Manipulating genomes
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Who was dna sequencing Discovered by ?
Fred Sanger
What is dna sequencing ?
to identify nucleotide sequences within a larger piece of DNA
What did Sanger use ?
4 seperate dishes:
dna polymerase
single stranded DNA
Primer
Modified DNA nucleotides
What is the difference between normal and modified nucleotides ?
Normal have a hydroxyl group on the third carbon which acts as a hook for the next nucleotide to join onto, the modified don’t have this so chain is terminated
What is a primer ?
Short single stranded length of DNA that binds to template DNA as a starter in a large piece of DNA.
Describe the shortest length DNA sequence creation
The primer binds to the single stranded DNA-template at the 5” end
Starting from the primer, DNA polymerase joins nucleotides that have paired up by complementary base pairing by forming phosphodiester bonds
The first nucleotide that was added was modified so the chain ends there
describe the process with a normal nucleotide of DNA sequencing (chain termination)
Same as before
Same as before
The chain continues until the modified nucleotide is added to the sequence
What is electrophoresis ?
Separating DNA fragments using electric current
Describe the process of electrophoresis
Add DNA fragments to the well at the cathode end. The shorter the fragment = the further they go as are faster.
At the anode there is a laser to illuminate the dyes to identify the specific modified nucleotide and it’s attached dye
What is pyrosequencing an example of ?
A high throughput method
What ingredients are needed to pyrosequencing
Same 4 but activated nucleotides which have two extra phosphoryll groups that are released upon the nucleotide binding to sequence
Describe pyrosequencing process (enzyme)
ATP sulfurylase converts pyrophosphate into ATP in the presence of APS
then luciferase converts luciferin to oxyluciferin in the presence of ATP
then apyrase digests any un used activated nucleotides and degrades them
Describe pyrosequencing method
Mechanically cut DNA length into fragments
Degrade fragments to be ssDNA
Add primer, incubate ssdna with correct enzymes substrates and activated nucleotides
If activated nucleotide is included the extra phosphoryll groups are released upon its addition
Apyrase
What is the use of comparing genomes ?
can work out evolutionary relationships by amplifying and sequencing and find out what diseases an individual may be susceptible to, which medicines work best and what side effects they may have
Application of gene sequencing
Human genome project
Work out evolutionary relationships
Synthetic biology: making useful biological devices and systems
comparisons between species
Predict amino acid sequence : read the codons to work out the amino acids in the sequence
What is genome sequencing purpose ?
Where we can determine the DNA sequence of a genome plus : mitochondrial,chloroplast and chromosomal DNA.
It allows us to to see similarities between genes in species to see what genes are conserved and to establish evolutionary relationships between species by comparison of their genomes
What do small changes in some genes lead to ?
A large change in function, eg FOXP2 is a transcription factor that controls hundreds of genes and is essential for development of language and speed in humans but is also present in mice and chimps
What are differences in organisms caused by ?
caused by shared genes working in different ways eg the FOXP2
Changes to regulatory regions of DNA leading to increased DNA expression
What variation do humans have ?
0.1%
What is an SNP ?
Single nucleotide polymorphism which is the location in DNA where substitution occurs which can alter protein, alter gene expression and can have no effect
What are epigenetics
The study into how behaviour and environment can cause changes that affect gene function.
Looks at changes that result in the gene being switched on and off
Name 3 types of epigenetics
Methylation of certain chemical groups in DNA prevents transcription factors from binding
Histone modification where DNA is tightly wrapped around histone proteins and is unreadable so switched off but if unwrapped, it is switched on. Adding chemical groups to histones determines whether gene is wrapped or unwrapped
Non coding RNA is attached to coding RNA and with other proteins, it breaks it down. The non coding RNA is important for gene expression therefore
How do you predict an amino acid sequence ?
The genome reveals the nucleotide sequence and we compare the triplets to our known amino acid code to identify them and reveal primary structure. To do this you have to know which parts of the sequence are introns (non coding) and which are exons(coding)
What is synthetic biology ? + examples
Designing and building useful devices and systems, you redesign organisms to make a substance or have a new useful function for us
Yeast can produce rose oil as a more sustainable way for the perfume industry
We can alter food to solve dietary problems like golden rice
What is information storage ?
The idea that digital info can be coded on a single strand of synthetic DNA
Each letter has a 8 digit binary code which we translate into a block of 5 Letters (ATGC)
1g of dna = 1 million CDs worth of info
What are some other uses of synthetic biology ?
Helping to create medicines such as E. coli and yeast making anti malarial drug artemisinin which had to previously be extracted from plant at certain life cycle stage
Creating novel proteins such as one similar to haemoglobin but without the bind of carbon monoxide
What is a downside of synthetic biology ?
Has risks of ethics and bio security so we need a board of advisors and regulations in place
What is PCR
An artificial replication method where small amounts of DNA get amplified and increase exponentially doubling each time
What does PCR require ?
Primer
DNA polymerase
Taq polymerase ?
DNA nucleotides
DNA sample
State the steps of PCR
Initially add sample to all the contents plus magnesium ions
Heat to 94-96C to break hydrogen bonds in sample, making two separate DNA strands however this is bad for DNA polymerase as it needs 35C !!
So cool it to 68 degrees so primer can anneal at the 5 prime end
We use taq polymerase instead from thermophilus aquaticus as it is thermophilic and can work in hotter conditions
We increase the temperature to 72C to suit the Taq polymerase and it forms phosphodiester bonds, creating a new complementary strand
This is a cyclic process so repeats
Name applications of PCR
tissue typing- can match recipient and donor tissues before a transplant to reduce risk of rejection
For forensic science
For research: take extinct animal DNA eg from a bone and use to assess evolutionary links and relationships
To identify viral infections: such as Covid as small amounts of viral DNA can be detected
Epidemiology- to study the spread and variants of pathogens
Oncology- to study genes that are linked to cancers
Mutations- to use in a pre-implantation genetic screening for IVF to check for certain genetic conditions
What does electrophoresis require
Agarose gel
Buffer solution
Tank with oppositely charged electrodes
Power supply
Why is DNA attracted to the anode
Due to the negative charge from all the phosphates in the structure
Describe the method of electrophoresis
restriction enzymes cut DNA at recognition sites at 35-40C for one hour
Make agarose gel and pour into the tank with a comb at the cathode end to make wells + set
Pour buffer solution over the gel and remove comb
Add loading dye to digested DNA
Use a pipette to add DNA to wells (hovering above)
Connect electrodes to the power supply and leave to run for 6-8h on low or 2 on high voltage
Disconnect power and pour buffer away. Add dye to gel
What is SDS
A charged detergent that nullifies any surface charges on proteins to they can be separated based on molecular mass. It forms them all into a rod like shape so different shapes don’t affect the separation.
used to diagnose sickle cell anaemia
What is a DNA probe
A short single stranded DNA strand that is complementary to DNA in DNA sample
They can be labelled with flourescent dye to be seen by UV or radioactive markers in photographic film
They locate certain genomes, identify same genes for a genome study and can identify certain alleles
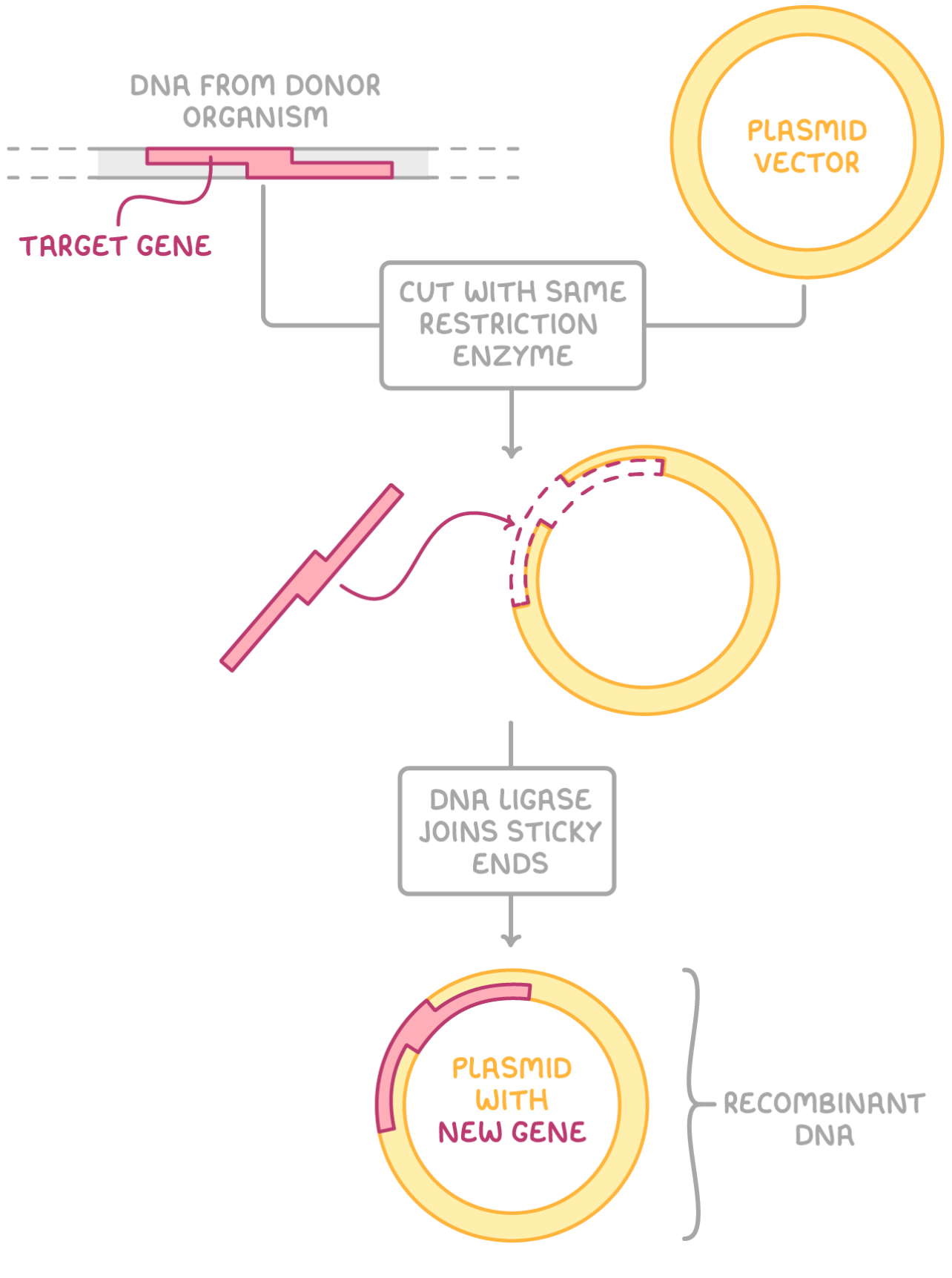
What is genetic engineering ?
Manipulation of DNA sequences and genetic material in an organism to modify their characteristics often involving gene transfer
Overview : obtain required gene
Insert copy of gene into vector
Vector used to insert gene into a host cell
Recipient expresses novel gene
Describe the first stage of genetic engineering
Method A : obtain MRNA via using reverse transcriptase to convert it to cDNA. Add primer and DNA polymerase to make it double stranded
Method B: DNA probe locates gene and cuts out using restriction enzymes
Method C : use restriction endonucleases like ecoR1 to recognise the specific restriction site on the genome (palindromic) making cuts at these points to seperate that fragment from the rest of the DNA and is staggered cut and leaves sticky ends with exposed bases
Desc 2 state of GE
Extract plasmid from bacteria or virus
Cut plasmid with same restriction endonucleases so they have complementary stick ends
DNA from plasmid and dna obtained from gene anneal using polymerase and ligase
Dec stage 3 GE
Vector carrying the gene into the recipient cell
Method A : heat shock so alternate periods of cold 0C and hot 42C in presence of calcium ions.
Ca2+ surround negative charged phospholipids and parts of DNA so make bacterial cell membrane and forging DNA less repulsion
Method B : electroporation so high voltage applied to cell to disrupt membrane and allow transfection by plasmid
Use of agrobacterium tumefaciens
Recombinant plasmid inserted into bacteria ^ this usually infects plant cells so naturally inserts its genome into the host
Some bacteria don’t take it up but those that do are transformed bacteria
What is reproductive cloning
It needs totipotent cells, it is important for genetically identical animals to be made and can be important for producing large numbers of genetically modified animals like goats with spider silk in milk
Desc embryo splitting
Collect embryo and sperm from desirable parents and fuse in vitro
That zygote divided by mitosis to form small ball of cells
Divide embryo into fragments
Each small mass of cells placed into uterus of surrogate mother
Can’t see the phenotype before it’s born
Desc SCNT
collect an udder cell and egg cell from donor
Remove nucleus from both cells
Use an electric chock to fuse the empty egg cell and skins nucleus
That shock also triggers nucleus to divide by mitosis as if it has just been fertilised causing mitosis
The embryo gets placed into a surrogate mothers uterus
The only way to clone an adult which is good as can see phenotype
Not 100% clone as there is some mitochondrial DNA from egg donor left
What is reproductive cloning and examples
Producing clones for some other reason than reproductive purposes.
Aka therapeutic cloning
Stem cells can replace whole organs and tissues eg skin grown in vitro to be a burn area graft
It’s like cloning your own cells so they are identical and don’t cause rejection and is often used for spinal injury
Advs and dis of cloning
Used in scientific research to test effects of medicinal drugs on - avoids humans
Whole herds can have desirable characteristics
Clone endangered animals
A lack of genetic variation
Cloned animals live shorter less healthy lives
Lack of animal welfare : chicken too much meat
How do plants naturally clone themselves ?
They have cells which can differentiate and do this anyway but do it via vegetative propagation:
Leaves: kalanchoe: plantlets on margin, drop off and form new plant
Runner and rhizome:strawberry : horizontal stems that form new roots at a certain point
Sucker: new stem that grows from plant roots and they replace old branch that may die
Bulbs: contain several apical buds to form new plant
Corm: same
Disadvs and advs of natural cloning
Good conditions for parent=good for child
Genetically identical
Fast so can exploit favourable conditions
Only need one parent
No genetic variation
What if environment changes ? - all suffer
So fast that plants may become crowded
What is tissue culture/micropropagation
Makes many clones from just one cutting it takes a small piece of plant the ex plant and uses growth substances to encourage growth and development into new plant
Stages of micropropagation
Use sterile forceps to remove growth tip, meristem is used as is viral infection free and sterilise plant with beach or alcohol as bacteria and fungi
Place explains into agar containing nutrients like glucose,AA and growth substances like Austin
Cells of explant divide by mitosis to form a callus a mass of undifferentiated totipotent cells
Callus divides to make more small clumps of undifferentiated cells
They differentiate into different types of tissue by moved to different growth media’s
Tiny platelets that grow get moved to greenhouse and repotted
Advs and disadvs of artificial cloning of plants
Very fast
Genetically identical
Using meristem so no viral infection
Can grow plants that can’t sexually reproduce
Takes skilled and is labour intensive
Expensive
No genetic variation
Issues with GM with animals + advs
We can breed mice for research
Gene knock out in rats to see if their genes function similar to ours
Animal welfare
Pharming ?
Using GM transgenic animals to produce pharmaceutical products/proteins/products like antithrombin in goat milk
Adv and disadv of pharming
Can produce proteins we need
Some proteins that we can make can’t be done in bacteria as are too large
Animal welfare issue
Food production adv and disadv
Eg salmon we can grow food more rapidly
Outcompete wild populations
Superweed formation that are herbicide resistant weeds
Soya
Resistant to herbicides so only weeds die
Superweed formation
Beta carotene rice + patent
Gene inserted into rice from daffodil that gets a precursor to vitamin A
But if parent put, poor farmers cannot afford and patent means they can’t procure for a period of time
describe the insertion of a DNA fragment into a vector
cut vector at a specific site using same restriction enzyme to create complementary sticky ends
DNA ligase forms phosphodiester bonds between sugar and phosphate groups on the two strands of DNA joining the sticky ends together
Forms recombinant FNA