Anatomy of the Brain Wish list
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Parts of the brain
Cerebrum, cerebral hemisphere, corpus callous, lateral ventricles, choroid plexus, gyri, sulci, longitudinal fissure, frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain and handles conscious thoughts and actions. Different areas also have different responsibilities like language, behavior, sensory processing and more. Telencephalon
cerebral hemisphere
each of the two parts of the cerebrum in the brain of a vertebrate
corpus callosum
a large band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain. Primarily function is to facilitate communication between the two hemispheres, enabling them to work together and integrate information for various cognitive functions. Largest white matter structure in the brain
lateral ventricles
a pair of large, c-shaped cavities located within each cerebral hemisphere, forming the largest part of the brain’s ventricular system. filled with cerebrospinal fluid and responsible for CSF production & circulation.
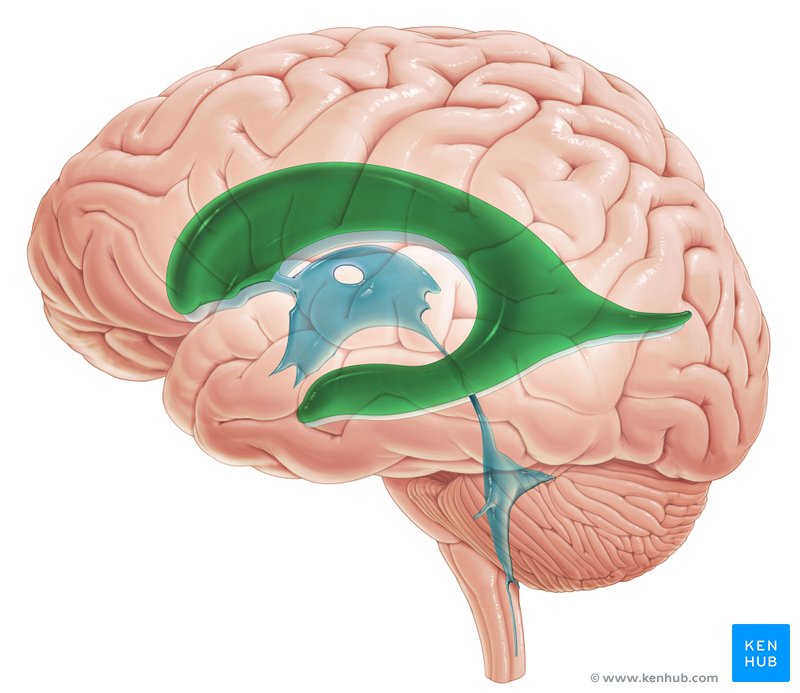
choroid plexus
a secretory tissue responsible for producing cerebrospinal fluid in the vertebrate brain.
gyri
a ridge or fold between two clefts on the cerebral surface in the brain
sulci
a groove or furrow, especially one on the surface of the brain
longitudinal fissure
a deep groove that divides the brain into the right and left cerebral hemispheres.
Transverse fissure
a deep groove in the brain that separates the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum. runs horizontally from side to side and contains the tentorium cerebella, a fold of dura mater that separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum.
frontal lobe
the largest of the brain’s 4 main lobes, located in the front of the cerebrum, behind the forehead. It plays a crucial role in various cognitive and behavioral functions, including executive functions like planning, organizing, and problem solving. It also controls motor movements, expressive language, personality and emotional regulation.
parietal lobe
a region of the brain primarily responsible for processing sensory information, particularly from the body, like touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception. On ‘top’ of brain
occipital lobe
part of the brain located at the back of the head. responsible for processing visual information and plays a crucial role in our sense of sight.
temporal lobe
located on the sides of the head near the temples, plays a role in auditory processing, language comprehension, memory formation, and emotional regulation.
parts of the Epithalamus
pineal gland, third ventricle
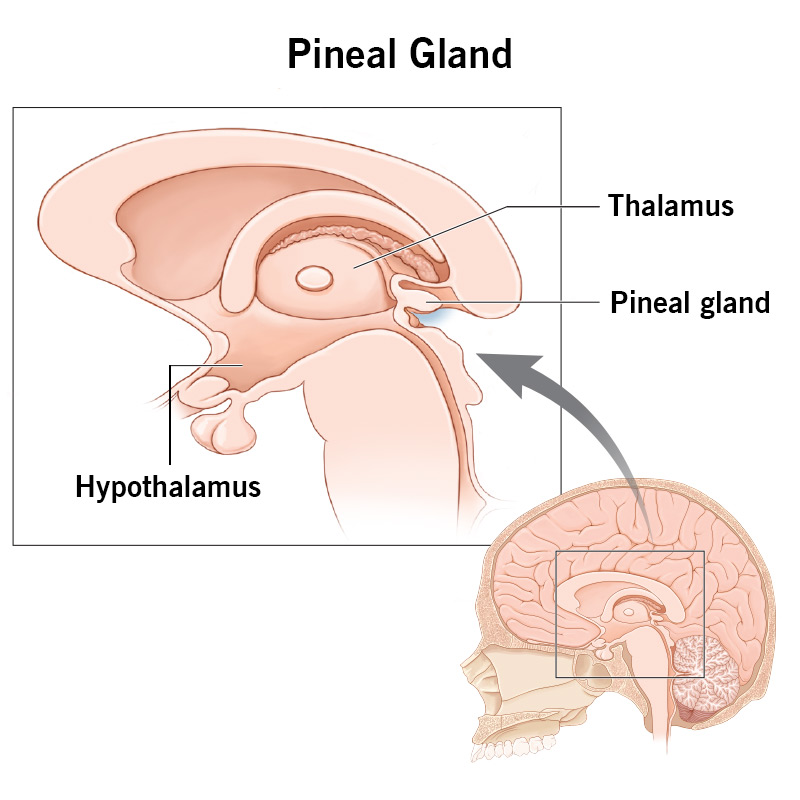
pineal gland
a tiny endocrine gland in the middle of your brain that helps regulate your body’s circadian rhythm by secreting the hormone melatonin
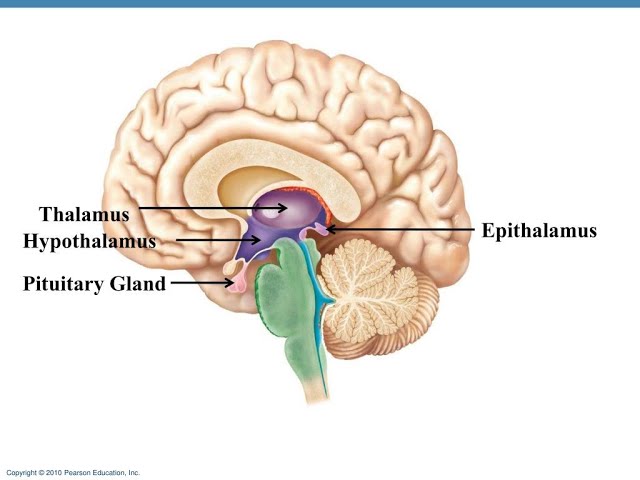
Epithalamus
art of the dorsal forebrain including the pineal gland and a region in the roof of the third ventricle of the brain
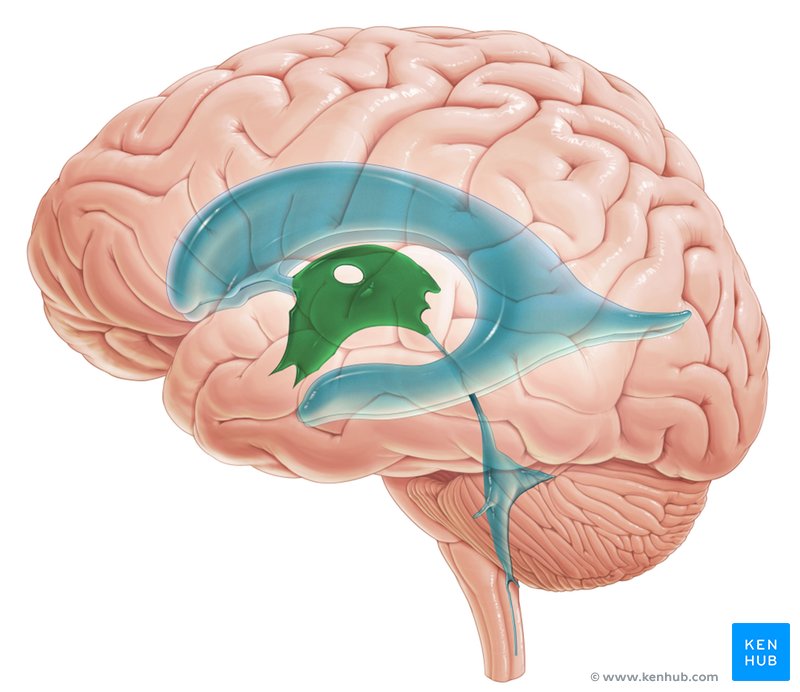
third ventricle
the central cavity of the brain, lying between the thalamus and hypothalamus of the 2 cerebral hemispheres
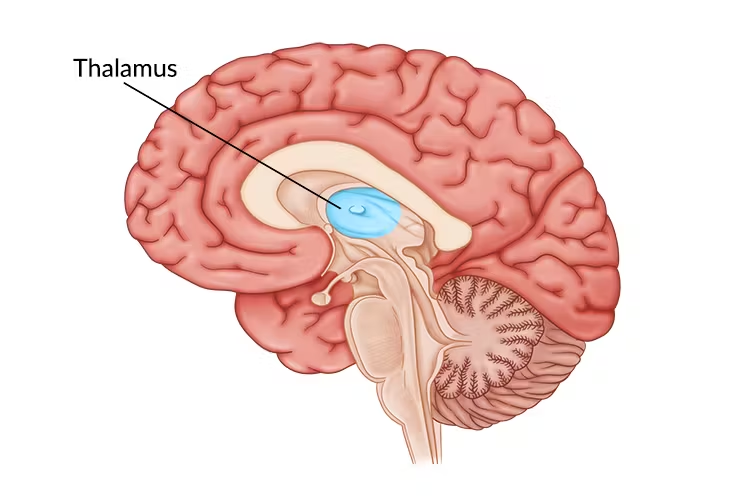
Thalamus
Dinecephalon, central brain structure that acts as a relay center for sensory and emotional information between the brain and the rest of the body. receives sensory input, processes it and sends it on to other brain areas for further processing. Plays a role in motor control, consciousness, sleep and memory.
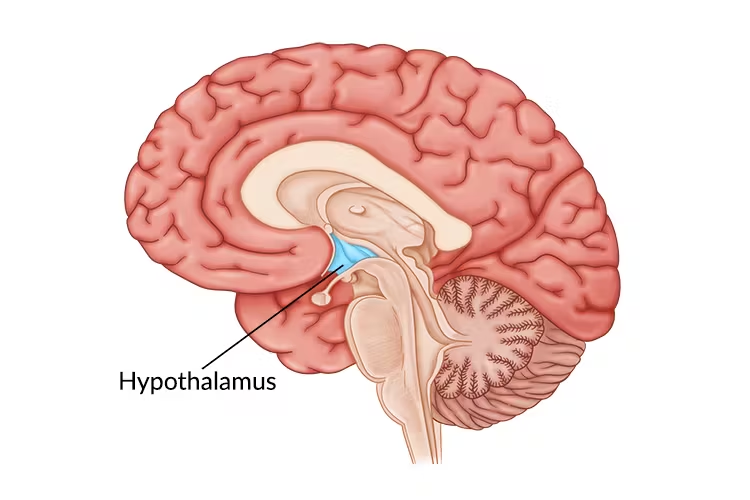
hypothalamus
a small but vital region of the brain located below the thalamus, acting as a central command center for regulating homeostasis, hormone release and various bodily functions like body temperature, hunger, and thirst. connects the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland
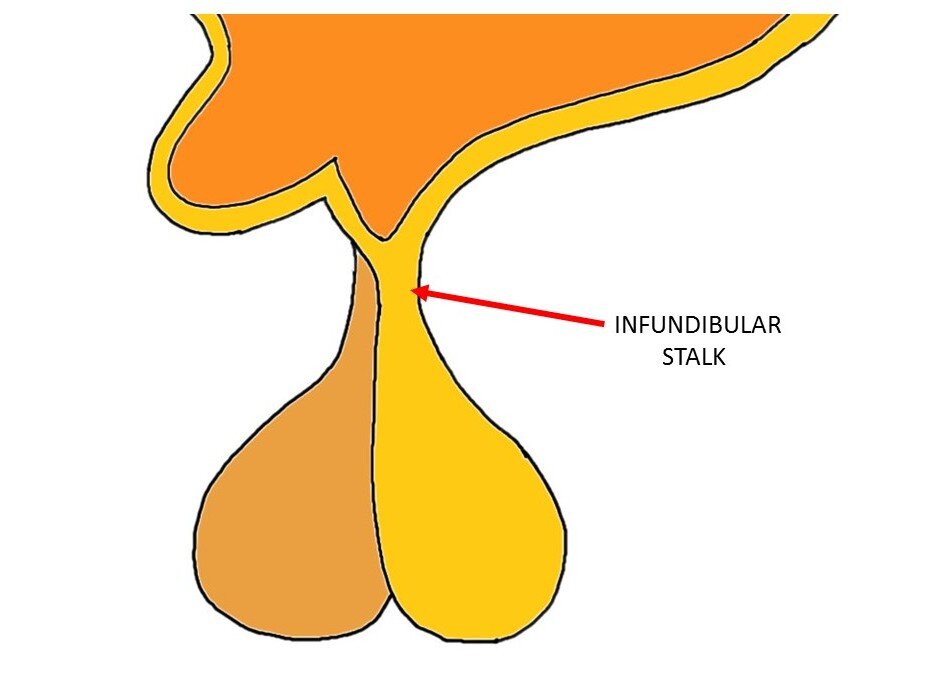
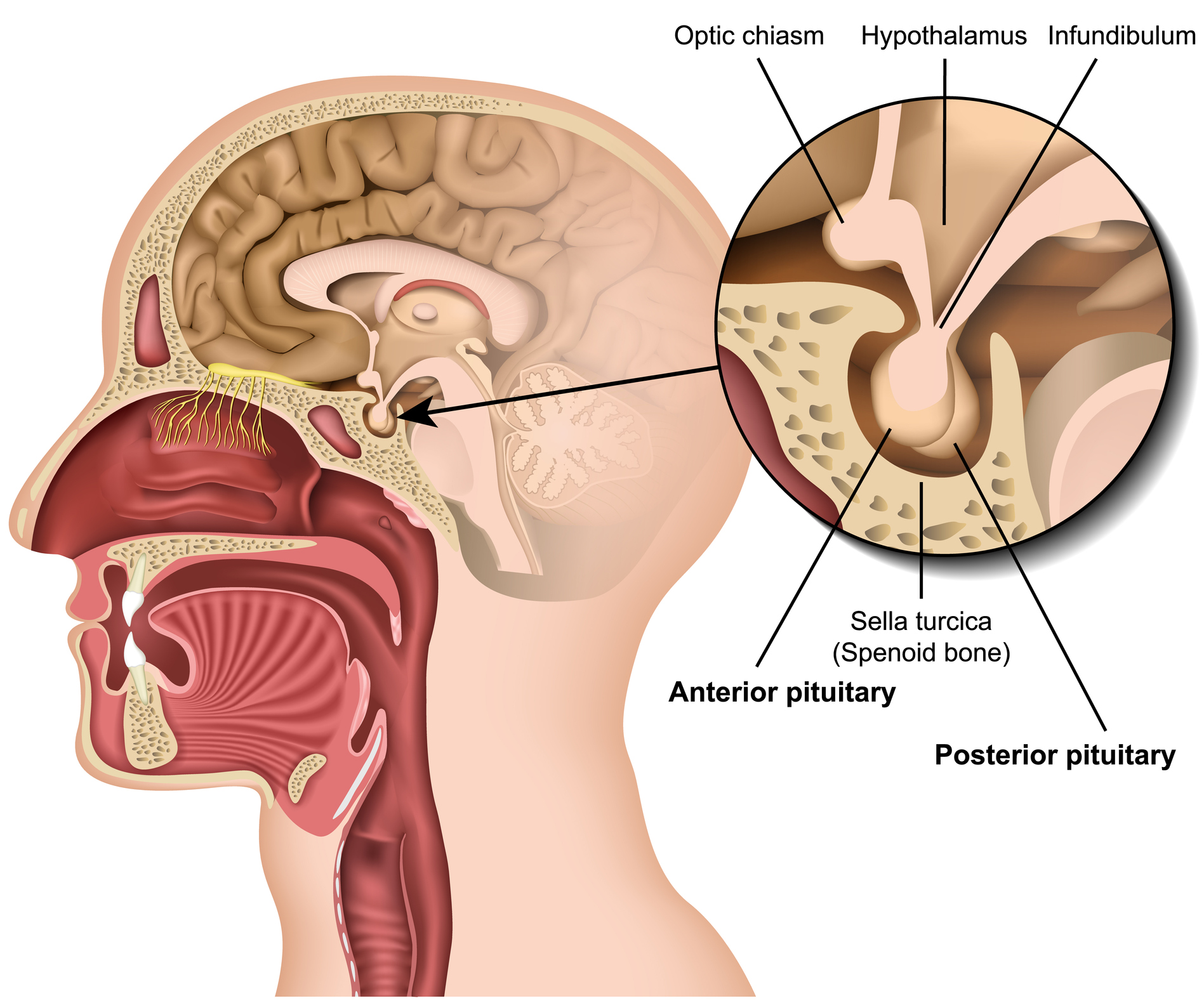
infundibulum
a funnel shaped cavity or structure — the hollow stalk that connects the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary gland
pituitary gland
a pea-sized endocrine gland located at the base of the brain, is often called the master gland because it produces hormones that control various bodily functions
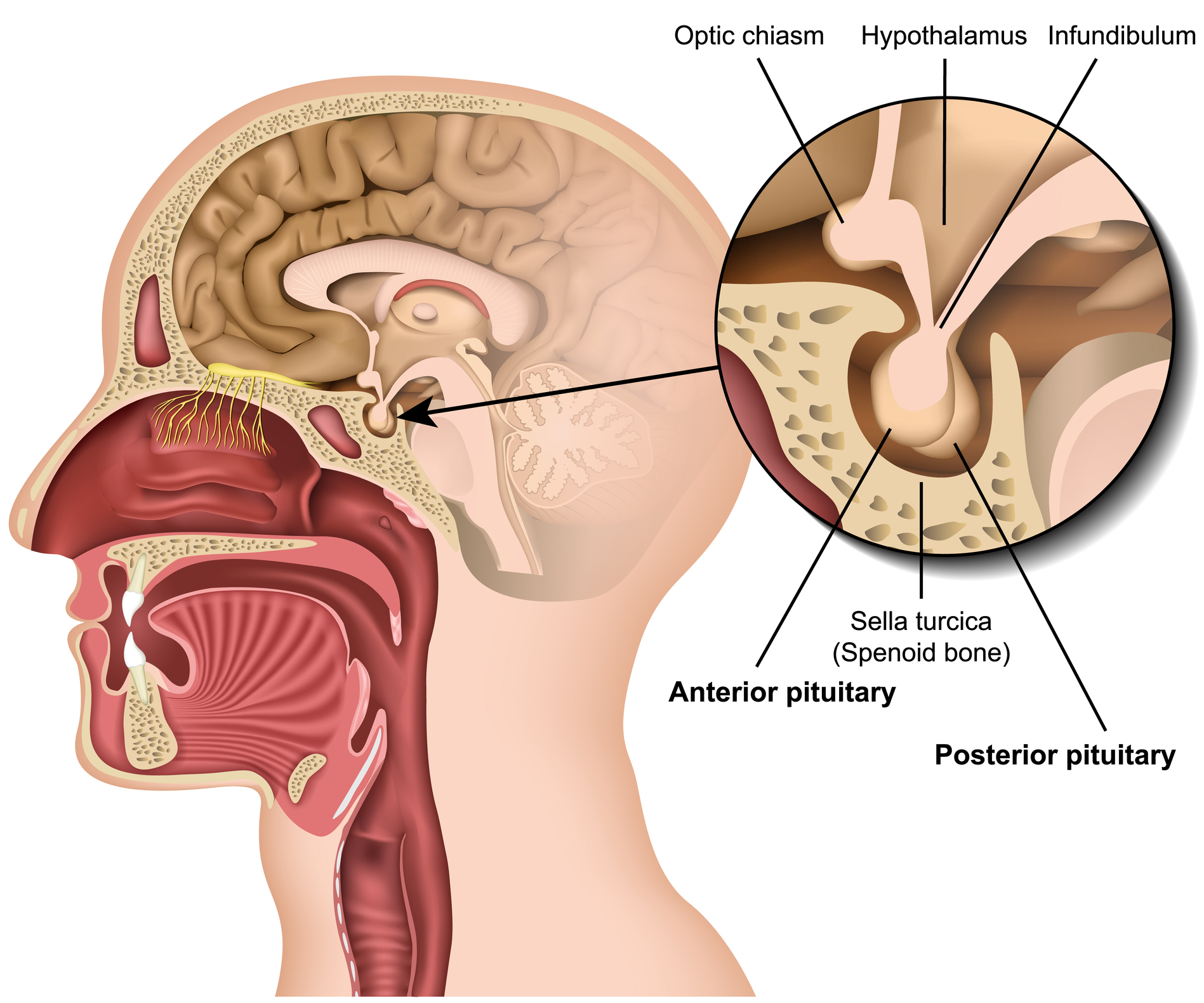
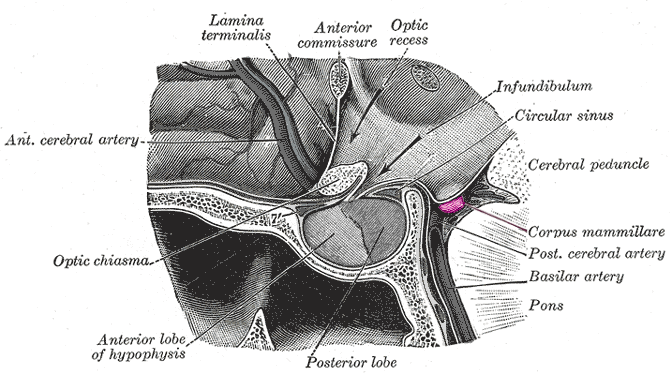
optic chiasma
a vital part of the visual pathway where the optic nerves from each eye converge and some of the fibers cross over to the opposite side of the brain
optic tract
the pathway between the optic chiasma and the brain
mammillary bodies
a pair of small, rounded structures located on the undersurface of the brain, specifically in the hypothalamus.
Midbrain
Mesencephalon, top most part of the brainstem, the connection between the brain and the spinal cord.
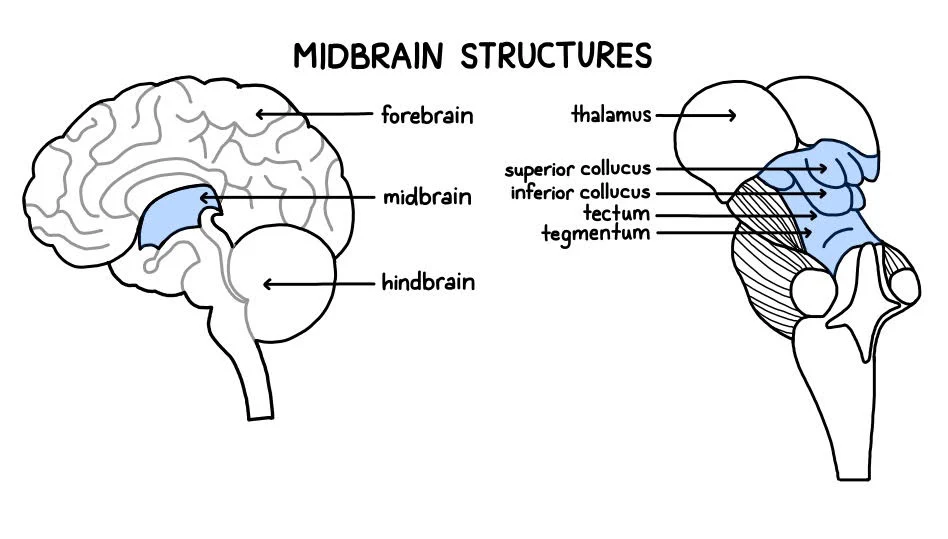
corpora quadrigemina
the four colliculi located on the dorsal surface of the midbrain, specifically on the tectum. Contains the inferior colliculi and superior colliculi
superior colliculi
a pair structure in the mid-brain crucial for integrating visual, auditory and somatosensory information to guide orienting movements of the head and eye
inferior colliculi
a key part of the auditory pathway located in the midbrain. It receives input from various brainstem nuclei and the auditory cortex, playing a crucial role in sound processing, localization and auditory reflexes. Has a superior part.
Cerebellum
contains arbor vitae & cerebral aqueduct, metencephalon, the part of the brain at the back of the skull in vertebrates. Its function is to coordinate and regulate muscular activity
arbor vitae
refers to the white matter within the cerebellum. Looks like a tree when viewed in the sagittal section.
cerebral aqueduct
a fluid filled canal that runs through the midbrain connecting the 3rd and 4th ventricles
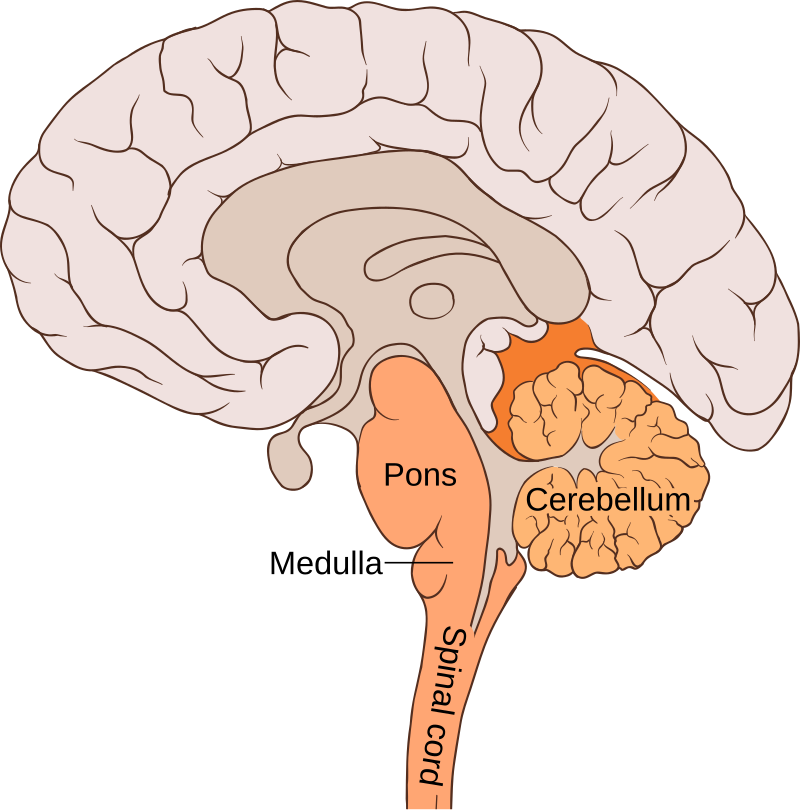
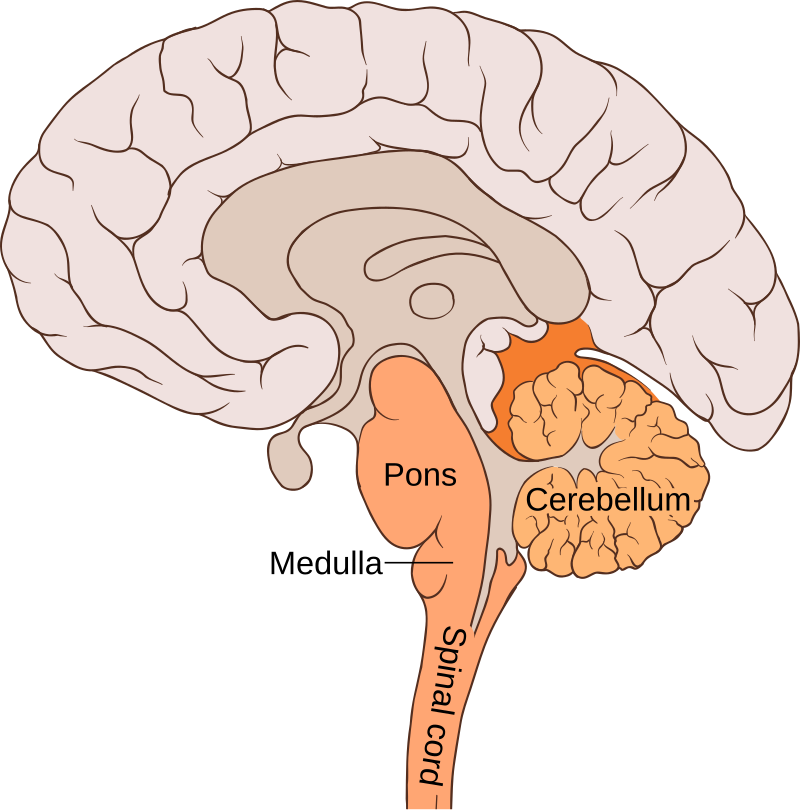
Pons
metencephalon, a crucial part of the brainstem, acting as a bridge between the cerebellum and the brain’s higher centers. located between the medulla oblongata and the midbrain.
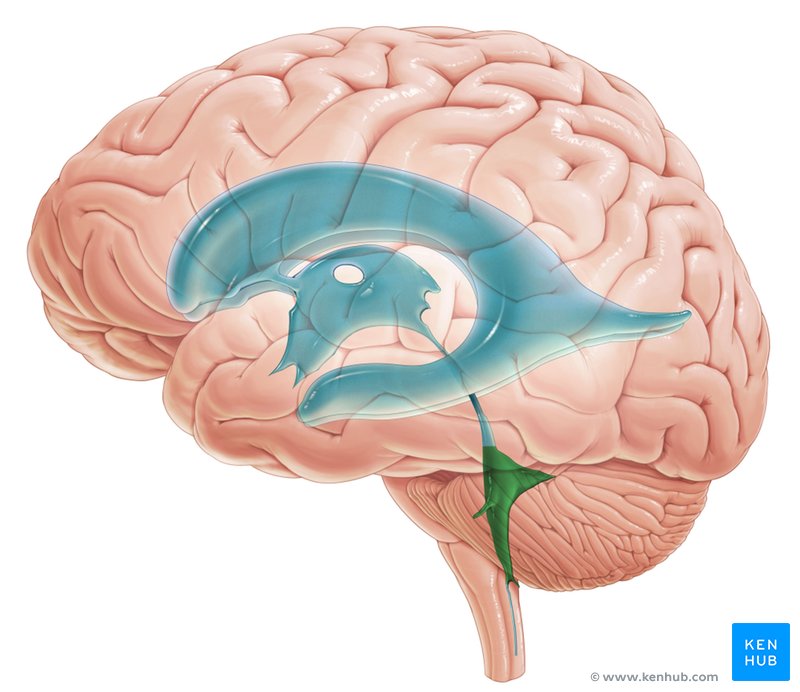
fourth ventricle
a fluid filled space within the brain, located between the brain stem and the cerebellum, shaped like a tent. Produces and circulates CSF
medulla oblongata
the continuation of the spinal cord within the skull, forming the lowest part of the brainstem and containing control centers for the heart and lungs.
Cranial Nerves
Olfactory 1, Optic 2, Occulomotor 3, Trochlear 4, Trigeminal 5, Abducens 6, Facial 7, Vestibulocochlear 8, glossopharyngeal 9, vagus 10, Accessory 11, hypoglossal 12
Olfactory I
responsible for the sense of smell, carries olfactory information from the nasal cavity to the olfactory bulb in the brain where its processed, innervates olfactory epithelium
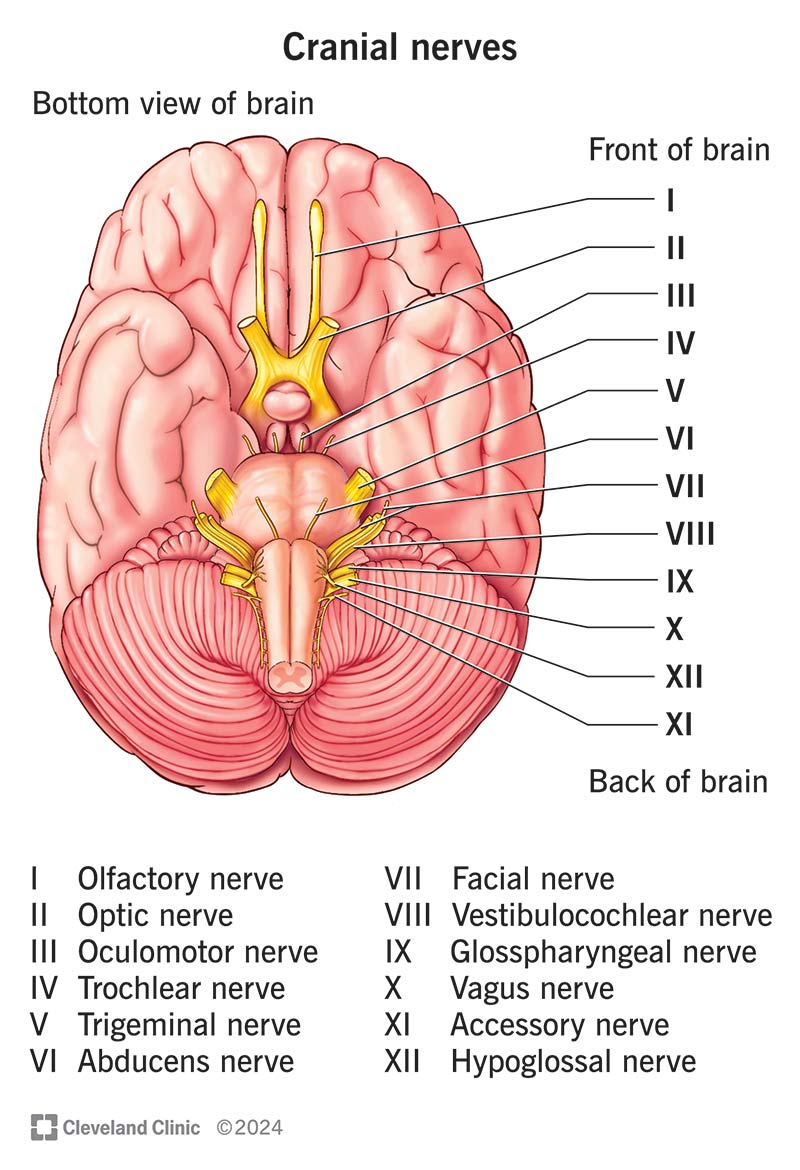
Optic II
a crucial part of vision, acting as a cable like bundle of nerve fibers that carries visual information from the eyes to the brain. Innervates the retina of the eye
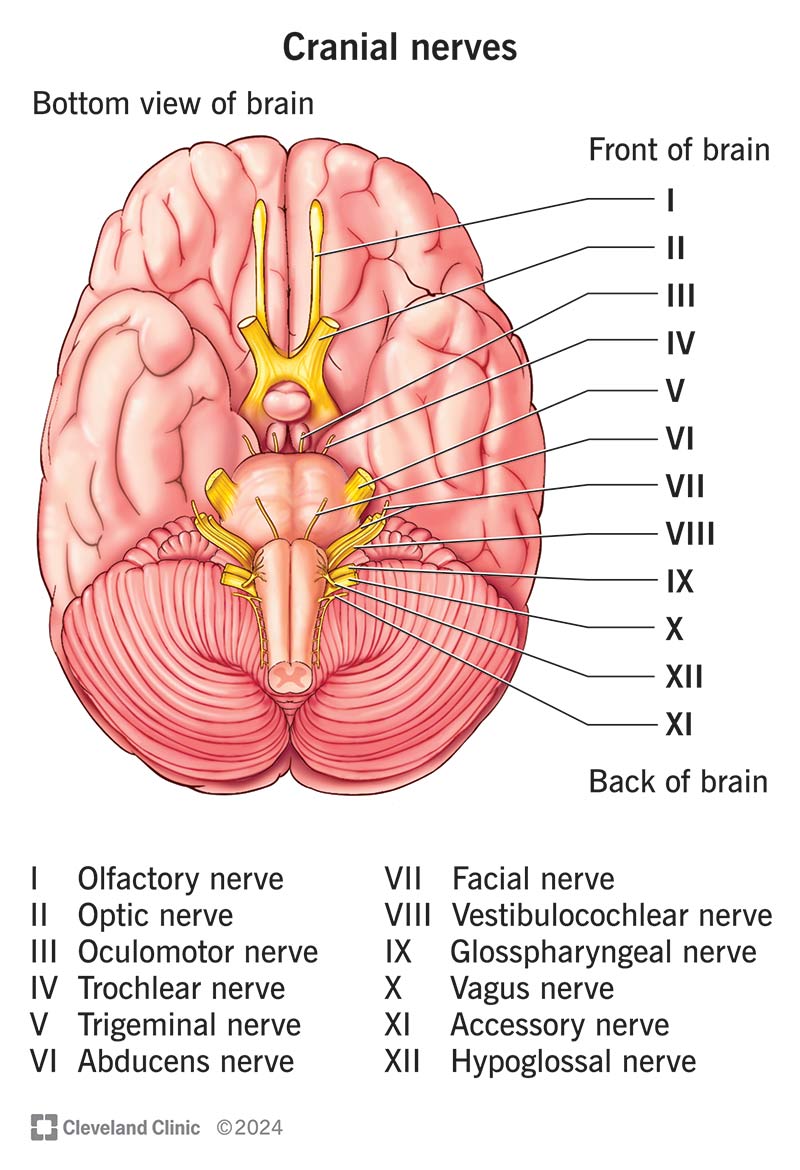
Occulomotor III
Innervates eye muscles. a major cranial nerve that controls eye movement, pupil constriction and eyelid elevation. has both motor and autonomic functions.
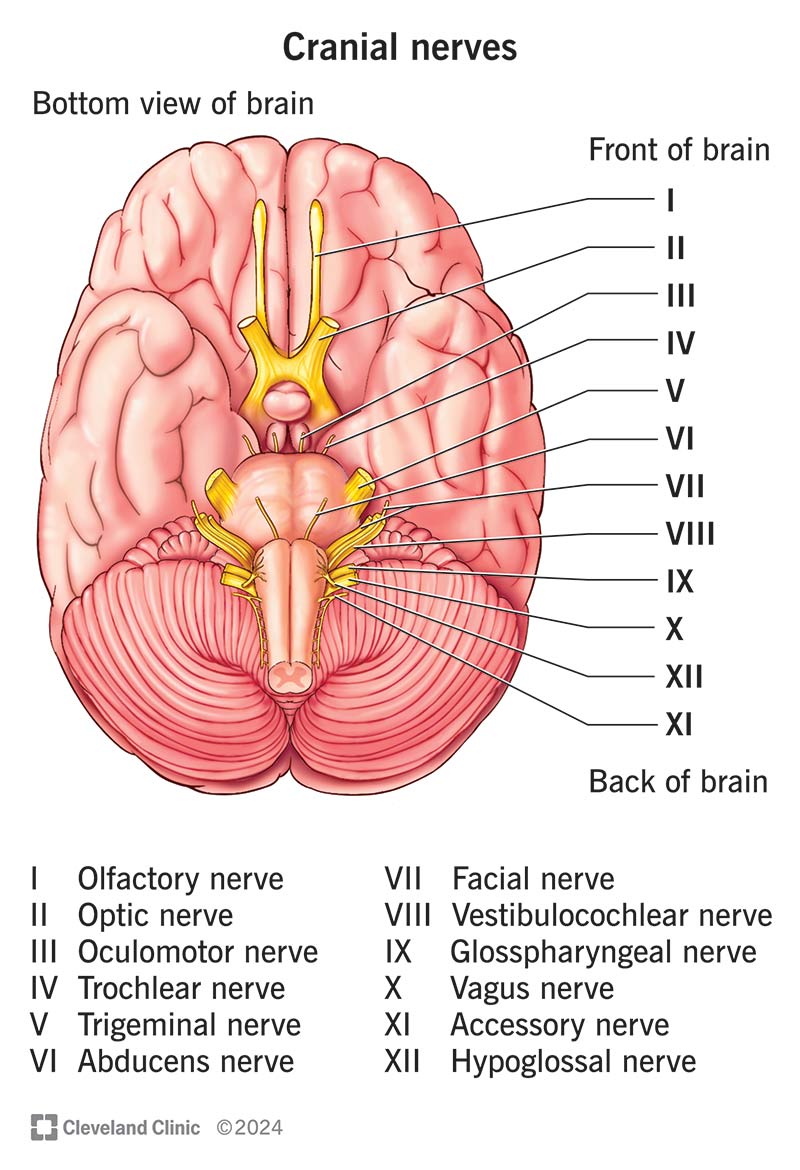
Trochlear IV
each of the 4th pair of cranial nerves, supplying the superior oblique muscle of the eyeball. Innervates eye muscle
Trigeminal V
cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor function in the muscles of mastication. innervates eye and haw area
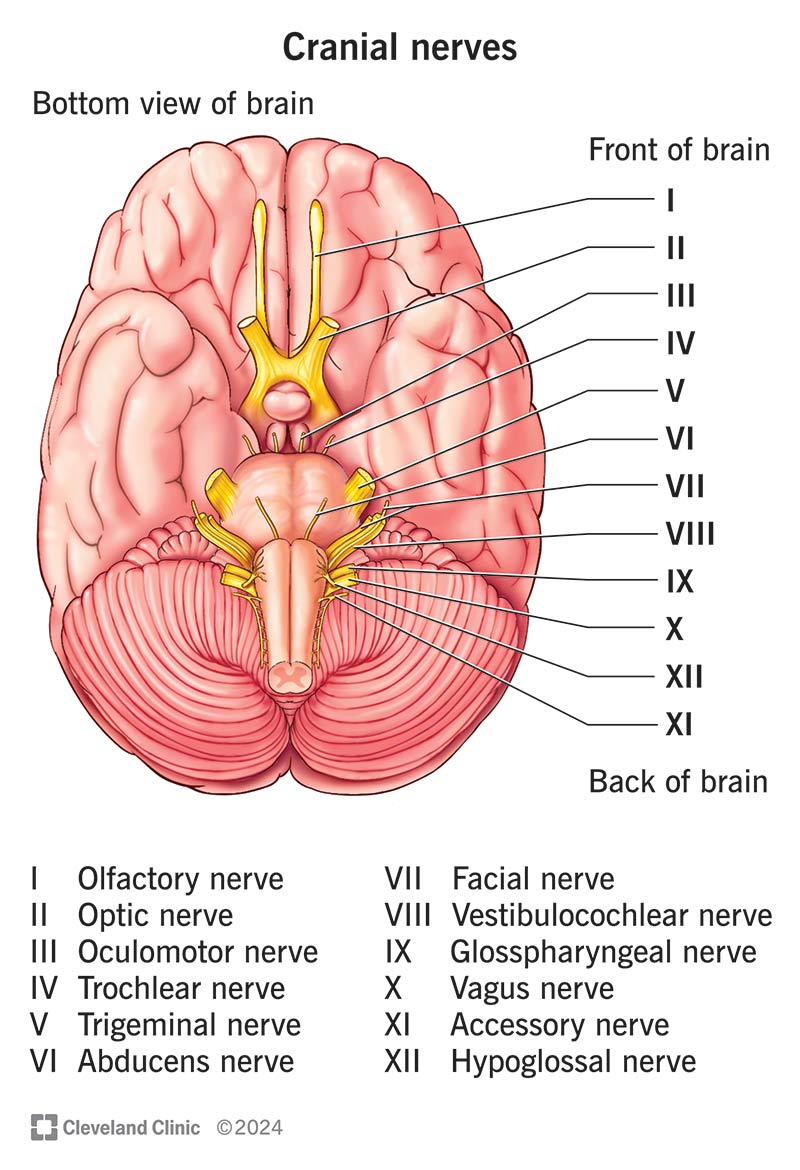
Abducens VI
Innervates eye muscle, responsible for controlling the lateral rectus muscle in the eye, which is responsible for moving the eye outward towards the side of the head. Arises from the pons in the brainstem and travels a long path to reach the lateral rectus
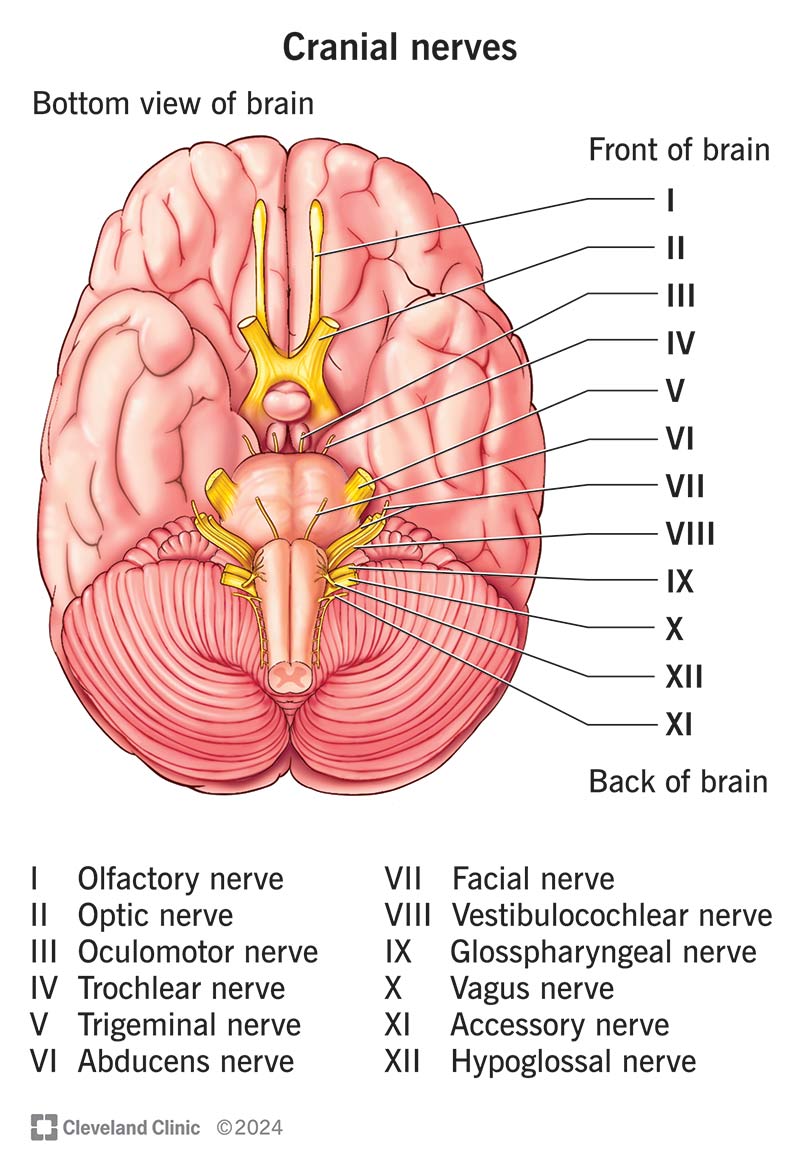
Facial VII
controls facial expressions and taste sensation from the anterior 2/3 of the lounge. It also has a role in tear production and some other functions. innervates face muscles
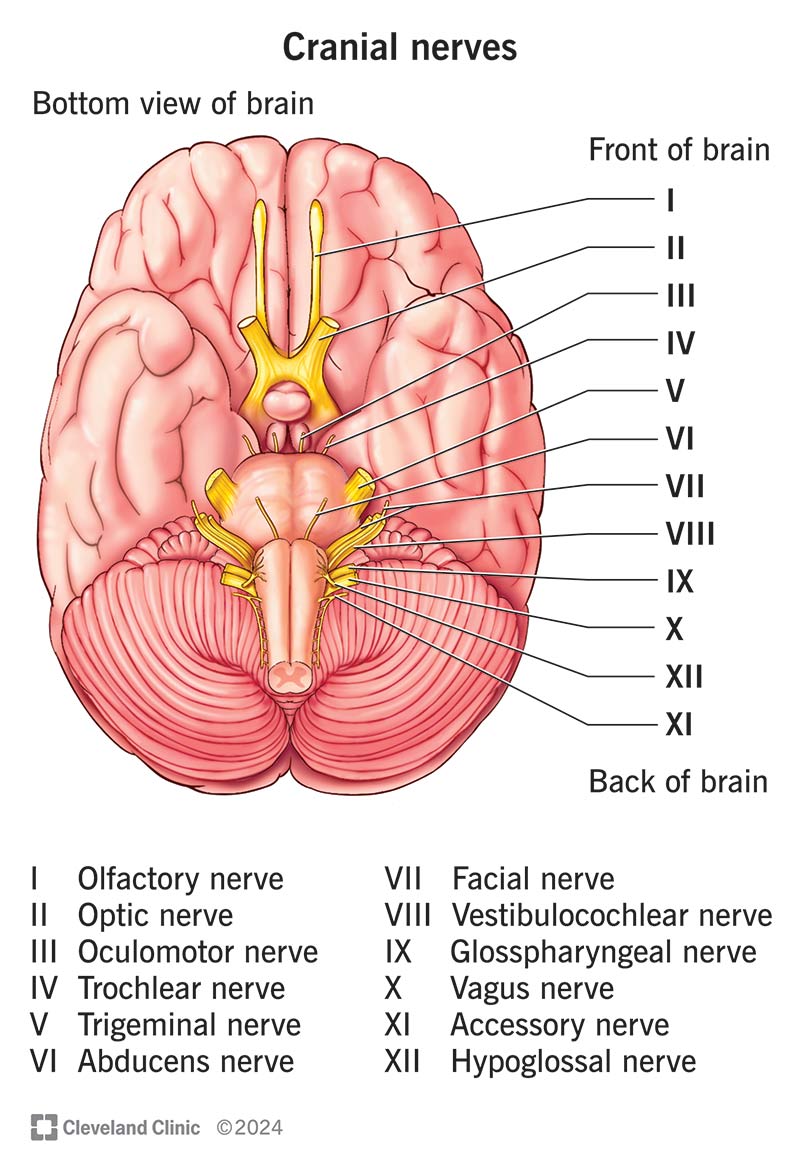
Vestibulocochlear VIII
Innervates inner ear, responsible for transmitting sensory information from the inner ear to the brain, specifically for hearing and balance. Purely a sensory nerve
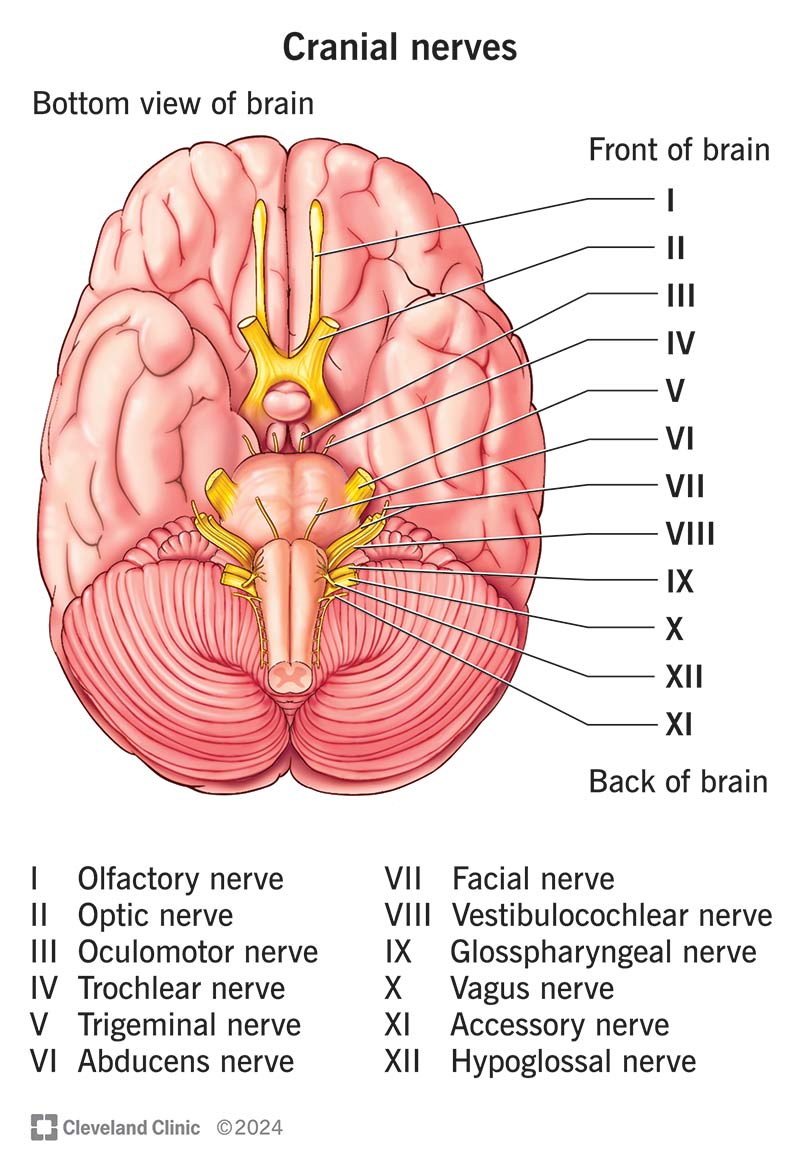
glossopharyngeal IX
a mixed nerve that carries both sensory and motor information - involved in functions like taste sensation, swallowing, and controlling the salivary glands. innervates lounge and pharynx
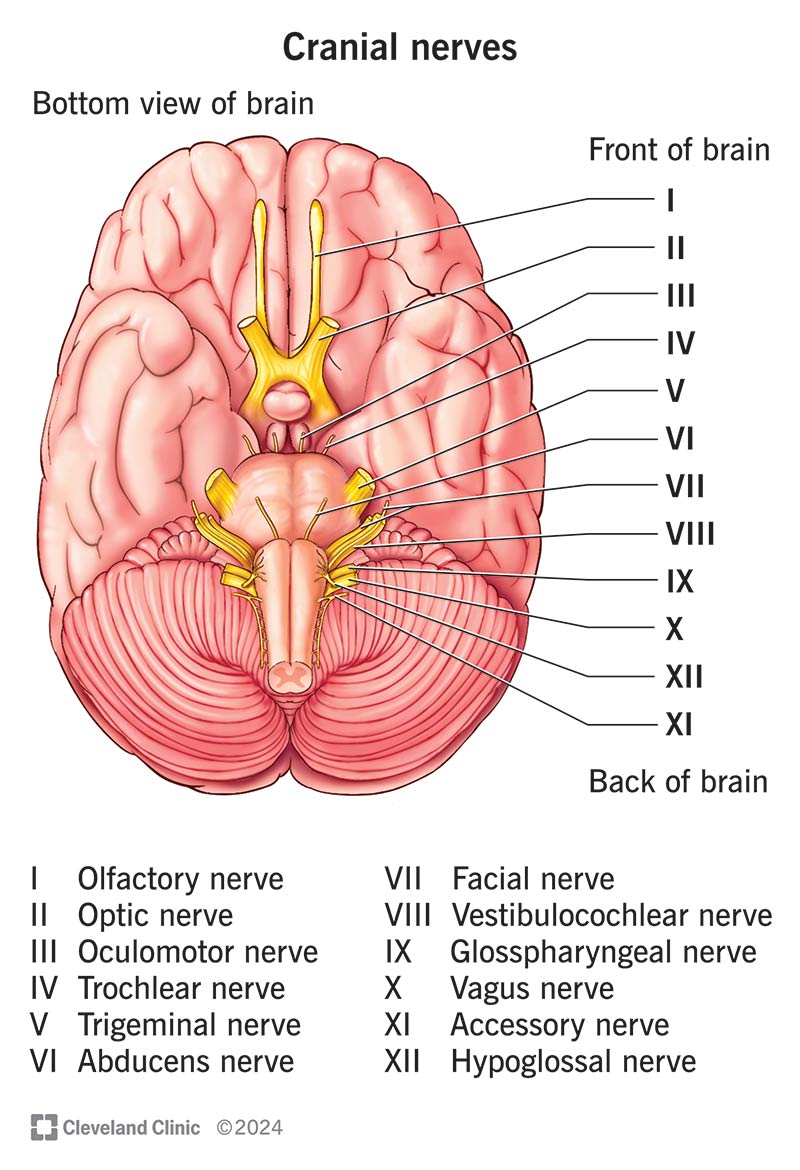
Vagus X
Innervates visceral organs. supplies the heart, lungs, upper digestive tract and other organs of the chest abdomen.
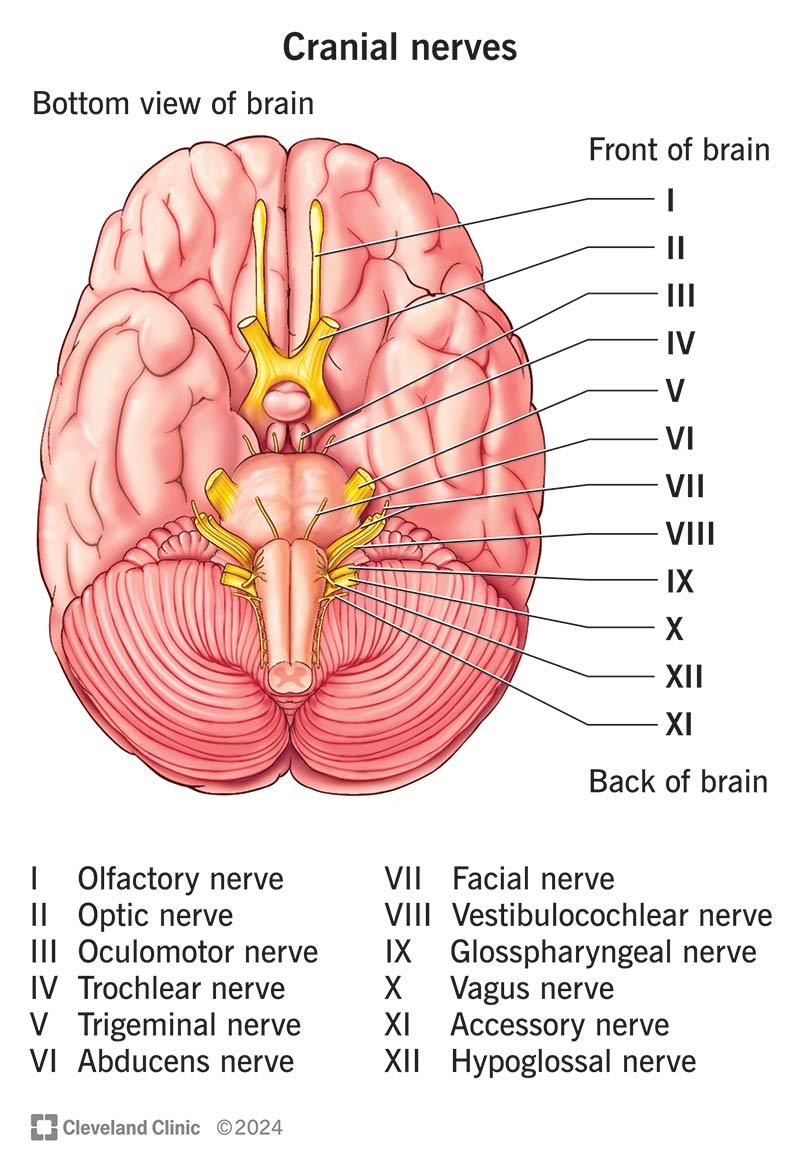
Accessory XI
a motor nerve primarily responsible for innervating the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, crucial for head and shoulder movement. Contributes to motor function of the larynx and other throat structures. Innervates pharynx and neck muscles
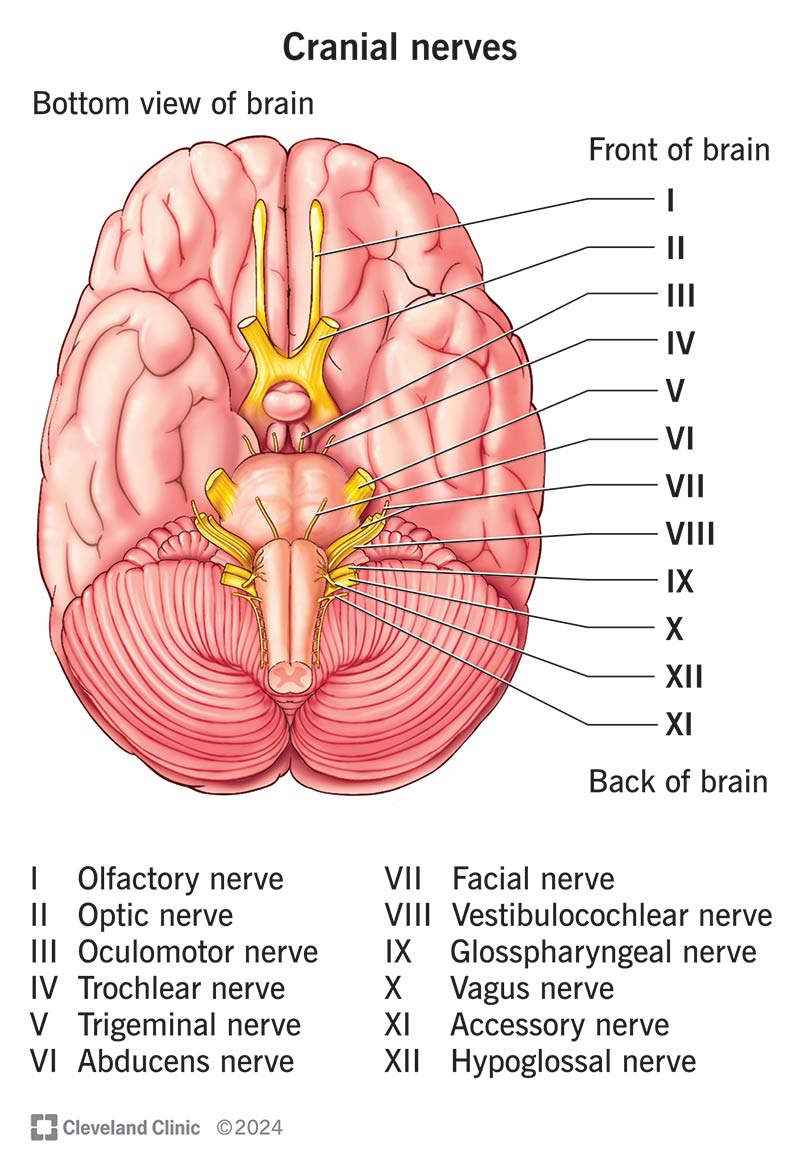
Hypoglossal XII
Innervates tongue muscles. controls the movement of the tongue. A motor nerve, meaning it carries signals from the brain to the tongue muscles.