Qualitative Alkene Test + IR and Studying SN1 + SN2 Reactions
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the 4 Main Classes of Hydrocarbons and which ones are saturated vs unsaturated?
Alkanes = SATURATED
Alkenes = UNSATURATED
Alkynes = UNSATURATED
Aromatic Compounds (The RING itself) = UNSATURATED
Stronger bases are _(Better/Worse) Nuclephiles. Why?
Better
(bc strong bases are very willing to give away their e- and “attack” another (+) part of a compound
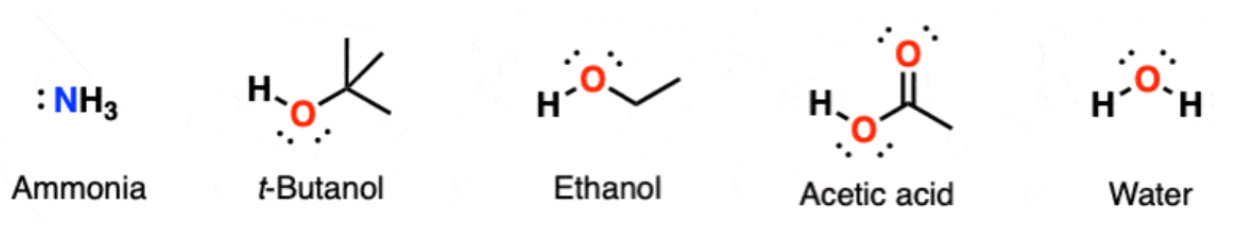
Polar Protic Solvents
What are they
What are they best for? (SN1 or SN2)
Polar Protic - compounds containing OH or NH group that is able to form hydrogen bonds. They are highly polar because of the OH or NH group
Best for SN1 rxns bc they effectively stabilize the carbocation intermediate, which is formed in the rate-determining step of the reaction
(See examples like ammonia)
How? p-protic solvents can stabilize the carbocation by forming strong hydrogen bonds with the leaving group in the transition state
What are three examples of good LG?
1) Halogens
2) OTs (“Tosylate”)
3) Water
What are the two types of rearrangents
(this is important to know since rearrangements are related to hyperconjugation)
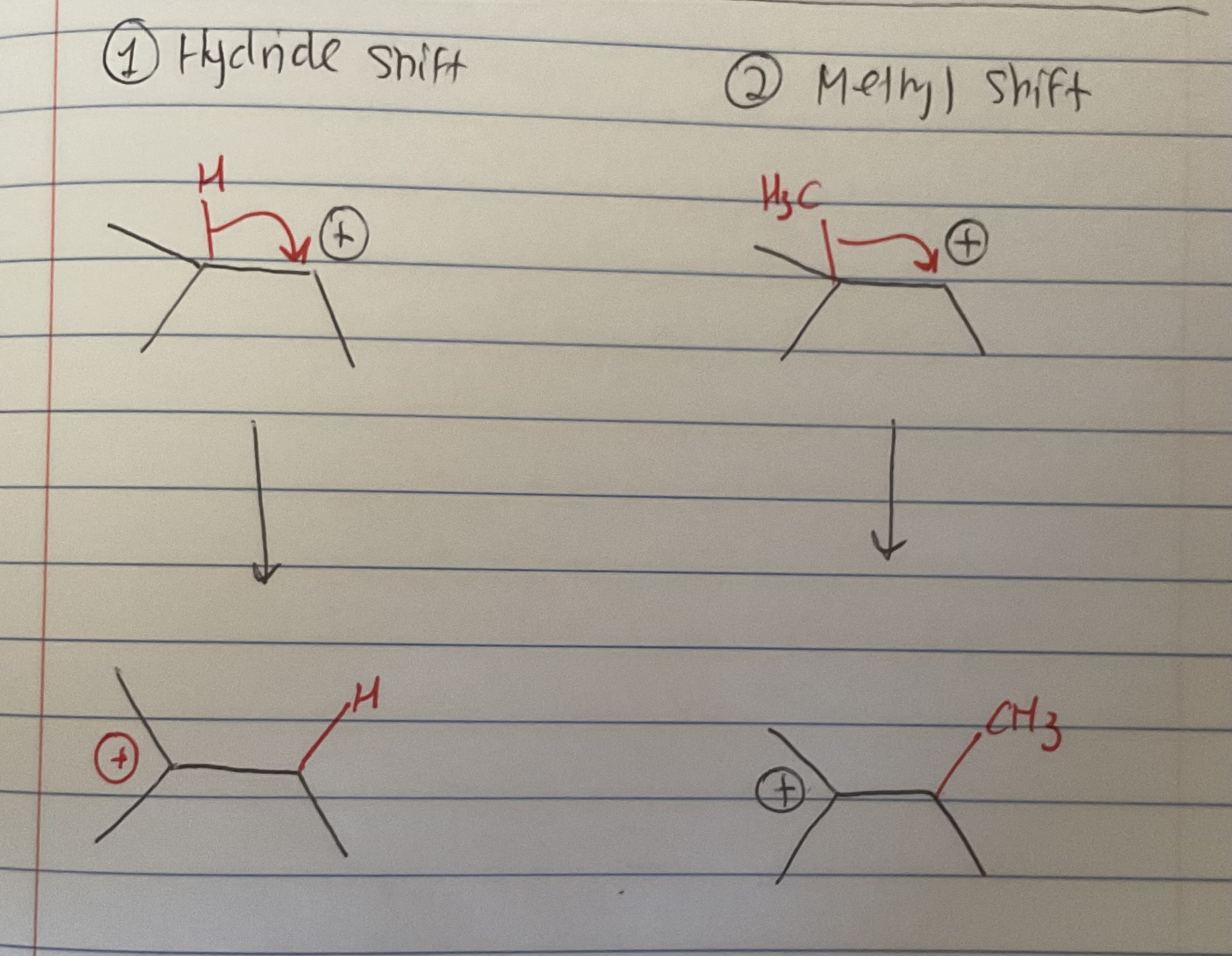
Why do good LG have lots of resonance (ie. Ots)
The resonance allows for the negative charge of a lone pair that they carry when they to be stabilized via delocalization
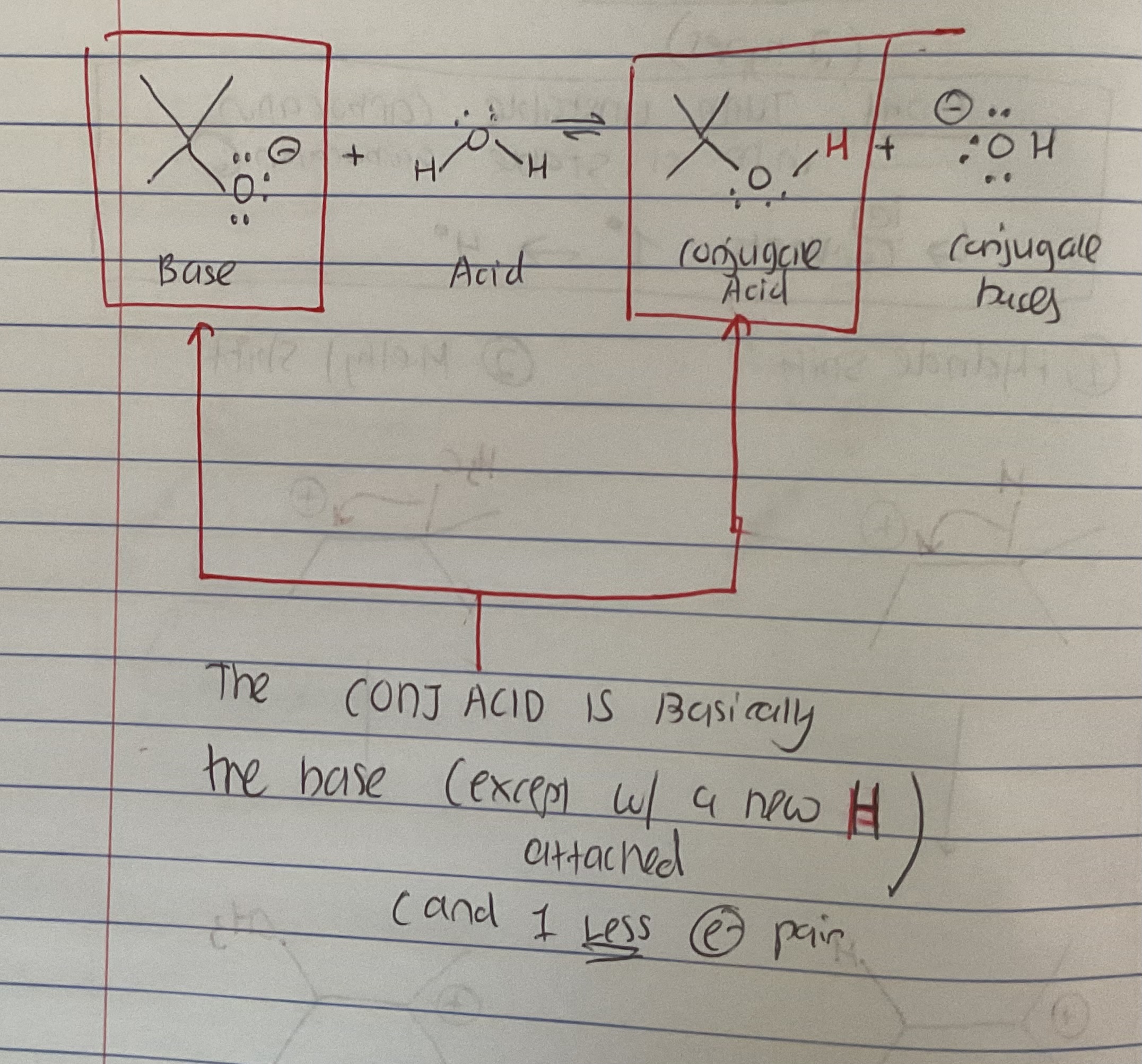
What is the conjugate acid?
Its basically the base (of an acid-base rxn) just with 1 new H and 1 LESS e- pair
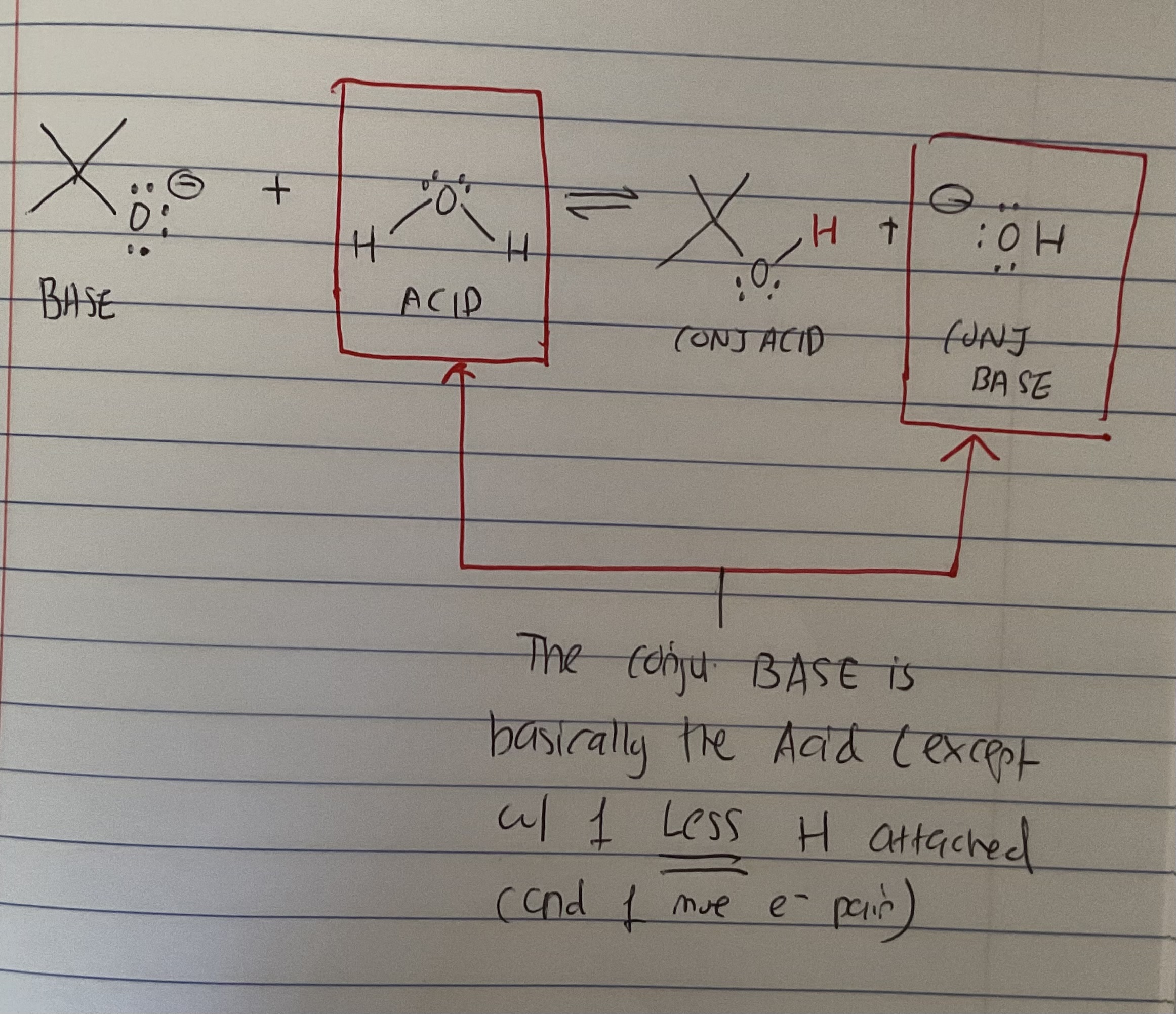
What is the conjugate base?
Its basically the acid (of an acid-base rxn) just with 1 LESS H and 1 new e- pair
What are examples of Bad LGs?
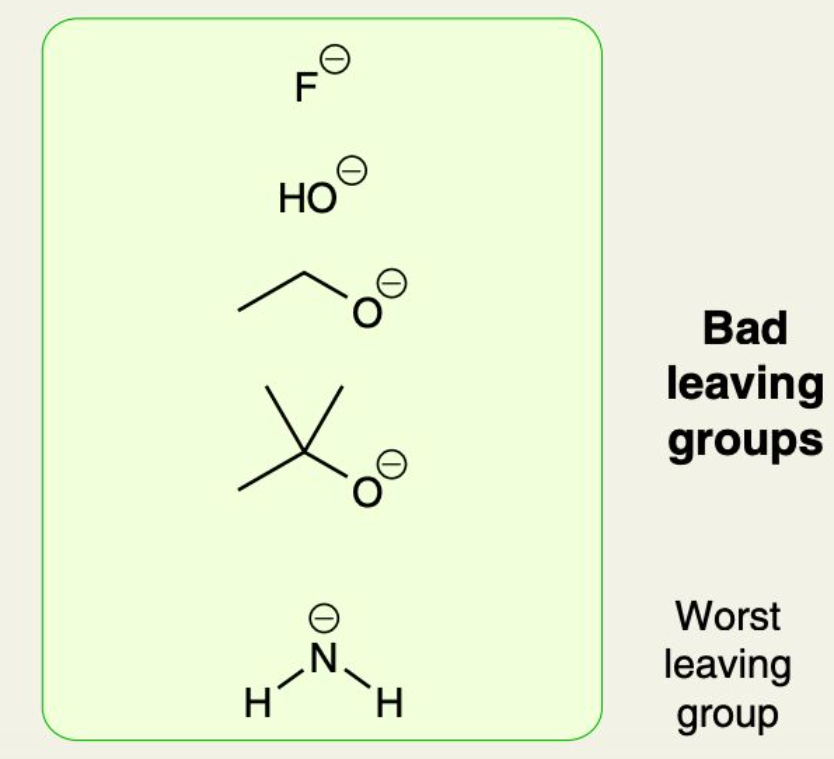
What is OTs?
By themselves, alcohols are bad LGs (since -OH is a strong base)
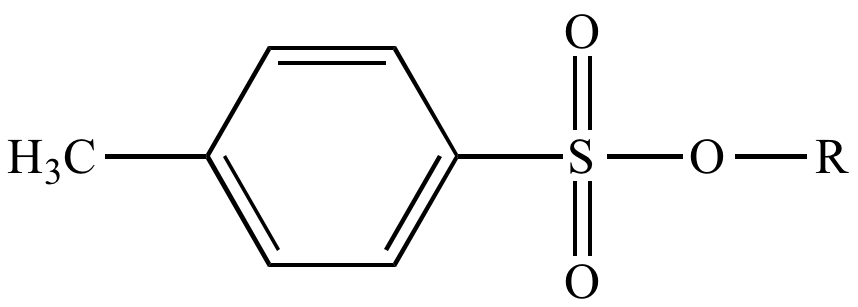
However, Alcohols can be CONVERTED into “sulfonates” (which ARE GREAT LGs)
OTs (“Tosylate”) is a a type of sulfonate
Draw the structure of OTs
What three factors makes a good LG?
1) Good LGs are weak bases (better at hogging e-)
2) Good LGs have lots of resonance (better at stabilizing neg charge)
3) Good LGs have large atomic size (better at stabilizing neg charge)
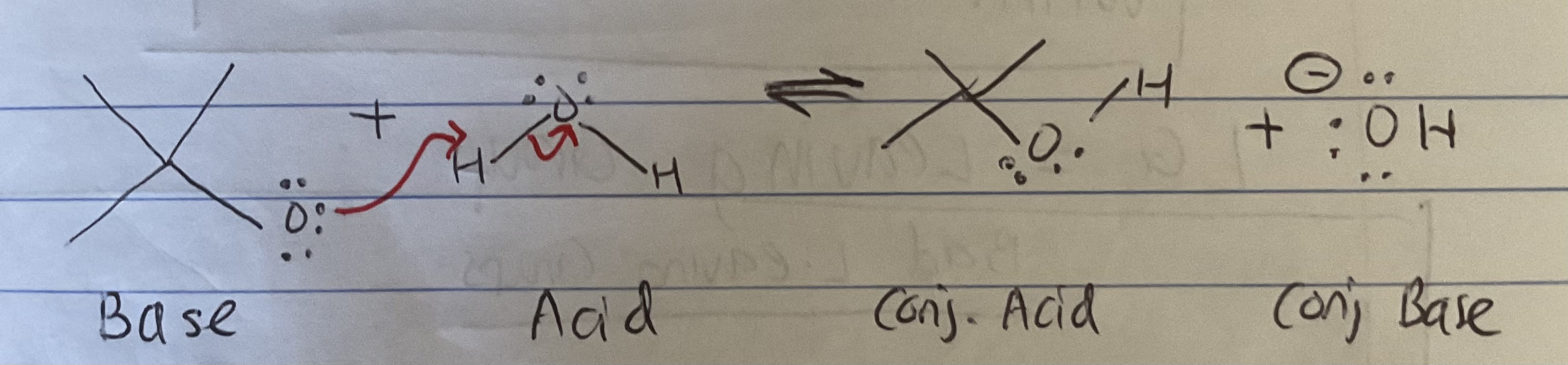
Why are Weak bases Considered Good LGs?
(as seen from pic) A Good BASE give away e- and trade it to obtain an H
A weak base is thus, not good at giving away its e- (it wants to hog it)
Similarly, a good LG is like a weak base bc it likes to hog e- (this makes the LG capable of leaving)
Most Acidic Acid
Is it a good LG or a bad LG? why
HI (Good LG, bc strong acids produce weak conjugate bases)
Draw out a primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary Carbon
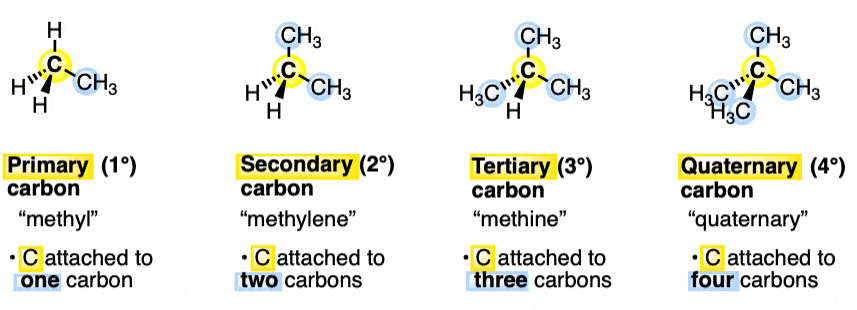
What is Steric Hinderance?
Rank Primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary C in terms of how steric hindrance they pose
Steric hindrance: The physical obstruction causes by bulky groups in a molecule which basically BLOCKS the chemical rxn
Less steric hindrance = faster rxn

SN2 Mechanism
(Do some pp in Wiley)
Nucleophile attacks from the backside (this can be blocked if steric hindrance is there)
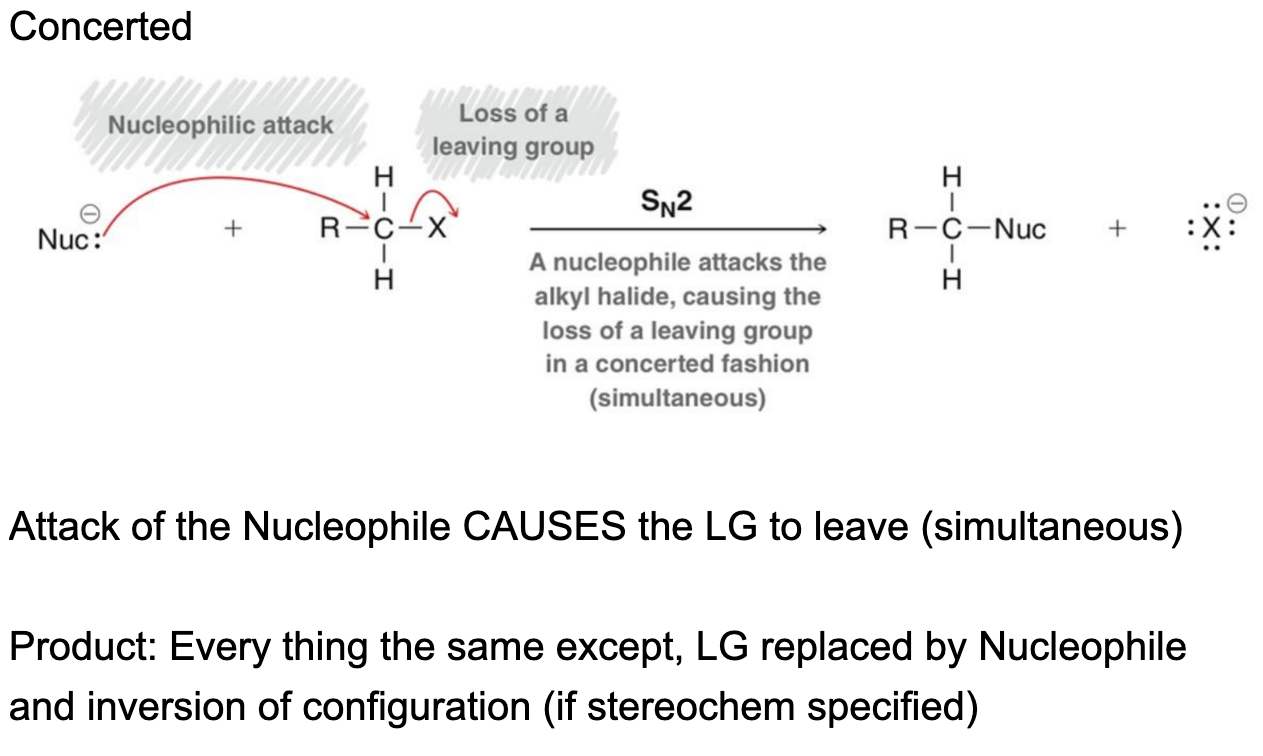
Both Sn1 and Sn2 compounds undergo
inversion of config (but always check R and S!!)
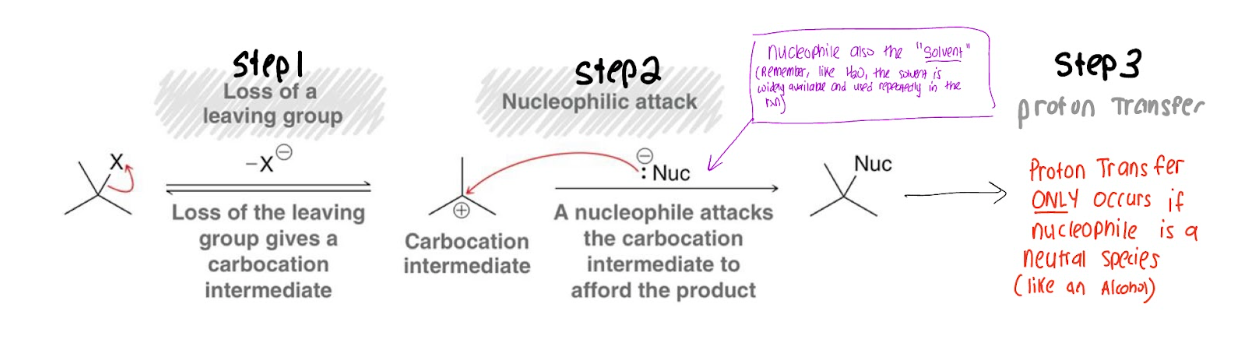
SN1 Mechanism
(Do some pp in Wiley)
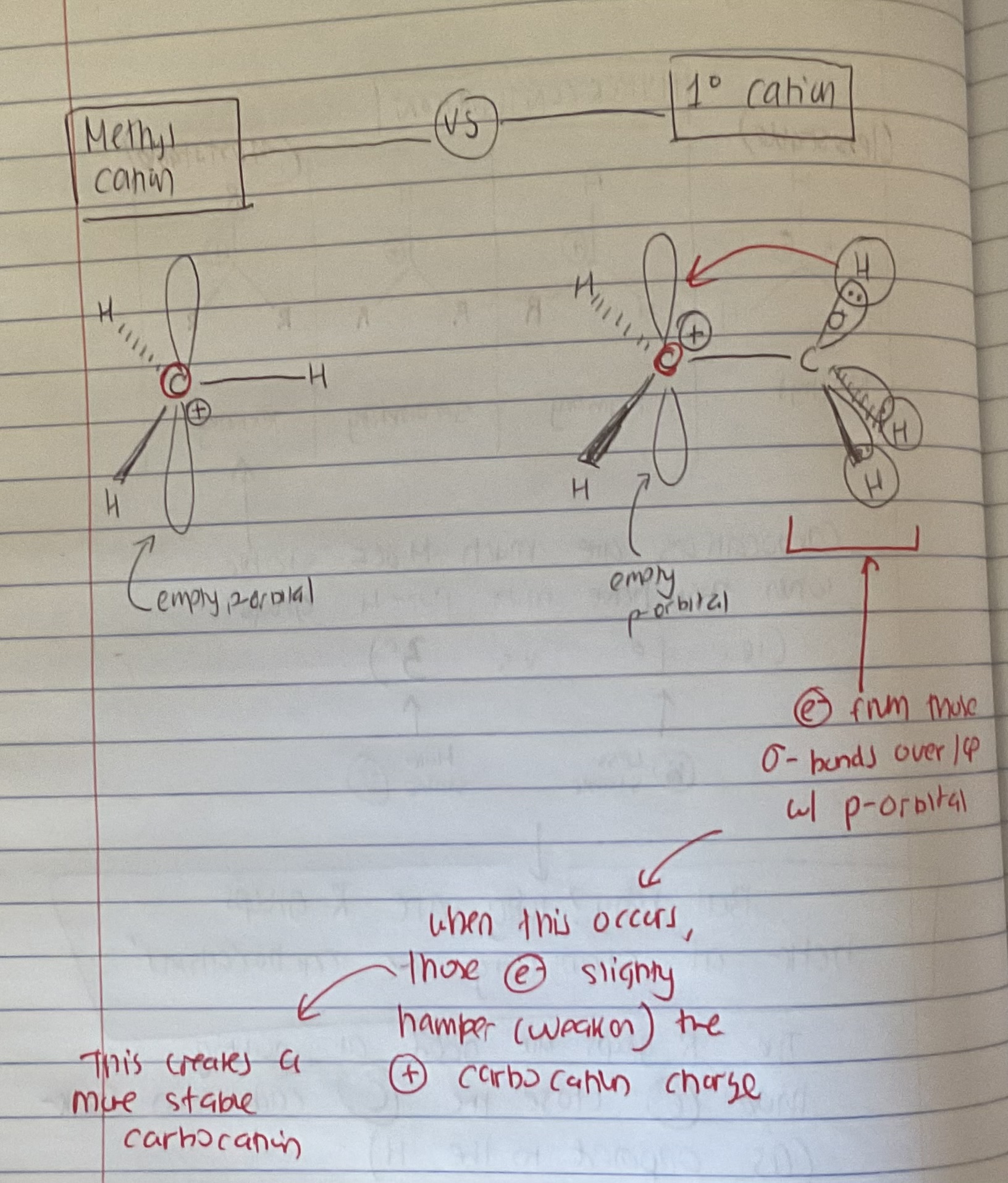
What is Hyperconjucation
(basis of understanding rearrangments)
What does Concerted mechanism mean?
All bond-breaking and making occur in 1 step all at once
Formula for Degrees of Unsaturation
[2C + 2 + N - X - H] / 2
What does the term Saturated hydrocarbons mean?
What does the term unsaturated hydrocarbons mean?
Saturated = (1x-bond) where each C atom is bonded to the maximum possible number of H atoms
Unsaturated = contains at least 1 double or triple bonds; Has less H bonds than the Maximum Capacity (so more atoms can bond to it)
Alkene General Formula
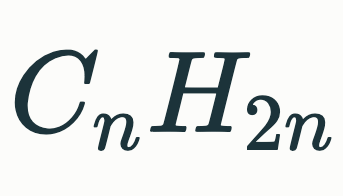
Alkyne General Formula
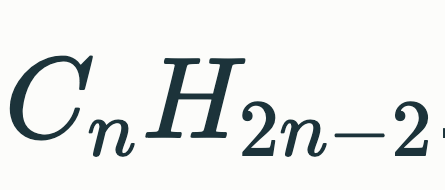
Alkane General Formula

What are the names of the 2 Decoloration Test for the presence of Alkenes?
1) Pyridium Bromide PerBromide (PBP) Test , can test for Alkynes and Alkenes
2) Potassium Permanganate Test (KMnO4) Test, can only test for Alkenes
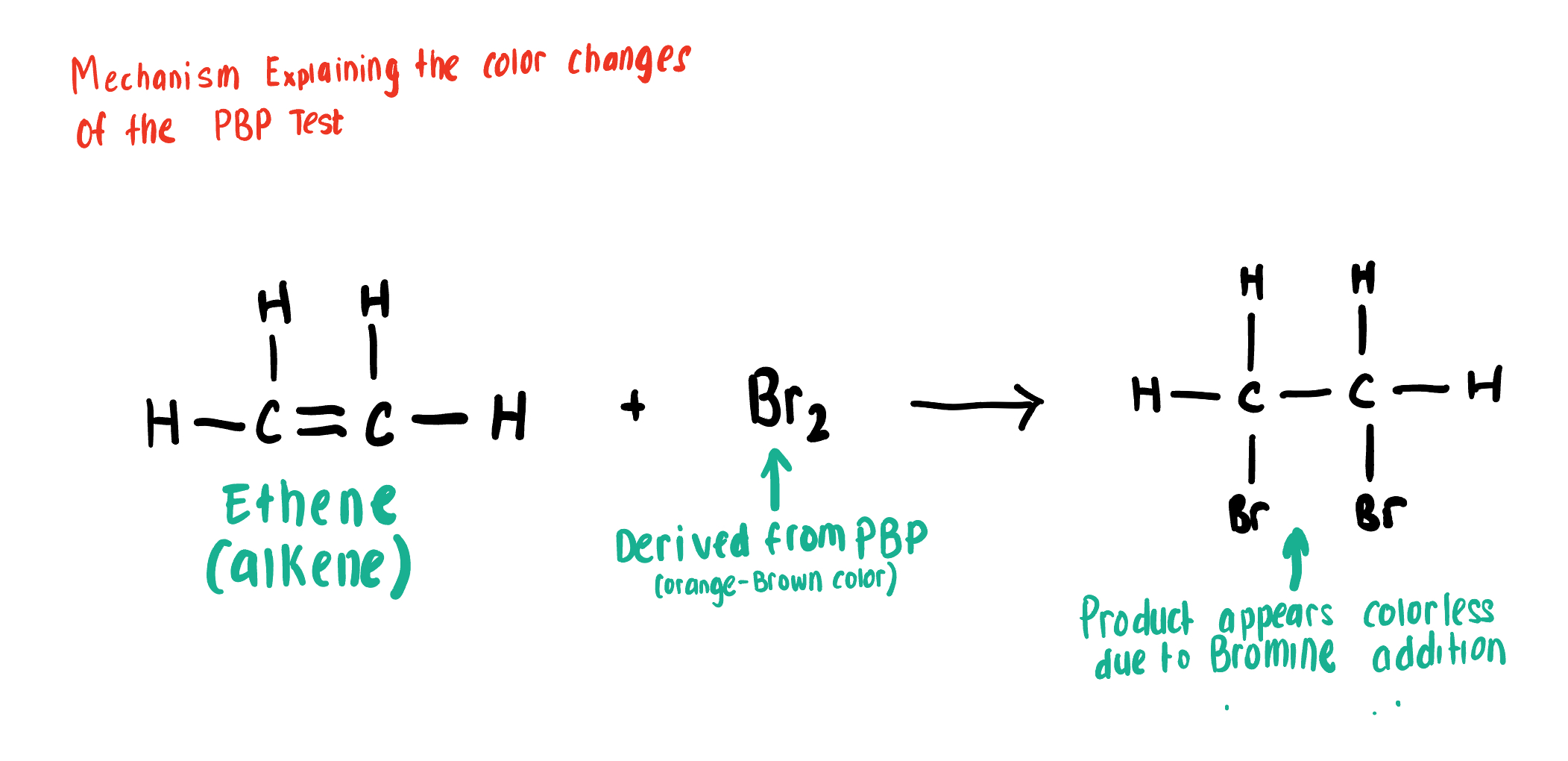
Explain how the PBP Test Works
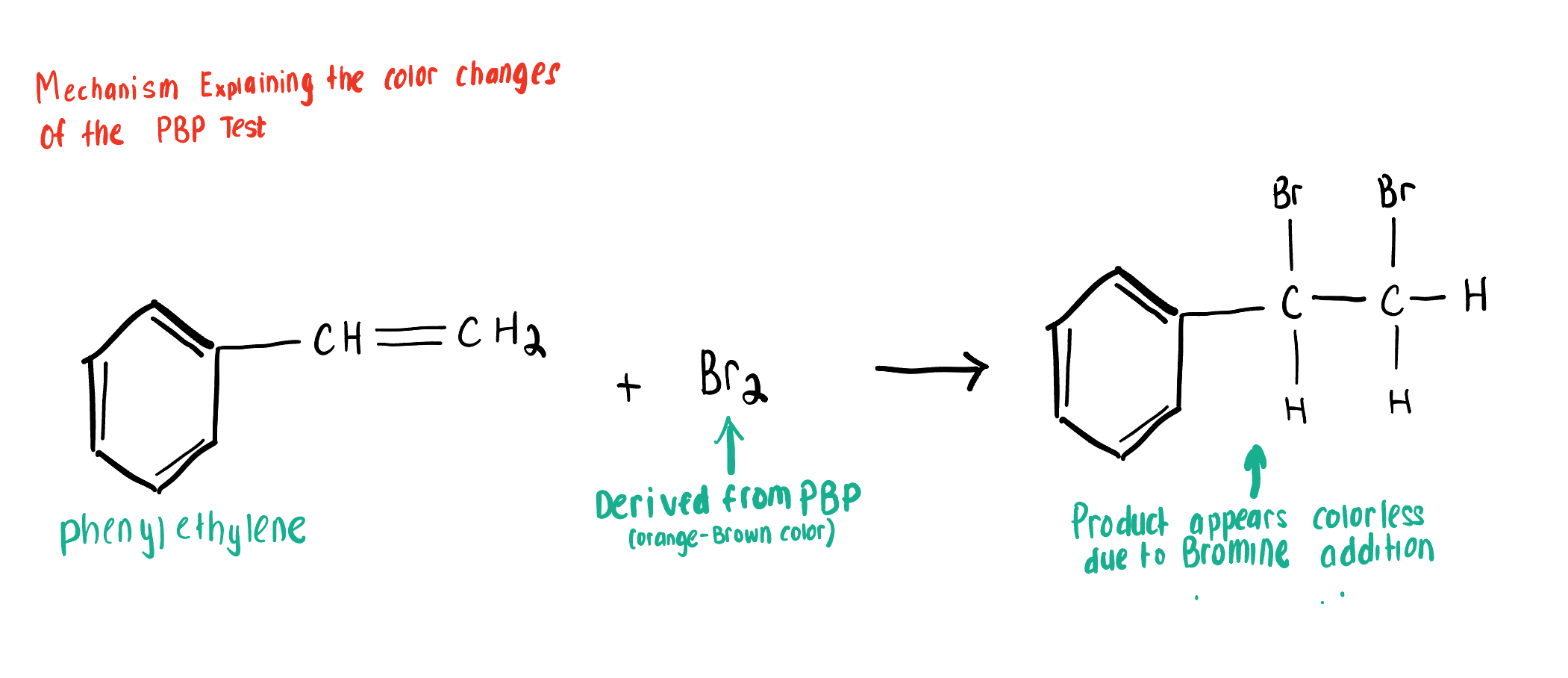
PBP (source of Br2 and is orange-brown) Conducts an Anti- Addition Rxn with Unsaturated compounds, adding Br to each end of the alkene or Alkyne C bond causing the solution to turn clear, or decolor
But PBP cannot react with saturated compounds (Alkanes), so the solution remains orange-brown
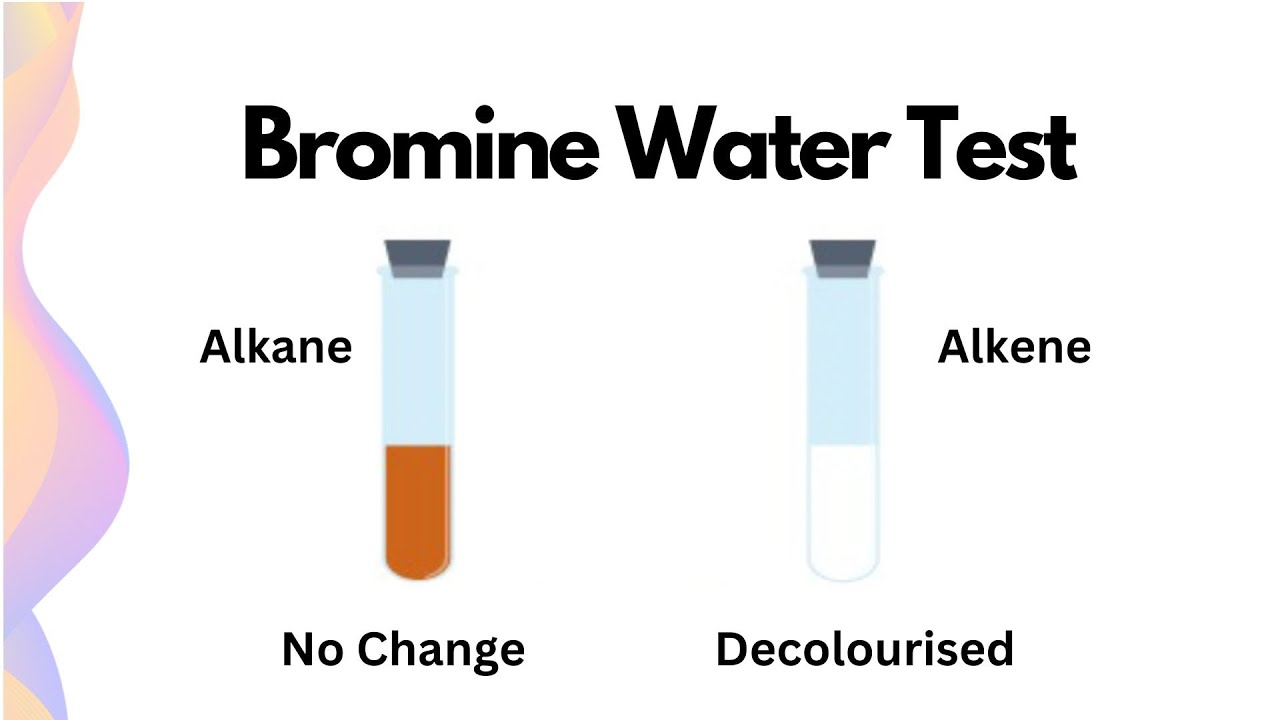
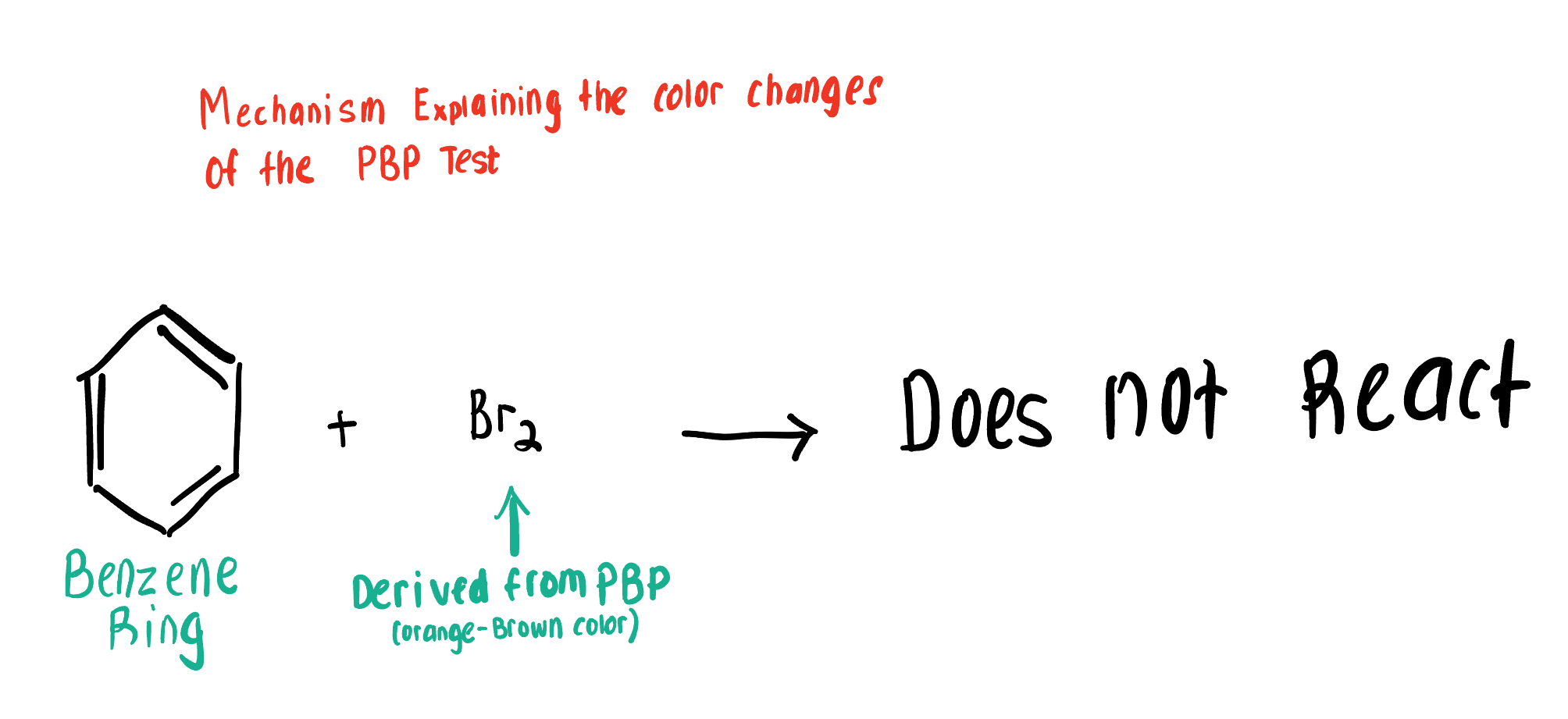
Does PBP react with Aromatic Compounds (the Ring itself) ? Explain why or why not.
PBP does NOT react w the Ring of Aromatic Compounds. Each C bears an e- that is shared with all of the Cs in the Ring.
Those shared electrons in the ring prevent Br(aq) from reacting with them and their inner circle
Typically the Bromide Test Uses Aqueous Br2.
But why did we choose to use PBP Instead?
Solutions like Br2(aq) that able to release Br2 are DANGEROUS (highly corrosive)
But, PBP is a safer option
Explain how the Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4) Test Works
Unsaturated Compounds (Alkenes specifically) donates e- to MnO4- (a purple solution) creating MnO2 Manganese Dioxide (a brown precipitate)
In turn, MnO4 donates an OH group to MnO4-, attaching it to each C end of the (C=C) 2x-bond (Syn Addition)
For the KMnO4 Test, why is Pure KMnO4 not used? Why is (2%) used instead?
Pure KMnO4 reacts with most organic compound
2% KMnO4 selectively reacts with C=C Alkenes only
In what direction do P-orbitals overap with each other?
Laterally (parallel)
They make up pi-orbitals
What is an Anti-addition?
an addition reaction where two substituents are added to a double or triple bond from opposite sides
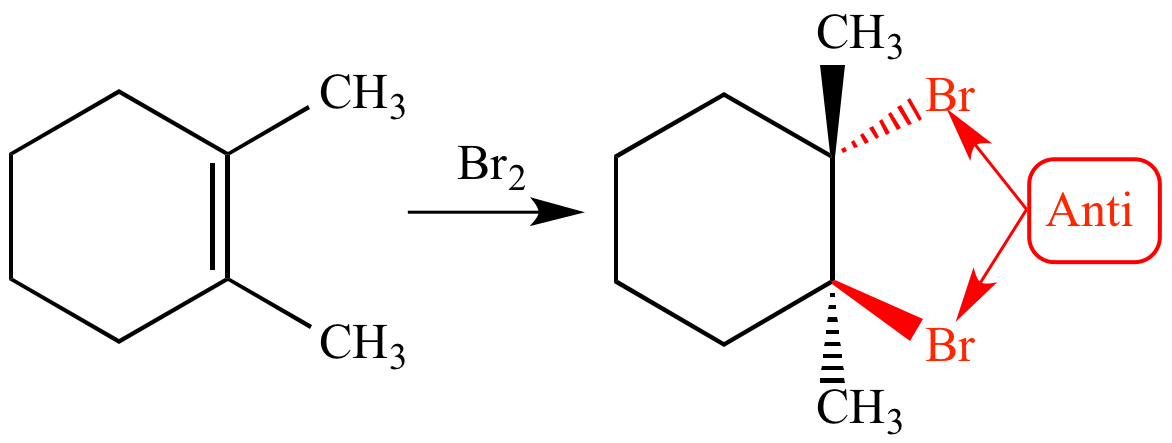
In
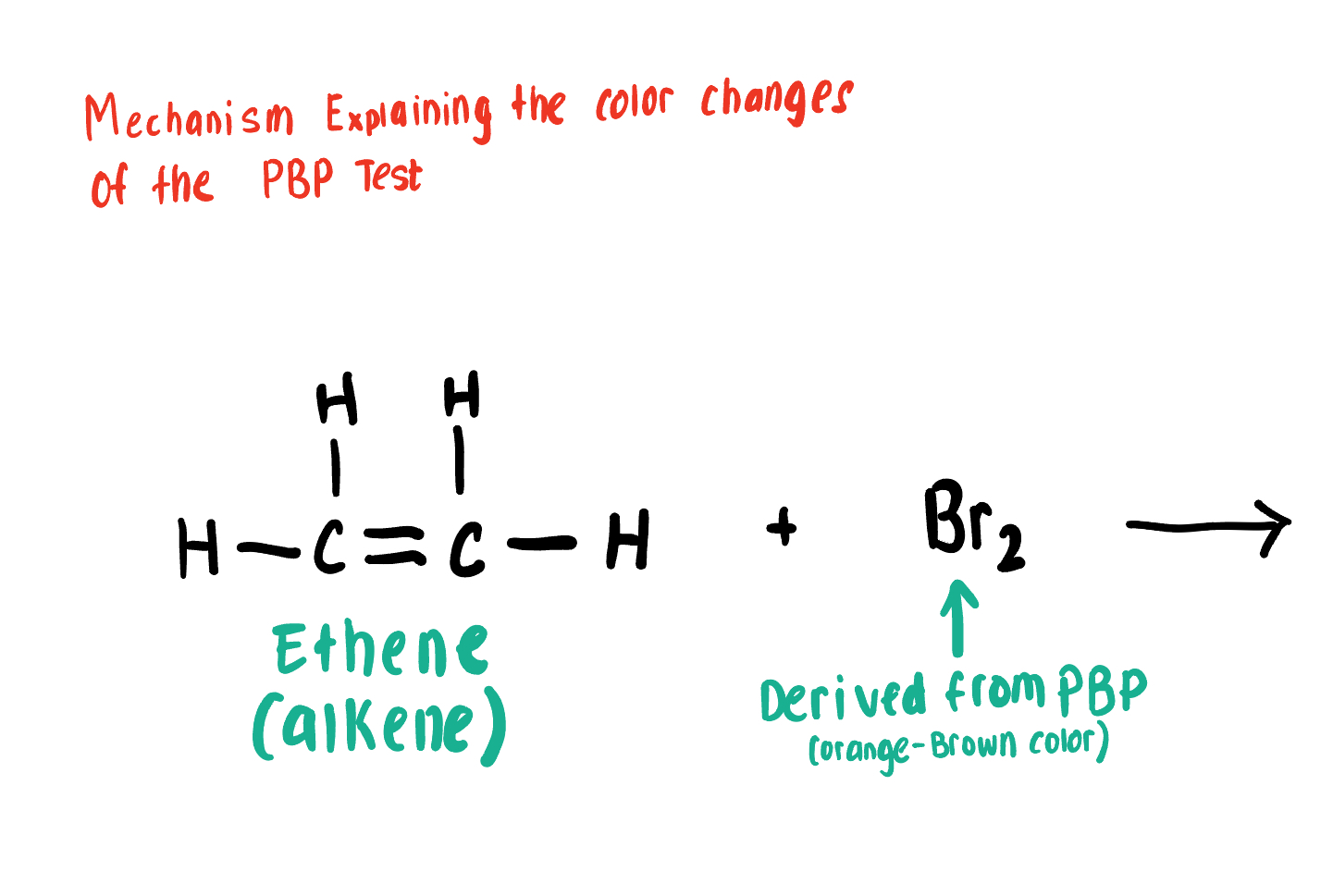
Draw the Product for this Bromide Test depicting the reaction of Br2 with the C=C alkene
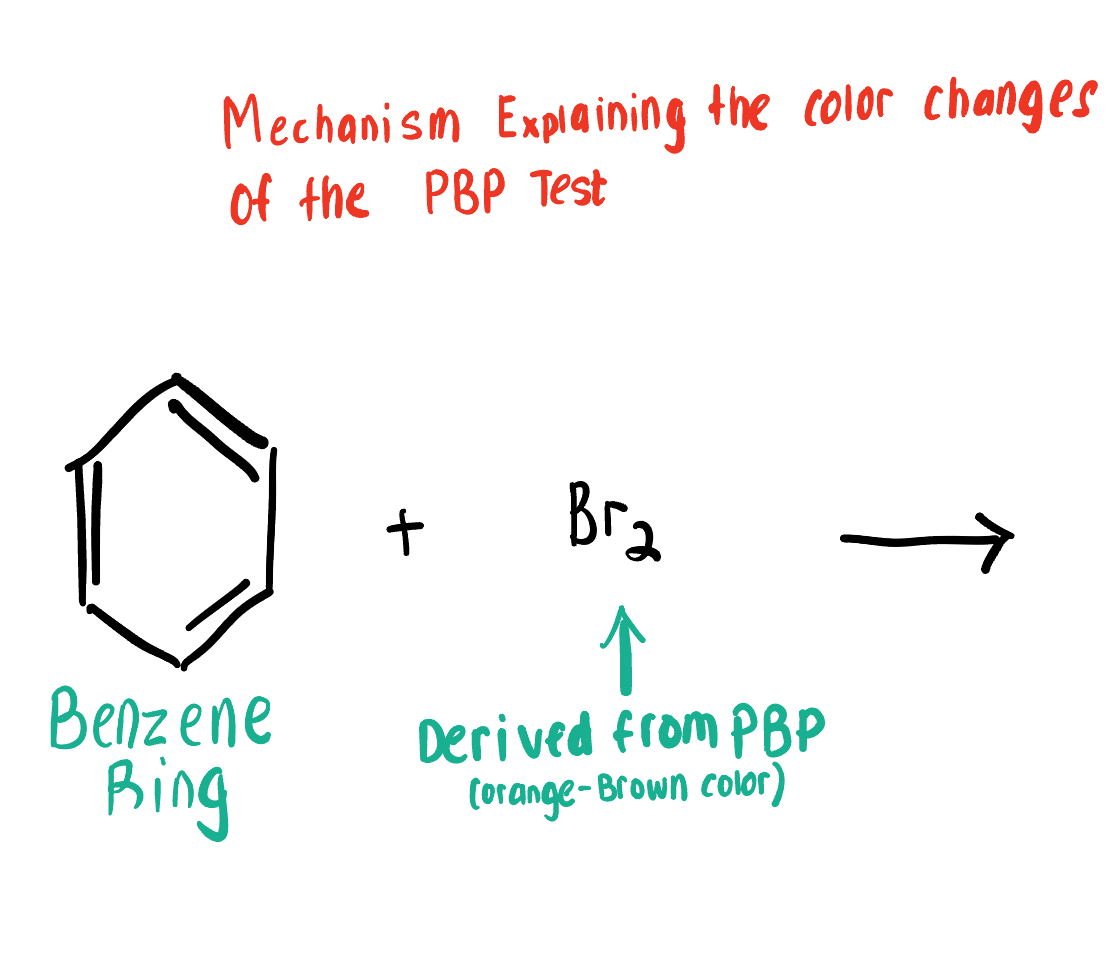
Draw the Product for this Bromide Test, depicting the reaction of Br2 with the Aromatic Compound.
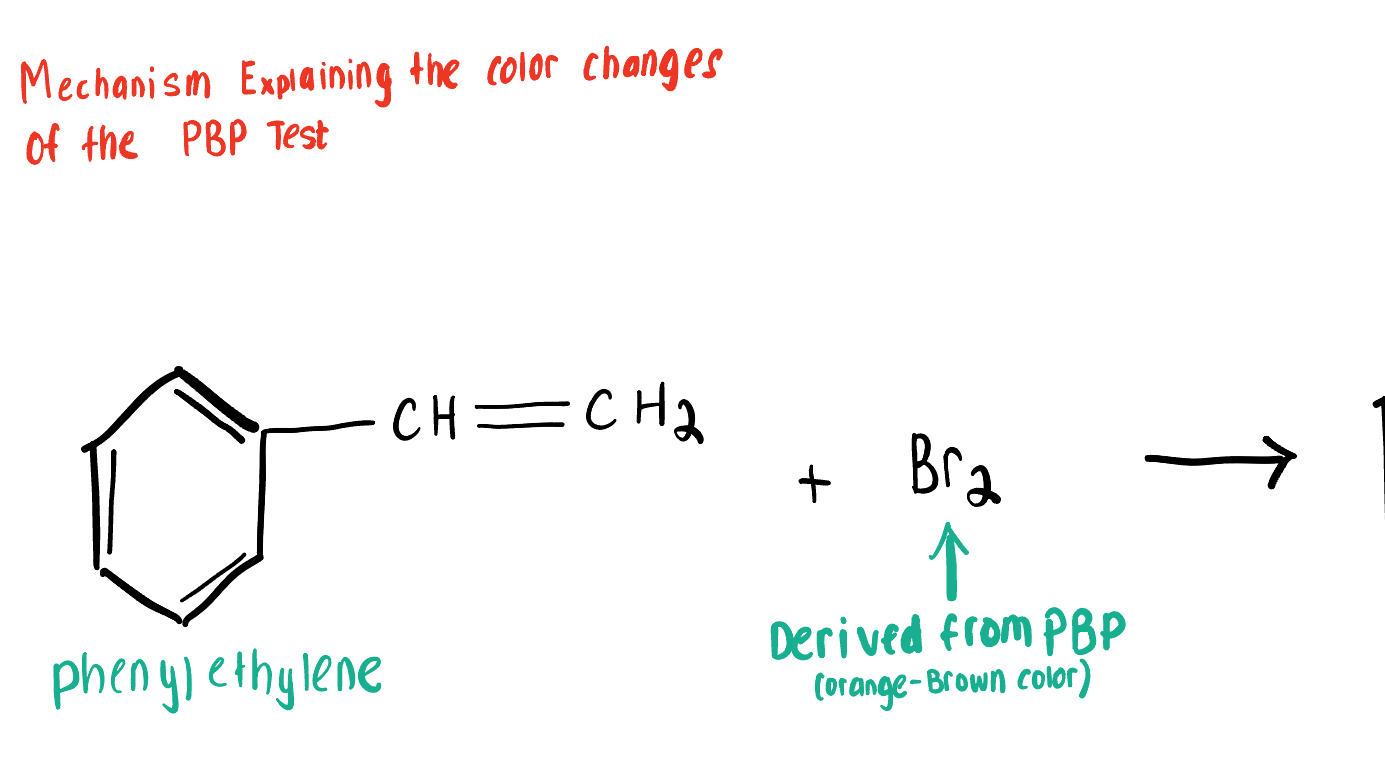
Draw the Product for this Bromide Test, depicting the reaction of Br2 with the Aromatic Compound bonded to a (C=C) 2x-bond alkene.
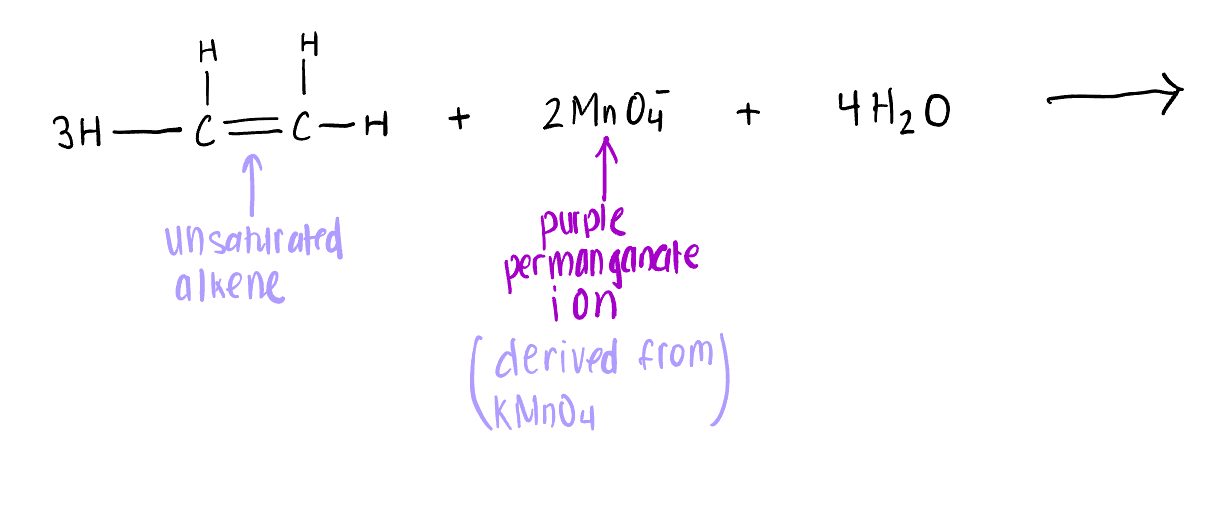
Draw the products for the Potassium Permanganate (MnO4) Test involving the reaction between a C=C 2x-bond and 2MnO4-
[Oxidation reaction] OH added to each C of the C=C bond,
The C=C bond becomes a C-C bond (bc it gives a way an electron pair to 2KMnO4-)
![<p>[Oxidation reaction] OH added to each C of the C=C bond, </p><p>The C=C bond becomes a C-C bond (bc it gives a way an electron pair to 2KMnO4-) </p><p></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/42a2d092-757d-427a-a3fc-884d7a961d4e.jpg)
Polar Aprotic Solvents
What are they?
a group solvents with medium range of polarity. They are polar because of polar bonds like C=O.
Lack OH or NH groups
Do not participate in H bonding
Polar Aprotic Solvents
What are they Better for? (SN1 or SN2)
Better for SN2 bc they don’t form hydrogen bonds with the Nucleophile, thus making it free to “attack” (increases nucelophile reactivity)
Bad for SN1 rxns bc they don’t stabilize the carbocation intermediate properly (BECAUSE they dont form those H-bonds)