Unit 2: Origins of US Government
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:13 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
What is the Magna Carta?
a document that put forth the idea that the monarchy and it's government are not above the law (June 1215)
2
New cards
What is the Petition of Rights?
A formal petition (written by the British parliament) that ensured individual Rights:
-Severely limited the king’s power
-No taxation without Parliament’s consent
-can't imprison people without just cause
- can't house troops in private homes without permission of the owner
-declared martial law
-Severely limited the king’s power
-No taxation without Parliament’s consent
-can't imprison people without just cause
- can't house troops in private homes without permission of the owner
-declared martial law
3
New cards
What did the English Bill of Rights do?
-They prevented the abuse of power by the monarchy.
-Ensured that Parliament must consent to suspend laws, levy taxes, and maintain an army.
-Monarch cannot interfere with parliamentary elections & debates
-People have the right to a fair & speedy trial by a jury of their peers & should not be subjected to cruel & unusual punishments
-Ensured that Parliament must consent to suspend laws, levy taxes, and maintain an army.
-Monarch cannot interfere with parliamentary elections & debates
-People have the right to a fair & speedy trial by a jury of their peers & should not be subjected to cruel & unusual punishments
4
New cards
What were the English Bill of Rights?
The document established the principles of frequent parliaments, free elections and freedom of speech within Parliament. (aka Parliamentary Privilege)
5
New cards
What are Royal colonies?
A colony that is governed by the monarchy through an appointed governor/council ( New Hampshire, New York, New Jersey, North Carolina, South Carolina and Georgia) (few became proprietary)
6
New cards
What are Proprietary colonies?
A colony given to a person by the monarchy through a grant, usually bicameral legislature (Maryland, South Carolina, North Carolina, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania)
7
New cards
What are charter colonies?
A self-governing colony that elected it's own governor and did not need the king's approval to pass laws. (Each colony was established on the basis of a charter (a written grant of authority from the king)) (Connecticut, Massachusetts Bay Colony and Rhode Island)
8
New cards
What is limited government?
Where a government is restricted in what it can do and citizens have certain rights that can not be taken away from them.
9
New cards
What is ordered government?
an orderly regulation of government in which they created several local governments
10
New cards
What is a representative government?
a government that serves the will of the people and where the people decide what the government should and should not do
11
New cards
What is an unicameral Legislature?
a type of legislature that has one assembly and votes as one (Pennsylvania use unicameralism)
12
New cards
what is a bicameral legislature?
a type of legislature composed of two assemblies (Pennsylvania was the only non-bicameral colony
13
New cards
What did John Locke and Voltaire & Rousseau think of Social Contract?
Locke and others believed that people should make a contract among themselves to form governments to protect natural rights
14
New cards
What is Separation of Power?
a belief that a government should divide responsibilities and assign them to different branches within the government. (idea was popularized by Montesquieu)
15
New cards
What did John Locke believe?
He believed that in nature all people are born free and equal and that government is only legitamate as long as the people consent to it.
16
New cards
What is the Virginia house of Burgesses?
An assembly of elected officials in Virginia that met from 1643 to 1776. They originated laws, granted supplies, and operated as the British House of Commons in the American Colonies
17
New cards
What are the Articles of Confederation?
They're documents that pushed for a unicameral congress that handle the government.
18
New cards
What did the Articles of Confederation advocate for?
-Committees of state: settled disputes when congress wasn't in session
-No federal court system
-Every state legislature selected its own representatives to Congress
-No federal court system
-Every state legislature selected its own representatives to Congress
19
New cards
What are the functions of a unicameral congress?
-Executive positions were chosen from Congress
-Settled disputes between states
-Each state had one vote no matter the size or population
-Only had powers expressed in the Articles
-War & peace, raise & maintain an army & navy; appoint senior military officers
-send/receive ambassadors, treaties, Indian affairs
-Settled disputes between states
-Each state had one vote no matter the size or population
-Only had powers expressed in the Articles
-War & peace, raise & maintain an army & navy; appoint senior military officers
-send/receive ambassadors, treaties, Indian affairs
20
New cards
What was shay's rebellion?
a series of violent attacks on courthouses and other government properties in Massachusetts
21
New cards
what caused shay's rebellion?
the increasing debt that the government could not pay off led farmers to start shay's rebellion
22
New cards
What was the constitutional convention?
a formal meeting held with the purpose of writing a constitution for the United States
23
New cards
Who was at the constitutional convention?
The framer of the Constitution. ( George Washington, James Madison, Benjamin Franklin, James Wilson, John Rutledge, Charles Pinckney, Oliver Ellsworth, and Gouverneur Morris.)
24
New cards
Where was the constitutional convention?
It was in Philadelphia Pennsylvania from May 25 -Sept 17, 1787
25
New cards
What was the Virginia Plan?
A plan made by James Madison that outlined a strong national government with three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial (federal)
26
New cards
What were some problems after the war?
-states were arguing about boundary lines
-tariffs (NJ farmers had to pay fees to sell veggies in NY)
-Some states started to deal directly with foreign nations
- the government was $40m in debt to foreign nations and soldiers from the war
-with no money the government couldn't raise enough money to run a government
-tariffs (NJ farmers had to pay fees to sell veggies in NY)
-Some states started to deal directly with foreign nations
- the government was $40m in debt to foreign nations and soldiers from the war
-with no money the government couldn't raise enough money to run a government
27
New cards
What was the New Jersey Plan?
a Plan made by William Paterson that proposed a unicameral government where each state had the same number of votes ad where executives were elected by the national assembly. (parliamentary)
28
New cards
What was Connecticut's Compromise (Great Compromise)?
A system that assigned a number of legislative seats to each state based on it's population
29
New cards
What was the ⅗ Compromise?
a law that counted ⅗'s of a state's slave population in determining taxes and representation in the house of representatives
30
New cards
What were the Federalist papers
a series of papers that advocated for the US to adopt a strong federalist government. It was written by Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and James Madison under the Pen name Publius. (October 1787 - May 1788)
31
New cards
What were the Anti-federalist papers?
a series of papers that discussed the problems with adopting a strong federalist government. Written under the pen name Brutus (25 September 1787)
32
New cards
Who was the "father of the constitution)?
James Madison: he made a major contribution to the ratification of the constitution by writing the federalist papers.
33
New cards
What three documents established a system of limited government & rule by law in each of the colonies?
the Mayflower Compact, Great Fundamentals, and the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
34
New cards
What are the 3 key parts of the Declaration of Independence?
-a general statement of natural rights theory and the purpose of government
-a list of grievances against the British King
-the declaration of independence from England
-a list of grievances against the British King
-the declaration of independence from England
35
New cards
What are 3 specific achievements of the Articles of Confederation.
-maintained war and peace
-established foreign ambassadors, treaties, Indian affairs
-Settled disputes between states
-established foreign ambassadors, treaties, Indian affairs
-Settled disputes between states
36
New cards
What 3 main ideas did the delegates at the Constitutional Convention (May 27, 1787) agree upon?
-Limited & representative government
-Powers of national government should be divided among legislative, executive, & judicial branches
-National government must be strengthened
-Powers of national government should be divided among legislative, executive, & judicial branches
-National government must be strengthened
37
New cards
Why did James Madison publish under the pen name Publius?
He did this because he views himself as trying to establish a strong unicameral federalist government. Publius is an ancient Roman official who overthrew the Roman government to create the Roman Republic
38
New cards
Why did an anti-Federalist write under the pen name Brutus?
They write under this Pen name because they were protecting the people from tyranny. Brutus was a Roman official who killed Julius Caesar to prevent the Roman government from becoming a monarchy.
39
New cards
What are the 2 great points of difference between a democracy & a republic, according to Federalist #10?
-In a pure democracy, anyone can contribute (which can lead to the majority overrunning the minority) while in a republic you delegate a government to represent the people
-A republican government is better at making a country united and centralized than a democracy ( democracy makes the country factious).
-In a pure democracy, it is more likely for one party/ group of people to dominate and infringed on the rights of others.
-A republican government is better at making a country united and centralized than a democracy ( democracy makes the country factious).
-In a pure democracy, it is more likely for one party/ group of people to dominate and infringed on the rights of others.
40
New cards
What are the advantages of a large, central government described in Federalist #10
-A large central government is elected by the people to represent their interests.m 2
-In a large republic there is more likely to be people who are fit for government than in a small republic
-It will be more difficult for unqualified people to become government officials
-Allows for a pluralist society.
-With a large government there are many points of view so no one rights
-In a large republic there is more likely to be people who are fit for government than in a small republic
-It will be more difficult for unqualified people to become government officials
-Allows for a pluralist society.
-With a large government there are many points of view so no one rights
41
New cards
What are the disadvantages of a large, central government according to Brutus #1?
-With the multitude of ideas, there will be too much disagreement and nothing will get done.
-The central government will be too powerful and prevent states from being able to do anything
-Once a republic expands across a large some of people it becomes a dictatorship
-The people’s interest will not really be taken into account
-In order for a Republic to work people have to be in general agreement or have the same ideas, otherwise there will be too much indecision
-The representatives will be removed from the people and start oppressing them
-The central government will be too powerful and prevent states from being able to do anything
-Once a republic expands across a large some of people it becomes a dictatorship
-The people’s interest will not really be taken into account
-In order for a Republic to work people have to be in general agreement or have the same ideas, otherwise there will be too much indecision
-The representatives will be removed from the people and start oppressing them
42
New cards
What is an accurate comparison of the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution?
Articles of Confederation: Created a weak central government with few independent powers
the Constitution: Created a strong national government with many powers
the Constitution: Created a strong national government with many powers
43
New cards
Which two were weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation?
-The federal government could not levy taxes
-The federal government could not raise an army
-The federal government could not raise an army
44
New cards
"Our Debts being unfunded and unprovided for, the Interest cannot be paid. Those therefore who trusted us in the Hour of Distress are defrauded. To expect that under such Circumstances others will confide in the Government would be Folly, and to expect that Foreigners will Trust a Government which has no Credit with its own Citizens must be madness . . .
"The United States have call’d for eight Million of Dollars early in November last, of which the first quarterly Payment was to have been made on the first Day of April next. But I cannot find that a single State has laid the Taxes."
-Robert Morris, letter to the president of Congress, 1782
Based on the text, which of the following statements would the author most likely agree with?
"The United States have call’d for eight Million of Dollars early in November last, of which the first quarterly Payment was to have been made on the first Day of April next. But I cannot find that a single State has laid the Taxes."
-Robert Morris, letter to the president of Congress, 1782
Based on the text, which of the following statements would the author most likely agree with?
The national government under the Articles lacks necessary tax enforcement power
45
New cards
"When the Articles of Confederation were drafted, Americans had little experience of what a national government could do for them and bitter experience of what an arbitrary government could do to them. In creating a central government they were therefore more concerned with keeping it under control than with giving it the means to do its job."
-Edmund S. Morgan, The Birth of the Republic, 1763-89, 1956
Which of the following concepts is most consistent with the author’s argument?
-Edmund S. Morgan, The Birth of the Republic, 1763-89, 1956
Which of the following concepts is most consistent with the author’s argument?
Limited government
46
New cards
The relationship between the states under the Articles of Confederation could best be described as which of the following?
A loose league of friendship
47
New cards
An example of a weakness of the articles of confederation
Amending the Articles required a unanimous vote of the states, which was nearly impossible
48
New cards
"When the Articles of Confederation were drafted, Americans had little experience of what a national government could do for them and bitter experience of what an arbitrary government could do to them. In creating a central government they were therefore more concerned with keeping it under control than with giving it the means to do its job."
-Edmund S. Morgan, The Birth of the Republic, 1763-89, 1956
Which of the following pieces of evidence would best support the author’s conclusion?
-Edmund S. Morgan, The Birth of the Republic, 1763-89, 1956
Which of the following pieces of evidence would best support the author’s conclusion?
The lack of centralized military power under the Articles of Confederation
49
New cards
"The insurgents who were assembled at Worcester in Massachusetts have disbanded. The people at Boston seem to be glad at this event and say it was the effect of fear. But the fact is that the insurgents effected their object . . .
"The commotions of Massachusetts have wrought prodigious changes in the minds of men in that State [with regard to] the Powers of Government. Everybody says they must be strengthened and that unless this shall be effected there is no Security for liberty or Property. Such is the State of things in the east, that much trouble is to be apprehended in the course of the ensuing year."
-Henry Knox, letter to his former commander George Washington, 1786
Based on the text, which of the following statements would the author most likely agree with?
"The commotions of Massachusetts have wrought prodigious changes in the minds of men in that State [with regard to] the Powers of Government. Everybody says they must be strengthened and that unless this shall be effected there is no Security for liberty or Property. Such is the State of things in the east, that much trouble is to be apprehended in the course of the ensuing year."
-Henry Knox, letter to his former commander George Washington, 1786
Based on the text, which of the following statements would the author most likely agree with?
The lack of centralized military power under the Articles of Confederation poses a serious threat to the stability of the United States
50
New cards
Shays’s Rebellion demonstrated what weaknesses of the national government under the Articles of Confederation?
It could not raise money to pay a militia to put down the rebellion
51
New cards
What was a strength of the Articles of Confederation that the Constitution retained?
The federal government could negotiate treaties with other countries
52
New cards
“When land-forces are raised by any state for the common defence, all officers of or under the rank of colonel, shall be appointed by the legislature of each state respectively, by whom such forces shall be raised, or in such manner as such state shall direct, and all vacancies shall be filled up by the State which first made the appointment.”
-Articles of Confederation, Article VII, 1777
What is a consequence of the policy described in the passage above?
-Articles of Confederation, Article VII, 1777
What is a consequence of the policy described in the passage above?
The federal government did not have the power to create a centralized military during peace times
53
New cards
"Our Debts being unfunded and unprovided for, the Interest cannot be paid. Those therefore who trusted us in the Hour of Distress are defrauded. To expect that under such Circumstances others will confide in the Government would be Folly, and to expect that Foreigners will Trust a Government which has no Credit with its own Citizens must be madness . . .
"The United States have call’d for eight Million of Dollars early in November last, of which the first quarterly Payment was to have been made on the first Day of April next. But I cannot find that a single State has laid the Taxes."
-Robert Morris, letter to the president of Congress, 1782
What best summarizes the author’s argument?
"The United States have call’d for eight Million of Dollars early in November last, of which the first quarterly Payment was to have been made on the first Day of April next. But I cannot find that a single State has laid the Taxes."
-Robert Morris, letter to the president of Congress, 1782
What best summarizes the author’s argument?
The taxation structure under the Articles poses a serious threat to the economic well-being of the United States
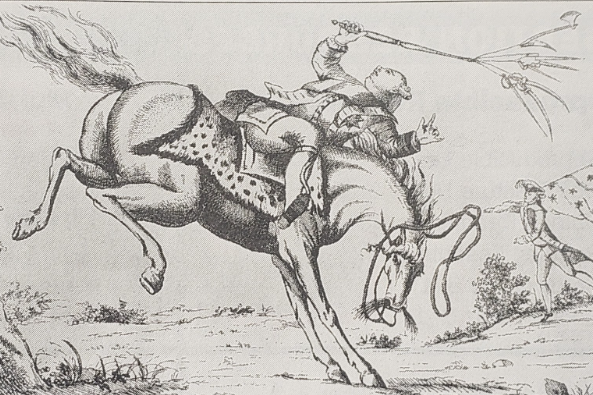
54
New cards
What is this political cartoon about?
American Revolution: The horse represents America and the person riding the horse is King George. America is separating from King George and the British Monarchy.