Contraception
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Describe the expanding role of the pharmacist in this area
Multiple states have passed legislation to allow licensed pharmacists to prescribe some hormonal contraceptives
There is a WI bill that would permit pharmacists to prescribe and dispense hormonal contraceptive patches and self administered oral contraceptives with certain procedures in place
List available pharmacologic contraceptive options
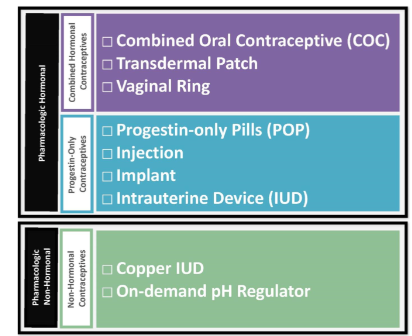
Progestin only contracpetives MOA
Thicken cervical mucus, inhibit LH surge, atrophy of endometrial lining, decrease ovum motility
Combined hormonal contraceptions MOA
Same as progestin + Estrogen suppresses ovulation via negative feedback
Explain the difference between typical and perfect use
Typical Use | Perfect Use |
Takes into consideration human error and is generally what happens in real life | When a patient uses contraceptive method correctly at ALL times |
Combined hormonal contraceptives advantages
Easy to use
Rapid reversibility
Menstrual cycle improvements
Decreased risk of iron deficiency anemia
Can tailor COC to specific patient
Suppression of endometriosis
Reduction of several cancers
Combined hormonal contraceptives disadvantages
No STI protection
Patient adherence
Expense and access
Side effects
Serious adverse effects
Menstrual cycle changes
Drug interactions
benefits of Combined hormonal contraceptives agents beyond prevention of pregnancy
Acne treatment
Hirsutism treatment
Endometriosis
Cycle regulation
DysmenorrheaAnemia
PCOS
Premenstrual dysphoric disorderDecreased risk of ovarian , uterine and colon cancer
Transition therapy for perimenopause
Combined hormonal contraceptives side effects
Abdominal pain
Chest pain
Headaches
Eye problems
Severe leg pain
Combined hormonal contraceptives contraindications
Breast cancer
<21 days postpartum
Severe cirrhosis
Acute DVT/PE
HIgh risk for recurrent DVT/PE
Major surgery with prolonged immobilization
Migraine with aura
Uncontrolled HTN
Vascular disease
Ischemic heart disease
Multiple ASCVD risk factors
Age >35 >15 cigs/day
History of stroke
Describe how estrogenic and androgenic activity change depending on the progestin generation
1st gen | 2nd gen | 3rd gen | 4th gen |
Norethindrone | Levonorgestrel | Norgestimate | Drospirenone |
*As generation inceases, androgenic activitydecreases and estrogenic activity increases
How to start Norethindrone &Norgesterol containing POP
Start anytime, backuo needed for 48 hours unless started within first 5 days of menstraul cycle
Dose considered missed if >3 hours late
DMPA injection adverse effects
BBW bone loss, signif weight gain, contraindicated in breast cancer
Copper IUD
Lasts 10 years
Menstrual bleeding increases 35-55%
Insufficient estrogen is associated with….
Early breakthrough bleeding
Insufficient progestin is associated with….
Late breakthrough bleeding (2nd half of cycle)
Excess estrogen is associated with…
N/V, Cyclical Weight gain, Bloating, Fluid retention, Breast tenderness
Excess progestin is associated with…
Acne, Hirsutism, Depression, non cyclical weight gain
Describe how a patient should initiate contraception
First Day- Start COC on first day of menstrual cycle
+No back up needed
Sunday start- Start COC on first sunday after menstrual cycle begins
+standard pack labeling, avoids periods over weekends
Quick Start- Start COC on day that patient received prescription
+increases likelihood that pt starts contraceptive
Describe how a patient should resolve missed doses
1 pill late or missed- take ASAP, OK to take 2 pills on same day
2 or more missed 48 hours- take ASAP, OK to take 2 pills on same day, back up contracpetion until 7 days of adherence
when emergency contraception should be recommended
Used to prevent unintended pregnancy after unprotected sexual intercourse
EC options
Copper &Levonorgestrel IUDs
Levonorgestrel
Ulipristal acetate
EC counseling
N/V, irregular bleeding