Developmental Frameworks and Psychotherapy
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is a Developmental Framework?
Developmental Framework are a structured approach for understanding how psychological, emotional, and behavioral capacities evolve across someone’s life. Act as a model that explains the stages of development
→ allows for clinicians to understand mental health symptoms within stages of human development
What is the difference between Freud’s Topographical and Structural Theory of the Mind?
Freud’s Topographical Theory of the Mind
Subdivides the mind into three regions based on levels of awareness
→ Conscious: thoughts, feelings, and perceptions we are aware of
→ Preconscious: information not currently in awareness but is easily accessible
→ Unconscious: most influential and is the repressed desires and instincts that influence our behavior
Freud’s Structural Theory of the Mind
Builds off of Freud’s initial theory dividing the mind into three components
→ Id: primitive instinctual drives
→ Ego: mediator between our id and superego
→ Superego: internalized moral standards
What are Freud’s Psychosexual Stages?
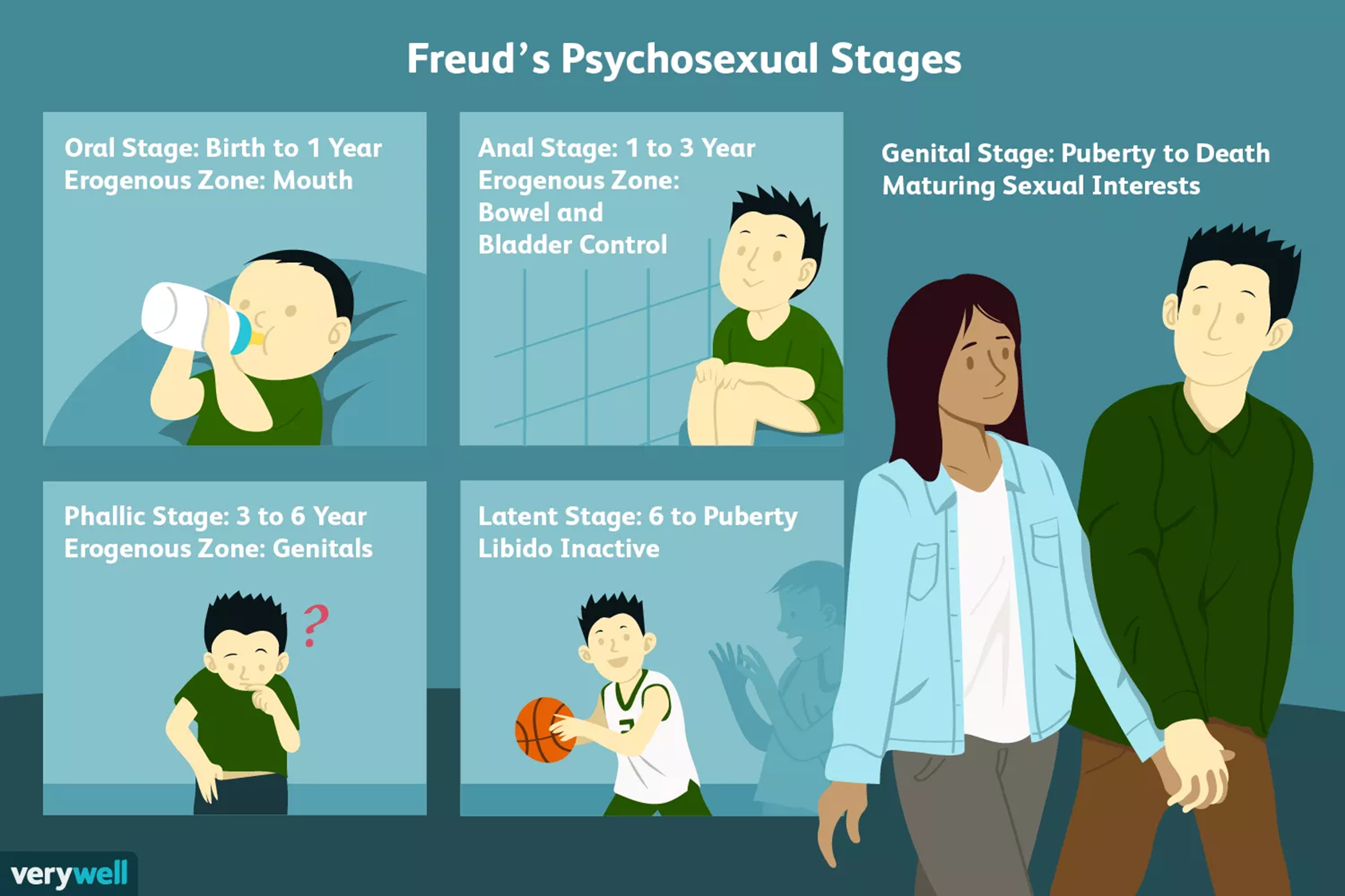
Subdivided into stages that have primary conflicts at each stage that each person must overcome
1) Oral - 0-1 years
→ erogenous zone is the mouth and the primary conflict is weaning
2) Anal - 1-3 years
→ erogenous zone is our anus and the primary conflict is potty training
3) Phallic - 3-5 years
→ erogenous zone is penis/clitoris and the primary conflict is the Oedipus complex
4) Latent - 5-12 years
→ no erogenous zone and the primary conflict is external gratifications
5) Genital - puberty to adulthood
→ primary conflict is the consensual relationship
What is Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory
Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory builds on Freud’s Developmental Model:
1) Introduces the epigenetic principle that stages that development occurs in sequential stages
→ each stage must be resolved for a healthy progression
→ virtues are associated with each successful resolution while failure leads to unresolved psychological conflict and pathology
2) Subdivided into eight stages of development
What are Erikson’s Psychosocial Stages?
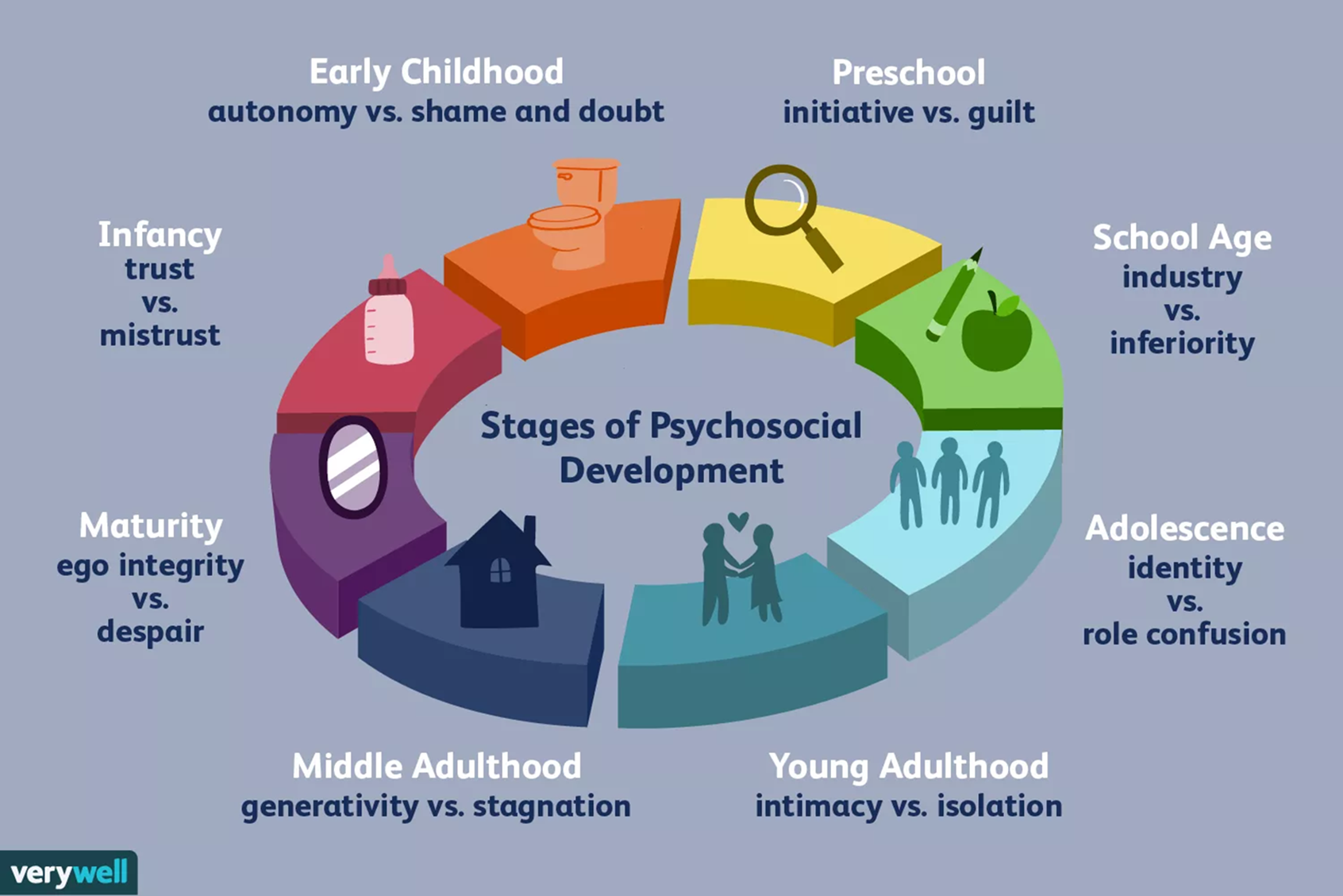
Erikson’s Psychosocial Stage is subdivided into eight stages with a primary psychosocial conflict that occurs at each stage
1) Infancy - Trust vs Mistrust
→ learning to trust a caregiver
2) Toddlerhood - Autonomy vs Shame/Doubt
→ learning to gain independence
3) Early Childhood - Initiative vs Guilt
→ learning to take the initiative to follow through on what they do
4) Middle Childhood - Industry vs Inferiority
→ confidence
5) Adolescence - Identity vs Role Confusion
→ teenagers test different hobbies and figure out what they are
6) Early Adulthood - Intimacy vs Isolation
→ seeking out partners and personal relationships
7) Middle Adulthood - Generativity vs Stagnation
→ focusing on contributing to society
8) Late Adulthood - Ego Integrity vs Despair
→ adults reflect on their life with either fulfillment or regret
What is Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development?
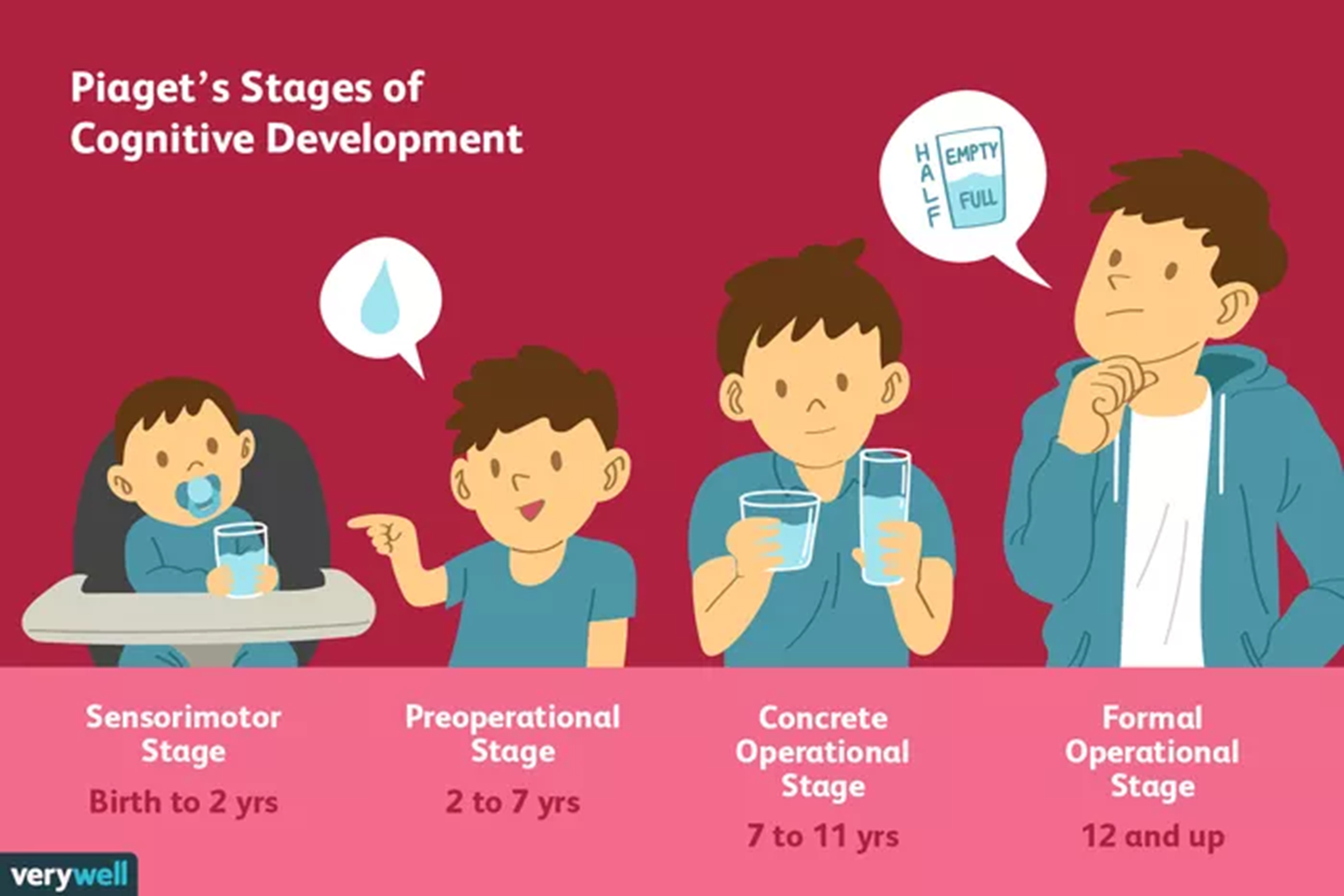
Jean Piaget proposed that children progress through four stages of cognitive development
1) Sensorimotor (0-2)
→ children begin learning through senses and actions where they develop object permanence
2) Preoperational (2-7)
→ children learn symbolic thinking and imagination
→ kids will have limited logic and egocentrism where they think of themselves
3) Concrete Operational (7-11)
→ logical thinking about concrete objects
→ begin understanding concepts like math and cause/effect
→ begin understanding that same amount of liquid is in two different sized cups
4) Formal Operational (12+)
→ abstract, hypothetical reasoning
→ thinking about the future and complex ideas
What is Acting Out, Denial and Displacement?
Three immature defense mechanisms
1) Acting Out - avoiding personally unacceptable feelings by acting in an attention-getting, socially inappropriate manner
2) Denial - not believing personally intolerable facts about reality
→ patients will be unable to accept idea
3) Displacement - transfer of emotions from unacceptable to acceptable person or object
→ you get bullied by your boss so you take it out on a friend
What is Dissociation, Identification, and Intellectualization?
Immature Defense Mechanisms:
1) Dissociation - separation of function of mental processes
→ disconnecting from experiences that are stressful
2) Identification - unconsciously patterning one’s behavior after someone who they consider powerful
3) Intellectualization - using the mind’s higher function to avoid experiencing uncomfortable emotions
→ someone with a disease will just go on google/pubmed and look up a bunch of stuff about the disease
What is Isolation of Affect, Projection, and Rationalization?
Immature Defense Mechanism:
1) Isolation of Affect - inability to experience the feelings associated with a stressful life event, even though they understand the significance of the event
→ patients will understand the significance of the event, but will not accept the emotions with the event - similar to denial
2) Projection - attributing one’s personally unacceptable feelings to others
→ if someone is cheating, and then they see their partner hiding their phone, they will assume that they are also cheating
3) Rationalization - giving seemingly reasonable explanations for unacceptable or irrational feelings
→ if i was speeding and got pulled over, it was okay I was speeding because I needed to go home
What is Reaction Formation, Regression and Repression?
Immature Defense Mechanism
Reaction Formation
→ denying unacceptable feelings and adopting opposite attitudes in order to reduce anxiety
→ ie: some gay people will have anti-gay views
Regression
→ appearances of childlike patterns or behaviors in response to stress
Repression
→ unconsciously putting aside unwanted feelings or ideas from awareness
What is Somatization, Splitting and Undoing?
Immature Defense Mechanism
Somatization
→ turning unacceptable feelings into a physical symptom
→ kids who get bullied at school will develop a stomach ache to avoid going to school
Splitting
→ believing people or events are either all bad or all good
→ patient’s will be like “you are the best doctor ever, my last doctor was horrible”
Undoing
→ erasing an unacceptable event in the past by adopting acceptable behavior in the present or by atonement or confession
→ someone will do something they feel morally wrong and then going to a priest to confess, feels like it absolves them of the consequence
What are the four mature defense mechanisms

1) Altruism
→ unselfishly assisting others to avoid negative personal feelings
→ I went through trauma and then turning that experience into a positive
2) Humor
→ expression of feeling without causing discomfort
3) Sublimation
→ rerouting an unacceptable drive in a socially acceptable way
→ i am anxious so I go and exercise
4) Suppression
→ Consciously putting aside unwanted feelings or ideas from awareness
→ I understand that something is bad to me, but I consciously compartmentalize it to focus on other stuff
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
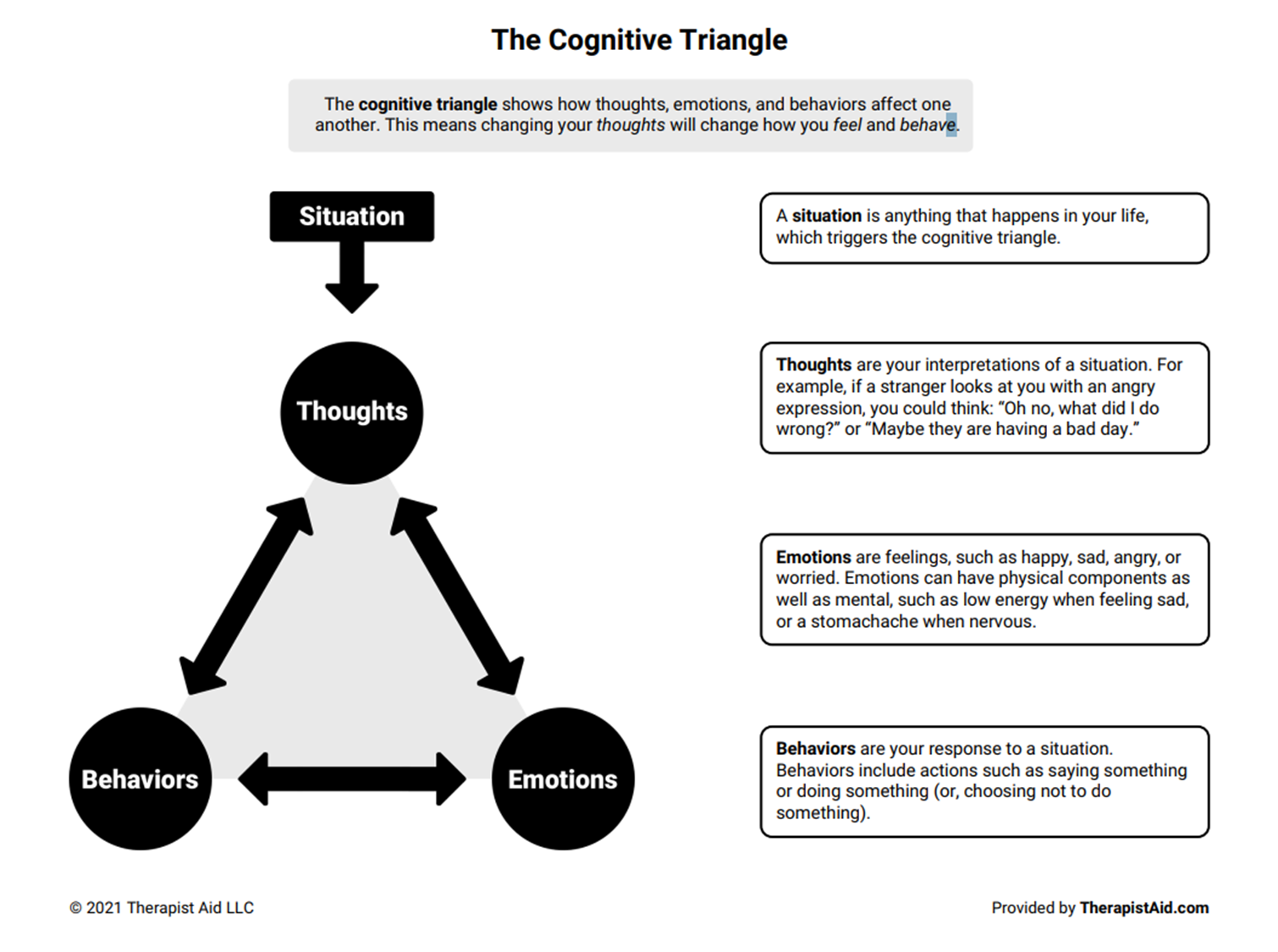
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy focuses on maladaptive thoughts that can lead to mental disorders
1) Uses the cognitive triangle showing the relationship between thoughts, behaviors, or emotions in response to a situation
→ We identify how we think about situations and how our thoughts affect our behaviors and emotions
→ by identifying our thought patterns we can improve emotional well-being
What is Exposure and Response Prevention Therapy?
Exposure and Response Prevention Therapy is used in OCD treatment
→ exposure patient to their obsessive thoughts such as making them touch a doorknob they perceive as dirty
→ response prevention where we make them resist the urge to perform compulsion
What Psychotherapies are used for the treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder?
Cognitive Processing Therapy - gold standard
→ Cognitive Behavioral Therapy applied to their trauma
→ finding their automatic thoughts to their trauma and helping them find tactics to avoid their thoughts
Prolonged Exposure Therapy
→ detailed imaging of the trauma and expose them to trauma to reduce fear
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing
→ uses bilateral stimulation like eye movements while recalling trauma
What is Dialectical Behavior Therapy?
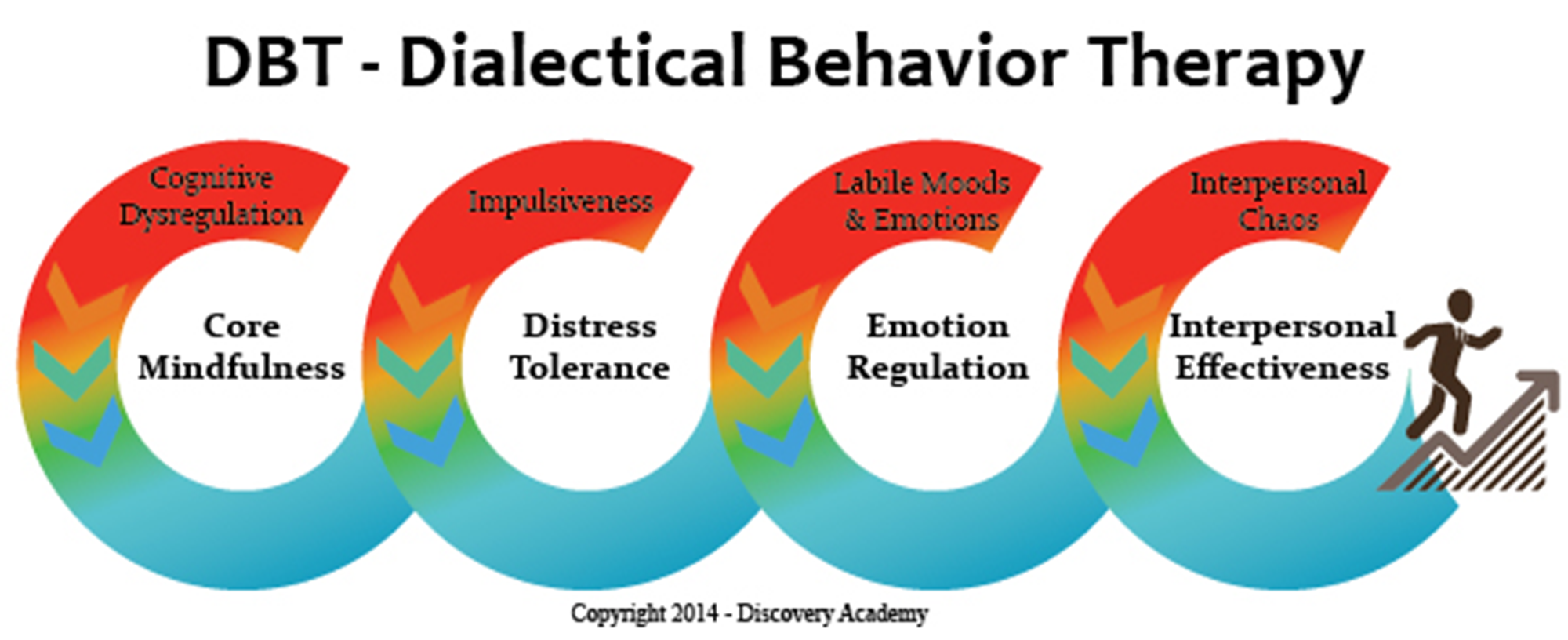
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy is used in the treatment of Borderline Personality Disorder
→ is a combination of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy + Mindfulness + Emotional Regulation
→ helps to improve interpersonal skill and decrease self-destructive behaviors
What is Supportive Therapy
Supportive therapy is a flexible therapy method that allows for symptom relief without exploration of unconscious conflicts
→ you support them while avoiding looking deeper into their inner thoughts
→ specific for acute crisis
What is Psychodynamic and Psychoanalytic Therapy?
Psychodynamic and Psychoanalytic Therapy is focused on increasing self-awareness and insight into unresolved emotional issues and is based on Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theory
→ tries to explores our unconscious thoughts and defense mechanisms
1) Uses techniques like free association and interpretation of transference and dream analysis
→ free association: patients will verbalize thoughts spontaneously while the therapists analyzes patterns
→ transference: is where a patient unconsciously redirects feelings from past relationships onto the therapist