3.3.3 Halogenooalkanes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Halogenoalkane
An alkane with at least one halogen atom in place of a hydrogen atom
Polarity of halogenoalkanes
Given that halogens are generally more electronegative than carbon, most carbon-halogen bonds are polar
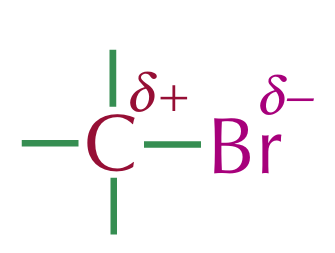
Electrophile
An electron deficient (and usually positively charged) species which is attracted to regions of high electron density
The δ+ carbon (in the halogenoalkane) doesn’t have enough electrons, hence it is classed as an electrophile
Nucleophile
A species that forms a bond with an electrophile by donating a pair of electrons

Nucleophilic substitution
A reaction mechanism where a nucleophile substitutes for an atom (or group of atoms) in a molecule

Nucleophilic substitution of halogenoalkanes
In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, a nucleophile attacks a polar molecule, kicks out a functional group and settles itself in its place
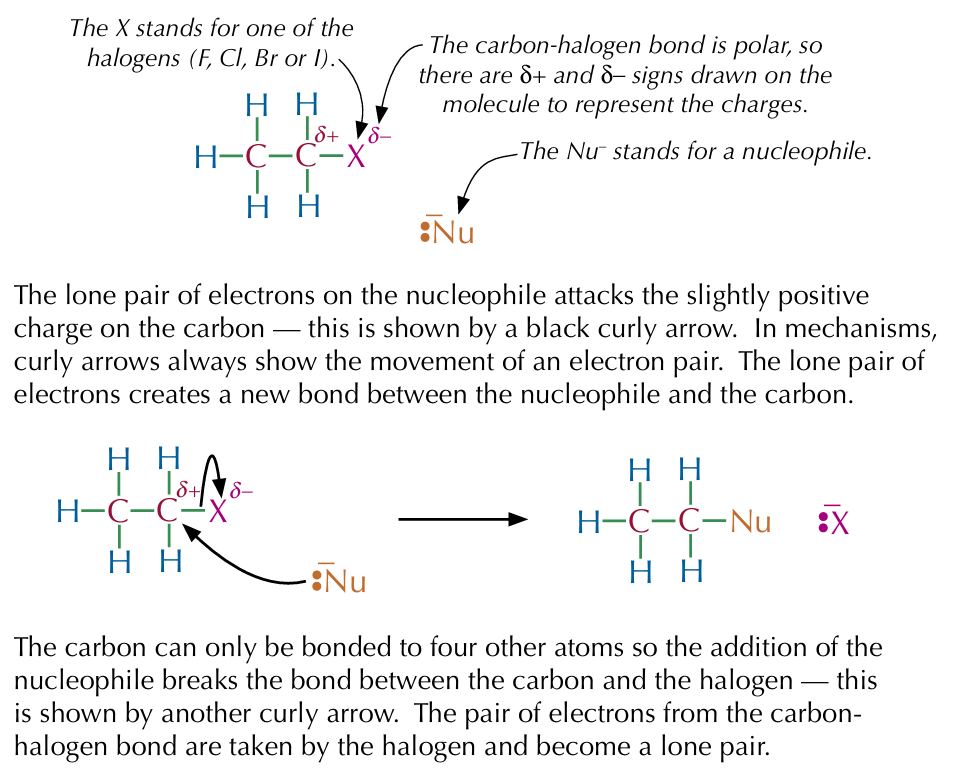
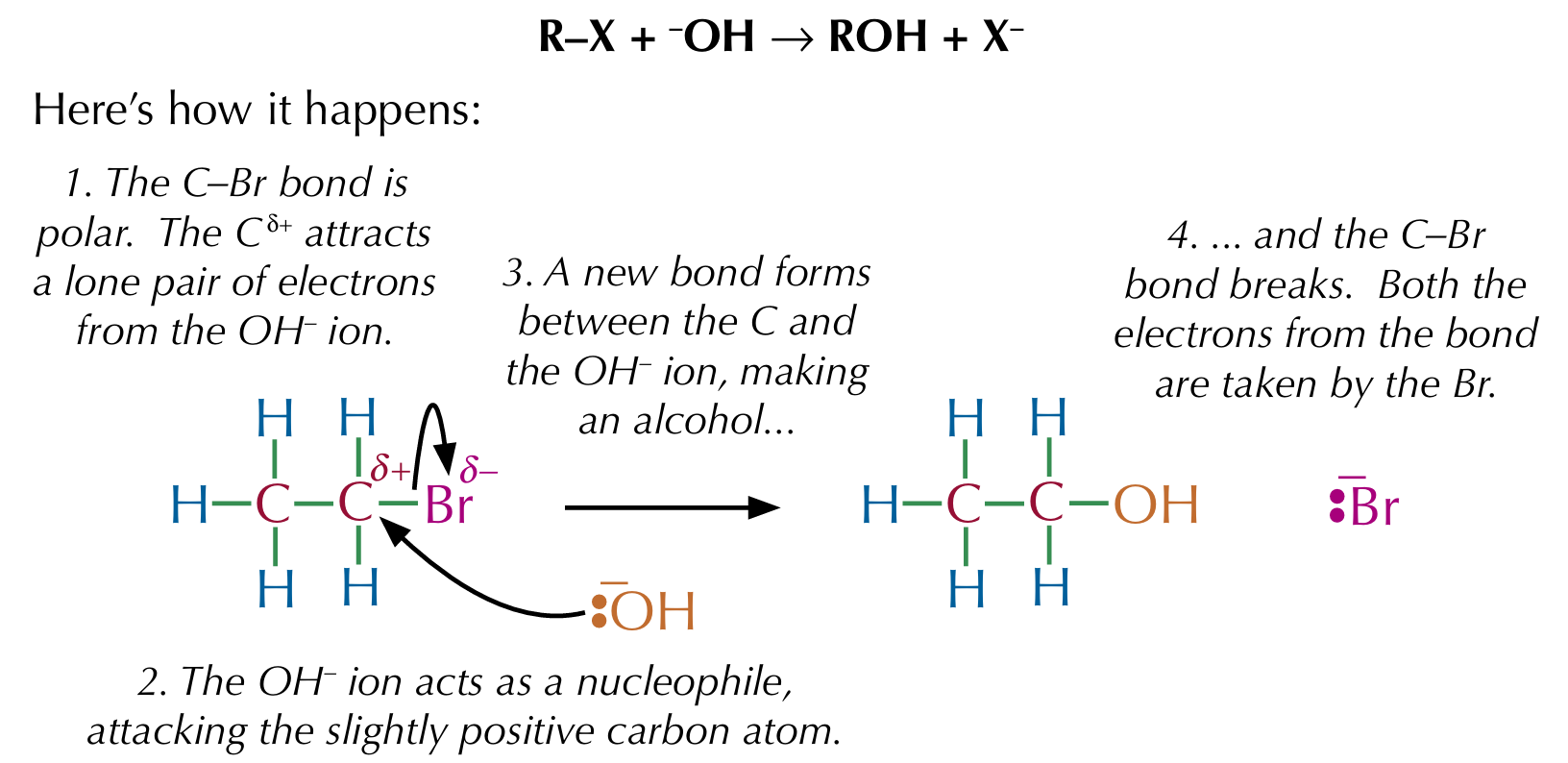
Reaction of halogenoalkanes with hydroxides
Bromoethane can be changed to ethanol in a nucleophilic substitution reaction, where warm aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide is used
Nitriles
Nitriles have a CN group, the carbon atom and the nitrogen atom are held together by a triple bond

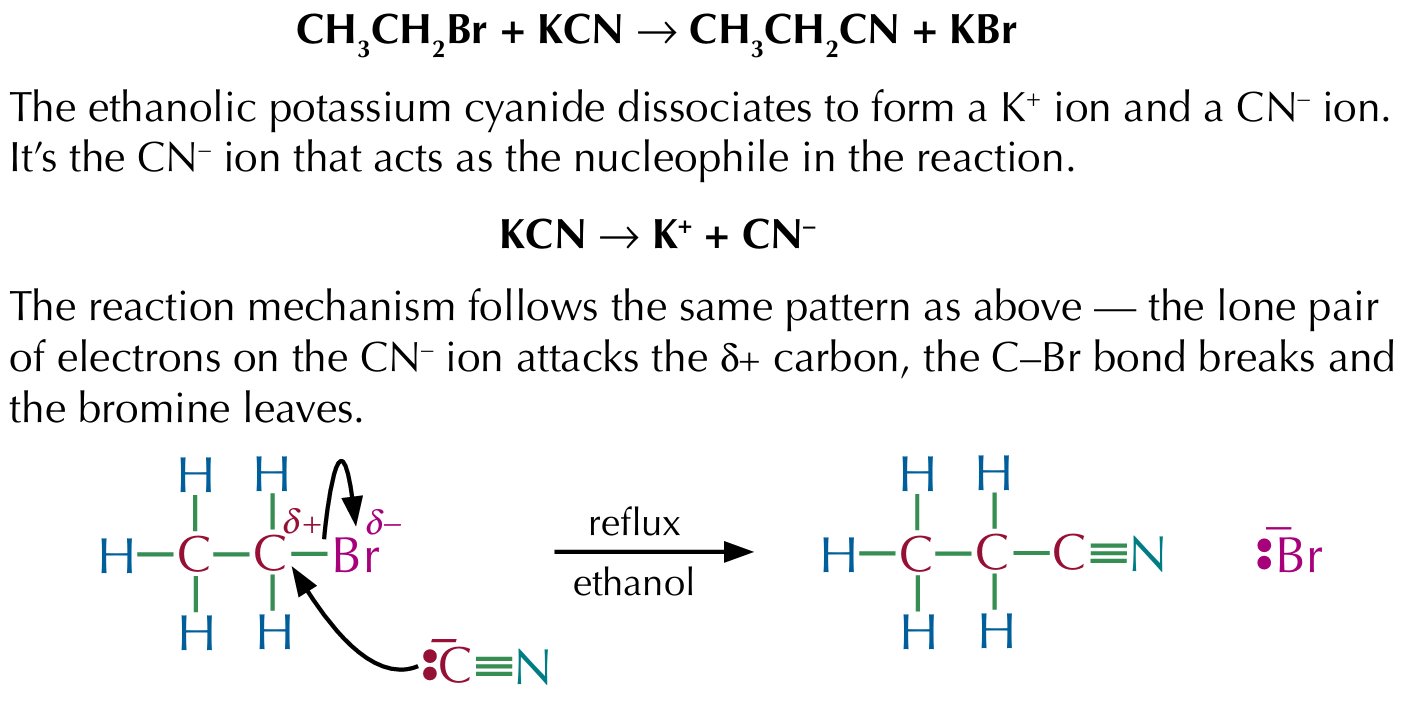
Making nitriles from halogenoalkanes
Reacting bromoethane with potassium cyanide under reflux will produce propanenitrile and potassium bromide
Amines
An amine has the structure R₃N, the R groups can be hydrogens or another group
In amines, the nitrogen always has a lone pair

Making amines from halogenoalkanes
If you warm a halogenoalkane with excess ethanolic ammonia (ammonia dissolved in ethanol) in a sealed tube, the ammonia swaps places with the halogen to form an amine
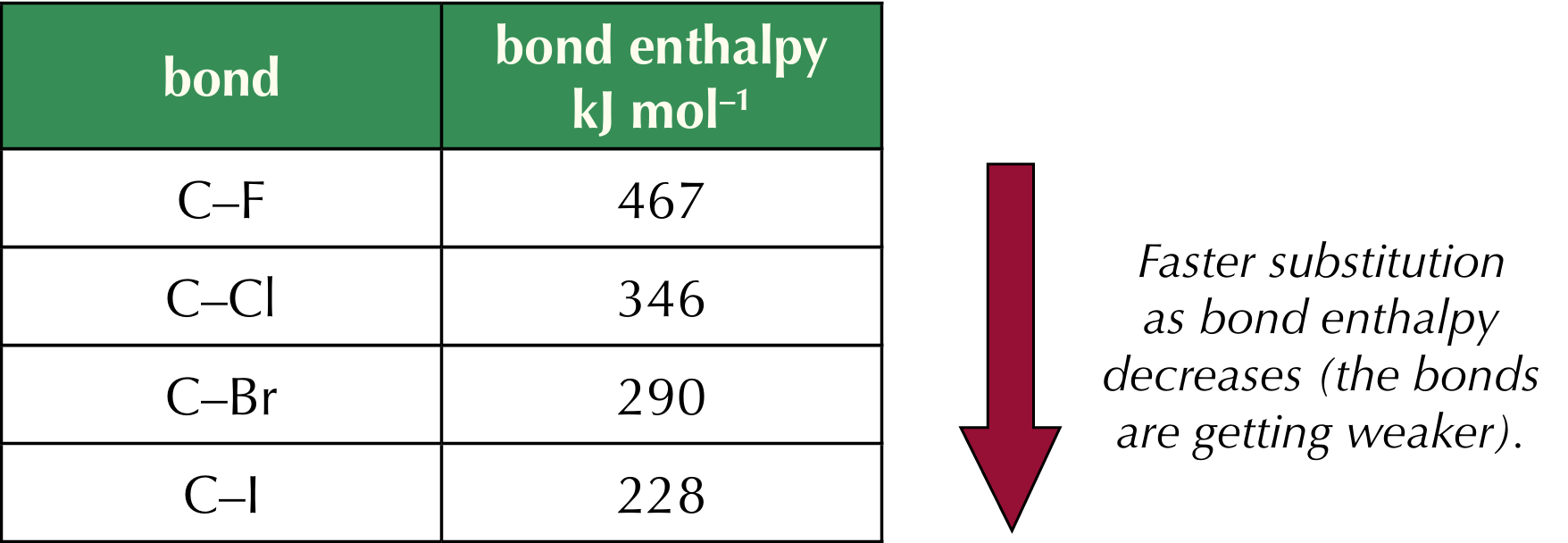
Reactivity of halogenoalkanes
The carbon-halogen bond enthalpy decides reactivity, the C-F bond is the strongest, hence it has the highest bond enthalpy, thus fluoroalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions more slowly than other halogenoalkanes
Elimination reactions
A reaction mechanism in which a molecule loses atoms or groups of atoms
Halogen elimination from a halogenoalkane
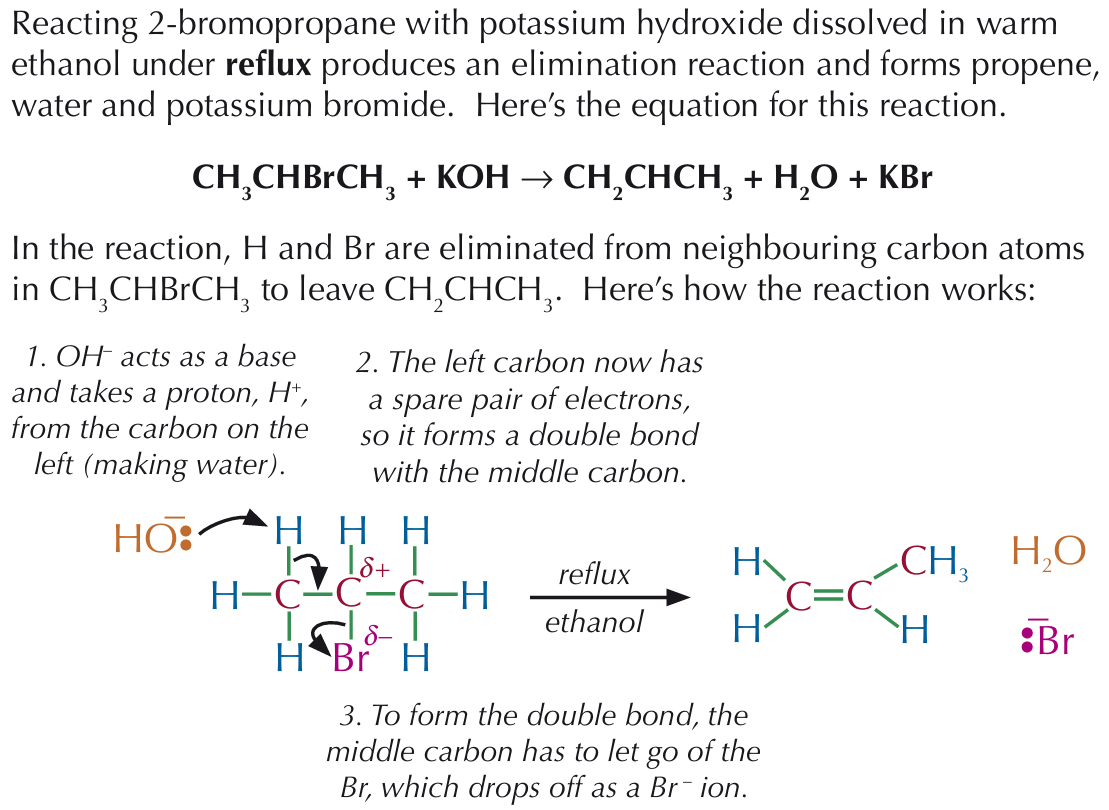
If you warm a halogenoalkane with hydroxide ions dissolved in ethanol instead of water, an elimination reaction occurs where you end up with an alkene