2.1: blood
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
blood
-is connective tissue: contains ____ + _____ matrix
functions
-transport, ____, regulation
cells, extracellular, protection
components of blood
plasma
~45-65% of blood volume
~90% water
~8% proteins
→albumin: protein for ____, primary influence on osmotic pressure (keeps fluid inside vessels)
→globulins: for ____
→fibrinogen: for ____
→serum = plasma without fibrogen
~2% other solutes like gasses, nutrients, hormones
transport, immunity, clotting
components of blood
red blood cells aka ____
~35-55% of total blood volume: hematocrit
erythrocytes
components of blood
buffy coat
-white blood cells aka ___
<1% of total blood volume
leukocytes
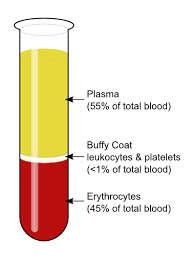
components of blood
.
viscosity
-resistance to flow of a liquid
-whole blood: ___ times as viscous as water
-plasma: ___ times as viscous as water
-changes to viscosity can impact ___ ___
5, 2, circulatory functions
osmolarity
-concentration of ___ ___ in plasma
-determines movement of water, based on ___ ____
-high blood osmolarity: water moves into blood vessels → ____ (decreased/ increased) blood pressure
-low blood osmolarity: water moves out of blood vessels → edema (swelling due to buildup of fluid)
-body regulates Na+, proteins, RBSs to maintain optimal blood viscosity & osmolarity
dissolved particles, osmotic pressure, increased
hemopoiesis: blood production
-all blood cells begin as ______ (HSCs)
-fetal: red bone marrow, liver, spleen
-postnatal: red bone marrow
→extramedullary hemopoiesis: liver & spleen can still contribute to hemopoiesis in severe ___
hemopoietic stem cells, illness
erythrocytes
-primary function: _____: hemoglobin
-plasma membrane proteins
→antigen: ____
→cytoskeletal proteins: ____
-lose all internal organelles during maturation
→no nucleus/ DNA
→no mitochondria: rely on aerobic respiration
gas transport, blood type, durability
hemoglobin (Hb)
-4 protein chains
→each has a heme group
→each heme group has 1 ____
→oxygenation influences color
→% saturation: % of _____
→iron atom at center binds oxygen
oxygen, heme groups occupied by oxygen
erythropoiesis: red blood cell (___) production
→cells take ~5 days to mature
→lifespan of about 120 days
-requires erythropoietin (EPO)
→released by ___ in response to hypoxia
→stimulates erythropoiesis in ___ marrow
→more RBCs = greater gas transport
→synthetic EPO administered for anemia, kidney failure
RBC, kidneys, bone
erythropoiesis
also requires:
iron
→some iron lost daily via urine, feces, injuries, menstruation
→dietary iron helps replenish losses
vitamin B12
→primarily from animal sources
→requires intrinsic factor (protein that binds to food for) for absorption
.
anemia
-RBC or ___ deficiency
causes:
-hypoplastic/ aplastic anemia: inadequate ___
-hemorrhagic anemia: ___ loss
-hemolytic anemia: ___ destruction
-pernicious anemia: vitamin B12 deficiency
consequences:
-impaired gas transport
-tissue hypoxia
erythropoiesis, blood, RBC
blood types
-based on interactions between antigens & antibodies
antigens: _____
-used to _____
antibodies: _____
-each matches specific ___
-bind to mark antigens for destruction
cell surface proteins, distinguish self cells from foreign cells
proteins formed by immune system, antigen
blood types
ABO groups
-determined by hereditary presence/ absence of ____ on RBC membranes
antigens A & B
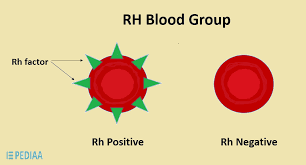
blood types: Rh group
Rh+: antigen D ____ (absent/ present)
Rh-: antigen D ____(absent/ present)
present, absent
agglutination
-immune system produces antibodies for ______
→bind to ___ RBC surface antigens
→can match to several RBCs at once→agglutination
nonself blood antigens, matching
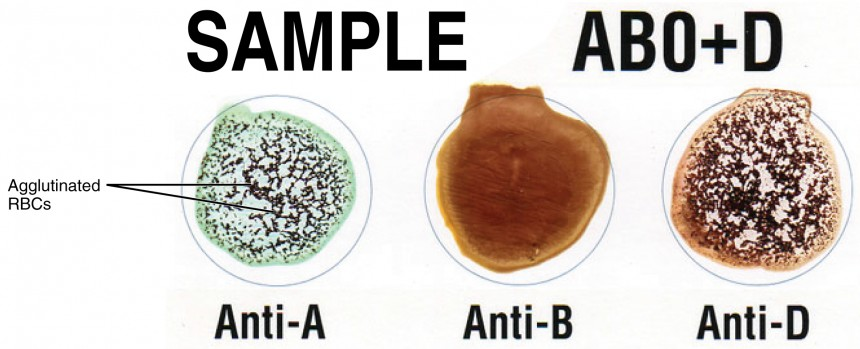
-reactions used to determine blood type
-important consideration for transfusions
→mismatched blood can cause hemolytic transfusion reaction
→O- blood is universal ____
→AB+ blood is universal ___
donor, receiver
maternal-fetal mismatch
-expectant mother carrying fetus with mismatched blood type
→___ mismatch most severe
-first pregnancy not typically impacted
→not maternal immune system can start to develop anti-D antibodies
-antibodies can enter fetal circulation during subsequent pregnancies
→agglutination of fetal blood can lead to hemolytic anemia
-Rh mothers typically medicated at ~28 weeks to prevent reaction
→prevents development of maternal Rh antibodies
Rh
leukocytes
-immune response cells: defend body against bacteria, viruses, parasites, toxins, tumor cells
list its characteristics:
no hemoglobin (oxygen transport), retain all organelles, can leave bloodstream, several different types
platelets
list its characteristics
-not true cells: fragments of larger cells
-tiny but abundant
-no nucleus: but have other organelles
-important of hemostasis: cessation of bleeding
hemostasis
1) vascular spasm: ____
triggered by: rupture of broken vessel, chemical release of platelets
-adjacent vessels also constrict
-minimizes blood loss
2) platelet plug forms
-rupture disrupts prostacyclin (platelet repellant) coating, exposes collagen fibers
-platelets develop pseudopods: projections that allow ____
-mass of platelets block rupture
3) coagulation (clotting)
-procoagulants start a complex reaction cascade
-___ converted into ____
-fibrin sticks to platelets, blood cells, & walls of blood vessel
→forms a clot to seal broken vessel
constriction of broken vessels, platelets to stick to vessel wall & to each other, plasma fibrinogen, fibrin
vessel repair
-clot retraction: ____ → _____
-platelets secrete growth factors to _____
-fibroblasts produce ____
-fibrinolysis
→2nd reaction cascade produces plasmin
→plasmin breaks down ___ → allows clot to ____
-dried external clot = scab
platelet pseudopods contract, close vessel & make clot more compact, induce cell division in vessel wall, collagen, fibrin, dissipate,
thrombosis: abnormal clotting of blood in unbroken vessel (usually veins)
-occlusive thrombus: ___
-embolus: ____
→can potentially block other vessels: embolism
-can be treated with anticoagulants
blocks flow of blood, blood clot travels in bloodstream