ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES (copy)
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Hydrocarbons
compounds that only contain C and H atoms
Saturated
Saturated or Unsaturated?
carbon-carbon single bonds
Unsaturated
Saturated or Unsaturated?
carbon-carbin multiple bonds
Aromatic compounds
special class of cyclic compounds related in structure to benzene
Aliphatic and Aromatic Hydrocarbons
What are the types of hydrocarbons?
Alkane
This is an example of what type pf Hydrocarbon?
Alkanes
Hydrocarbons with a single carbon-carbon bond
Cn H2n+2
General formula of Acyclic Alkane
CnH2n
General formula of Cycloalkane
Methane
What is the simplest Alkane?
sp3; ~109.5°
Every C atom of an Alkane is ___ hybridized with bond angles of ____.
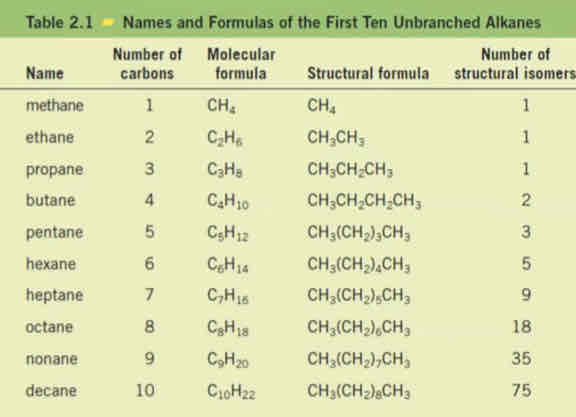
4 Carbons
maximum number of carbons of Acyclic Alkanes
Unbranched alkanes or normal (n-alkanes)
Branched alkanes
Two forms of Alkanes
Suffix
In the nomenclature of Organic Compounds, this part of determines what functional group is present
Parent name
In the nomenclature of Organic Compounds, this part of determines the longest Carbon chain
Prefix
In the nomenclature of Organic Compounds, this part of determines what and where are the subtituents
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
IUPAC stands for
• Systematic (IUPAC name)
• Generic- official, internationally approved drug name
• Trade- name assigned by the drug manufacturing company
3 common names of drugs
Propyl/Isopropyl
Ana alkyl group which has three carbons
Substituents
groups attached to main chain of a molecules
Only C and H molecules
Saturated substituents
R
General symbol for alkyl
2 C
secondary carbon is bonded to how many Carbons?
3 C
A tertiary carbon is bonded to how many carbons?
Propane
major constituent of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
Butane
gas of choice in some areas.
Petroleum
This is a source of Alkane which is composed of a complex mixture of compounds that must be refined to separate it into usable fractions.
Natural Gas
Often found associated with petroleum deposits, consists mainly of about 80% methane and 5% to 10 % ethane, with lesser amounts of some higher alkanes.
contain only non-polar C-C and C-H bonds
exhibit only weak intermolecular forces
they are insoluble in water
have lower boiling points
Physical properties of an Alkanes:
van der Waals or London Dispersion Forces
An intermolecular force that has temporarily polarized molecule causes its neighbor to become temporarily polarized
Hydrogen Bonding
Strongest intermolecular forces
O, N, or F
The intermolecular force, Hydrogen Bonding enables a hydrogen atom to bond to?
Dipole-dipole
An intermolecular force that exhibits attractive forces between molecules with permanent dipoles
Hydrogen Bonding
This intermolecular force gives the helix structure of DNA stability
Boiling point
point at which liquid is converted to the gas phase
Melting point
Point at which solid is converted into liquid
Directly proportional
Relationship of stability of the intermolecular forces and the boiling & melting point
Naming Alkanes
prefix (What and where are the substituents) + parent (What is the longest carbon chain) + suffix (What is the functional group)
Naming Alkanes
prefix + parent + suffix
Alkyl Group
A substituent group derived from an alkane by removal of a hydrogen atom
Molecular weight
In Alkanes, boiling and melting points increase with increasing _________
Branching
In Alkanes, boiling point decrease with more _________
Naming Cycloalkanes
prefix + cyclo + parent + suffix
Naming Cycloalkanes
prefix + cyclo + parent + suffix
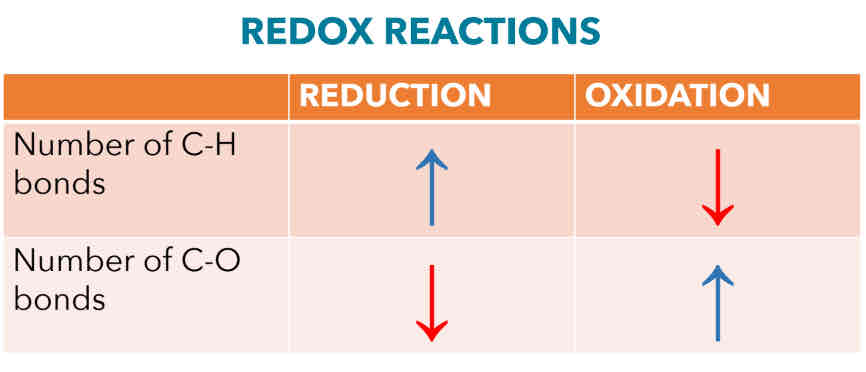
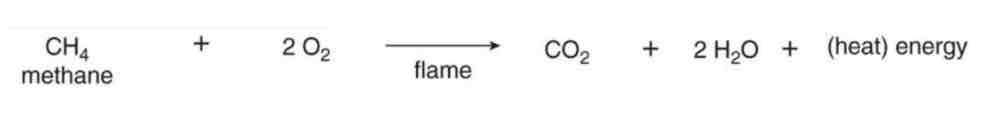
Oxidation (Combustion)
*C-H bonds inthe starting material is converted into C-O bond in the product
Identify the rxn
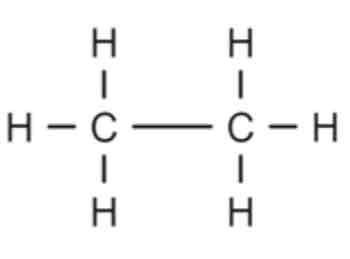
Halogenation (Substitution Rxn)
Identify the rxn
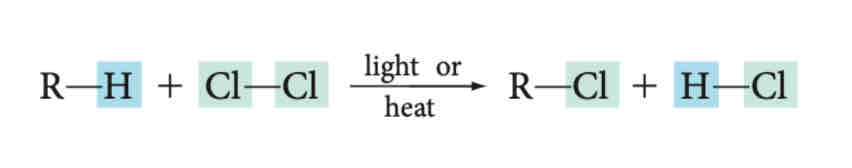
Halogenation → Polyhalogenated products
Identify the rxn