Anatomy Q4 Exam
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
T or F The medial indentation of the kidney where several structures such as the ureters, renal blood vessels, and nerve center enter and exit the kidney is called the Hilus
True
T or F Diabetes mellitus can lead to severe dehydrationand electrolyte imbalances leaving affected persons continually thirsty.
F, Insipidus
T or F The lumen surfaces of the tubule cells within the proximal convoluted tubule are covered with microvilli
True
T or F The capillary bed that is surrounded by Bowman's capsule but does not drain the glomerulus is called the peritubular capillary bed
F, glomerulus
T or F The specific gravity of urine is typically lower than the specific gravity of pure water
F, higher
T or F Tubular Secretion which seems to be important for removal of substances not already in the filtrate is essentially reabsorption in reverse
True
T or F Urine moves down the ureters into the bladder due to gravitational pull alone
False, by peristalsis
T or F A descending urinary tract infection is the most common type of UTI
False ascending
T or f The urethra which carries urine exiting the bladder by peristalsis is typically shorter in females than in males
True
T or F Following the Micturition reflex it is impossible to postpone bladder emptying
F possible
T or F Antidiuretic hormone causes increased water loss through the urine
F decreased
T or F The most important trigger for aldosterone release is the renin-angiotensin mechanism mediated by the renal tubules
True
T or F A person with arterial blood pH above 7.45 is said to have acidosis
False Alkalosis
T or F The kidneys help maintain acid-base balance of the blood by excreting bicarbonate ions
True
t or f Sexually transmitted diseases are primarily infections of the reproductive tracks but may also cause urinary tract infections
True
T or F Incontinence is often the final outcome of the urinary system during the aging process
True
RBCs in the urine due to trauma or infection
hematuria
Hemoglobin in the urine due to hemolytic anemia or a transfusion reaction
Hemoglobinuria
Glucose in the urine due to diabetes mellitus
glycosuria
Bile pigment in the urine due to hepatitis
bilirubinuria
Pus containing WBCs and bacterial in the urine due to urinary tract infection
Pyuria
Proteins in the urine due to pregnancy or excessive exercise
proteinuria
Cup shaped extensions of the pelvis
Calyces
Outer lighter region of the kidney
Renal cortex
Vessel supplying each kidney with blood to be filtered
Renal artery
Cortex-like extensions that separate the pyramids
renal columns
Darker reddish brown internal area of the kidney
renal medulla
Triangular regions with striped appearance
medullary pyramids
Flat basin like cavity medial to the hilus of the kidney
renal pelvis
Term that describes the location of the kidneys
retroperitoneal
The enlarged, cup-shaped closed end of the renal tubule that completely surrounds the glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule
Filtration slits and openings exist between pedicels of the glomerulus, forming a ______ membrane around the glomerulus
porous
Blood pressure within the glomerulus is extremely _____, which forces fluids and relatively small solutes out of blood and into the capsule
high
Of the capillary beds associated with each nephron, the one that is both fed and drained by the arterioles
glomerulus
The peritubular capillaries arise from the ______ arteriole, which drains the glomerulus
efferent
Which is NOT typically reabsorbed by the tubules under normal healthy conditions: water, glucose, amino acids, urea, sodium
urea
In contrasting urine and filtrate by the time it reaches the following, it could be said that filtrate contains almost ______ that plasma does
everything
In a healthy young adult female, water accounts for approximately __% of body weight
50
Regardless if aldosterone is present or not, the percentage of sodium that is reabsorbed within the proximal convoluted tubules of the kidney is __%
80
Extracellular fluid is found everywhere in the body EXCEPT within
living cells
A simple rule concerning water and electrolyte regulation is ___ passively follows____
Water; salt
The results of the renin-angiotensin mechanism mediated by the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the renal tubules include suppression of
Aldosterone
The chemical buffer system that includes carbonic acid and its salt, which ties up the H+ released by strong acids is called the _______
Bicarbonate buffer system
the chemically buffered combination of strong acids that dissociate completely in water and weak bases such as hydroxides leads to a weak ___ and a ____
Acid; salt
when carbon dioxide enters the blood from tissue cells, it is converted to _____ ion for transport within blood plasma
Bicarbonate
When blood pH begins to rise, the respiratory control centers in the brain are
Depressed
The most potent of all mechanisms and substances that the body used to regulate blood pH are the
Kidneys
Functional kidneys develop in the womb by the third month after conception from the ____ set of tubule systems
Third
The average output of urine for a normal healthy adult is __ ml/day
1500
Control of the voluntary urethral sphincter in normal children is related to the _____ system development
Nervous
The noninvasive treatment for kidney stones that uses ultrasound waves to shatter calculi is called
Lithotripsy
The bladder is able to expand as urine accumulates within it due to the presence of ___epithelium.
Transitional
The average adult bladder is moderately full with ___ ml of urine within it.
500
The voluntarily controlled sphincter fashioned by skeletal muscle at the point where the urethra passes through the pelvic floor is called the external ______ sphincter.
Urethral
Typical symptoms of urinary tract infection in adults include:
Urinary urgency, dysuria, urinary frequency, and cloudy urine
Incontinence can result from pressure on the
Bladder
Incontinence is normal in children __ years old or younger
2
_____ occurs in older children who sleep soundly
Incontinence
______ occurs when we are unable to voluntarily control the external sphincter
Incontinence
Enlargement of the prostrate gland that surrounds the neck of the bladder in adult men is called _____ which may cause voiding difficulty.
Hypertrophy
In one 24-hour period, the kidneys of an average-sized healthy adult filter approximately _____ liters of blood plasma through glomeration into the tubules.
150-180
Kidneys in a healthy adult excrete _____-containing waste
Nitrogen
Kidneys in a healthy adult maintain _____ balance in blood
Water
Kidneys in a healthy adult maintain _____ balance of the blood
Electrolyte
Kidneys in a healthy adult ensure proper blood ____
pH
A function of the kidneys is to regulate ____ pressure
Blood
A function of the kidneys is to convert vitamin _ to its active form
D
A function of the kidneys is to manufacture
Urine
A function of the kidneys Is to dospose of ____ waste products
Metabolic
The kidneys are aided in the excretion of fluids by the _____ and _____
Lungs; skin
The correct pathway of the arterial blood supply through the kidney is___artery → _____ arteries → ____ arteries → ____arteries
Renal; interlobular; arcuate; interlobar
Each kidney contains about __ million nephrons.
4
Most nephrons are located within the renal
Cortex
The nonselective, passive process performed by the glamorous that forms blood plasma without blood proteins is called
Filtration
T or F: Urine under normal healthy conditions is sterile
True
Urine under normal healthy conditions is more dense than
Distilled water
Urine under normal healthy conditions Is slightly
Aromatic
Urine under normal healthy conditions typically contains ___
Ammonia
Substances normally found in urine are urea, ammonia, and _____
Creatine
The bladder is described as _____ collapsible, smooth, and retroperitoneal.
Muscular
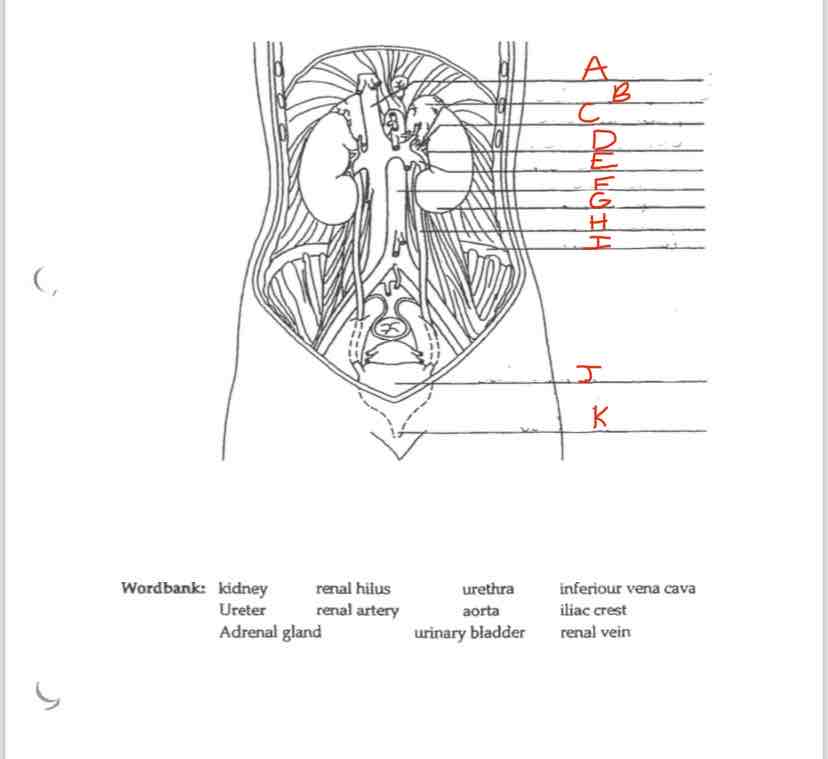
Label A
Inferior vena cava
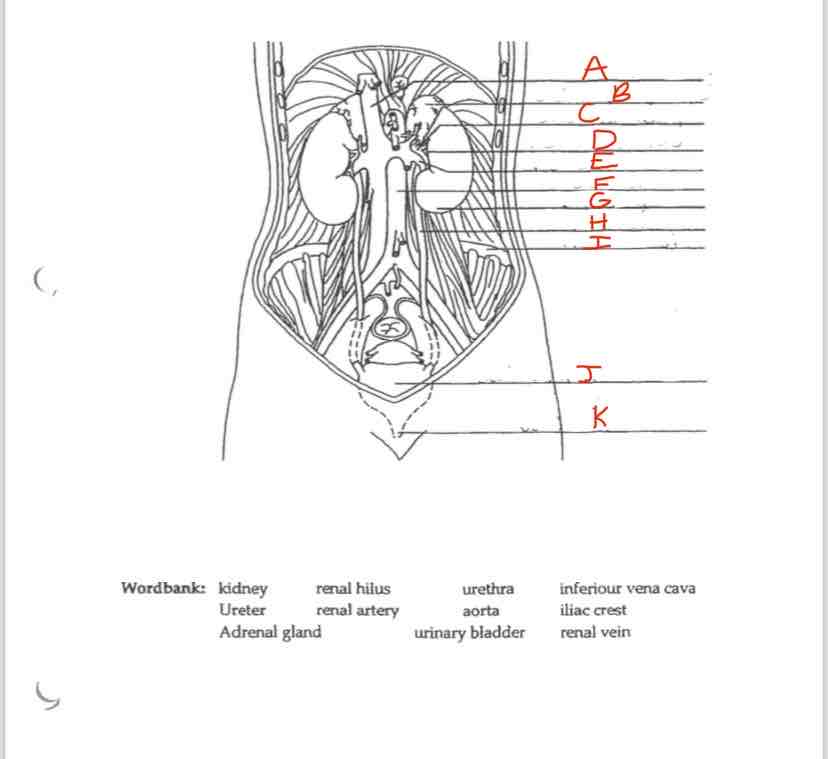
Label B
Adrenal Gland
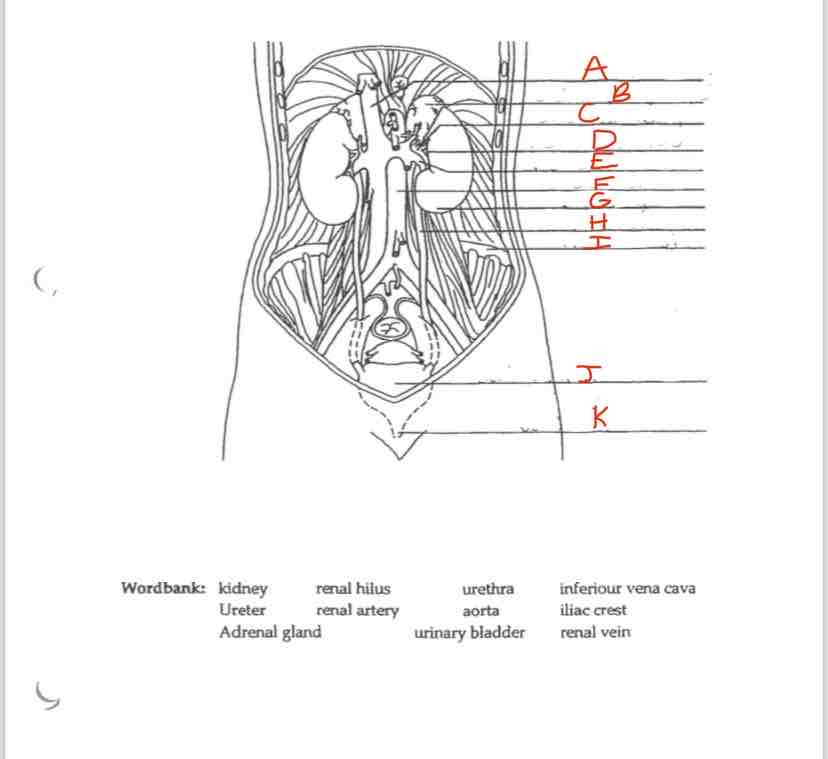
Label C
Renal artery
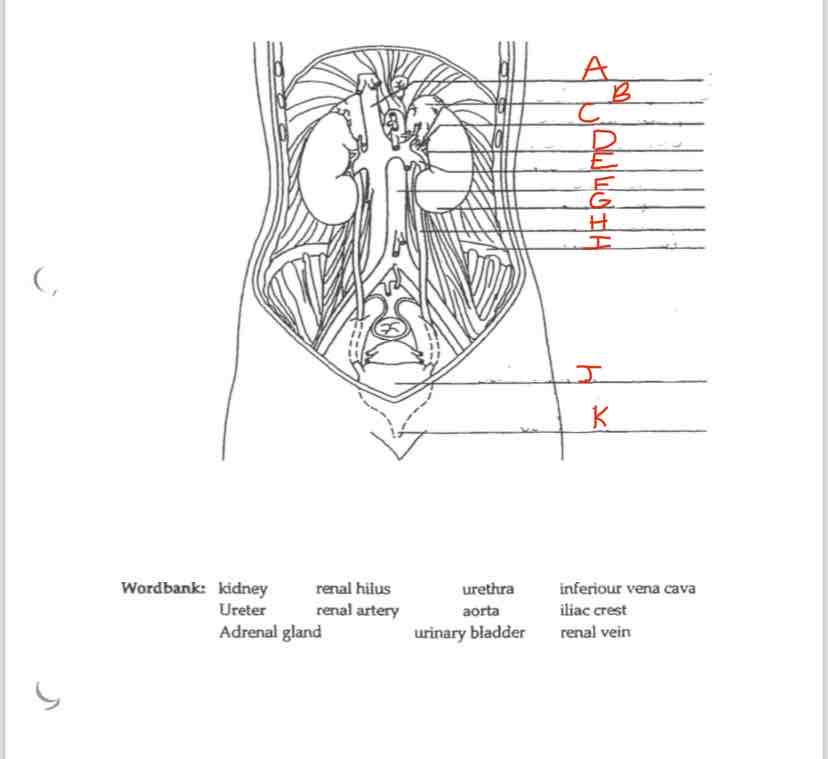
Label D
Renal hilus
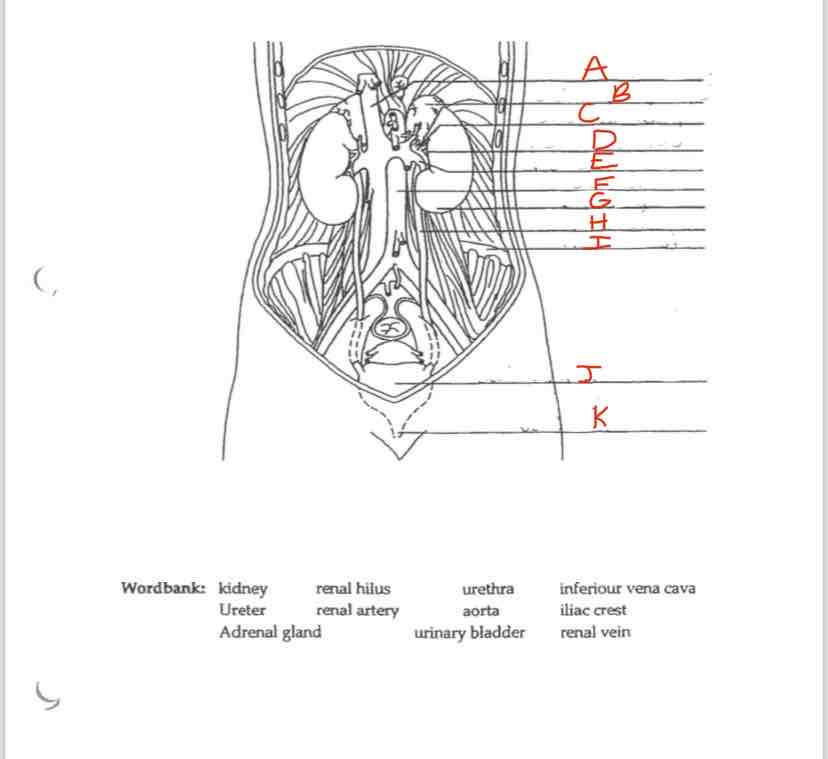
Label E
Renal Vein
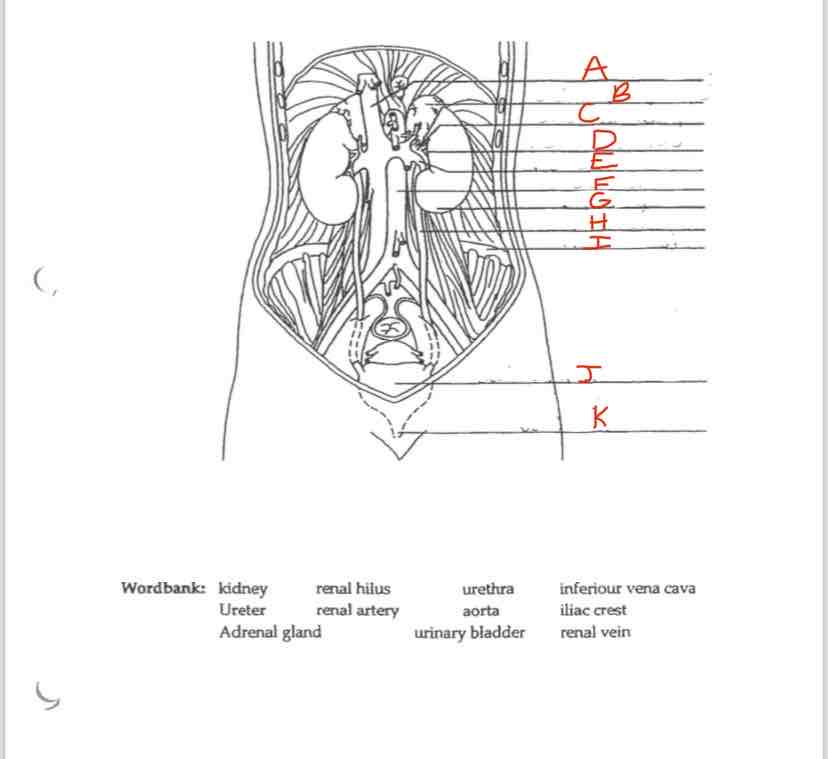
Label F
Aorta
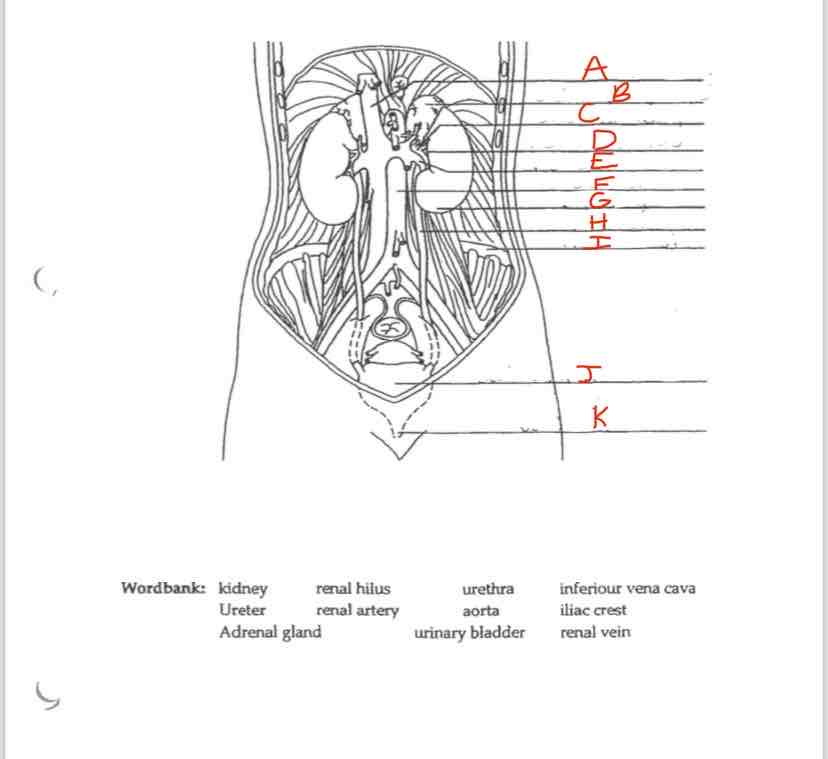
Label G
kidney
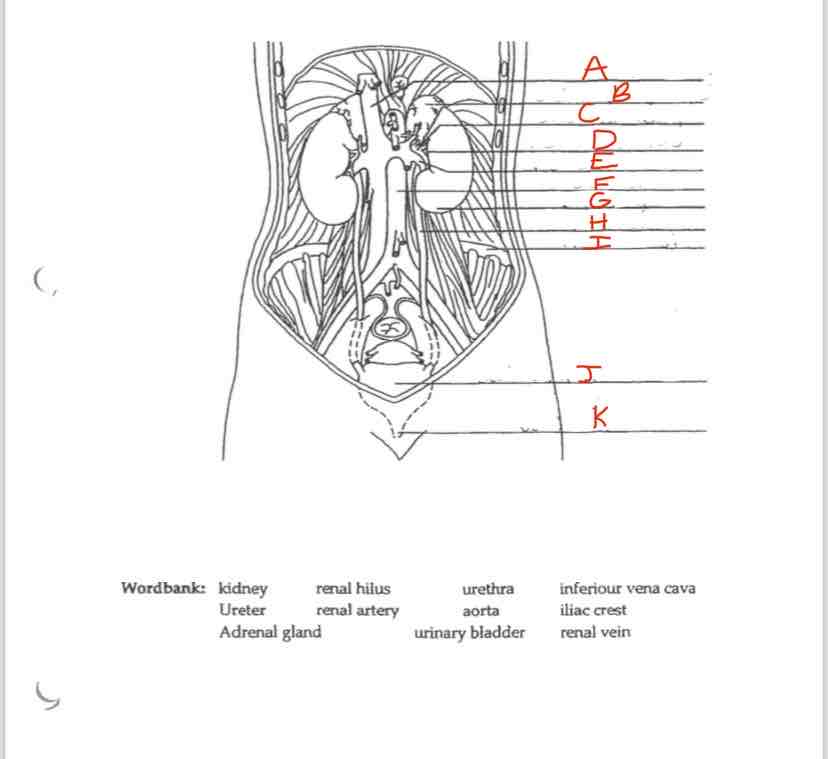
Label H
Ureter
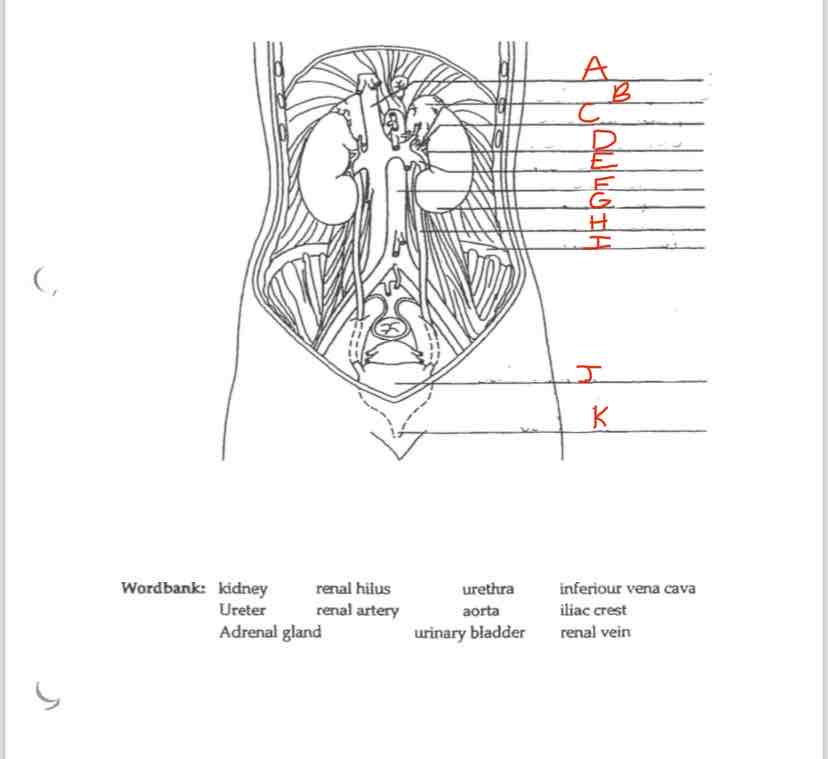
Label I
Iliac crest
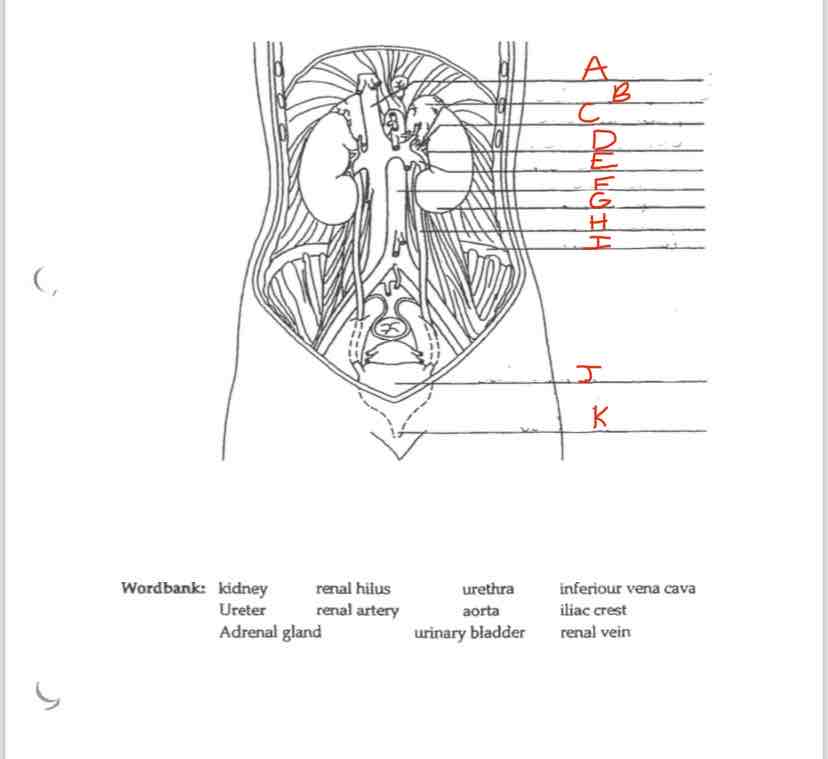
Label J
Urinary Bladder
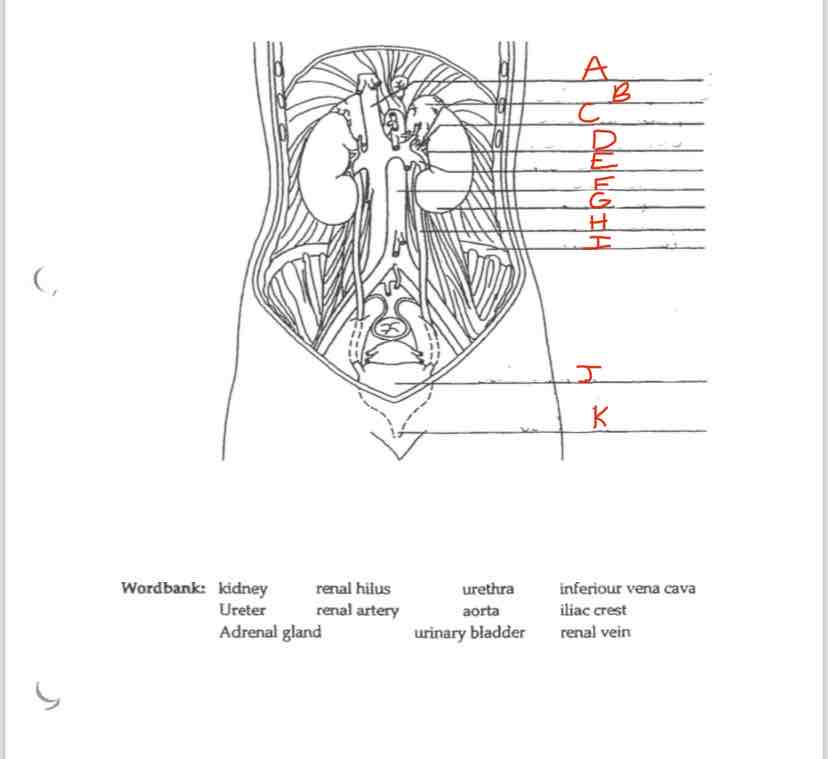
Label K
Urethra