Chem 1 (College) Final Study Guide
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Atomic Mass
The weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of the element

Protons
Atomic mass - neutrons
Neutrons
Atomic mass - protons
Electrons
Protons ± charge
*negative charge = more electrons
*positive charger = less electrons
Electron shells (n)
A group of atomic orbitals representing a specific energy level where electrons are found. While numbers greater than 0 (1-7).
Electron Sub-shells (cursive l)
Subdivisions of a shell (s, p, d, f)
S-orbitals
2 electrons
P-orbitals
6 electrons
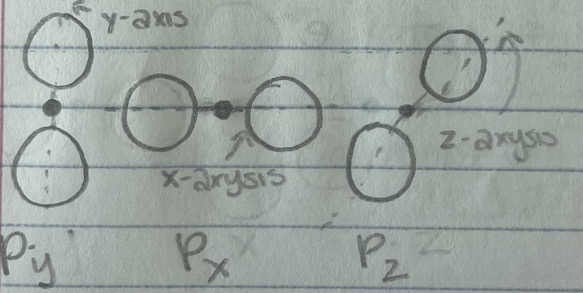
d-orbitals
10 electrons
f-orbitals
14 electrons
Coulumb’s Law
F=k(q1•q2)/(r2)
K=constant
(q1•q2)=particle charge
r=distance between particles
F=attractive/repulsive force
Orbital Chart
Always fill entirely before moving on and fill a degenerate before pairing
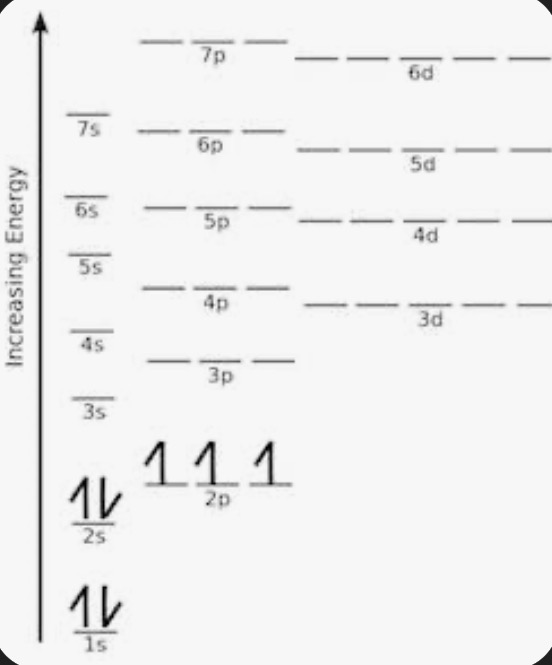
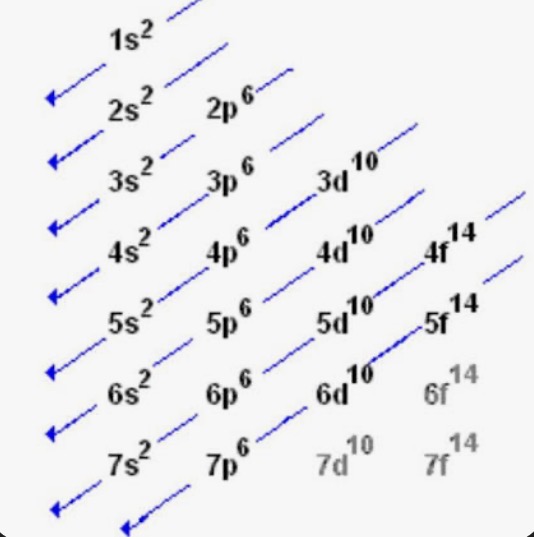
Order to fill orbitals
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p
Electron configuration
Shortened notation of the electronic structure of an atom or ion
Steps:
Determine total number of electrons involved
Start with lowest energy orbitals (1s) and add two electrons to each orbital till you run out
Double check that your used electrons = the total electrons
Electron configuration example (O)
Oxygen : 1s² 2s² 2p^4
Ion electron configuration
Anions = add extra electron to next available orbital
Cations = remove electron from the highest energy orbital
Noble Gas Abbreviations
[He] - 1s²
[Ne] - 1s² 2s² 2p^6
[Ar] - [Ne] 3s² 3p^6
[Kr] - [Ar] 4s² 3d^10 4p^6
[Xe] - [Kr] 5s² 4d^10 5p^6
[Rn] - [Xe] 6s² 4f^14 5d^10 6p^6
Effective Nuclear Charge (Zeff)
The pull on valence electrons by the nucleus.
Major: decreases from period 1-7
Minor: increases from group 1-18
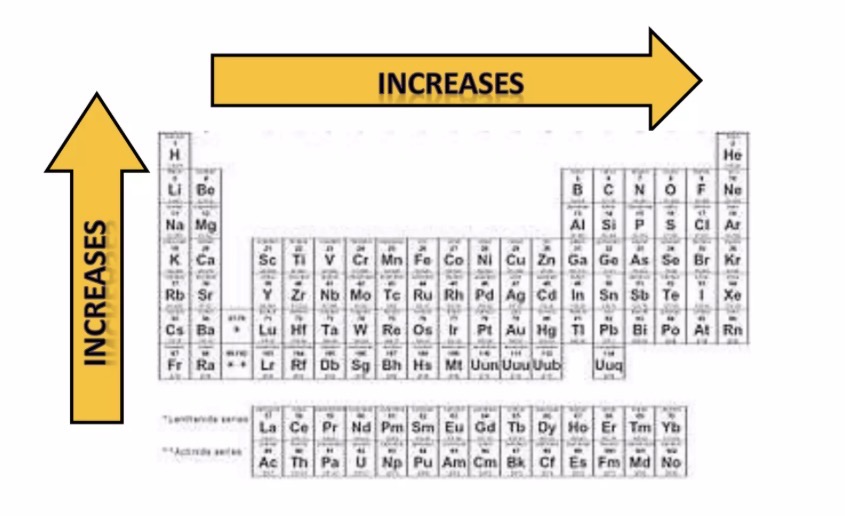
Atomic Size Trend
The diameter of the element in its neutral state
Major: increased from period 1-7
Minor: decreases from group 1-18
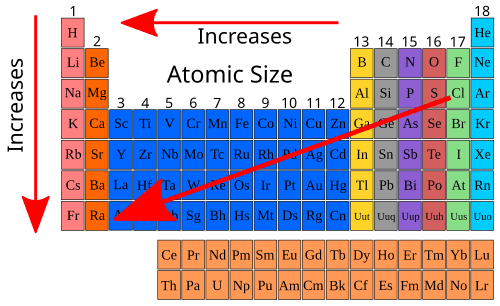
Ionic Size Trend
The diameter of an element in its charged state
Cations: size decreases with each electron removed
Anions: size increases with each electron added
Isoelectronic
Same electron configuration but different element.
Ex. Na+, Ne, F- (all have 10 electrons)
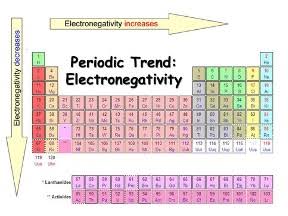
Electronegativity (EN)
An atoms tendency to attract electrons to itself. High EN=want electrons, low EN=doesn’t want electrons
Major: decreases from period 1-7
Minor: increases from group 1-17
Formula mass
The mass of 1 formula unit of a compound.
Atomic mass of element x number of atoms in the formula
Ex: C6H12 = (6•12.01)+(12•1.008) = 84.156 amu (atomic mass unit)
Ionic bonds
Electrons are exchanged between atoms
Cations +
Anions -
Polar covalent bonds
Electrons are shared between atoms unevenly
Covalent bonds
Electrons are shared between atoms equally
Change in EN
EN(atom 1) - EN (atom 2)
change in En < 0.4 its pure covalent
1.8 > change in EN > 0.4 its polar covalent
Change in EN >1.8 (or it’s a metal) its ionic
Naming Cations
Polyatomic: Ammonium (NH4+)
Monatomic: name of element + Roman numerals (if charge is variable)
I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII
Group 1 (+1), group 2 (+2), Ag (+1), Zn/Cd (+2), Al/Sc (+3)
Naming Anions
Polyatomic: later
Monatomic: base name + ide (Chlorine —> Chloride)
fixed charges: Halogens (-1), group 16 (-2), group 15 (-3), group 14 (-4)
Octet Rule
Elements wants to hold onto 8 valence electron to be stable
Exceptions:
H (only needs 2)
Any atom below period 2 (can have more than 8)
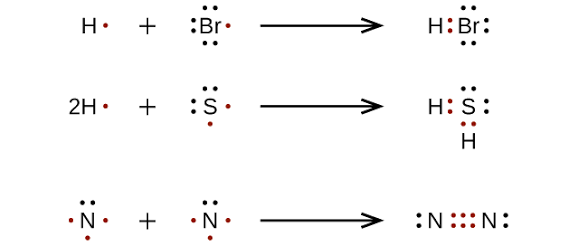
Lewis Dot Structures
Determine total number of valence electrons
Arrange atoms (least EN atom in the center unless H or specified)
Add VE to each atom (dots)
Draw bonds between atoms (lines)
Check if every atom has a full octet and total VE matches ones used.
*if ion, add an electron for anions and take away one for cation
Formal Charge
A hypothetical charge an atom would have if the bonding electrons were equally shared
FC = (# of VE) - (# of non bonding electrons) - (1/2 # of bonding electrons)
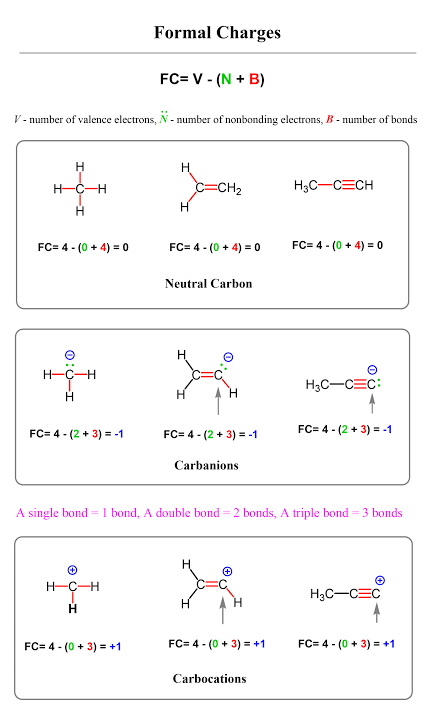
Resonance Structure
Has the same chemical formula, same connectivity of atoms (formation), but a different arrangement of electrons in the compound
Isomer
Has the same chemical formula, but a different connectivity of atoms (formation) and different arrangement of electrons.
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
Electron groups will adopt a geometry with the largest possible angle between electron groups. Electron groups being one lone pair, one single bond, one double bond, one triple bond.
Electronic Geometry
Treat all electron group identically.
Linear, trigonal plantar, tetrahedral, trigonal bypyramid, and octahedral
Molecular Geometry
Differentiates between bonding and nonbonding electron groups
*has lone pairs
Sigma Bond
Always one sigma bond in every atom
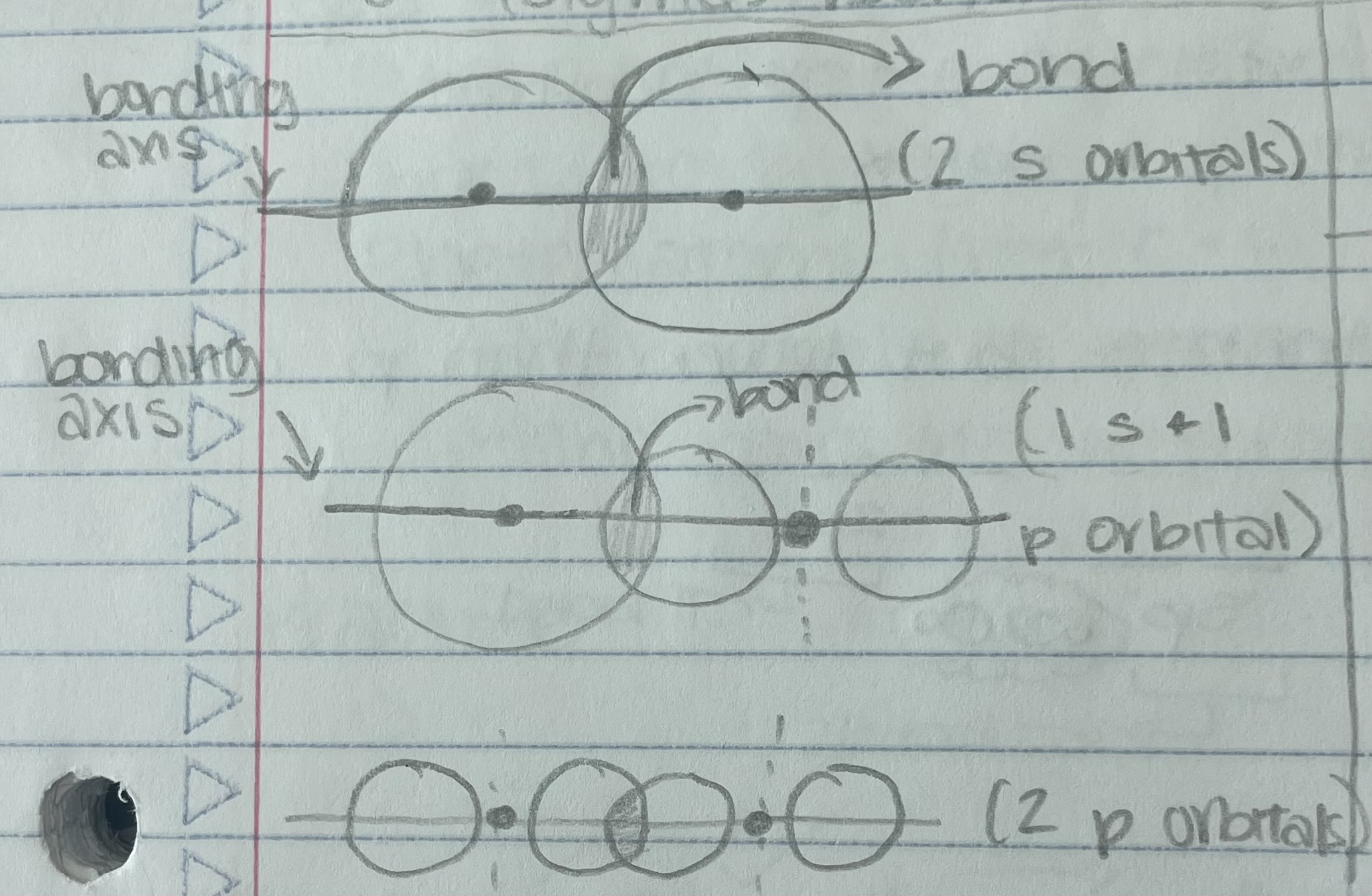
Pi Bond
Only always between 2 p-orbitals
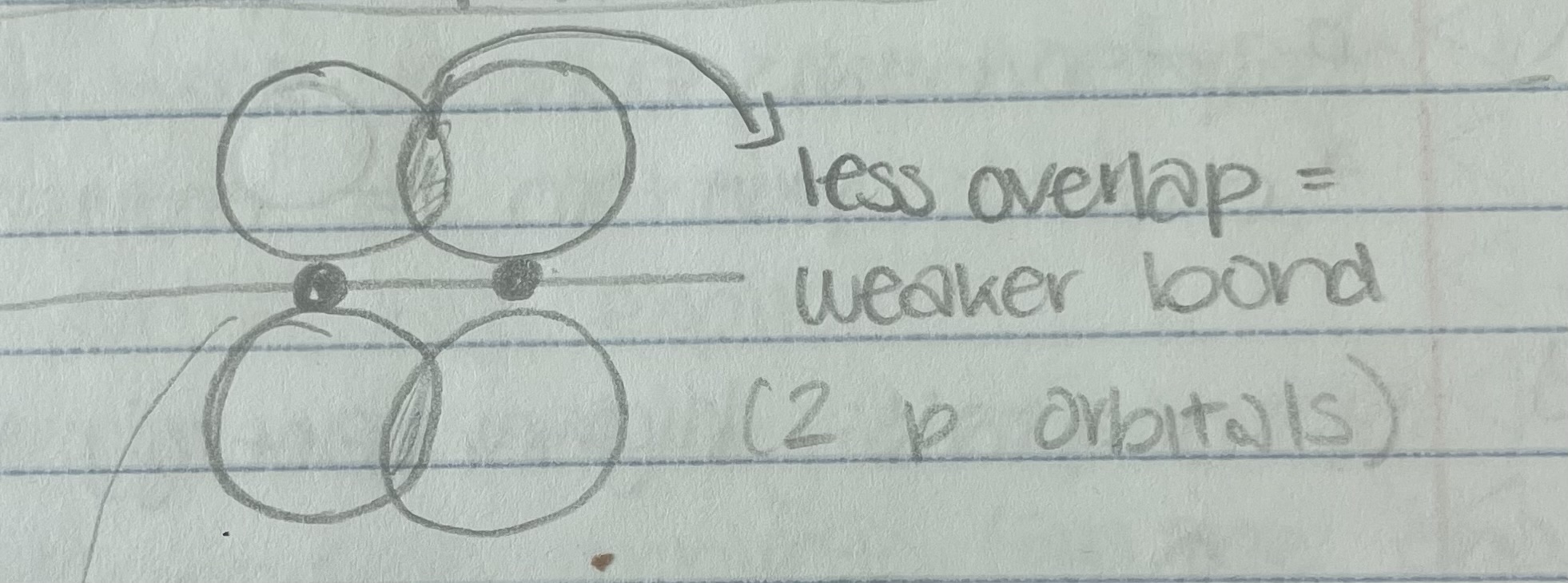
Hybridized Orbitals
sp orbitals, sp² orbitals, sp³ orbitals
orbital = 1s + 1p = 2sp orbital
sp² orbital = 1s + 2p = 3sp² orbital
sp³ orbital = 1s + 3p = 4sp³ orbital
*orbitals put in = orbital put out
*look for number of electron groups 2 groups = sp, 3 groups = sp², 4 groups = sp³

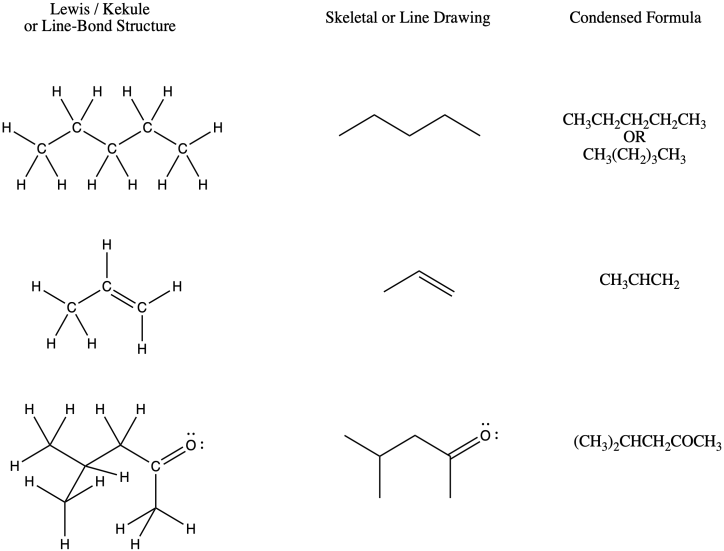
Line angle drawings
A method of drawing structures where C and H are implicit. C goes on the end of every line and H goes on C to fill an octet unless otherwise specified.
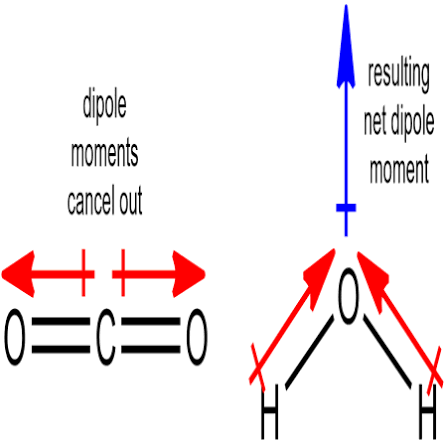
Net dipole moment
Overall measure of a molecules polarity
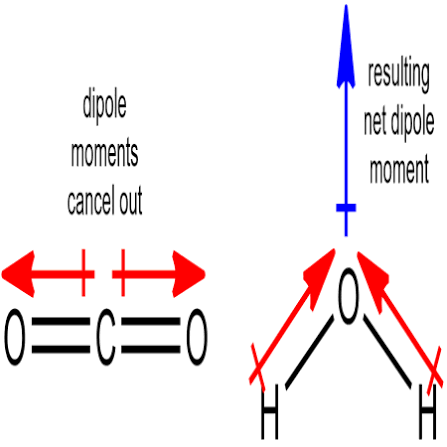
Polar molecules must
Have at least one polar covalent bond
Have an overall net dipole moment (doesn’t cancel out)
Intermolecular forces (IMFs)
Attractive forces between molecules
Ex: dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds
Dispersion forces (LDFs)
Arise from temporary dipoles in molecules. If the molecule has electrons, it has dispersion forces.
Dipole-Dipole forces (Dip-Dip/Dip²)
Arise from permanent dipoles in molecules aligning. Must be a polar molecule. In general, string than LDFs
Hydrogen Bonding (H-Bonds)
A subset of dip² forces. Molecule must contain a H bonded to N, O, or F. Externally strong bonds
Boiling point
Liquid to gas. A higher/stronger IMF means a higher boiling point and vise versa.
Melting point
Solid to liquid. A higher/stronger IMF means a higher melting point and vise versa
Viscosity
Resistance to flow (thickness). A higher/stronger IMF means a higher viscosity and vise versa.
Surface tension
Liquid state. A higher/stronger IMF means a higher surface tension and vise versa
Solubility
Dissolving. Molecules with the same/more similar strength IMF dissolve each other
Mass to moles
Molar mass
Moles to objects
Avogadro’s number (6.022×10²³)
Molarity (M)
M = moles/liters
Also concentration ( [L] )
Keq formula
[products]^# / [reactants]^#
only (aq) and (g) reactions
Keq numbers
Keq>1 products>reactants
Keq<1 products<reactants
Keq=1 products=reactants
Acids
HCl, H2, Se, H20, NH4+, Hbr, HNO3, etc.
Carboxylic Acid
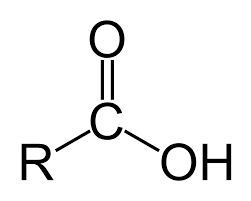
Alcohol Acid
Thiol Acid
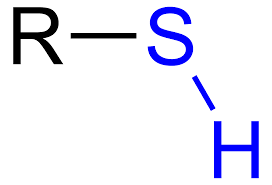
Bases
OH-, NH3, C2H3O2-, H20, etc.
Primary Amine
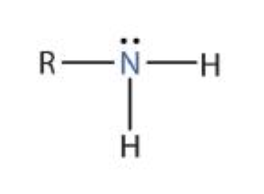
Secondary Amine
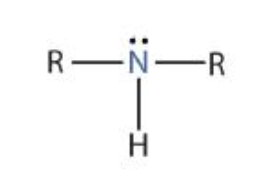
Tertiary Amine
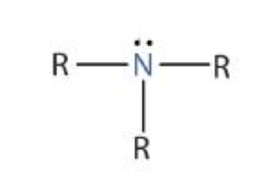
Strong acids/bases…
completely dissociate in water
Weak acids/bases…
dont completely dissociate in water
pH formula
-log[H3O+]
[H3O+]
10^(-pH)
Percent Ionization
[H3O+] / [HA] x100
Ka formula
[A-] x [H3O+] / [HA]
weak acid = Ka<1
strong acid = Ka>1
pKa formula
-log(Ka)
Kb foruma
[OH-] x [HA] / [A-]
weak base = Kb<1
strong base = Kb>1
pKb formula
-log(Kb)
Kw formula
[OH-] x [H3O+]
1×10^14
pKw
14
pKa + pHb
Keq>Q
makes more products
Keq<Q
makes more reactants
Keq=Q
at equilibrium
Exothermic
produces heat and increases the temp of their surrounding, heat is a product
Endothermic
absorbs heat and decreases the temp of their surroundings, heat is a reactant