rates of reaction chapter 16
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
factors affecting rates of reaction
nature of reactants
particle size
concentration
temperature
catalysts
homogenous catalyst
reactants and catalyst in same phase
heterogenous
reactants and catalyst in different phases
eg oxidation of methanol
adsorption
lower activation energy due to the platinum catalyst present
autocatalysis
where one of the products of the reaction acts as a catalyst
surface adsorption theory
adsorption, reaction on surface, desorption stage
catalytic converters
platinum, palladium, rhodium
carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide
catalyst poisons
lead
effective collison
is one that results in the formation of products
activation energy
is the minium energy that colliding particles must have for a reaction to occur
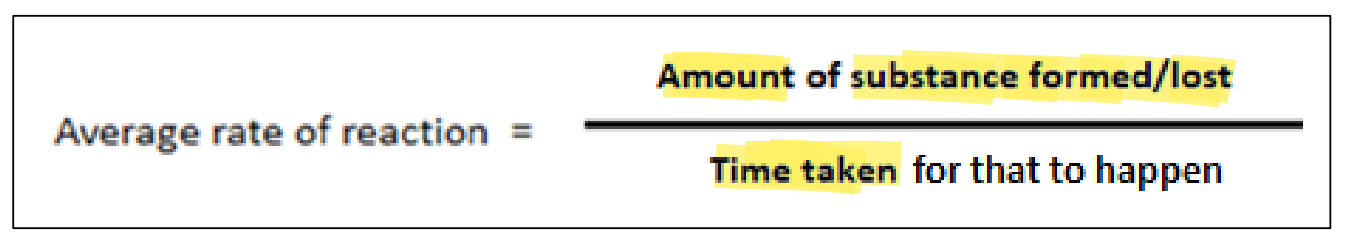
rate of reaction
change in concentration per unit time of any one reactant
How are rates of reaction measured?
a) The formation of a product per unit time can be measured
b) The loss of a reactant per unit time can be measured
Note:
- Reactions will not have the same rate throughout
- Two types of ‘rate’ can be measured
Average rate of reaction
What is meant by instantaneous rate of reaction?
Instantaneous reaction is the rate of a reaction at any one particular time during the reaction
Finding the instantaneous rate of reaction from a graph
a) Draw a tangent to the curve at the time asked
b) Choose two good points on the tangent
c) Find the slope of the tangent using:
Instantaneous rate of reaction = slope at that point
What determines whether a reaction does or does not take place i.e. if products are formed or not?
• Reactants will collide with each other when mixed
• These reactants have a certain amount of energy
• If the colliding reactants meet the required energy (activation energy), it will be an effective collision
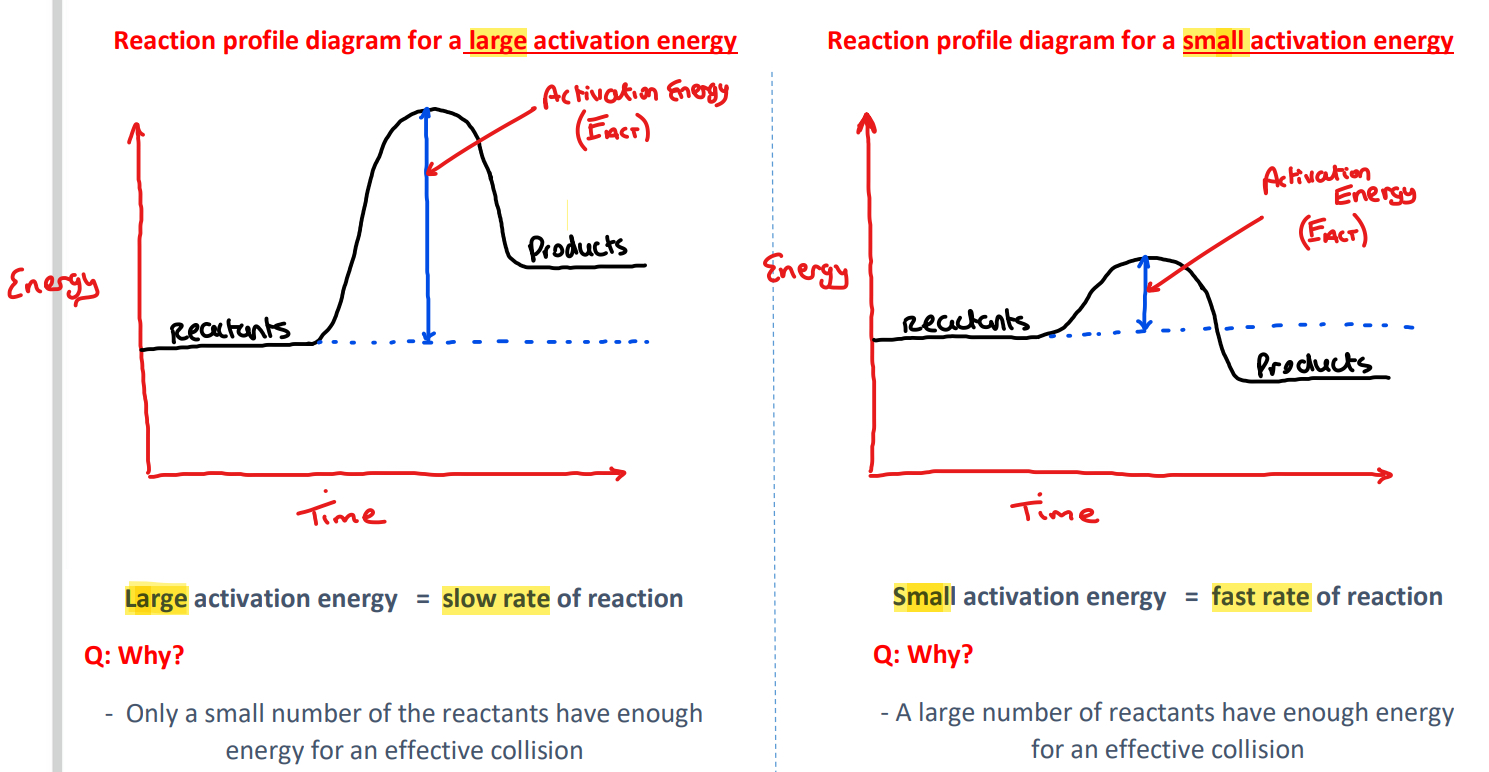
What is activation energy?
Activation energy is the minimum combined energy of colliding particles for effective collisions/for a reaction to take place
What is meant by an effective collision?
An effective collision is one that reaches activation energy and that results in the formation of products
Using reaction profile diagrams to represent the energy changes in a reaction
1) Large activation energy Vs small activation energy
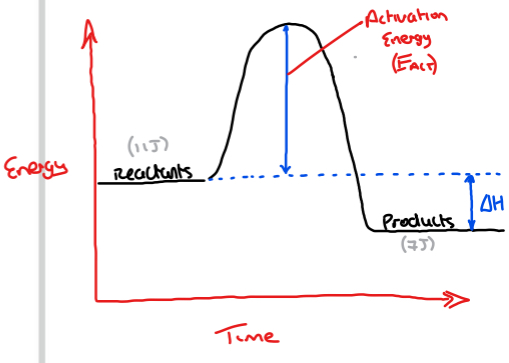
Reaction profile diagram for an exothermic reaction
Produces and gives out heat to its surroundings
A + B → C + D + Energy
Reactants → Products
Notice: In an exothermic reaction
- Energy of products is less than energy of reactants
△H = Energy of products - Energy of reactants
(△H will be a negative value)
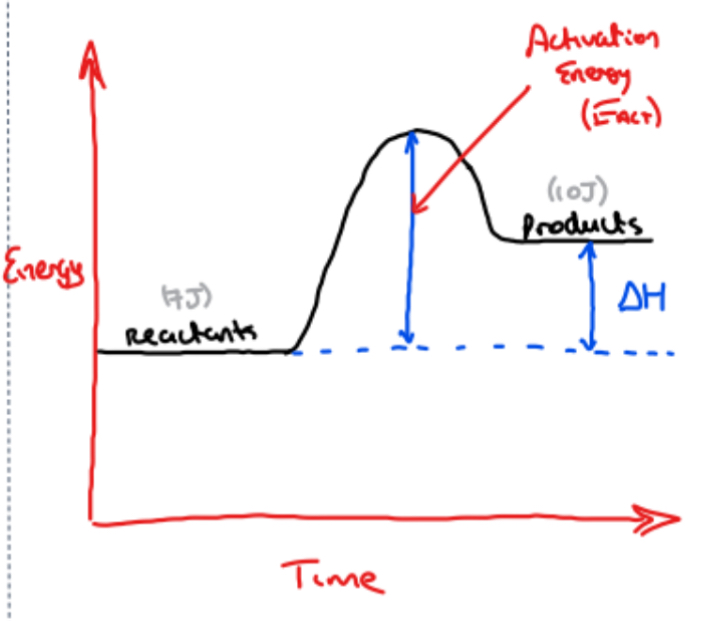
Reaction profile diagram for an endothermic reaction
Takes in heat from its surroundings
A + B → C + D + Energy
Reactants → Products
Notice: In an endothermic reaction
- Energy of products is greater than energy of reactants
△H = Energy of products - Energy of reactants
(△H will be a positive value)
Factors affecting the rate of a reaction: 1) NATURE OF REACTANTS
a) Reactions involving ionic compounds in solution - Faster reactions
Reason:
- In solution, ionic compounds are dissociated, and present as free ions
- No bond breaking is required, the activation energy is lower, and the reactions are fast
Example: Reaction of solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride
Note:
- Silver nitrate will not react with sodium chloride at all when they are in the solid state
- In the solid state the ions are not dissociated and are held tightly by ionic bonding in a crystal lattice
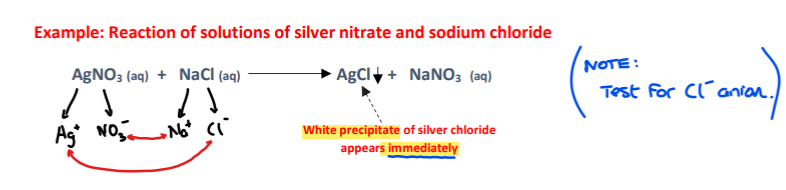
Factors affecting the rate of a reaction: 1) NATURE OF REACTANTS
b) Reactions involving covalent compounds → Slower reactions
Reason:
- Covalent compounds are not dissociated
- The covalent bonds need to be broken and new ones reformed, the activation energy is higher, and the reactions are slow
Example: Reaction of solutions of hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulfate
