Chapter 18 Review-Cold War Conflicts
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1. The Soviets and the Americans disapproved of each others' political and economic systems.
2. The Soviets were angry that the U.S. had taken so long to launch an attack against Hitler in Europe.
3. Stalin did not like that the U.S. had kept the development of the atomic bomb a secret.
4. The Americans were also angry that the Soviets signed a treaty with Hitler before WWII.
What were 4 issues that led to hard feelings between the Soviet Union and the United States?
Unites Nations
Both the United States and the Soviet Union joined this organization after World War II. This organization was created to keep peace among nations.
Encouraging the spread of democracy in Europe
Which of the following was a goal of President Truman in Europe?
Extending communism and controlling Eastern Europe
Which of the following was a goal of Stalin in Europe?
Countries that were occupied by Soviet troops and became dependent on and dominated by the Soviet Union
What were the satellite nations created by the Soviet Union?
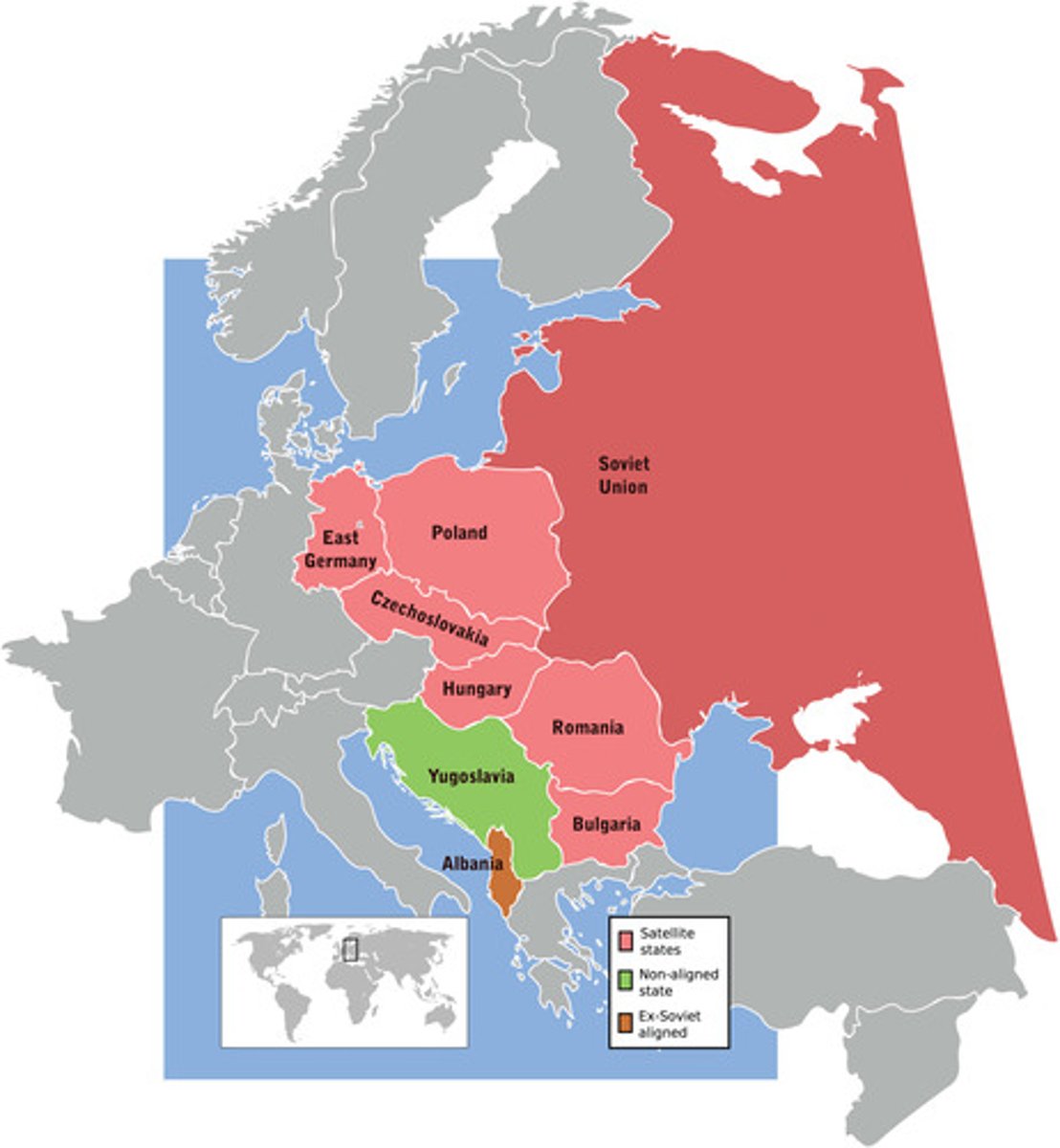
Containment Policy
This was an effort to block Soviet influence by making alliances and supporting weaker nations in order to stop the spread of communism.
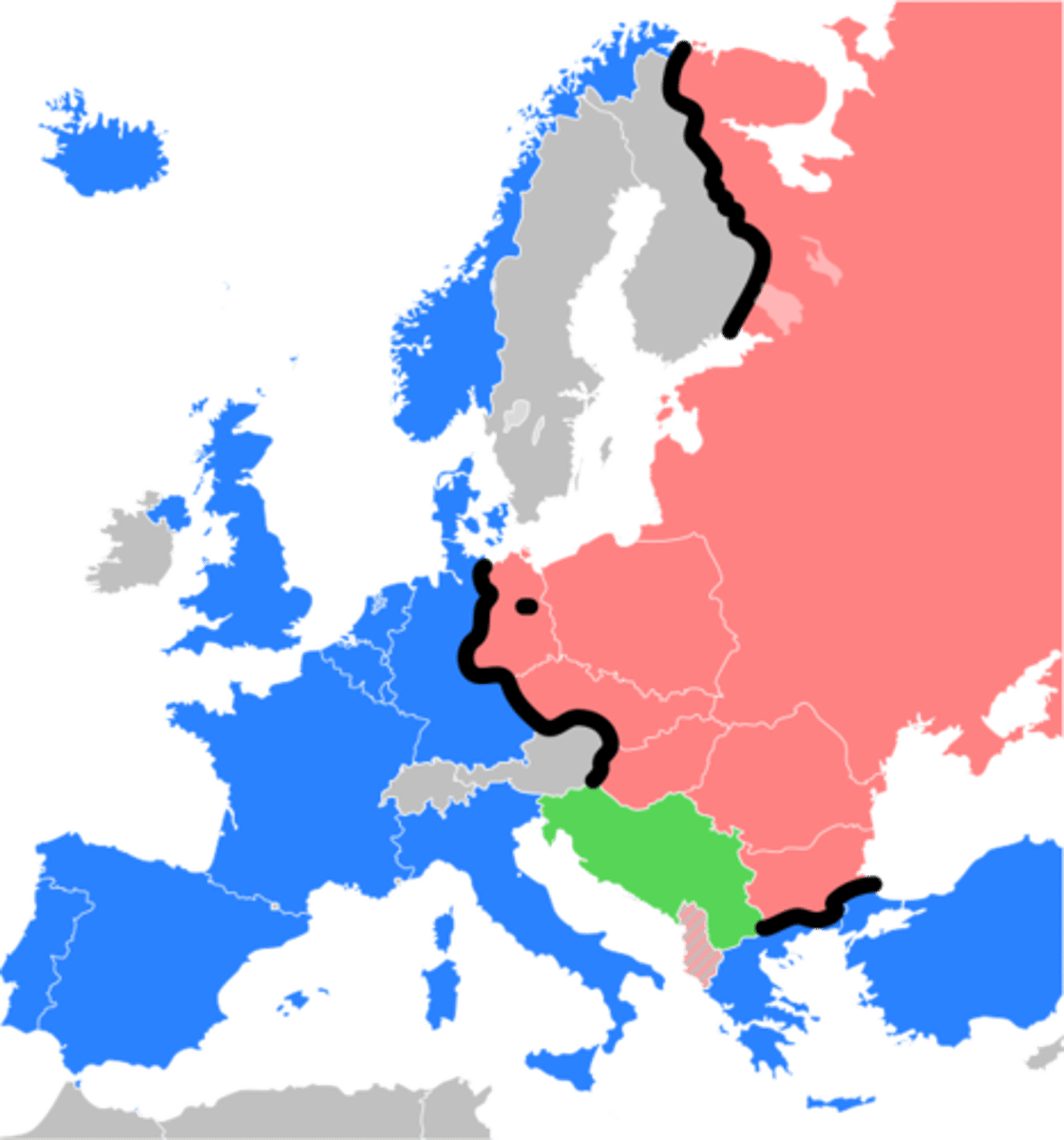
Iron Curtain
What separated the communist nations in the East from the democratic nations of the West?
Cold War
What term refers to the indirect but hostile conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union that began at the end of World War II, in which each tried to spread its political and economic influence worldwide?

Truman Doctrine
What was the U.S. policy that aimed to send aid to any nation trying to prevent communists from taking over?

Harry S. Truman
Who arranged for economic and military aid to be sent to postwar Turkey and Greece in an attempt to stop the spread of communism?

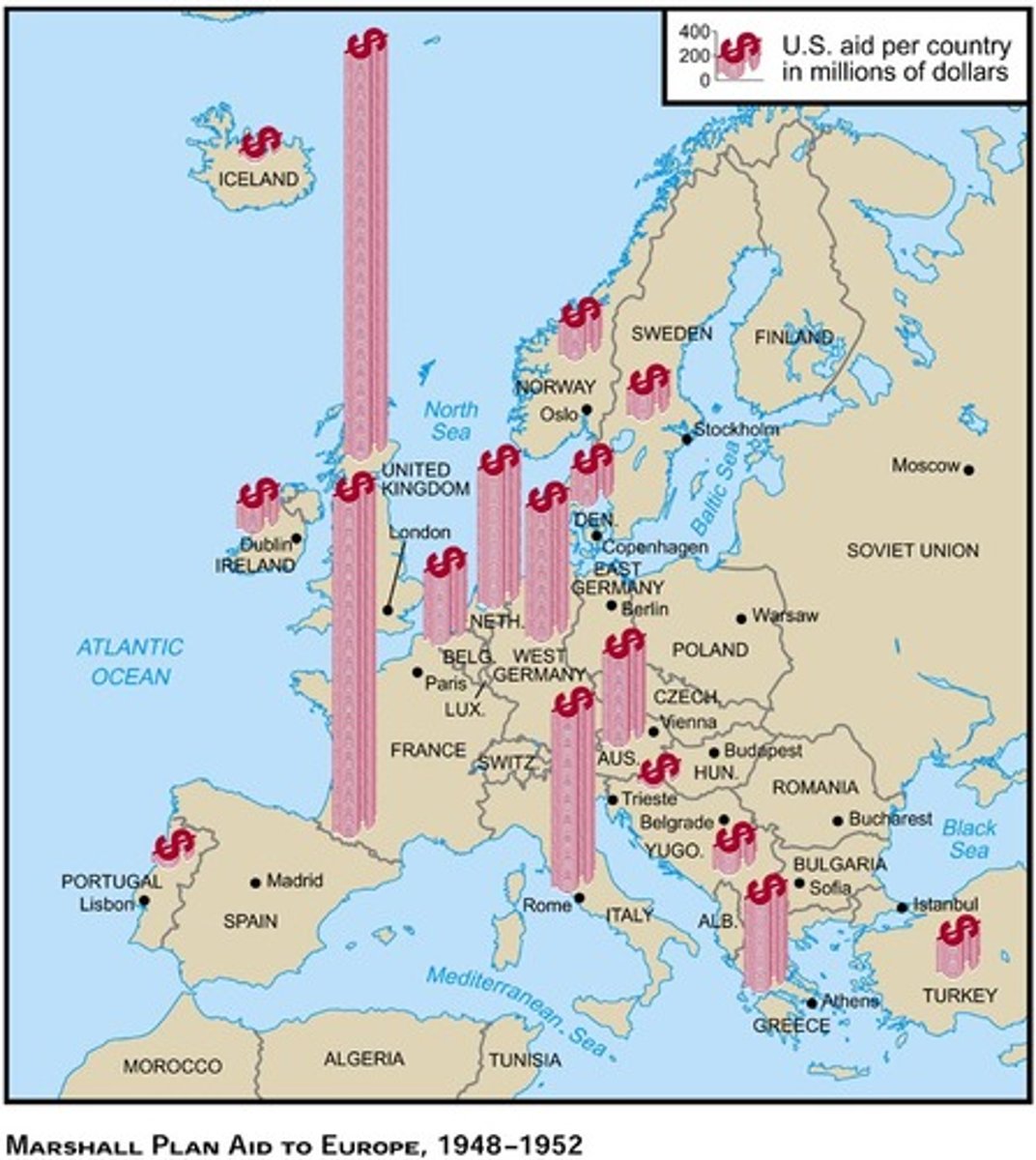
Marshall Plan
What was the program under which the United States gave economic aid to rebuild postwar Western Europe in an attempt to build strong, stable governments that would resist communism?
To keep Germany weak and divided
What was the goal of Stalin in regards to Germany?

The Soviet Union blockaded Berlin after Britain, France, and the United States combined their occupied zones into the nation of West Germany.
What was the reason for the Berlin blockade?

The Soviet Union's attempt to cut off all transportation to West Berlin until the West gave up the idea of German reunification.
What was the main goal of the Berlin blockade?
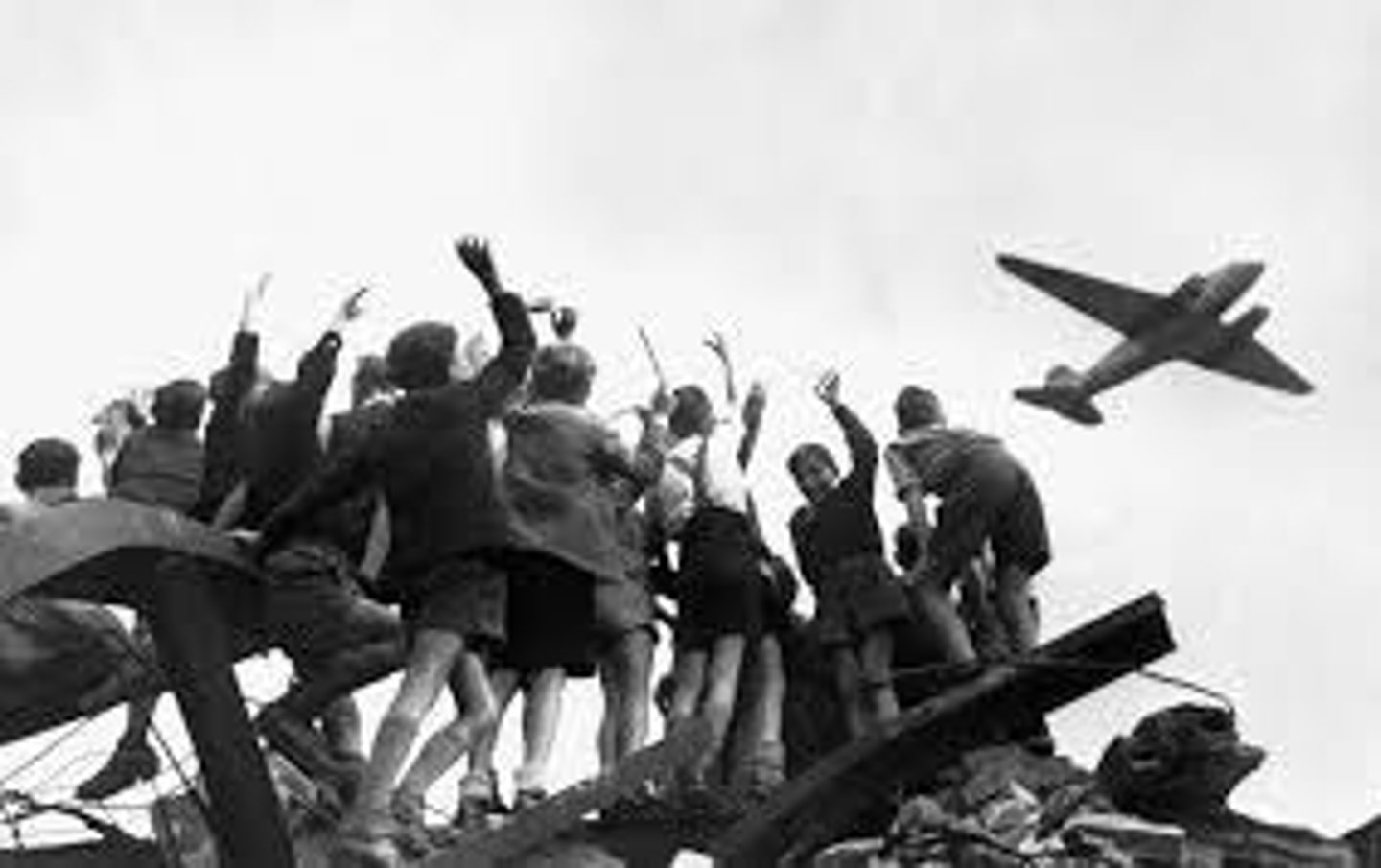

The Berlin Airlift successfully provided supplies to West Berlin and the Soviet Union ended the blockade
What was the outcome of the Berlin Blockade?
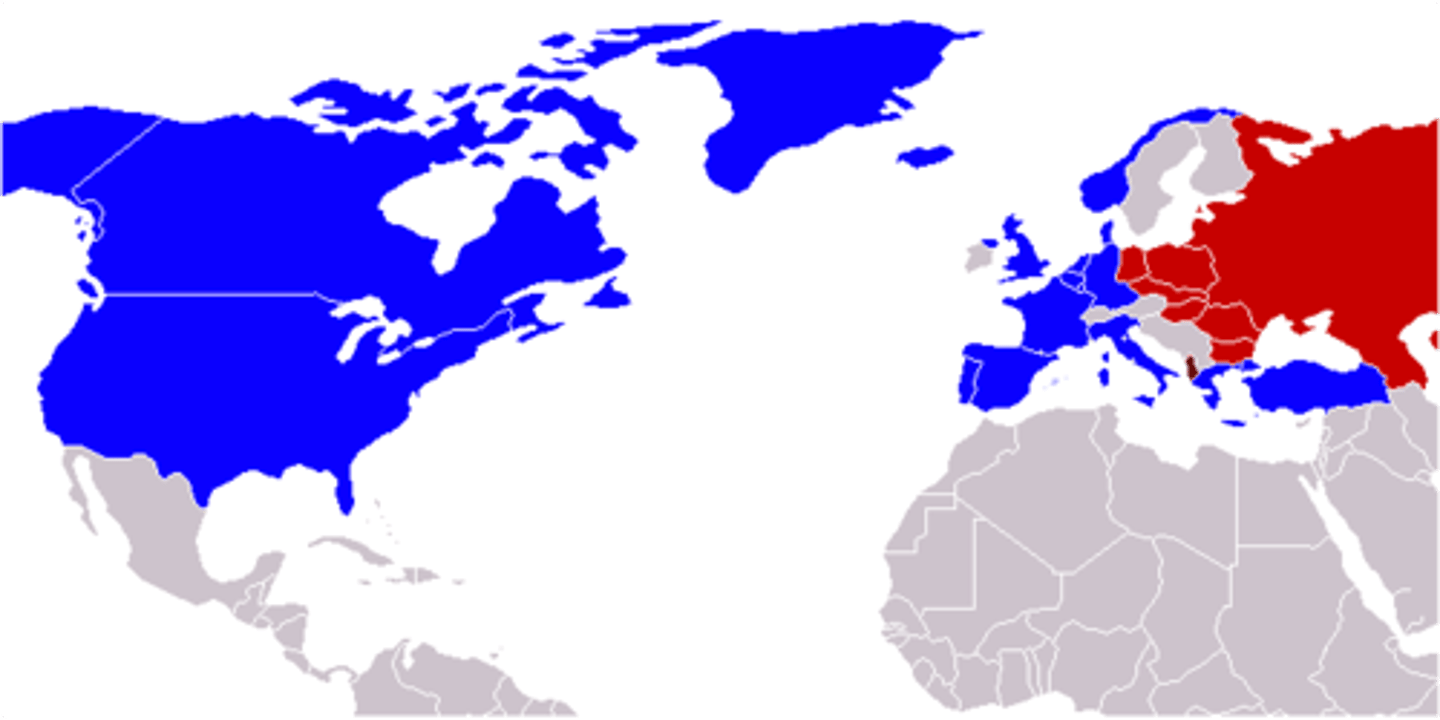
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
Worried about Soviet aggression, the U.S. and Canada joined with ten other European nations to form this defensive military alliance.
Chinese Civil War
War between communists led by Mao Zedong and nationalists led by Chiang-Kai Shek. The communists took over and forced the nationalists to retreat to Taiwan

The weak and corrupt leadership of Chiang Kai-shek.
Which of the following best describes the reason for the failure of Chiang Kai-shek's forces in the Chinese Civil War?

his weak and corrupt leadership
The failure of Chiang Kai-shek's forces in the Chinese Civil War can largely be blamed on
Mao Zedong was a Communist.
Why did Mao Zedong fail to win American support despite winning the hearts of Chinese peasants?

Nationalists
They were defeated in the civil war in China despite 2 billion dollars in aid sent to them from the U.S.
Taiwan
Island off the coast of China.
the Chinese Nationalists
Who was forced to retreat to Taiwan?
1. The peasants supported the Communists instead of the corrupt Nationalists.
2. Mao had an experienced army with high morale.
3. Truman sent aid but refused to send troops to help the Nationalists.
How did Communists gain control of China?
North and South Korea
The 38th parallel became an important dividing line between which two countries?
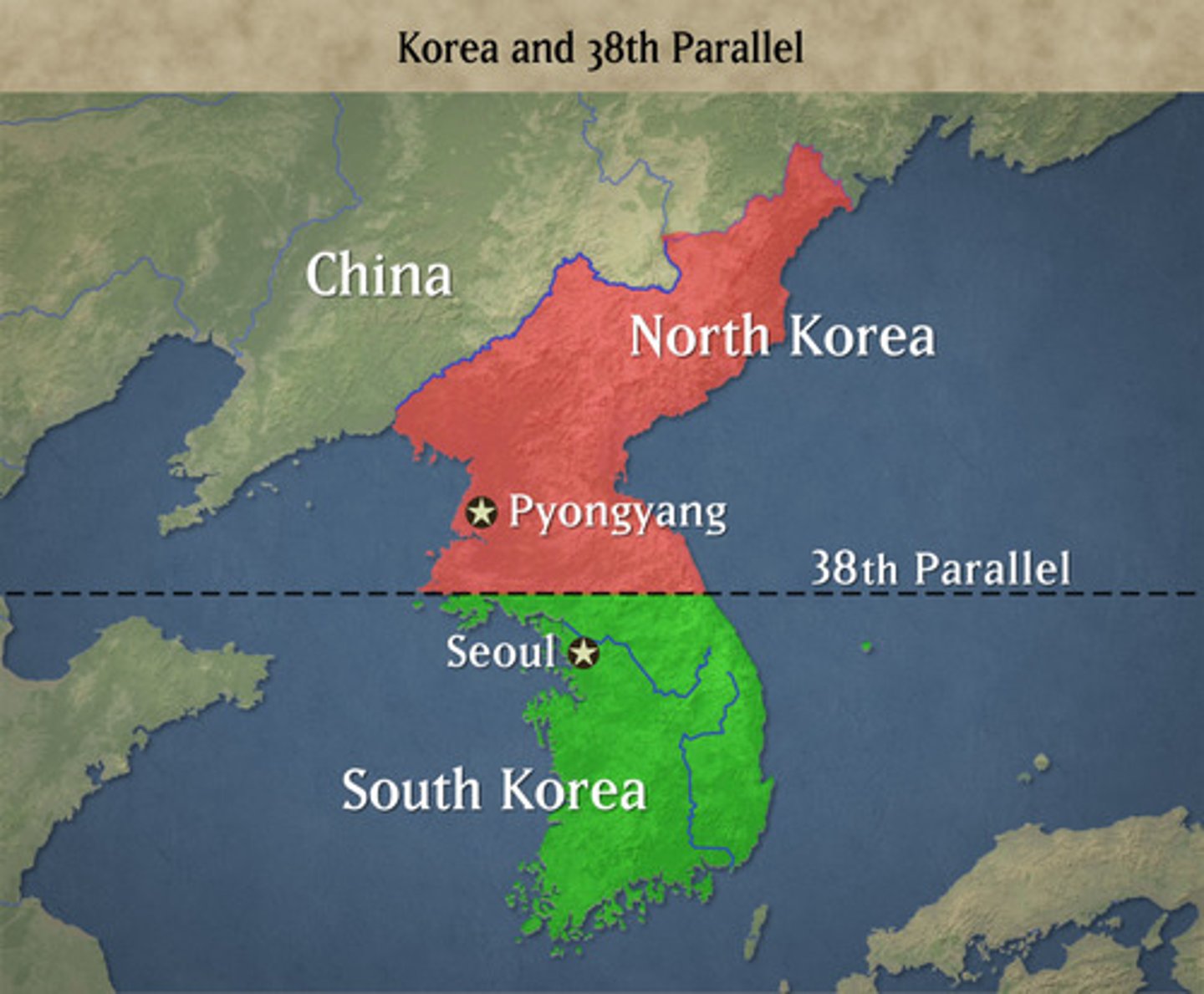
The Korean War
The conflict between Communist North Korea and Non-Communist South Korea. The United Nations (led by the United States) helped South Korea.
North Korea
Who started the Korean War by invading South Korea in June 1950?
To prevent the spread of communism
Why did President Truman order air and naval support for South Korea?
China
Which country fought on the side of the communists during the Korean War?
They feared American troops would approach their border
Why did China oppose UN forces moving into North Korea?
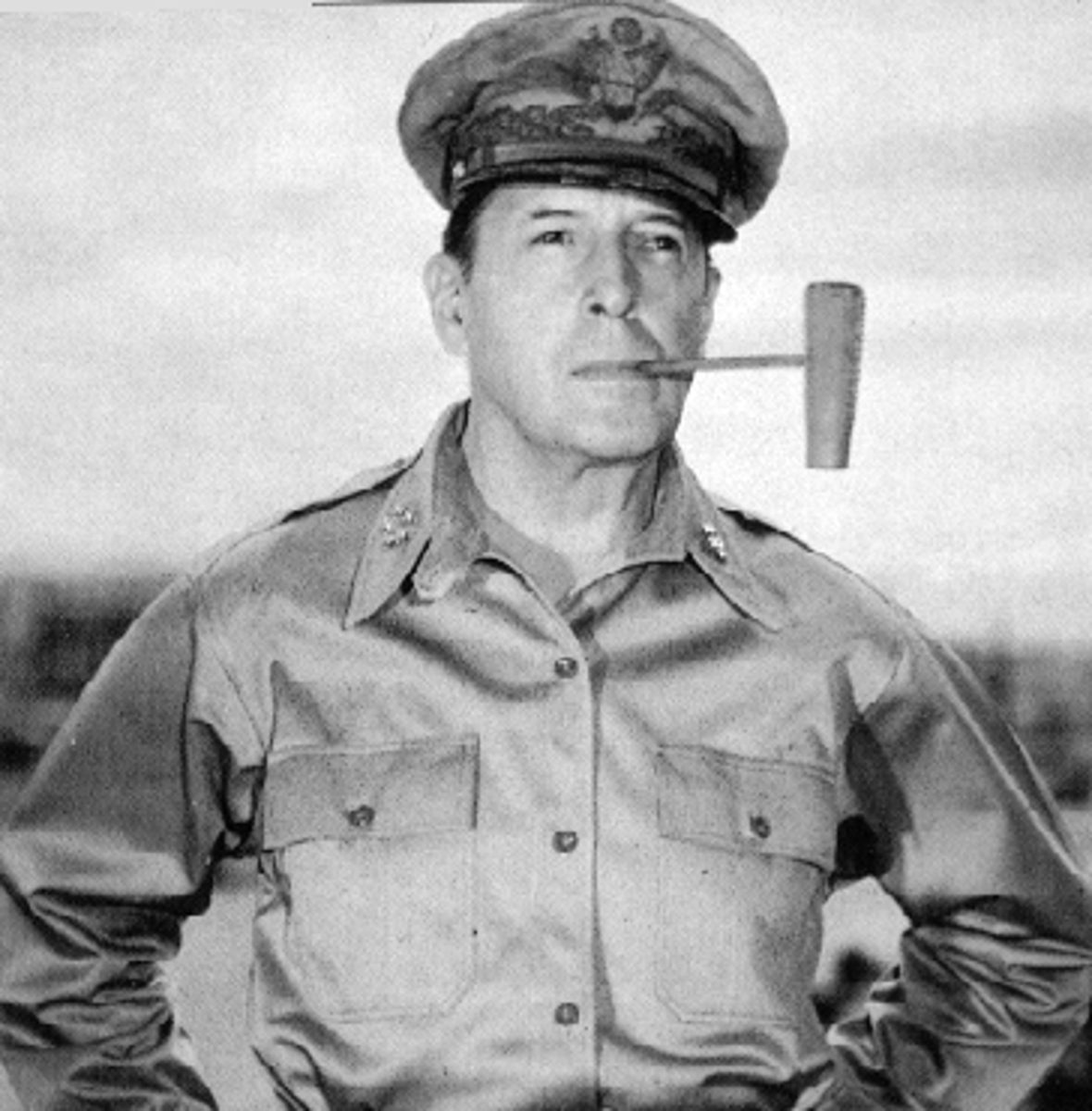
General Douglas MacArthur
He commanded US forces in Korea. He wanted to use atomic bombs on China for sending troops to North Korea. He was fired for insubordination by Truman for continuing to argue his plan to the press and to Congress.

South Koreans
they appeared to be winning the Korean war until China actively entered the conflict
A demilitarized zone was established at the 38th parallel
What was the result of the cease-fire agreement in June 1951?
1. The North Koreans were forced out of South Korea.
2. Communism was stopped from spreading to South Korea
What was gained by the Korean War?
They felt that too many American lives had been lost for little gain
How did the American public feel about the Korean War and its outcome?
That they would threaten the U.S. government from within.
What did some Americans fear about Communists during the Cold War?
HUAC (House Un-American Activities Committee)
Committee responsible for rooting out communists in American Government and Society; best known for investigating suspected communists influences in the Hollywood film industry.

To investigate suspected Communists both inside and outside government.
What was the purpose of the House Committee on Un-American Activities (HUAC), set up by Congress in 1947?
Hollywood Ten
What was the name given to the group of writers, directors, and producers who were called before the House Committee on Un-American Activities (HUAC) to testify and later sent to prison for their refusal to testify?
Blacklist
List of people in the Hollywood film industry who were refused jobs because they did not cooperate with HUAC.

A list of individuals who Hollywood executives believed to be Communist-influenced.
Which of the following best describes the Hollywood blacklist that resulted from the HUAC hearings?
1. Americans tried to keep Communists out of the government.
2. Truman set up the Loyalty Review Board to investigate suspected people working for the communists.
3. HUAC investigated Hollywood. Many suspected communists were blacklisted.
What are three ways that the United States reacted to fear of communism at home?
The Alger Hiss case and the Rosenberg case
Which two spy cases contributed to the fear of communism in the United States during the Cold War?
Alger Hiss
A former Soviet spy accused this State Department official of being a Communist spy. He was convicted of perjury and went to jail.

Ethel and Julius Rosenberg
Husband and wife tried/executed for treason under suspicion of communist influence and trading atomic bomb secrets with the Soviet Union

Joseph McCarthy
Which US senator claimed that there were Soviet spies and Communists within the US government but had no evidence to support his claims, and was eventually discredited by the US Senate?

McCarthyism
What is the name for the technique of making unsupported charges of disloyalty against suspected Communists without regard for the basic rights of the accused?

hydrogen bomb
In response to the Soviet Union's explosion of an atomic bomb in 1949, what new weapon did the United States intensify efforts to develop?

Dwight D. Eisenhower
He led the nation that developed the first hydrogen bomb.

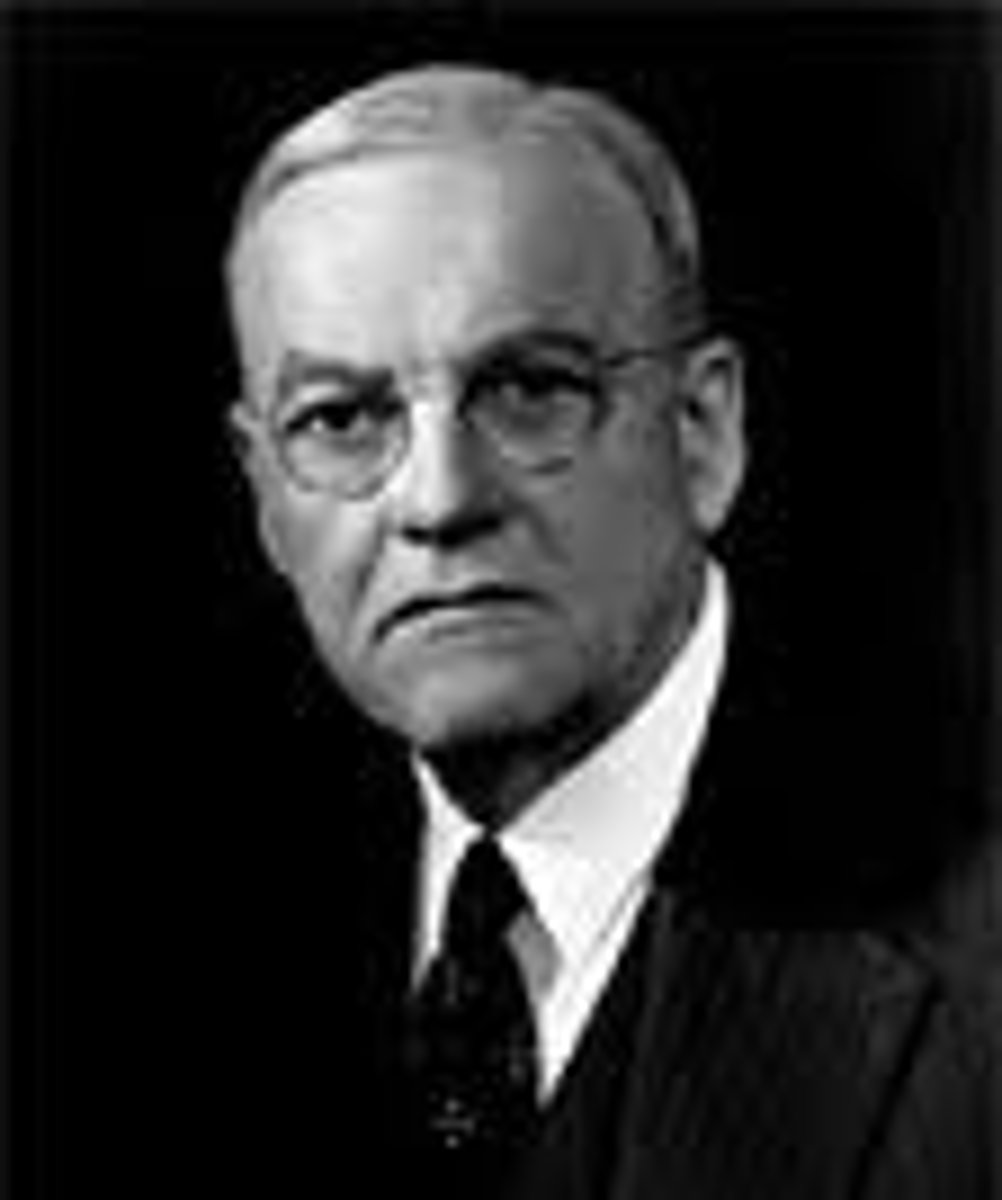
John Foster Dulles
As Secretary of State, he proposed that the United States declare its intention to use massive retaliation against any aggression.

Brinkmanship
Which U.S. policy was based on the willingness to go to the edge of war to protect national interests?

A competition between the United States and the Soviet Union to develop new military technologies and strategies
What was the arms race?
To carry out covert actions to weaken or overthrow governments unfriendly to the United States
What is the main purpose of the CIA?

To use spies to gather information on the Soviet Union
What was the CIA's role in the competition between the United States and the Soviet Union?
1. The CIA convinced the Shah of Iran to get rid of a prime minister who was not friendly to the West.
2. The CIA overthrew the government of Guatemala by training an army.
Which of the following are examples of the CIA's involvement with other countries?
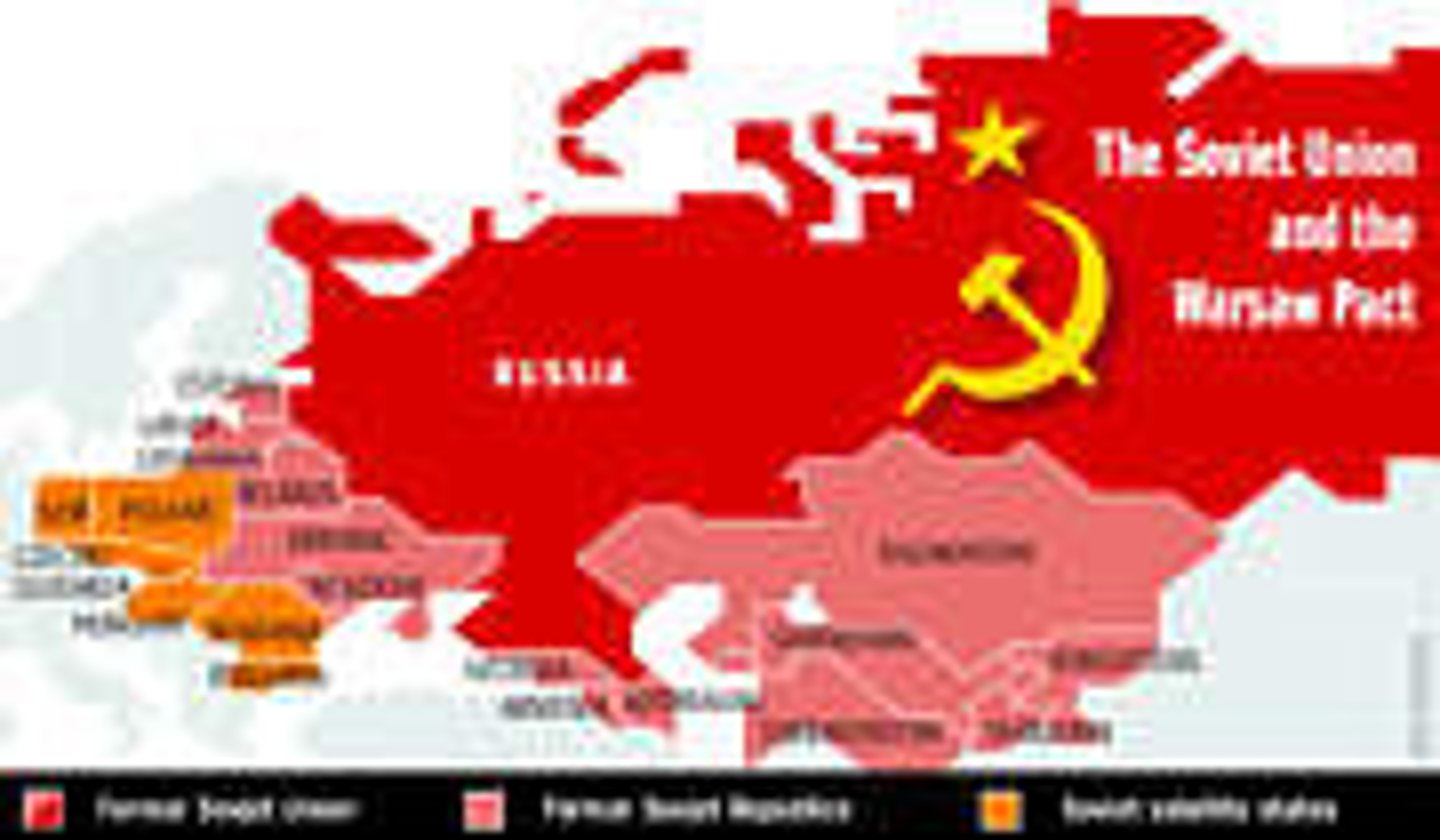
Warsaw Pact
Which military alliance did the satellite nations of the Soviet Union belong to?
A warning to defend the Middle East against Communist attack
What was the Eisenhower Doctrine?
The two countries never fought each other directly, but their allies came into conflict around the world
How did hostilities increase between the United States and the Soviet Union during the 1950s?
Francis Gary Powers
This pilot was convicted of espionage after his plane was shot down and he was forced to parachute into Soviet-controlled territory.
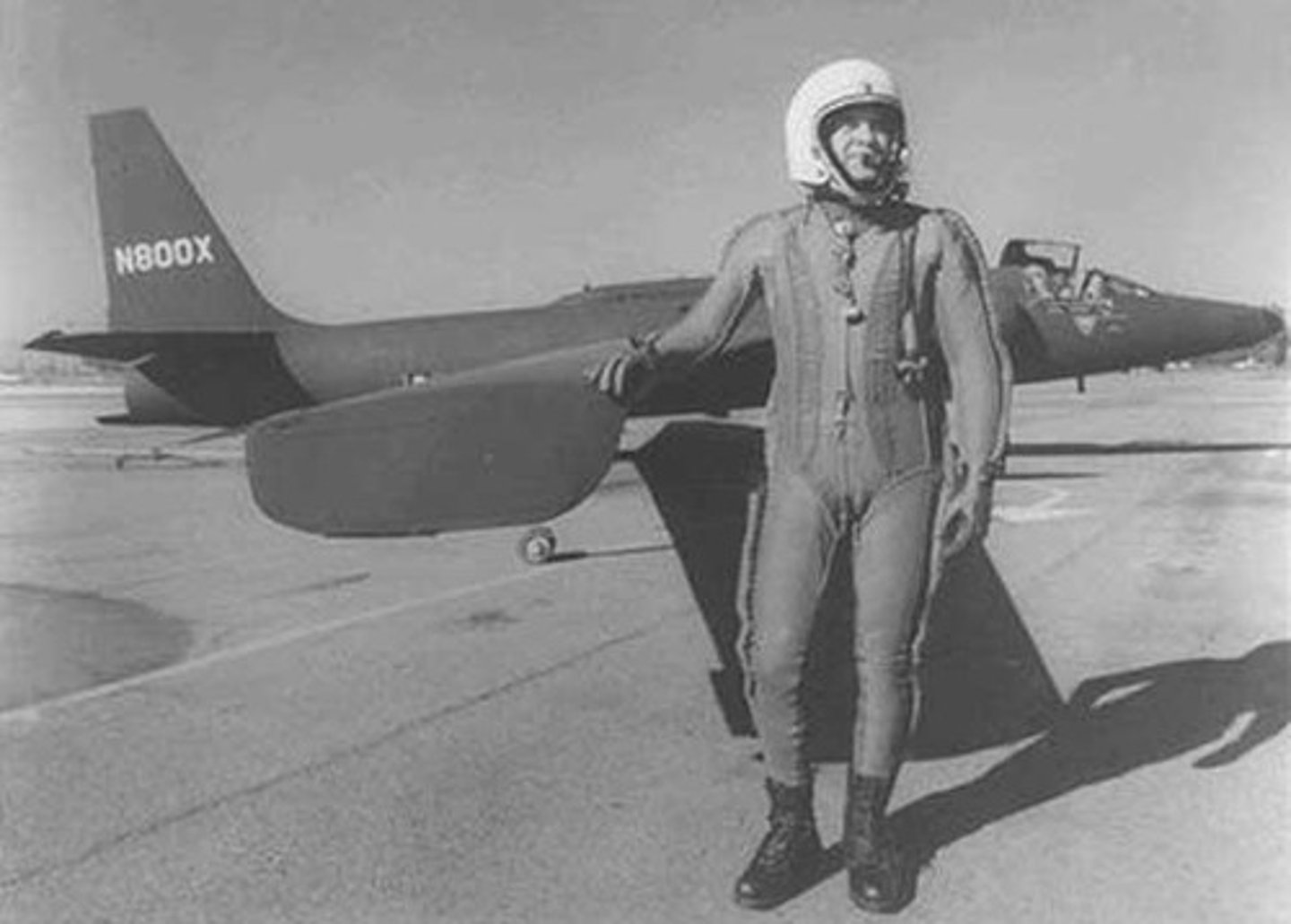

He was conducting espionage for the United States
What was the pilot doing when his plane was shot down?
U2 Incident
The downing of a U.S. spy plane and capture of its pilot by the Soviet Union in 1960.

It hurt his ability to deal with the Soviets
What effect did the U-2 incident have on Eisenhower's ability to deal with the Soviets?
1. The launching of the Sputnik I satellite
2. The U-2 spy plane incident
Which of the following are ways the Cold War was fought in the skies?