IGCSE🤍
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
newton’s first law
an object at rest will remain this way unless it’s acted upon by an external force
newton’s second law
a net force causes an object to accelerate in the direction of the net force (the harder someone pushes me the faster I’ll move)
What’s the formula of force?
Force (newtons) = Mass (kg) x Acceleration (n/kg) {F = M x A}
inertia
a measure of how difficult it is to change velocity
What is the formula of inertia?
Inertia = Force / Acceleration
newton’s third law
when two objects interact they exert an equal and opposite force on each other
what are the equations of notion?
S displacement
U initial velocity
V final velocity
A acceleration
T time
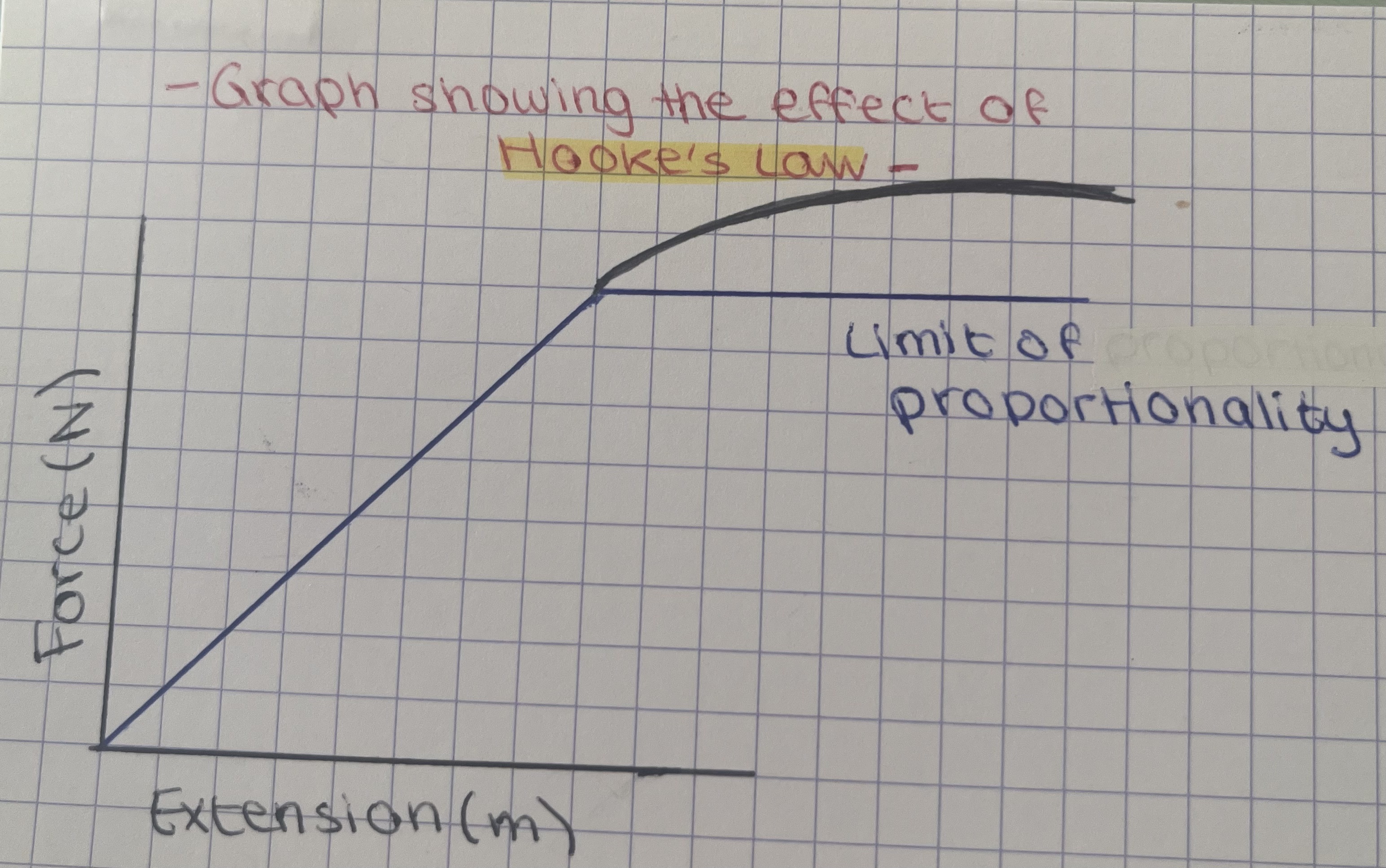
what does Hooke’s Law state?
the extension object is proportional to the force applied (springs, extensions and elasticity)
deformation
when a force may produce a change in size and shape of a body
elastic deformation
the object returns to its original shape
plastic deformation
the object does not return to its original shape
elastic limit
when an object is stretched out to a point where it cannot return to its original shape
what is the formula of Hooke’s Law?
F = kx or F = K x E
F is the force applied to the spring in Newtons
k is the spring constant in Nm -1
z or E is the extension in meters (m)
energy
the ability to do work
cannot be created or destroyed
8 types of energy
it can be stored or transferred from one form to the another
measured in Joules (J)
gravitational potential energy
any object in a gravitational field has a gravitational potential energy due to its position in that filed
depends on the distance between 2 objects
what is the formula for the gravitational potential energy?
GPE (joules) = weight (newtons) x height (meters)
GPE = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (newtons per kilogram {Nkg-1}) x height (meters)
what is the formula for work?
work done = force x distance
what is the formula for power?
power = energy / time = power = work / time
unit of power: WATTS
conduction
the movement of heat through a solid
convenction
the movement of heat in a fluid
radiation
the emission of energy as electromagnetic waves
thinking distance
the distance the car travels in split second between a hazard appearing and the driver applying the brakes
braking distance
the distance the car travels during its deceleration whilst the brakes are being applied
what are the main effects of both thinking and breaking distance?
Thinking distance:
How fast you are going
Being wide awake (tiredness, drugs, carelessness, alcohol, old age)
Visibility- rain, on going lights, fog and the night
Braking distance:
How fast you are going
The mass (or load) of the vehicle
If the car is poorly maintained (brakes & tires)
The grip of the road surface - on a wet road you can skid twice as long
what are the different types of energy?
Electrical
Light
Sound
KInetic
Thermal
Gravitational
Elastic
Chemical
kinetic energy
anything which moves
(example: running)
gravitational
anything above the ground has gravitational potential energy
efficiency
useful energy transferred by the device (J)
what is the formula for efficiency?
energy supplied = useful energy delivered + wasted energy
density
the mass of a substance per unit volume
usually expressed in g/cm 3
What is the formula for density?
density = mass / volume
mass = density x volume
volume = mass / density
what is the formula for pressure?
pressure = force / area
Force is measured in Newtons (N)
Area is measured in meters squared (m2)
The unit of pressure is Newtons per second meter (N/m2)
what is the formula for sankey diagrams?
output / total input x 100
how is electricity transported from the source to your home? (formula)
power station → transmission lines → home
electrical circuit
a closed loop that allows electric current to flow from a power source, through various components and back to the power source
What are the parts of a plug ?
earth wire: protects the user if there is a fault
live wire: electrical energy travels through this wire to the appliance
neutral wire: completes the circuit
socket: the insert for the plug
conductors
allows transports of electricity
(example: copper)
what’s the role of a conductor?
make the device/appliance work
insulators
doesn’t allow transport of electricity
(example: plastics)
what is the role of insulators?
protect users from getting electrocuted
current rating
level of current, if electricity power surges or deliver overcurrents (“goes over current rating”), the fuse burns out or breakers turn off
what are conditions needed for appliance with metal casting?
to have an earth wire connected to casting and ground
needs to drain electricity to the ground for protection if there’s a damage on the circuit and accidentally connects the wire to casting
this is dangerous
what’s the role of appliance switches?
connects and disconnects device to main electrical circuit
electrical resistance
the opposition to flow of electric current, electrical energy is converted to heat or/and light
what is the formula for electrical power?
the higher the electrical power, the brighter the light produced
energy input / used per unit time (Js = W)
what’s the formula for electrical current?
power {P} (watts) = current {I} (c/s) x voltage {V} (J/c)
what’s the formula for electrical energy?
Power {P} = Electricity energy used {E} (joules) / Time duration {T} (sec)
voltage
“potential difference”
this is what drives the current to flow
pushes charges to flow
cathode - anode, which one is positive and which one is negative?
cathode is a POSITIVE charge
anode is a NEGATIVE change
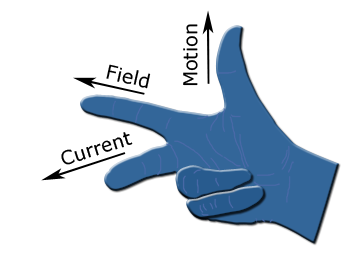
the diagram shoes Fleming’s right hand rule
ammeter
a device that measures current in a circuit
what are the properties of a ammeter?
connected in series with the component
has very low resistance it will have no effect on the current on the circuit
it measures the amount of charges passing per unit time (Q/t)
voltmeter
a device that measures voltage in a circuit
what are the properties of a voltmeter?
connected in parallel with the component
has very low resistance it will have no effect on current on the circuit
measures the amount of energy transferred to a coulomb of charge
circuit diagram
simplified pictorial representation of an electrical circuit where in electrical components are represented by circuit symbols
used to easily see the connectivity of electrical compounds
easy to draw
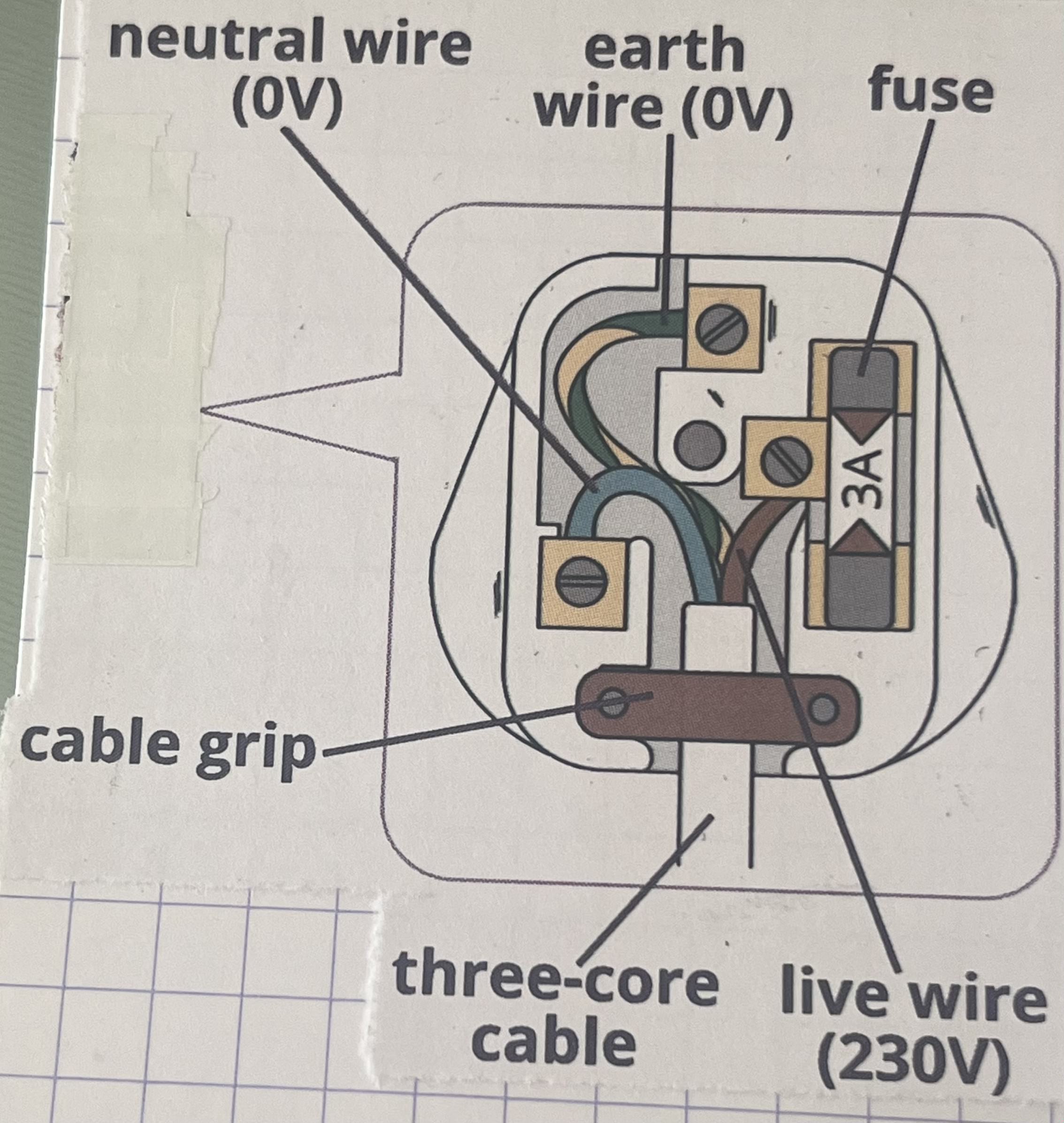
What’s the function of each part of a plug?
earth wire: provides a path for electric current to flow from the casting of the appliance to the ground
live wire: carries to the alternating potential difference of 230V from the supply
neutral wire: completes the circuit
fuse: designed to melt and break the circuit if the current flowing through it exceeds its rating
cable grip: holds cable tightly in place so that wires don’t become loose and touching the external castings
what will happen if a surge of current flows a fuse?
it will melt and the circuit will be broken
if fuse is said to have blown, would then need to be replaced
what is the role of circuit breakers?
switches on circuit breakers are driven by electromagnets
detects surges in current
when detected, a switch is opened, immediately breaking the circuit
can be reset by clicking the switch back to its original position
makes them much more convenient than fuses
resistor
an electrical component that resists the flow of an electric current
how does a electrical fault develops?
electrical fault develops → surge of current through earth wire → fuse melts, isolating appliance from live → appliance safe
what are fuses and circuits designed to do?
cut off the flow of electricity to the appliance
only occur of a surge of electricity flows through the appliance
what is the resistors used for?
to limit the amount of current that flows through a circuit
Ohm’s law (Ω)
as the resistance of circuit increases, the current will decreases
as temperature increases, resistance also increases
what is power in physics?
when work is done on a object, energy is transferred. The rate at which this energy is transferred is called power. So the more powerful a device is , the more energy it will transfer each second
power
amount of energy that is transferred per second
measured in joules per second or watts (W)
devices that transfer lots of energy are measured in kilowatts (kW)
what does the power of an appliance (P)?
Energy (joules) {E} = Power (watts) {P} x Time (seconds) {t}
how much energy it transfer each second
meaning total energy (E) transferred by an appliance is equal to its power multiplied by the length of time (in seconds) the appliance is being used
how would direct current appear on a voltage-time graph?
a straight horizontal line at a constant voltage
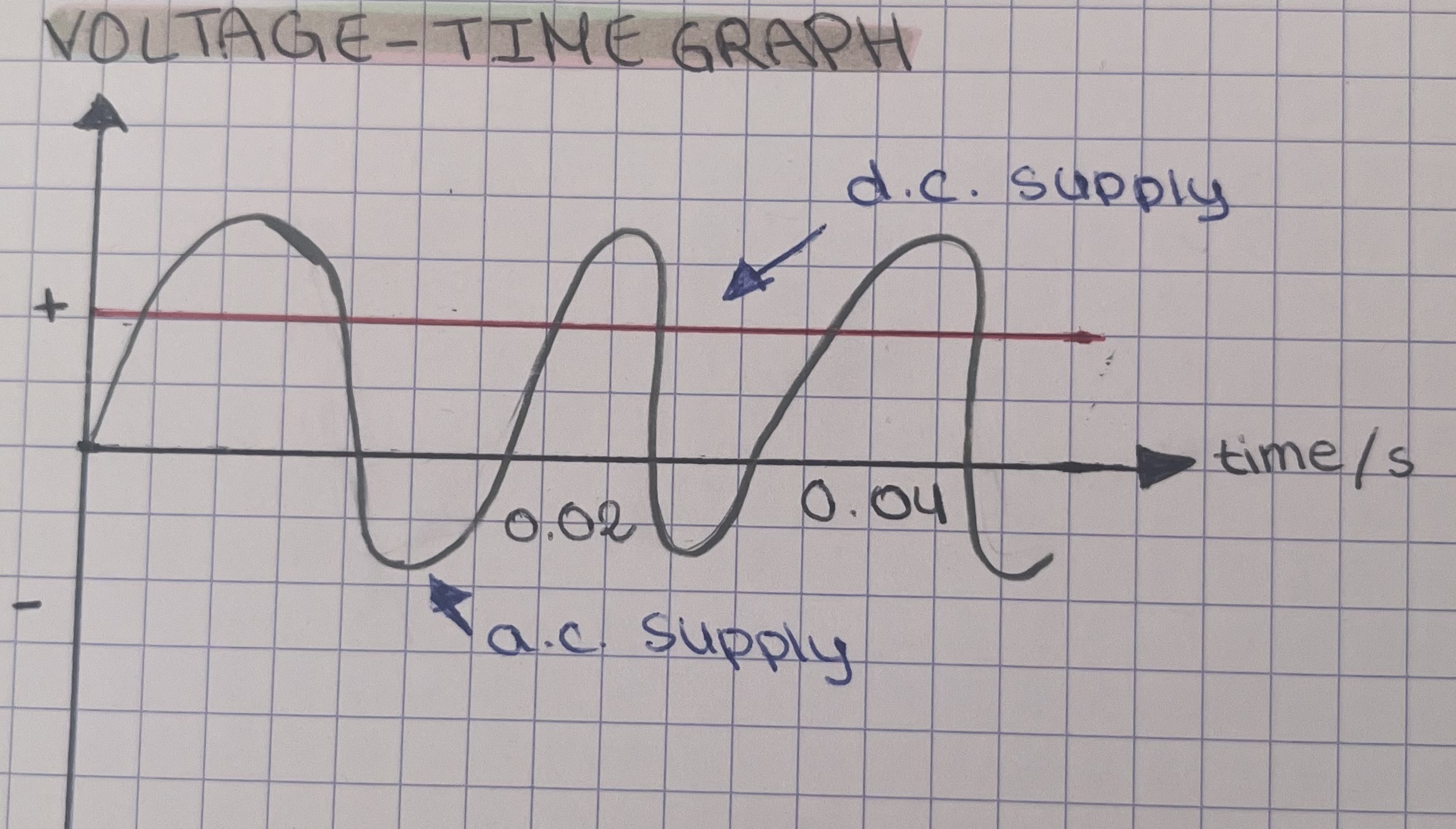
how would alternating current appear on voltage-time graph?
a curve alternating between positive and negative voltages
the positive and negative values indicate the direction of current flow
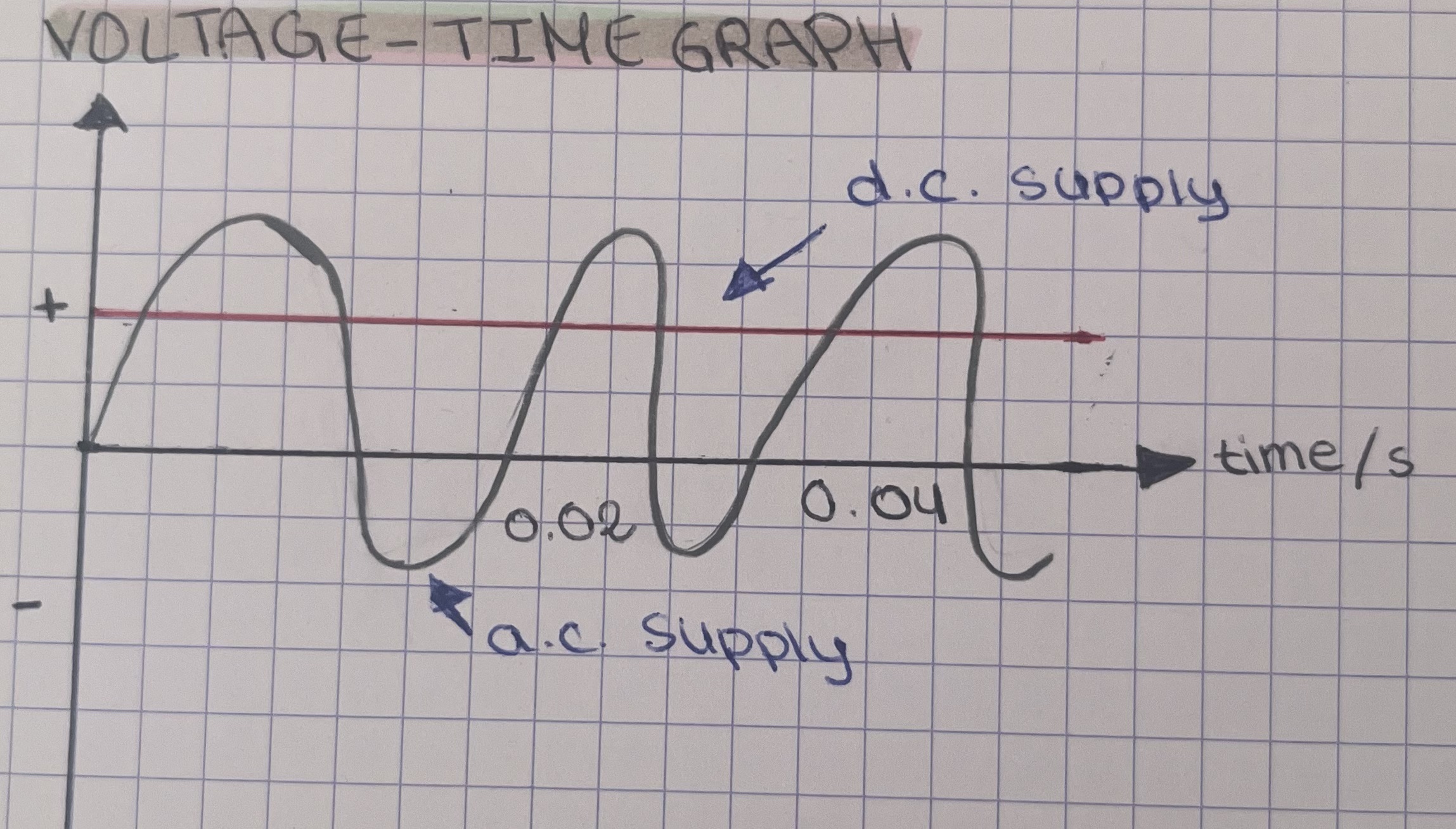
what are the main differences between alternating and direct current?
alternating current changes direction, while direct current flows in one direction
step down transformer
decreases the potential difference of the electricity transported through the transmission cables to around 230V, making it safe for domestic use
step-up transformer
increases the potential difference of the electricity produced in this generator to around 400 000V
this allows the same electrical power to be transferred at a lower current
means electricity can be transmitted along the cables of the National Grid MORE EFFICIENCY because less energy is dissipated as heat
pylon
tall structures which carry high-voltage transmission cables above the ground
what is the generator effect?
when energy is transferred from the kinetic energy store of the moving turbine to induce an electric current
What are the properties of the national grid?
The power station is fueled to power generators
The generators produced electricity
Electricity is transmitted to a step-up transformer
The voltage is increased to 400 000V
Electricity is transmitted through overhead cables on pylons
Electricity is transmitted to a step-down transformer
The voltage is decreased to 230V
Electricity is supplied to consumers in their homes at a safe voltage
what causes a transfer in energy?
the work you do because to apply a force you need to move something
the work done by a force depends on the size of the force and the distance moved
what’s the formula for work done?
work done (joules) = force applied (newtons) x distance moved in the direction of the force (meters) {energy transferred = work done}
what does work done overcome ?
friction is transferred as energy that heats the objects that rub together and heats the surroundings
the power of an appliance in measured in watts (w)
what’s the formula for power?
Power (watts,w) = work done (joules, J) / time taken (sec, s) = useful energy transferred (Joules, J) / time taken (sec,s)
gravitational potential energy
energy stored in an object because of its position in the Earth’s gravitational field
when you lift an object up, some muscles transfer chemical energy from the muscles into gravitational potential energy of the object
What are the properties of gravitational potential energy?
the upward force you need to apply to it is equal to the object’s weight
when an object is moved up, its gravitational potential energy increases
when an object is moved down, its gravitational potential energy decreases
The work done when an object moves or down depends on, what?
1) how far it is moved vertically (its change of height)
2) its weight
what’s the formula for the change of gravitational potential energy?
change of gravitational potential energy (J) = weight (N) x change of height (m)
change of gravitational potential energy (J) = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg) x change of height 9m0
What is the main properties of energy?
energy CANNOT be created or destroyed
What’s the formula for kinetic energy?
kinetic energy (joules) = ½ x mass (kg) x speed² (m/s²)
elastic potential energy
the energy stored in an elastic object when work is done on it to change its shape (example: when you stretch a rubber band the work you do its stored in it as elastic potential energy)
wasted energy
dissipated (spreads out) to the surroundings
useful energy
eventually transfers to the surroundings too
energy is less useful the more it spreads out
how can you represent any transfer in which energy is wasted?
sankey diagram
what’s the formula for input energy?
input energy (energy supplied) = useful energy transferred + energy wasted
what’s the formula for efficiency?
efficiency = useful power out / total power in x 100 %
what is THE property of energy?
it CANNOT be created or destroyed
exothermic
transfer energy from the reacting chemicals to their surroundings
what’s an example of exothermic reactions?
the burning of fuels such as combusion of methane gas
what happens when methane burns?
when methane (the main gas present in natural gas) burns, it gets oxidised and releases energy to its surroundings
what is another example of exothermic reactions?
netralisation
how can you measure the rise in the temperature?
by using simple apparatus
the products of exothermic reactions have a lower energy content than reactants
what is used to measure the differences in energy?
kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol)n
endothermic
transfer energy from the surroundings to the reacting chemicals
what is an example of endothermic reactions?
decomposition of calcium carbonate
thermal decomposition reaction
what happens to the decomposition of calcium carbonate?
when heated, it forms calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. This reaction only takes place if you keep heating the calcium carbonate strongly
the calcium carbonate needs to absorb energy from the surroundings
the products have a higher energy content than the reactants
what can exothermic changes be used for?
they can be used in hand warmers and self-heating cans