Properties of waves
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
What do waves transfer
Energy and information without transferring mass
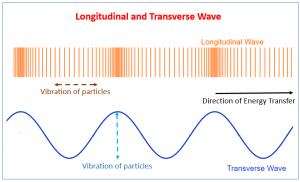
What are the differences between longitudinal and transverse waves?
Longitudinal waves vibrate parallel to the direction of travel (sound)
Transverse vibrate perpendicular to the direction of travel (light)
Longitudinal waves consist of compressions and rarefactions
Transverse consist of peaks/crests and troughs
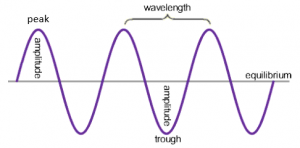
What is the definition of amplitude, wavefront, frequency, wavelength and time period?
Amplitude: The maximum displacement of particles from their equilibrium position.
Wavefront: An imaginary surface representing points of a wave that are at the same point in their cycle.
Wavelength: The distance between a particular point on one cycle of the wave and the same point on the next cycle.
Frequency: The number of waves passing a particular point per second. Is measured in Hertz (Hz).
Time Period: The time it takes for one complete wave to pass a particular point.
What is the doppler effect?
When a car is not moving and its horn sounds, the sound waves the observer receives are a series of evenly spaced wavefronts.
If a car is moving, wavefronts of the sound are no longer evenly spaced.
Ahead of the car wavefronts are compressed as the car is moving in the same direction as the wavefronts. This creates a shorter wavelength and a higher frequency to the observer.
Behind the car wavefronts are more spread out as the car is moving away from the previous wavefronts. This creates a longer wavelength and a lower frequency to the observer.
What are the qualities of reflection?
All waves can be reflected
frequency, wavelength and speed are unchanged
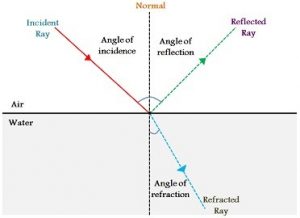
What are the qualities of refraction?
All waves can be refracted, which is when the speed of a wave changes when it enters a new medium
If a wave enters a denser medium, its speed decreases, and the wave bends towards the normal. Wavelength decreases as frequency stays the same, and velocity decreases (velocity = frequency x wavelength)
If a wave enters a less dense medium, its speed increases, and it bends away from the normal. Wavelength increases as frequency stays the same, and velocity increases.
