AP HUG Unit 7 Vocab
1/73
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
consumption
the using up of goods & services
developed country
wealthy, economically stable country
developing country
a country that is at a relatively early stage in the economic development
GDP
the total value of goods & services a country produces
per capita
per person
industry
any economic activity that uses machinery on a large scale to process raw materials into finished goods
raw materials
the basic, natural materials used to make a product intended for sale to costumers
ex: metals, wood, plant products, animal products
industrialization
the process by which the interaction of social and economic factors leads to the development of industries across a community, region or country
industrial revolution
in 18th century Britain when there was a shift from small-scale, hand-crafted production to power-driven mass production
use of steam power; growth of textile, coal, iron, and steel and railroad industries (1784)
cottage industries
small-scale industries based in the home, usually in rural areas
2nd industrial rev.
use of electricity and internal combustion engine; growth of steel, automobile, airplane, chemical, and consumer appliance industries (1870/19th century)
3rd industrial rev.
growth of computer, electronics, and information industries after WW2 (1950)
colonialism/imperialism
a system where a stronger nation dominates a weaker nation: politically, socially & economically
4th industrial rev.
growth of robotics, information, and biomedical industries today
economic sector
collections of similar, distinct economic activities based on the creation of raw materials, the production of goods, the provision of services or other activities that help structure a countries economy
primary sector
activities involving the extraction of natural resources
ex: agriculture, fishing, forestry, mining, extracting of liquids/gas (oil)
secondary sector
the production of goods from raw materials extracted/harvested in the primary sector
ex: manufacturing, construction, production
tertiary sector
provides services (commercial & personal)
ex: transportation, storage marketing, selling of goods
quaternary sector
workers process and handle information and environmental technology
ex: Google, Microsoft, Apple employees
portion of tertiary sector
quinary sector
work involving top leaders in the gov., science, universities, media, overall people who have high levels of education & leadership
branch of quaternary sector
postindustrial economy
extremely low primary sector employment, low secondary sector employment, and lots of tertiary employment with rising quaternary and quinary jobs
found in US, Japan, Australia, Singapore
GDP
total value of all goods and services produced by a country’s citizens and companies within the countries borders in a year
Dual economies
two distinct divisions of economic activity across the economic sectors
ex: Vietnam
least cost theory
model developed by Alfred Weber according to the theory businesses locate their facilities in a particular place because that location minimizes the costs of production (transport, labor and agglomeration)
Agglomeration
describes the advantage for companies in the same or similar industries in locating near each other in order to take advantage of specialized labor, materials and services
Bulk-of-break point
locations where it is more economical to break raw materials into small units before shipping them a far
often located in areas where the more of transport changes
bulk-reducing industry
industries where raw materials cost more to transport than the finished goods
lumber, copper smelting, furniture manufacturing
bulk-gaining industry
industries where raw materials cost less to transport than finished goods
car manufacturing, bread production, construction equipment
industrial park
collection of manufacturing facilities/land made for factories, which are found in suburbs & close to highways
human development
the processes involved in the improvement of people’s freedoms, rights, capabilities, choices and material conditions
GNP
the total value of the goods & services produced by a countries citizens & companies both domestically and internationally in a year
GNI
per capita, the total value of goods and services globally produced by a country in a year divided by the countries population (includes the income of non-citizens living in the country as well.)
formal sector
includes businesses, enterprises, and other economic activities that have government supervision, monitoring, and protection and are taxed
informal sector
any part of a country’s economy that is outside of government monitoring or regulation and is not taxed
ex: street vendors selling flowers, unlicensed/unregulated food & beverage stands
Literacy Rate
% of population that is literate/can read
helps see level of development in a country
HDI (Human Development Index)
measures overall level of development of a country using life expectancy at birth, a dad to education measured in expected and mean years of schooling, and standard of living measured by GNI per capita
GDI (gender development index)
calculates gender disparities based on health, knowledge, and standard of living of the genders
measured using female HDI as % of male HDI
GII(gender inequality index)
calculates inequality using reproductive health, empowerment, and labor-market participation
measured using a range of 0.0-1.0, 0.0 = men and women share equal roles and 1.0 = women have little equality
Women’s empowerment
includes women’s options and access to participate fully in the social and economic spheres of a society
LMP
measures an economy’s active labor force and is calculated by taking the sum of all employed workers and dividing that # by the working-age population
Microloans
Very small short-terms loans with low interest intended to help people in need
Grameen Bank
started by a Bangladeshi professor, first ever micro loan institution , helped many people (mainly women) break away from poverty, get financial security
Rostow’s Theory
model that measures how countries economic level using 5 stages its limits are that it assumes:
all countries want to be democratic, capitalist, & industrialized
all countries do/will follow these stages of growth
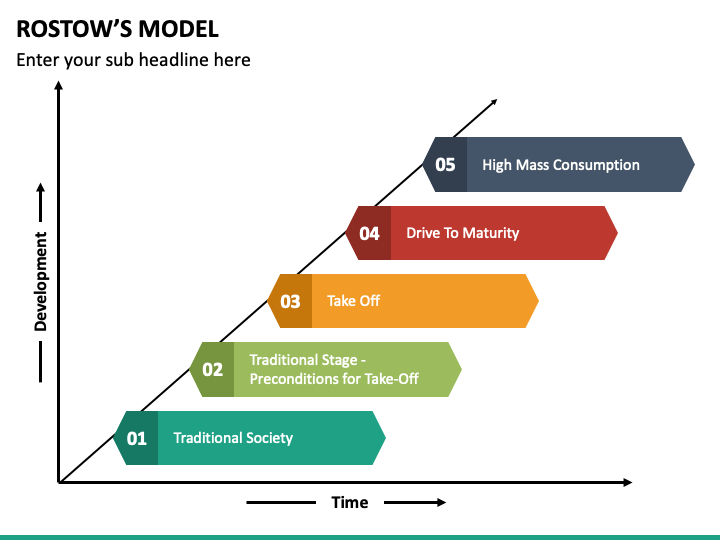
Rostow Stage 1
traditional society - subsistence farming, pre industrial
rostow stage 2
preconditions for takeoff - increased outputs, beginning of industrialization, workforce shifts from primarily farming to manufacturing
rostow stage 3
take off - industrialization, urbanization increase, rapid improvement in some industries due to tech. advances
rostow stage 4
drive to maturity: stable growth, industries have reached max effectiveness, increased income = increased consumption
rostow stage 5
high mass consumption - shift from dominant production of industrial manufacturing to dominant production of consumer goods and services, overconsumption issues
wallerstein’s theory
describes the relationship between countries and helps explain the history of uneven economic development in the world economy, its limits are that:
its too focused on economics therefor can’t categorize countries easily (there’s political and societal factor and differences)
doesn’t take into account other measures of dominance in the periphery and core country relationship such as cultural influence
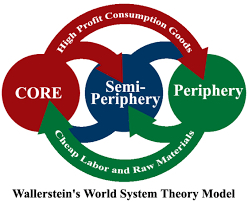
core regions
regions that dominate and take advantage of periphery countries for cheap labor & raw materials
peripheral regions
regions that are underdeveloped, & dependent on core countries for capital (consumer goods & money)
semi-periphery
regions that have qualities of both core and periphery regions
dependency theory
describes the development challenges & limitations faced by poorer countries, & the political/economic relationships poorer countries have with the richer countries, its limits are that:
there’s no standard to distinguish dependent and non dependent countries
it doesn’t take in other factors of underdevelopment such as corruption within a country
commodity dependence
when more than 60% of a countries exports & economic health are tied to one or two resources such as oil, timber or plantation crops
comparative advantage
refers to the relative cost advantages of producing certain goods & services for trade
complementarity
refers to the mutually beneficial trade relationship between two countries that results when they have different comparative advantages
neoliberalism
the belief that open markets and free trade(two key characteristics of capitalism) across the globe will lead to economic development everywhere, lesson tensions between countries by fostering support for common values and spread democracy and human rights
supranational organizations
organization of three or more countries to promote shared objectives
deindustrialization
the change that occurs with the decline in the % of workers employed in the secondary sector, & a reduction of a regions industrial capacity/ activity, like heavy industry and manufacturing
growth poles
places of economic activity clustered around one or more high-growth industries that stimulate economic growth by capitalizing on some special asset
globalization
the process by which businesses or other organizations develop international influence or start operating on an international scale
just-in-time delivery
materials are delivered when they are needed for short-term production, so that companies can avoid paying to store extra inventory at their facilities
fordism
the manufacturing economy and system derived from assembly-line mass production and the mass consumption of standardized goods
post-fordism
the system of production that relies on automation through the use of robots and computer systems and is centered on low-volume manufacturing and flexible systems that allows for quick responses to changes in the market
offshore outsourcing
the process in which companies move production to places outside the country they are headquartered in
division of labor
the type of arrangement in which each worker specializes in a particular task or job
international division of labor
the specialization, by countries, in particular products for export
multiplier effects
opportunities that can potentially develop from an economic change
SEZ (special economic zones)
- an area within a country that is subject to different & more beneficial economic regulations than other areas
EPZ (export processing zones)
sites where manufacturing of exports is done without tariffs or other financial incentives such as taxes
FTZ (free trade zones)
provide customs-related advantages & exemptions from tariffs and taxes
sustainable practices
practices that provide ongoing economic & social benefits without degrading the environment
sustainable development goals
17 goals adopted by the UN intended to reduce the inequalities among countries in the core, periphery & semi-periphery and to achieve a more sustainable future for all
Ecotourism
A form of tourism based on the enjoyment of scenic areas or natural wonders that aims to provide an experience of nature or culture in an environmentally sustainable way