IB Physics Topic 7
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:27 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
1
New cards
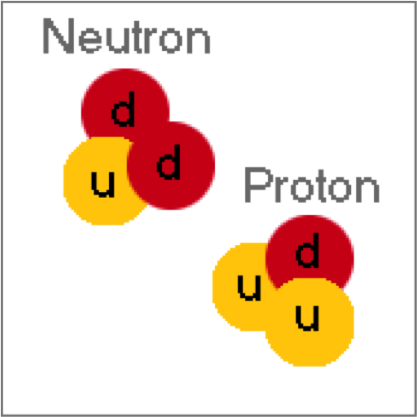
Quarks
-distinct group of subatomic particles
-up,top,charm
-down,bottom,strange
-up,top,charm
-down,bottom,strange
2
New cards
Leptons
-distinct group of subatomic particles
-electron,muon,tau
-electron neutrino, muon neutrino, tau neutrino
-electron,muon,tau
-electron neutrino, muon neutrino, tau neutrino

3
New cards
Protons and neutrons are made up of...
Quarks
(Which qualify as baryons)
(Which qualify as baryons)
4
New cards
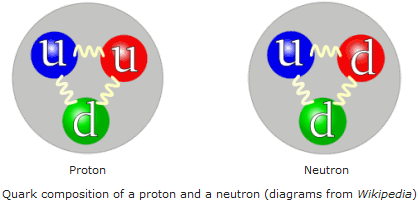
Baryons
Particles containing three quarks or three antiquarks
5
New cards
Mesons
Particles containing exactly a quark and an antiquark
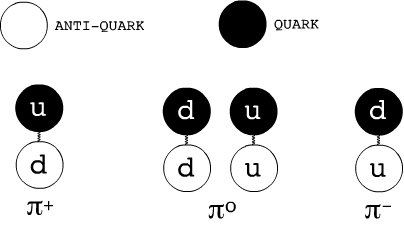
6
New cards
Hadrons
Any particle made from quarks and/or antiquarks
7
New cards
Electromagnetic force:
-mediated by photons, y
-does not act upon neutrinos
-does not act upon neutrinos
8
New cards
Strong nuclear force
-mediated by gluons, g
-acts upon only quarks
-acts upon only quarks
9
New cards
Weak nuclear force
-mediated by W+ bosons, W- bosons, Z0 bosons
-acts upon all matter particles
-acts upon all matter particles
10
New cards
Gravitational force
-particle physics can't explain it
-acts upon all matter particles (everything with mass)
-acts upon all matter particles (everything with mass)
11
New cards
Matter particles
------>------ (move forwards in time)
12
New cards
Antimatter particles
------
13
New cards
Exchange particles
~~~~~~~~~~~~~
14
New cards
Vertex
-intersection of two arrows and one wiggly line
-one arrow must point in and the other must point out of the vertex
-one arrow must point in and the other must point out of the vertex
15
New cards
Bound electrons
Are attached to a nucleus by electric attraction
-bound by an electric force
-bound by an electric force
16
New cards
Electronvolt
-a unit of energy
-the energy an electron gain when moved across 1 V of potential difference
-the energy an electron gain when moved across 1 V of potential difference
17
New cards
How are energy levels described?
As discrete or quantized
-the electron's energy levels are not continuous
-the electron's energy levels are not continuous
18
New cards
What does absorb a photon mean?
Go up a level
19
New cards
An electron the reaches the highest energy level (0eV) is...
Free and the atom in ionized
20
New cards
An electron is bound to the atom as long as its energy...
Is negative
21
New cards
What does release a photon mean?
Go down a level
22
New cards
Ground state
The first/lowest energy level (n=1)
23
New cards
Excited states
Higher energy levels (n > 1)
24
New cards
If a bound electron is struck by a photon whose energy doesn't match any of the energy changes between the electron's discrete energy levels, then...
The photon won't be absorbed by the electron
25
New cards
An electron jumping between discrete energy levels produces...
Discrete emission and absorption spectra
26
New cards
Explain why only certain colors are emitted from a hydrogen atom when its bound electron is repeatedly excited.
-certain photons' frequencies don't fit the discrete energy levels of a hydrogen atom
27
New cards
Nucleus of an atom
Contains neutrons (N) and protons (Z)
28
New cards
Because neutrons and protons are both in the nucleus, they are called...
Nucleons (A)
29
New cards
Element
Nucleus with a particular number of protons
30
New cards
Nuclide
A nucleus with a particular number of protons and neutrons
31
New cards
Isotopes
A particular element which all have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
32
New cards
State two differences between the electrostatic/Coulomb/electric force and the strong force.
-Coulomb is long range, nuclear is short range
-coulomb can be repulsive but strong is attractive
-electric force acts on charged particle but nuclear forces act on nucleons
-coulomb can be repulsive but strong is attractive
-electric force acts on charged particle but nuclear forces act on nucleons
33
New cards
How do the forces acting between two extremely close protons compare with the forces acting between two distant protons?
-when they're close together strong force dominates
-when they're far away electric force dominates
-when they're far away electric force dominates
34
New cards
Explain why larger nuclei need more neutrons than protons in order to b e stable.
-the strong nuclear force is short range and attractive whereas the electric force is long range and repulsive
-in smaller nuclei, the protons are so close the electric repulsion between protons is overcome by the attractive nuclear force
-in larger nuclei, the electric repulsion is not overcome by the strong nuclear force because protons are spread over larger distances
-so, in larger nuclei, a greater proportion of neutrons is needed for stability
-in smaller nuclei, the protons are so close the electric repulsion between protons is overcome by the attractive nuclear force
-in larger nuclei, the electric repulsion is not overcome by the strong nuclear force because protons are spread over larger distances
-so, in larger nuclei, a greater proportion of neutrons is needed for stability
35
New cards
Unified atomic mass (amu)
One-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom
36
New cards
Mass and energy are equivalent; therefore...
All energy has an associated mass and all mass has an associated energy
-revealed through the equation E=mc^2
-revealed through the equation E=mc^2
37
New cards
When nucleons join together to form a nucleus...
The individual nucleons lose some of their mass, which is converted into a gamma ray photon
38
New cards
A nucleus which is bound always has _________ energy and _______ mass than the free nucleons collectively (when unbound)
Less
39
New cards
Mass defect/deficit
The mass lost when a nucleus forms
40
New cards
The mass lost and its equivalent energy is release as a...
Photon
41
New cards
Binding energy
-The total energy released when a nucleus is formed from its nucleons
-the total energy required to completely separate the nucleons
-the energy equivalent of the mass defect
-the total energy required to completely separate the nucleons
-the energy equivalent of the mass defect
42
New cards
How is stability measured?
Using the binding energy per nucleon
43
New cards
Steps for calculating binding energy
1) calculate the mass parts (*remember to multiply the mass by the number of particles)
2) calculate the difference between the mass parts and the amu
3) multiply this value by the correct conversion factor to find the BE
2) calculate the difference between the mass parts and the amu
3) multiply this value by the correct conversion factor to find the BE
44
New cards
The higher the binding energy per nucleon...
The more stable the nucleus
45
New cards
Radioactive decay
When some nuclei are unstable so they spontaneously emit an alpha particle, beta particle, or gamma ray photon
46
New cards
What does "spontaneous" mean?
The decay occurs without any influence from the external environment and without any input of energy
47
New cards
Alpha particle
4^ He 2
-has no electrons
-has no electrons
48
New cards
Alpha decay
A heaver nucleus emit an alpha particle
-atomic number and mass number are conserved
-mass and energy are not conserved
-atomic number and mass number are conserved
-mass and energy are not conserved
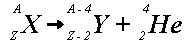
49
New cards
Parent nucleus
The nucleus before the decay
50
New cards
Daughter nucleus
The bigger nucleus after the decay
51
New cards
Negative beta particle
An electron with no mass and a proton number of -1
52
New cards
Positive beta particle
Anti-electron/positron with no mass and a proton number of +1
53
New cards
Negative Beta Decay
-emit an electron and an antineutrino
-within the nucleus one of the neutrons transmutes into a proton
-within the nucleus one of the neutrons transmutes into a proton
54
New cards
Positive Beta Decay
-emit a positron and a neutrino
-within the nucleus, one of the protons transmutes into a neutron
-within the nucleus, one of the protons transmutes into a neutron
55
New cards
In gamma decay...
The parent nucleus does not transmute or change identity as it does in beta and alpha decay
56
New cards
Gamma Decay
-the parent nucleus simply loses some energy and mass which is emitted as a gamma ray photon (high energy)
-sometimes occurs with alpha or beta decay
-sometimes occurs with alpha or beta decay
57
New cards
In all radioactive decays...
Mass-energy and momentum are conserved
58
New cards
Half-life
The time it takes for half of a sample of a radioactive substance to decay
59
New cards
Range/Penetration and Ionizing Ability of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation:
a: stopped by a piece of paper(1), strongest ionising ability because highly charge and big mass
B: stopped by tin foil(2), medium ionising ability because they have less charge and smaller mass
y: stopped by several cm of lead(3), weakest ionising -> can only cause 1 ionisation
B: stopped by tin foil(2), medium ionising ability because they have less charge and smaller mass
y: stopped by several cm of lead(3), weakest ionising -> can only cause 1 ionisation
60
New cards
Explain why a particle that is highly ionising has a short range
-because it come into contact with more particles it begins to ionise sooner and at a shorter range
-the more interactive/ionising the emission, the quicker it loses its energy and stops
-the more interactive/ionising the emission, the quicker it loses its energy and stops
61
New cards
Natural transmutation
Alpha, beta, gamma decay
-spontaneous
-spontaneous
62
New cards
Artificial transmutation
Requires energy/bombardment by other particles
63
New cards
Fusion
-what occurs in stars (like the Sun)
-it is extremely difficult to produce in a laboratory setting
-energy is released
-produces a bigger nucleus from smaller nuclei
*usually has H in the reactants
-it is extremely difficult to produce in a laboratory setting
-energy is released
-produces a bigger nucleus from smaller nuclei
*usually has H in the reactants
64
New cards
Fission
-what occurs in nuclear reactors/power plants
-the two main fission products must be roughly equal-sized
-one or more free neutron must be produced
-energy must be released
-the two main fission products must be roughly equal-sized
-one or more free neutron must be produced
-energy must be released
65
New cards
Conclusion of Geiger-Marsden-Rutherford Experiment
-nucleus is dense and positively charged
-most of the atom is empty space
-most of the atom is empty space
66
New cards
Analysis of electron scattering, showed that protons contained...
3 scattering centers (evidence for Quarks)
67
New cards
Are neutrinos affected by electromagnetic fields?
No because they don't have charge
68
New cards
When a matter particle and its exact antimatter counterpart collide they....
Annihilate producing 2 gamma ray photons
69
New cards
Exchange particles/bosons
Transmit forces across empty space
70
New cards
Four fundamental forces
-electromagnetic force
-strong nuclear force
-weak nuclear force
-gravitational force
-strong nuclear force
-weak nuclear force
-gravitational force
71
New cards
Electromagnetic force carrier
-photons, y
-acts upon all but neutrinos
-acts upon all but neutrinos
72
New cards
Strong Nuclear Force
-gluons, g
-acts upon only quarks
-acts upon only quarks
73
New cards
Weak Nuclear Force
-W+, W-, Z0
-acts upon all matter particles
-acts upon all matter particles
74
New cards
Gravitational Force
-can't be explained by particle physics
-acts upon everything with mass
-acts upon everything with mass
75
New cards
Standard model
The theory that uses quarks, leptons, and exchange particles to explain the four fundamental interactions and all types of particles
76
New cards
Higgs Field
Gives mass to all exchange particles (except g and y, which are massless)
77
New cards
Pair production
When a photon interacts with a nucleus to spontaneously convert into a matter particle-antimatter particle pair
78
New cards
A strange quark can only decay by what force?
Weak force
79
New cards
Neutron
Udd
80
New cards
Proton
Uud
81
New cards
Confinement
-states that quarks are confined and cannot exist by themselves
-this is because when 2 quarks in a meson, for example, are being separated, as the separation distance increases so does the energy in the gluon field. Once enough energy is built up, it reaches the threshold for pair production where the stored energy converts into a new antiquark-quark pair. Therefore, a quark can never be separated and exist by itself due to the conditions which confine it.
-this is because when 2 quarks in a meson, for example, are being separated, as the separation distance increases so does the energy in the gluon field. Once enough energy is built up, it reaches the threshold for pair production where the stored energy converts into a new antiquark-quark pair. Therefore, a quark can never be separated and exist by itself due to the conditions which confine it.
82
New cards
List the four fundamental forces in order of decreasing strength:
-strong nuclear forces
-electromagnetic force
-weak nuclear force
-gravitational force
-electromagnetic force
-weak nuclear force
-gravitational force