Thyroid
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/30
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
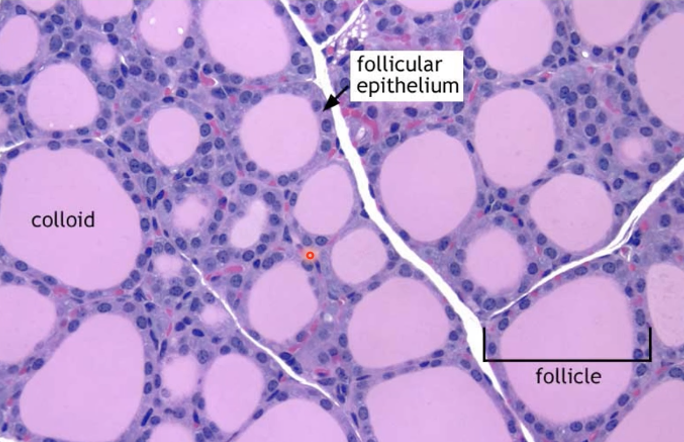
Describe follicular structure
Colloid in the centre
Follicular epithelium surrounds colloid
Some blood vessels present between follicles
Follicular epithelium surrounds colloid
Some blood vessels present between follicles
2
New cards
What is thyroid hormone derived from
tyrosine
incorporates iodine
incorporates iodine
3
New cards
Forms of thyroid hormone
Precursor
* Thyroglobulin
Thyroid hormone
* T4
* T3
* Thyroglobulin
Thyroid hormone
* T4
* T3
4
New cards
Describe synthesis of TH
1. Protein synthesis produces thyroglobulin and associated enzymes
2. Above transported and stored in colloid
3. Iodide co-transported into cell and colloid via transporter making it available to be added to thyroglobulin – makes T3 and T4
4. Thyroglobulin taken back into cell when needed
5. Enzymes separate T3 and T4 enzymes from backbone
6. T3 and T4 available for circulation
5
New cards
Which makes up most proportion - T3 or T4
T3 - 10%, T4 - 90%
T3 is more active and so most effects are due to it
T3 is more active and so most effects are due to it
6
New cards
Half life of T3 vs T4
T3 - 1 day
T4 - 6 days
T4 - 6 days
7
New cards
Describe the hormonal pathways which regulate secretion of TH
1. Neuroendocrine cells secrete TRH into hypophyseal portal system
2. TRH goes into anterior lobe of pituitary gland where it binds to thyrotrophs where it stimulates TSH
3. TSH released into circulation and travels to thyroid gland
4. TSH causes synthesis and release of T3 and T4
8
New cards
Effect of sympathetics on TH release
activates it
9
New cards
How does TSH work?
1. Secreted from thyroid tropes within the anterior pituitary lobe
2. Bind to receptor on thyroid follicular epithelial cells
3. Stimulates functions of thyroid glands
1. Inc iodine uptake
2. Inc protein synthesis
3. Inc re-uptake of colloidal thyroglobulin
4. Increases size, number and secretory activity of thyroid cell
5. Increases synthesis and release of T3 and T4
10
New cards
3 physiological actions of thyroid hormone
* Growth
* Cardiovascular
* Basal metabolic rate
* Cardiovascular
* Basal metabolic rate
11
New cards
How does thyroid hormone contribute to growth?
* Thyroid hormone essential for normal growth in childhood
* Critical for CNS development
* Critical for CNS development
12
New cards
Effects of lacking T3/4 in late foetal/early neonatal period
Irreversible CNS development
* Reduction in neurone number
* Reduction in myelination
* Reduction in neurone number
* Reduction in myelination
13
New cards
How does thyroid hormone contribute to cardiovascular?
* Increased manufacture and incorporation of B1 adrenergic receptors
* Increased responsiveness
* Sets heart sensitivity to Ad/Nad
* Long term sensitivity of cardiac cells is regulated by plasma levels of thyroid hormone
* Increased responsiveness
* Sets heart sensitivity to Ad/Nad
* Long term sensitivity of cardiac cells is regulated by plasma levels of thyroid hormone
14
New cards
Define basal metabolic rate
Rate at which body uses energy to maintain vital functions whilst at rest
15
New cards
Changes in thyroid hormone can change basal metabolic rate
THis can be seen as…
This can be measured as…
THis can be seen as…
This can be measured as…
* Increased oxidative metabolism
* Increased heat production
* Increased heat production
16
New cards
Increased thyroid hormone … basal metabolic rate
increases
17
New cards
Effects of increased basal metabolic rate
* Catabolic and anabolic reactions in pathways affecting fats, carbohydrates and proteins stimulated
* Enzyme and structural proteins synthesised
* More glucose made available to meet elevated metabolic demand
* Increased lipid metabolism
* Enzyme and structural proteins synthesised
* More glucose made available to meet elevated metabolic demand
* Increased lipid metabolism
18
New cards
Action of TH on target cells
1. T3/T4 enter target cell
2. Most of T4 is converted to T3
3. T3 enters the nucleus and binds to the thyroid hormone receptor (THR)
4. Binding of THR to promoter elements activates gene transcription
19
New cards
How is T4 converted to T3
Removal of one iodine
20
New cards
What can hyperthyroidism be caused by
* Grave’s disease
* Tumours of follicular cells
* Tumours of follicular cells
21
New cards
Effects of hyperthyroidism
* Thyroid gland increases in size
* Hyperplasia
* Increased rate of TH secretion
* Increased metabolic rate
* Hyperplasia
* Increased rate of TH secretion
* Increased metabolic rate
22
New cards
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
* Weight loss
* Cardiovascular – inc. force and rate of contraction
* CNS – nervousness, irritability, sleeplessness
* Other – fatigue, heat intolerance, sweating, moist skin
* Cardiovascular – inc. force and rate of contraction
* CNS – nervousness, irritability, sleeplessness
* Other – fatigue, heat intolerance, sweating, moist skin
23
New cards
Cause of Grave’s Disease
Caused by thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin
* Over-stimulation of the thyroid
* Increased T4/T3 synthesis and secretion
* Immunoglobulins also stimulate connective tissue → exophthalmos (bug eye)
* Over-stimulation of the thyroid
* Increased T4/T3 synthesis and secretion
* Immunoglobulins also stimulate connective tissue → exophthalmos (bug eye)
24
New cards
Treatment of Grave’s disease
* Anti-thyroid drugs
* Thyroidectomy
* Radioactive iodine
* Thyroidectomy
* Radioactive iodine
25
New cards
What causes the thyroid gland enlargement?
* Thyroid gland stimulated
* Continued stimulation of T3/T4 formation
* Gland enlarges
* Continued stimulation of T3/T4 formation
* Gland enlarges
26
New cards
Causes of hypothyroidism
* Iodine deficiency – can’t synthesis T3/T4
* Hashimoto’s disease – autoimmune destruction of thyroid cells
* Hashimoto’s disease – autoimmune destruction of thyroid cells
27
New cards
Effect of hypothyroidism
* Low metabolic rate
28
New cards
How does hypothyroidism actually manifest?
Low T4/T3 secretion
29
New cards
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
* Body weight – increase body weight, decreased appetite
* Cardiovascular – decreased cardiac output, decreased force of contraction, decreased rate of contraction
* CNS – mental sluggishness, fatigue, cognitive dysfunction in children
* Other – myxoedema, cold intolerance, goiter
* Cardiovascular – decreased cardiac output, decreased force of contraction, decreased rate of contraction
* CNS – mental sluggishness, fatigue, cognitive dysfunction in children
* Other – myxoedema, cold intolerance, goiter
30
New cards
Iodine deficiency and thyroid gland enlargement
* No T3/4 formation
* No feedback control of TSH
* High TSH
* Continued stimulation of thyroglobulin by TSH
* Gland enlarges up to 500g
* No feedback control of TSH
* High TSH
* Continued stimulation of thyroglobulin by TSH
* Gland enlarges up to 500g
31
New cards
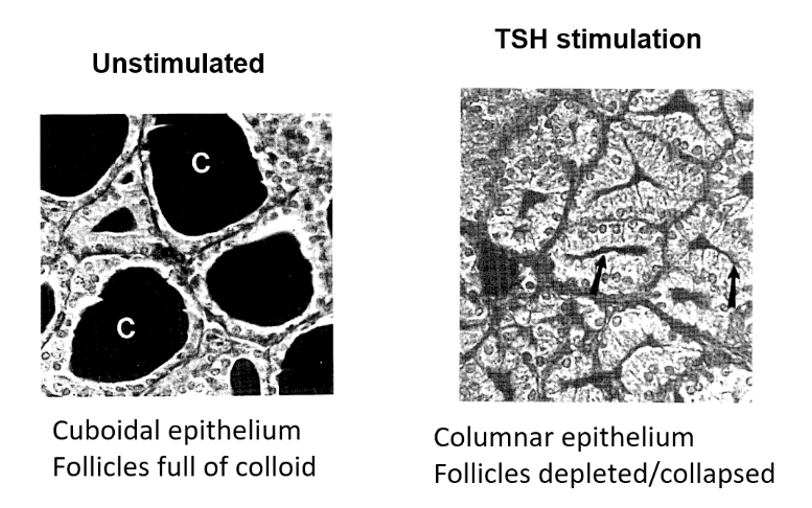
Thyroid gland morphology - depending on TSH stimulation
When TSH stimulated
* Hypertrophy of follicle cells due to increased uptake of colloid for T3/T4 production
* Folloicles depleted and collapsed
* Hypertrophy of follicle cells due to increased uptake of colloid for T3/T4 production
* Folloicles depleted and collapsed