Physics Master
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
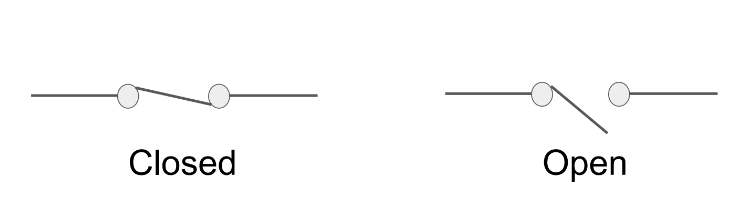
Draw the circuit symbol for a switch.
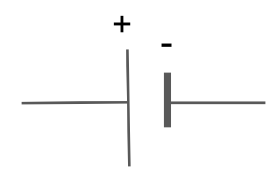
Draw the circuit symbol for a cell.
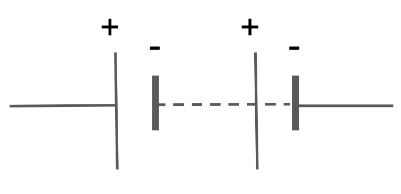
Draw the circuit symbol for a battery.
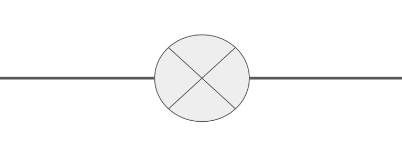
Draw the circuit symbol for a lamp.
Draw the circuit symbol for a fuse.

Draw the circuit symbol for a voltmeter.
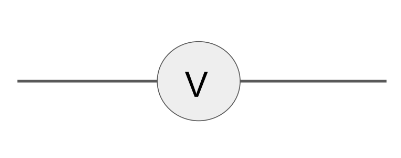
Draw the circuit symbol for an ammeter.
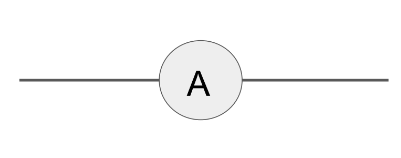
Draw the circuit symbol for a diode.
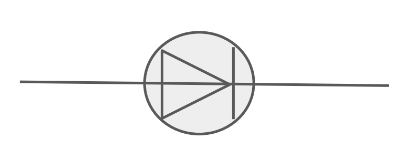
Draw the circuit symbol for a resistor.
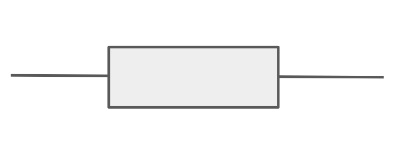
Draw the circuit symbol for a thermistor.
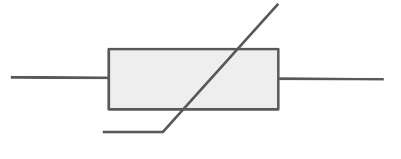
Draw the circuit symbol for a variable resistor.
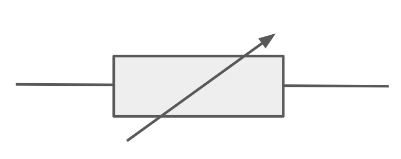
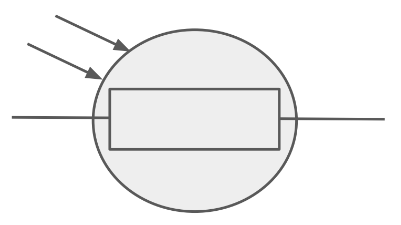
Draw the circuit symbol for an LDR.
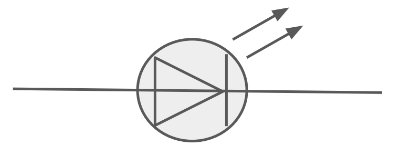
Draw the circuit symbol for an LED.
What is electric current?
The flow of electrical charge.
What can be said about the value of current at any point in a series circuit?
Current is the same at all points in a closed loop.
What two factors does the current in a circuit depend on?
Potential Difference (V) Resistance (R)
What equation should be used to calculate potential difference if current and resistance are known? State the units for all 3 quantities.
V = I R Potential Difference (V), Current (A), Resistance (Ω)
What is an ‘Ohmic Conductor’? State the condition required.
A conductor for which current and potential difference are directly proportional. Resistance remains constant as current changes. Temperature must be constant.
List four components for which resistance is not constant as current changes.
Lamps Diodes Thermistors Light Dependant Resistors (LDRs)
What happens to the resistance of a filament lamp as the temperature increases? Why?
Resistance increases. Ions in metal have more energy, so vibrate more, causing more collisions with electrons as they flow through the metal, creating greater resistance to current flow.
What is special about current flow through a diode?
The current only flows in one direction. Resistance is very high in the other direction, preventing current flow.
State what happens to the resistance of a thermistor as temperature increases.
The thermistor’s resistance decreases.
Give two examples of when a thermistor may be used.
In a thermostat to turn a heater on below a certain temperature. In a freezer to turn on a cooler when the temperature becomes too high.
State what happens to the resistance of a LDR as light intensity decreases.
The LDR’s resistance increases.
Give an application for a LDR.
Street lamps or night lights. When light levels become too low, the light gains sufficient current to turn on.
What are the two ways that a component can be connected in a circuit?
Series (same loop) Parallel (adjacent loop)
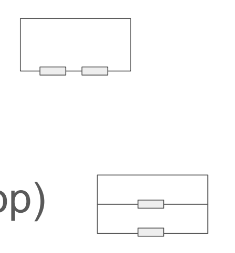
How does the potential difference across two components vary when connected in series and parallel?
Series: Total P.D is shared between each component. Parallel: P.D across each component is the same.
If two resistors are connected in parallel, what can be said about their combined total resistance?
Their total resistance is less than the smallest of the two individual resistances.
If two resistors are connected in series, what can be said about their total resistance?
Their total combined resistance is equal to the sum of the two individual resistances.
State two equations for the power of a circuit. Give appropriate units.
P = I V P = I² R Power P (Watts), Current I (Amperes), Potential Difference V (Volts), Resistance R (Ohms)
State an equation linking energy transferred, power, and time. Give appropriate units.
E = P t Energy E (Joules), Power P (Watts), Time t (Seconds)/
What is a renewable energy resource?
An energy source which can be replenished as it is being used up.
Give four examples of renewable energy resources.
Wind Energy Hydro-Electricity Tidal Energy Solar Energy
Give an example of a non-renewable energy resource.
Fossil fuels (for example coal, oil, and gas).
What are the advantages of generating power using gas rather than coal?
Flexible Generation: Gas power stations have short start-up times so can be switched on/off more readily. Lower emissions of carbon dioxide.
State two disadvantages of using renewable energy resources to generate power.
Output often determined by external factors (like wind speed), so supply is uncertain. Generating power through other means is often more efficient and economically beneficial (often renewable sources produce less energy per kg of fuel).
Explain the environmental impacts of burning fossil fuels.
Carbon Dioxide contributes to the greenhouse effect and causes global warming. Sulphur Dioxide leads to acid rain, which can damage buildings and crops.
State three advantages of fossil fuels as an energy resource.
Reliable: Not dependent on external factors so can generate power anytime. Can produce large amounts of energy for a given quantity. Still relatively abundant, so cost-effective.
State three advantages of nuclear power.
Very large quantity of energy for a relatively small quantity of fuel (lots of energy per kg). Doesn’t release greenhouse gases and so doesn’t contribute to climate change. Low fuel costs.
State three disadvantages of nuclear power.
Produces nuclear waste which is harmful to humans and must be safely stored for centuries. Nuclear fuel is a non-renewable energy source. Risk of nuclear accidents - fatal consequences on humans and the environment.
Give examples of social factors which may act as deterrents for certain types of energy production.
Visual Pollution Sound Pollution (Both of these are disadvantages of wind farms.)
What are the two types of transformers?
Step-Up Transformers Step-Down Transformers
Where are step-up transformers found in the National Grid? What do they do?
Step-Up Transformers are used when connecting power stations to transmission cables. They increase the potential difference (decreasing current).
Where are step-down transformers found in the National Grid? What do they do?
Step-Down Transformers are used when connecting transmission cables to domestic buildings (like houses). They decrease the potential difference (increasing current).
Why do transmission lines transfer electricity at high potentials?
A high potential difference results in a low current. The lower the current, the less energy is dissipated as heat. Therefore, transport is more efficient.
Why does the potential need to be decreased between transmission lines and houses?
Lower potentials are safer for domestic use and reduce the likelihood of severe electrocution. Household appliances are designed for 230V.
State two equations to calculate efficiency.
Efficiency = Useful Output Energy / Total Input Energy Efficiency = Useful Power Output / Total Power Output/
State three methods of reducing heat loss in a building.
Double glazing Loft and wall insulation Thicker walls
What is the definition of density? State the relevant equation with units.
The mass per unit volume of a material. ⍴ = m/v Density (kg/m³), Mass (kg), Volume (m³)
Give the 3 states of matter in order of lowest to highest density of atoms.
Lowest: Gas Liquid Highest: Solid
What is always conserved when a substance undergoes a change of state?
Mass
State the three different types of energy transfer.
Conduction Convection Radiation
Explain using a particle model, the process of convection. (Higher)
When heated, fluids expand, making the particles spread out, and making the fluid less dense. Less dense fluids rise above cooler, more dense fluids. These cooler fluids then heat up and rise upwards, creating a cyclic motion of particles (called a convection current).
Explain using a particle model, the process of conduction in a metal. (Higher)
A metal consists of positive ions and free electrons. As temperature increases, the ions gain kinetic energy and vibrate. This energy is then passed on via collisions to free electrons, which can move throughout the whole metal. These electrons transfer kinetic energy (again via collisions) to ions further through the metal, increasing their temperature./
What unit of power is normally used for domestic electricity?
The Kilowatt (kW).
What is the unit of energy associated with the kW?
The Kilowatt Hour (kWh).
State the equations used to calculate the cost of electricity. Give appropriate units.
Energy (kWh) = Power (kW) × Time (h)
Cost = Units used × Cost per unit energy (cost per kWh)
Is mains electricity an a.c supply or a d.c supply? What do each of these stand for?
It is an a.c supply.
a.c: Alternating Current
d.c: Direct Current
Define direct current.
Direct current: One-directional current flow.
Define alternating current.
Alternating current: Current that continuously changes direction at a specific frequency.
What is the frequency and voltage of the UK mains electricity supply?
Frequency: 50 Hz
Voltage: 230V
How many wires are usually in the cables connecting electrical appliances to the mains? Name these wires.
Live wire
Neutral wire
Earth wire
State the insulation colour used on the Earth wire.
Green and Yellow Stripes.
State the insulation colour used on the live wire.
Brown.
State the insulation colour used on the neutral wire.
Blue.
Explain when the Earth wire does and doesn’t carry a current.
Under normal circumstances, no current flows through the Earth wire. If a fault occurs in the appliance (such as a surge or the casing becoming live), current will flow.
What potential is the neutral wire at?
0 Volts.
State the potential difference between the live and earth wires.
230 Volts.
What is the purpose of the neutral wire?
To complete the circuit by connecting the appliance back to the mains supply.
What does MCB stand for?
Miniature Circuit Breaker.
What does RCCB stand for?
Residual Current Circuit Breaker.
For metal appliances, where is the Earth wire connected to? Why?
The Earth wire is connected to the metal casing of the appliance. If the live wire becomes loose and touches the casing, the casing will become live. The current will flow through the Earth wire, preventing electrocution.
What are the two types of waves?
Transverse
Longitudinal
What is a transverse wave?
A wave for which the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
What is a longitudinal wave?
A wave for which the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
Give two examples of transverse waves.
Electromagnetic waves
Seismic s-waves
Give two examples of longitudinal waves.
Sound waves
Seismic p-waves
What are the two parts of a longitudinal wave called?
Compressions and rarefactions.
What are the two parts of a transverse wave called?
Peaks and troughs.
What is a wave’s amplitude?
The maximum displacement of a point on a wave from its undisturbed position.
What is wavelength?
The distance from a point on a wave to the same position on the adjacent wave.
Most commonly peak to peak or trough to trough.
What is the frequency of a wave?
The number of waves that pass a given point each second.
What is the unit used for frequency?
Hertz, Hz.
What is meant by a frequency of 200Hz?
200 waves pass a given point each second.
What is wave speed?
The speed at which energy is transferred through a medium.
What does a wave transfer?
Energy.
Waves do not transfer matter.
State the equation used to calculate wave speed. Give appropriate units.
Wave Speed = Frequency × Wavelength
Speed (m/s), Frequency (Hz), Wavelength (m).
What word is used to describe when a wave bounces off a surface?
Reflection.
What type of spectrum do electromagnetic waves form?
A continuous spectrum.
Order the types of electromagnetic radiation from lowest to highest frequency.
Radio waves
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible Light
Ultraviolet
X-rays
Gamma Rays
Which types of electromagnetic radiation have the longest and shortest wavelength?
Longest: Radio waves
Shortest: Gamma rays
Which types of electromagnetic radiation have the lowest and highest energy?
Lowest: Radio waves
Highest: Gamma rays
How do the speeds of EM radiation differ in a vacuum and in air?
Electromagnetic waves all travel at the same speed in a vacuum and in air.
What property of waves in different mediums causes refraction?
Velocity.
Wave speed is slower in denser materials, causing refraction.
In which direction relative to the normal do waves refract when entering a denser medium?
They bend towards the normal.
The angle of refraction is less than the angle of incidence.
What is a geostationary satellite and what are they used for?
A satellite that has the same period as the Earth and so remains in a fixed position relative to the Earth.
Used for communications such as satellite TV signals.
What does TIR stand for?
Total Internal Reflection.
What form of information transfer makes use of TIR?
Optical fibres (aka fibre optic technology).
Give two uses for optical fibres.
High-speed internet connections.
Endoscopes (medical diagnosis tool).
What condition relating to the incident angle of the wave must be met for TIR to occur?
The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.