Chapter 8 Quiz
1/16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Torque
quantity that changes circular motion; a force changes linear motion, but a change in circular motion occurs because of a force applied at a specific distance from the axis of rotation
Torque Equation
τ = rF; angle is between force and rotating object
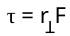
Torque SI Unit
mN
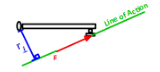
Line of Action
a line drawn collinear to the force that, by drawing a perpendicular line from it to the axis, we can use to determine the actual length of the lever arm
Torque in Equilibrium
Στ = 0; same as balanced
Balancing Torque
Στclockwise = Στcounterclockwise; same as in equilibrium
Center of Gravity
point at which the mass of an object, and therefore its weight, is centered; in geometric objects or uniform objects, it is at the geometric center
Stable Equilibrium
a small displacement results in a restoring force (torque) that brings the object back to equilibrium position
Unstable Equilibrium
a small displacement results in the object rotating farther from its equilibrium position
Rigid Objects
have wide bases and low centers of gravity; most stable
Moment of Inertia
If torque is applied, angular acceleration occurs. However, the amount of α is dependent on radius and on shape of the object
Moment of Inertia Equation
I = Σmr²
Moment of Inertia SI Unit
kgm²
Why does the equation to determine moment of inertia change for some objects?
it depends on mass and its distribution relative axis so it changes based on the object’s mass and distance from the axis (radius)
Parallel Axis Theorem
the moment of inertia of a body about an axis parallel to one through its center of mass
Parallel Axis Theorem Equation
I = Icm + md2; m = mass of the body, cm = center of mass; & d = distance between the center of mass and axis
Rotational Form of Newton’s Second Law
τ = Iα