social psychology (vs. personality psychology in prev. module)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
social psychology
-scientific study of how individuals think about, influence, and relate to each other
2
New cards
personality psychologists
study personality traits and processes that explain why people may act differently in a given situation
3
New cards
social psychologists
study social influences that explain why the same person may act differently in situations
4
New cards
conformity
refers to adjusting our behavior to thinking to fit in with a group standard
5
New cards
the power of conformity has many components and forms, including
-automatic mimicry, affecting behavior
-social norms affecting our thinking
-normative and informational social influence
-social norms affecting our thinking
-normative and informational social influence
6
New cards
automatic mimicry
some of our mimicry of other people is not by choice, bit automatic:
-contagious yawning, arm folding, hand wringing, face rubbing, etc.
-adopting accents, grammar, vocbulary
-empathetic shifts in mood
-adopting coping styles of parents or peers, including violence, yelling, withdrawal
-contagious yawning, arm folding, hand wringing, face rubbing, etc.
-adopting accents, grammar, vocbulary
-empathetic shifts in mood
-adopting coping styles of parents or peers, including violence, yelling, withdrawal
7
New cards
responding to social norms
-when we are with other people we percieve a social norm (a “correct” or “normal” way to behave or think in this group), our behavior may follow the norm rather than following our own judgement
-asch conformity studies
-asch conformity studies
8
New cards
asch conformity studies
square w/ 5 sides
results: about 1/3 of people will agree with obvious mistruths to go along with the group
results: about 1/3 of people will agree with obvious mistruths to go along with the group
9
New cards
what makes you more likely to conform
when...
-you are not firmly committed to set of beliefs or style of behavior
-the group is medium sized and unanimous
-you admire or are attracted to the group
-the group tries to make you feel incompetent, insecure, and closely watched
-your culture encourages respect for norms
-you are not firmly committed to set of beliefs or style of behavior
-the group is medium sized and unanimous
-you admire or are attracted to the group
-the group tries to make you feel incompetent, insecure, and closely watched
-your culture encourages respect for norms
10
New cards
normative social influence
ex. going along with others in pursuit of social approval or belonging (and to avoid disapproval/rejection)
-the Asch conformity studies; clothing choices
-the Asch conformity studies; clothing choices
11
New cards
informational social influence
ex. going along with others because their ideas and behavior make sense, the evidence in our social environment changes our minds
-deciding which side of the road to drive on
-deciding which side of the road to drive on
12
New cards
obedience
response to commands
13
New cards
miligram
wanted to study the influence of direct commands on behavior (shock test)
the question: under what social conditions are people more likely to obey commands?
the experiment: an authority figure tells participants to administer shocks to a “learner” (who was actually a confederate of the researcher) when the learner gives wrong answers
--> voltage increases; how high will people go?
-15-450
the question: under what social conditions are people more likely to obey commands?
the experiment: an authority figure tells participants to administer shocks to a “learner” (who was actually a confederate of the researcher) when the learner gives wrong answers
--> voltage increases; how high will people go?
-15-450
14
New cards
compliance in milligrams study
-in surveys, most people predict that in such a situation they would stop administering shocks when the “learner” expressed pain.
-but in reality, even when the learner complained of a heart condition, people complied with the experimenter’s directions:
-“please continue”
-“you must continue”
-“the experiment requires that you continue"
-but in reality, even when the learner complained of a heart condition, people complied with the experimenter’s directions:
-“please continue”
-“you must continue”
-“the experiment requires that you continue"
15
New cards
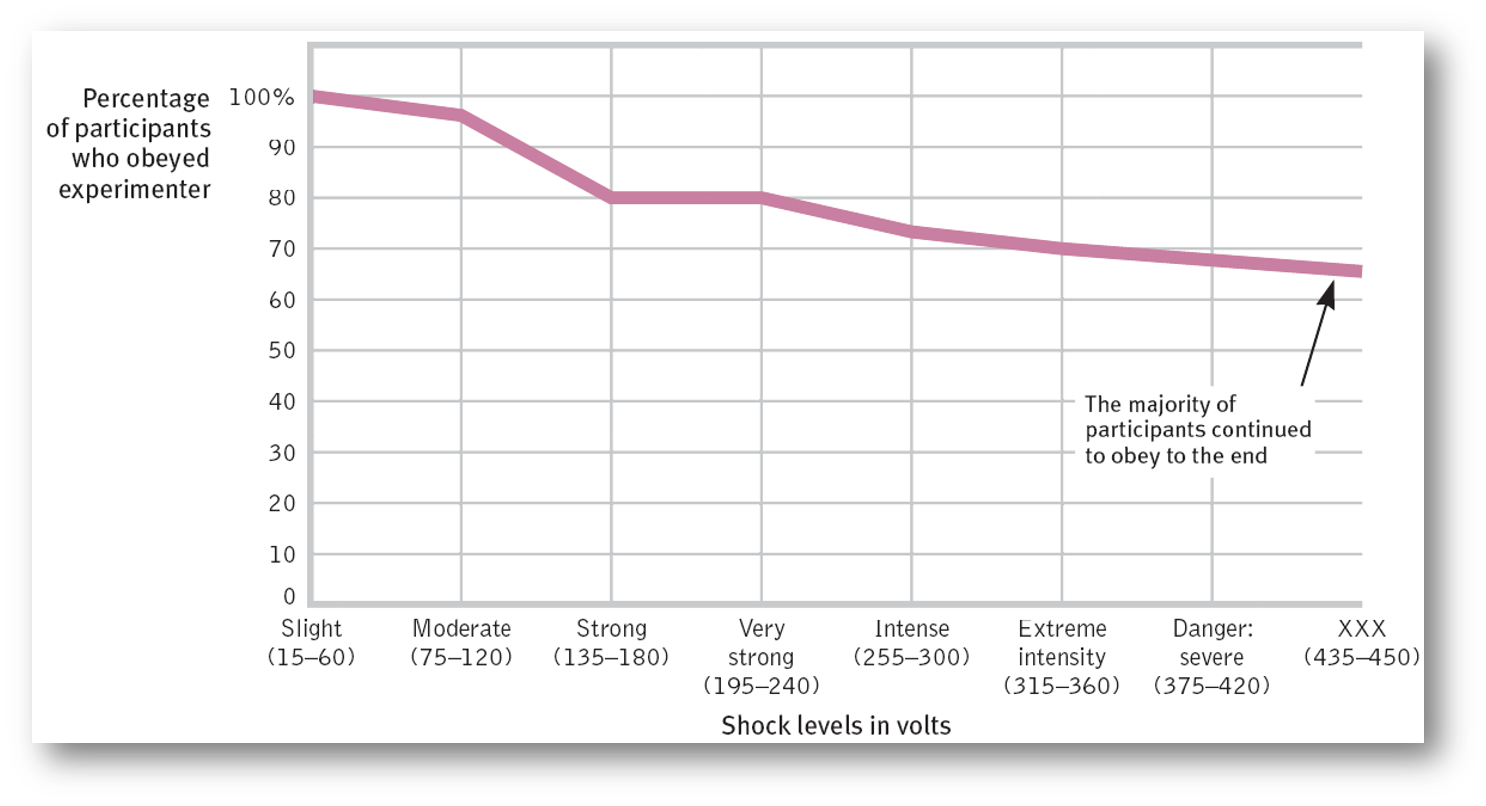
how far did compliance go?
majority of participants (65%) obeyed to the end
16
New cards
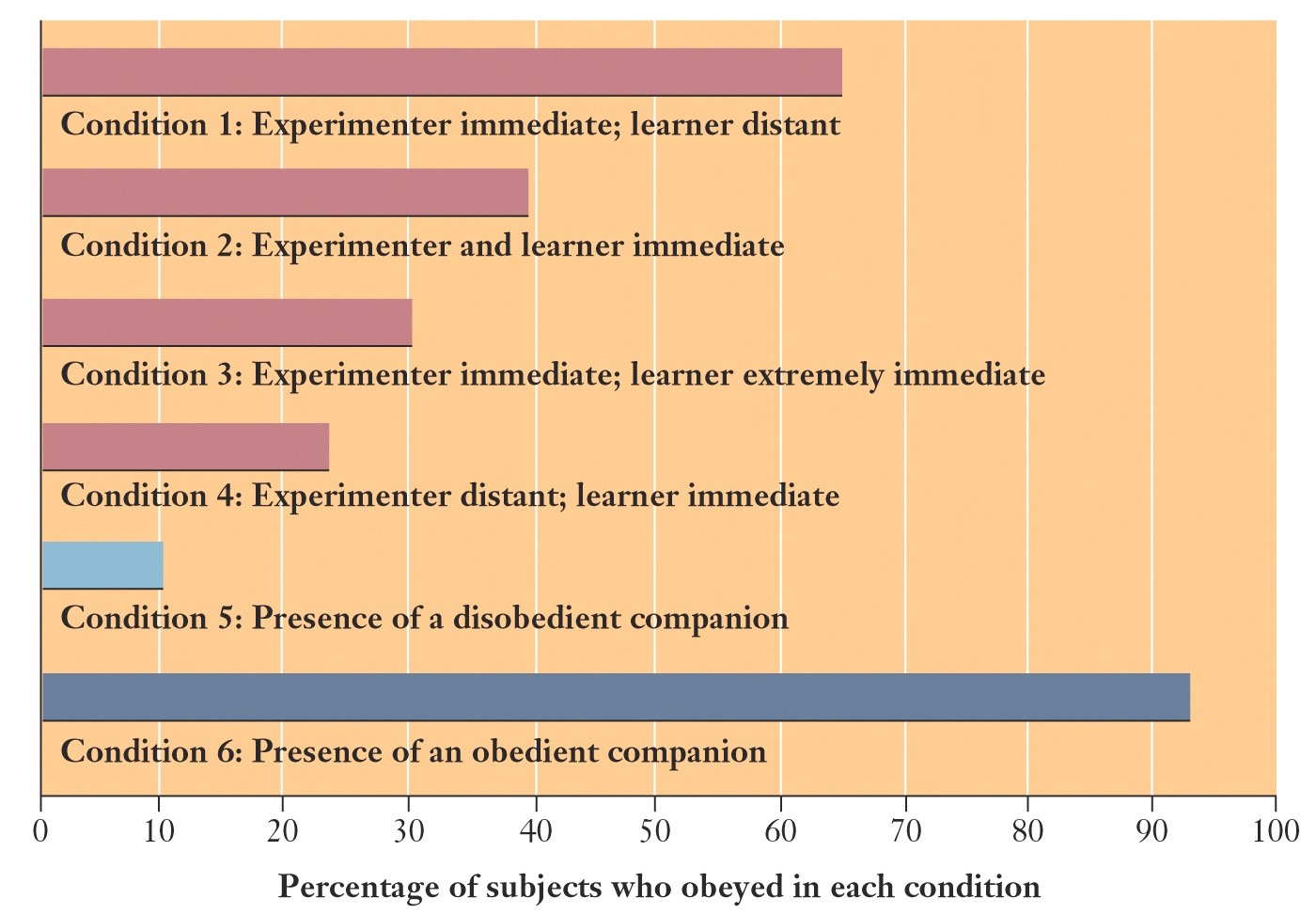
results of milligram’s experiments, by condition
-65% obeyed (almost most) when experimenter was immediate and learner was distant
-39% when experimenter and learner immediate
-30% when experimenter immediate and learner EXTREMELY immediate
-23% when experimenter distant, learner immediate
-10% when disobedient companion is present
-93% when obedient companion is present (MOST)
-39% when experimenter and learner immediate
-30% when experimenter immediate and learner EXTREMELY immediate
-23% when experimenter distant, learner immediate
-10% when disobedient companion is present
-93% when obedient companion is present (MOST)
17
New cards
what factors influence obedience
-when orders were given by
--> someone with legitimate authority
-->someone associated with a prestigious institution (Yale)
--> someone standing close by
-when the “learner”/victim is in another room
-when other participants obey and/or no one disobeys (no role model for defiance)
BAD NEWS: in war, ppl choose not to fight and kill at beginning, but obedience escalates and they end up killing even innocent ppl
GOOD NEWS: strengthens heroism, soldiers and others risk/sacrifice themselves even more when under orders
--> someone with legitimate authority
-->someone associated with a prestigious institution (Yale)
--> someone standing close by
-when the “learner”/victim is in another room
-when other participants obey and/or no one disobeys (no role model for defiance)
BAD NEWS: in war, ppl choose not to fight and kill at beginning, but obedience escalates and they end up killing even innocent ppl
GOOD NEWS: strengthens heroism, soldiers and others risk/sacrifice themselves even more when under orders
18
New cards
lessons from the conformity and obedience studies
-when under pressure to conform or obey, ordinary, principled people will say and do things they never would have believed they would do.
-->the real evil may be in the situation
-to look a person committing harmful acts and assume that the person is cruel/evil would be to make the fundamental attribution error
-->the real evil may be in the situation
-to look a person committing harmful acts and assume that the person is cruel/evil would be to make the fundamental attribution error
19
New cards
social influence: group behavior
besides conformity and obedience, there are other ways that our behavior changes in the presence of others, or within a group:
-social facilitation
-social loafing
-deindividuation
-groupthink
-group polarization
-social facilitation
-social loafing
-deindividuation
-groupthink
-group polarization
20
New cards
social facilitation
-individual performance is intensified when you are observed by others
-experts excel, people doing simple activities show more speed and endurance in front of an audience,,, but novices, trying complex skills, do worse
-experts excel, people doing simple activities show more speed and endurance in front of an audience,,, but novices, trying complex skills, do worse
21
New cards
Why would the presence of an audience “facilitate” better performance for everyone but newcomers?
being watched, and simply being in crowded conditions, increases one’s autonomic arousal, along with increasing motivation for those who are confident, but anxiety for those who aren’t
22
New cards
social loathing
the tendency of people in a. group to show less effort when not held accountable
- someone slaking off in a group project
- someone slaking off in a group project
23
New cards
when does social loafing happen?
-when your contribution isn’t rewarded or punished, you might not care what people think
-people may not feel their contributions are needed, that the group will be fine
-people may feel free to “cheat” when they get an equal share of the rewards anyway
-note: ppl in collectivist cultures don’t slack off as much in groups even when they could. why?
-people may not feel their contributions are needed, that the group will be fine
-people may feel free to “cheat” when they get an equal share of the rewards anyway
-note: ppl in collectivist cultures don’t slack off as much in groups even when they could. why?
24
New cards
deindividuation
loss of self-awareness and self-restraint
-ex.: riots, KKK rallies, concerts, identity-concealing online bullying
-happens when people are in group situations involving anonymity and arousal
-ex.: riots, KKK rallies, concerts, identity-concealing online bullying
-happens when people are in group situations involving anonymity and arousal
25
New cards
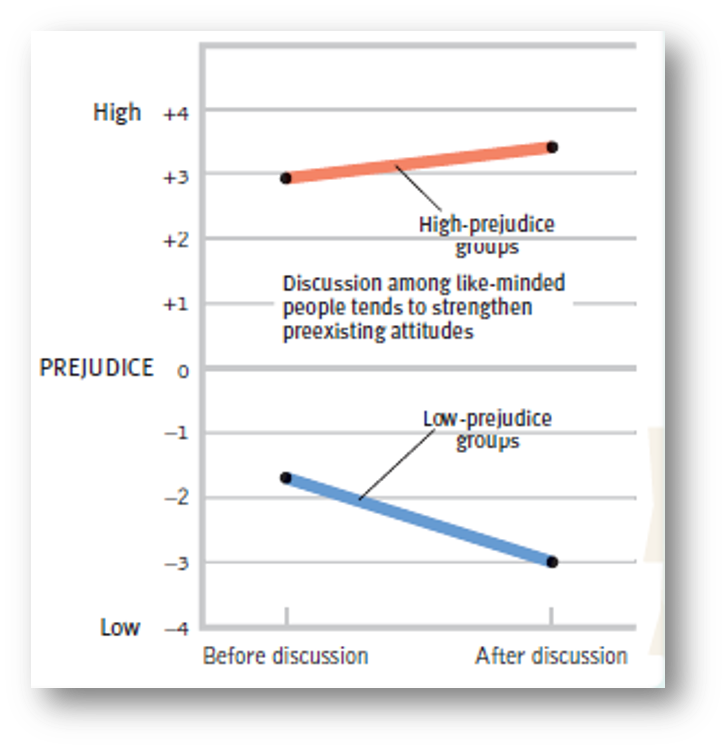
group polarization
-when people of similar views form a group together, discussion within the group makes their views more extreme
-thus, different groups become MORE different, more polarized, in their views.
-ppl in these groups may have only encountered ideas reinforcing the views they already held
-thus, different groups become MORE different, more polarized, in their views.
-ppl in these groups may have only encountered ideas reinforcing the views they already held
26
New cards
social influence: the power of individuals
despite all of these forces of social influence, individuals till have power:
-some people resist obeying and conforming
-individuals can start social movements and social forces, not just get caught up in them
-groupthink can be prevented if individuals speak up when a group decision seems wrong.
-some people resist obeying and conforming
-individuals can start social movements and social forces, not just get caught up in them
-groupthink can be prevented if individuals speak up when a group decision seems wrong.