of chromosomes rather than the normal 2 (occurs mostly in plants)
Changes in the number of individual chromosomes- when an organism has one extra or fewer chromosome- called non-disjunction (due to incomplete separation of chromosomes of chromatids in either division) e.g. Down’s syndrome→ additional 21 chromosome