Chapter 11: Modern Physics
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
Barron's AP
Physics 2
Modern Physics
Photons
Photoelectric Effect
Quanta
Photoelectrons
Quanta photons
Metal’s work function
Electronvolt
Bohr Model
Atomic Spectra
Balmer formula
wavelength
Wave-Particle Duality
de Broglie wavelength
Wave Function
Relativity
Theory of Relativity
Time dilation
Length contraction
Nuclear Physics
Nucleons
Isotopes
Atom’s atomic number
Neutron num
Nucleon number
nuclide
Nuclear Force
Binding Energy
Mass defect
Nuclear Reactions
Alpha Decay
Beta Decay
Gamma Decay
exothermic
endothermic
Disintegration Energy
AP Physics
University/Undergrad
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
**Quanta**
the origin of the name of quantum mechanics
2
New cards
**Photon**
is a quantum of electromagnetic energy
3
New cards
**Photoelectric effect**
is an illustration of light that behaves like a steam of photons
4
New cards
**Photoelectrons**
are the released electrons
5
New cards
**Metal’s work function, ϕ**
is a certain amount of energy had to be imparted to an electron on the metal surface in order to liberate it
6
New cards
**Electronvolt (eV)**
is equal to the energy gained (or lost) by an electron accelerated through a potential difference of one volt
7
New cards
In terms of electronvolts, the value of Planck’s constant is
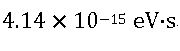
8
New cards
**Atomic Spectra**
the produced patterns of sharp lines when the light from a glowing gas, passed through a prism to disperse the beam into its component wavelengths
9
New cards
**Balmer formula**
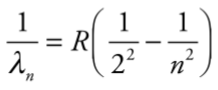
10
New cards
**Electromagnetic radiation**
propagates like a wave but exchanges energy like a particle
11
New cards
**Wave function, Ψ**
is the mathematical probability that a particle will be measured to be at a particular position when the position is measured
12
New cards
**Theory of Relativity**
a theory that have two postulates: (1) The results of physical experiments will be the same in any non-accelerating reference frames, and (2) The speed of light is constant.
13
New cards
**Time dilation**
is the difference in the elapsed time as measured by two clocks
14
New cards
Length contraction
a phenomenon in which moving along with the object, measures will observe the object to have a different length compared in a different reference frame
15
New cards
**Nucleons**
collectively are protons and neutrons
16
New cards
**Atom’s atomic number**
the number of protons in a given nucleus (denoted *Z*)
17
New cards
**Neutron number**
the number of neutrons in a given nucleus (denoted *N*)
18
New cards
**Nucleon number**
also called **mass number i**s the total number of nucleons, *Z* + *N* (denoted *A*)
19
New cards
**Isotopes**
are nuclei that contain the same numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons
20
New cards
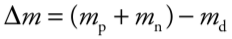
**Mass defect Δ*****m***
the difference between the mass of any bound nucleus and the sum of the masses of its constituent nucleons
21
New cards
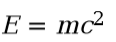
**Energy formula**
22
New cards
Binding energy
of the nucleus formula tells how strongly the nucleus is bound:
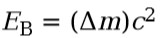
23
New cards
**Binding-energy-per-nucleon:**