ap human geo unit 3 by the emo cat but i fixed the problems this time
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Last updated 2:47 PM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
Culture
The shared beliefs, values, practices, behaviors, and technologies of a society.

2
New cards
Traditional/Local Culture
Also Called Folk Culture
Heart - Rural Areas, now in mostly LDCs
Diffusion - Relocation Diffusion
Practiced By - Small, homogenous (similar) groups of people
Architecture - Materials from local, physical environment
Ex: Snow, mud, stone, bricks, wood, pelts, and grass
Land-Use Agricultural, Sense of place, Distinctiveness
Example: Texas - mums, China - small feet for women
Heart - Rural Areas, now in mostly LDCs
Diffusion - Relocation Diffusion
Practiced By - Small, homogenous (similar) groups of people
Architecture - Materials from local, physical environment
Ex: Snow, mud, stone, bricks, wood, pelts, and grass
Land-Use Agricultural, Sense of place, Distinctiveness
Example: Texas - mums, China - small feet for women
3
New cards
Global Culture
Also called Popular Culture
Hearth - Urban centers, MDCs
Diffusion - Contagious, Hierarchical
Practiced By - Large Heterogenous (difficult) groups of people
Architecture - Materials from factories & manufactured
Ex: Glass, steel, drywall, cement
Land-use - Urban & suburban, placelessness
Hearth - Urban centers, MDCs
Diffusion - Contagious, Hierarchical
Practiced By - Large Heterogenous (difficult) groups of people
Architecture - Materials from factories & manufactured
Ex: Glass, steel, drywall, cement
Land-use - Urban & suburban, placelessness
4
New cards
Ethnocentrism
Judging other cultures in terms of one's own standards and often one's own culture/ethnic group is better/normal
Example: Hijab, Food from other cultures. university gestures, etc.
Example: Hijab, Food from other cultures. university gestures, etc.

5
New cards
Cultural Relativism
An unbiased way of viewing another culture, the goal is to promote understanding of cultural practices.
Ex: Asking why people eat this instead of judging.
Ex: Asking why people eat this instead of judging.

6
New cards
Cultural Norms
Agreed upon cultural practices or standards that guide the behavior of a culture.

7
New cards
Cultural Taboos
Behaviors heavily discouraged by a culture

8
New cards
Cultural Traits (just in case)
Visible and invisible attributes that combine to make up a group's culture.
Artifacts, Sociofacts, Mentifacts
Artifacts, Sociofacts, Mentifacts

9
New cards
Artifacts (just in case)
Visible, physical objects created by culture.
Houses, clothing, architecture, tools, etc.
Houses, clothing, architecture, tools, etc.

10
New cards
Sociofacts (just in case)
The ways in which a society behaves and organizes institutions.
Family, Schools, Government, Religion, Land use, Gender roles.
Family, Schools, Government, Religion, Land use, Gender roles.
11
New cards
Mentifacts (just in case)
The ideas, beliefs, values, and knowledge of a culture.
Religious beliefs, language, taboos.
Religious beliefs, language, taboos.

12
New cards
Cultural Landscape
Built environment.
Natural landscape that humans modified, reflecting their cultural beliefs and values.
Agricultural and industrial practices.
Religious and linguistic characteristics.
Sequent Occupancy.
Traditional and postmodern architecture
Land-use patterns.
Natural landscape that humans modified, reflecting their cultural beliefs and values.
Agricultural and industrial practices.
Religious and linguistic characteristics.
Sequent Occupancy.
Traditional and postmodern architecture
Land-use patterns.

13
New cards
Sequent occupancy
The idea that societies or cultural groups leave their cultural imprints when they live in a place, each contributing to the overall cultural landscape over time.
Mix of historic and modern structure.
Mix of historic and modern structure.

14
New cards
Ethnicity
Sense of belonging or identity within a group of people bound by common acestry and culture.

15
New cards
Ethnicity influencing cultural landscape.
1. Ethnic Neighborhoods/Enclaves
2. Ethnic Patterns in population distribution
2. Ethnic Patterns in population distribution
16
New cards
Ethnic Neighborhoods/Enclaves
People of the same ethnicity that cluster together in a specific location, typically within a major city.
Relates to chain migration.
Formed to maintain cultural identity, avoid racism and discrimination.
Ex: Chinatown
Relates to chain migration.
Formed to maintain cultural identity, avoid racism and discrimination.
Ex: Chinatown

17
New cards
Ethnic Patterns
Predictable distribution of ethnicities that can be examined at multiple scales.
United States: Historically and contemporarily there are clusters of ethnic groups in specific regions.
Southwest: Latin Americans & Native Americans
Southwest: Asians
Etc.
United States: Historically and contemporarily there are clusters of ethnic groups in specific regions.
Southwest: Latin Americans & Native Americans
Southwest: Asians
Etc.
18
New cards
Gender influencing Cultural Landscapes
Women's status.
Gendered Spaces.
Gendered Spaces.
19
New cards
Women's Status
Traditional cultures, primary role of women is to have children and not be active in education or the workforce.
More developed, women have access to further education, the workforce, and property rights.
Do women own property and businesses?
Are women present in colleges? Women's dorms?
Are there women working outside of the home?
More developed, women have access to further education, the workforce, and property rights.
Do women own property and businesses?
Are women present in colleges? Women's dorms?
Are there women working outside of the home?

20
New cards
Gendered Spaces
Places in the cultural landscape utilized to reinforce or accommodate gender roles for men and women.

21
New cards
Land-use influencing Cultural Landscape
Geographers study land-use patterns as seen on the cultural landscape which reflect the cultural values of the people living there.
Ex: Terrace Farming, US Reservation System, Subsistence Whaling
Ex: Terrace Farming, US Reservation System, Subsistence Whaling
22
New cards
Architecture influencing Cultural Landscape
Traditional Architecture.
Postmodern Architecture.
Postmodern Architecture.
23
New cards
Traditional Architecture
Influenced by environment and built with available local materials. Reflective of history, culture and climate.
Huts/Cabins, Stone and clay houses, Portable Mongolian yurts.
Huts/Cabins, Stone and clay houses, Portable Mongolian yurts.
24
New cards
Postmodern Architecture
Diverse designs, representative of popular culture, business and economic success.
Ex: Skyscrapers
Ex: Skyscrapers
25
New cards
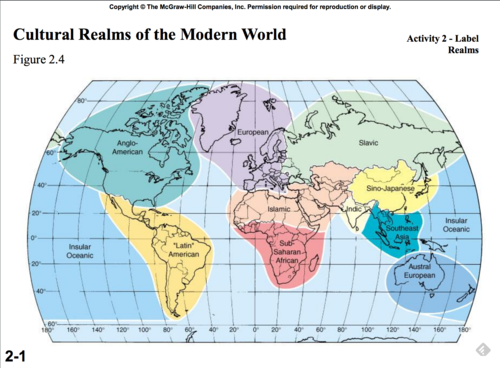
Cultural Realm
Areas of the world that share cultural traits such as language families, religious traditions, food preferences, architecture, shared history, etc.
1. North America
2. Latin America
3. Europe
4. Islamic
5. Sub-Saharan Africa
6. Slav
7. India
8. South-Eastern Asia
9. Australian-Oceanic
10. Sino-Japanese
1. North America
2. Latin America
3. Europe
4. Islamic
5. Sub-Saharan Africa
6. Slav
7. India
8. South-Eastern Asia
9. Australian-Oceanic
10. Sino-Japanese
26
New cards
centripetal force
Characteristics that unify a country and provide stability.
Ex: Common language, ethnicity, religion, history, etc.
Ex: Common language, ethnicity, religion, history, etc.

27
New cards
Centrifugal forces
Characteristics that divide a country and create instability, conflict, and violence.
Ex: Multiple competing ethnicity, languages, religions, cultural barriers, etc.
Ex: Multiple competing ethnicity, languages, religions, cultural barriers, etc.

28
New cards
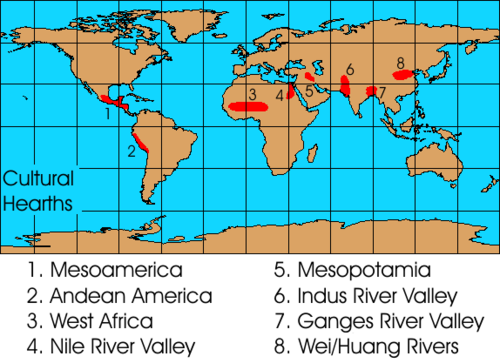
Cultural Hearths
The geographic origin of a culture or cultural trait.
Traits first diffuse from the cultural hearth.
Traits first diffuse from the cultural hearth.
29
New cards
Diffusion
The movement or spread of cultural traits, knowledge, ideas, trends from hearths to other geographic areas.

30
New cards
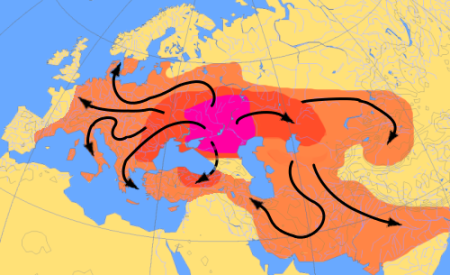
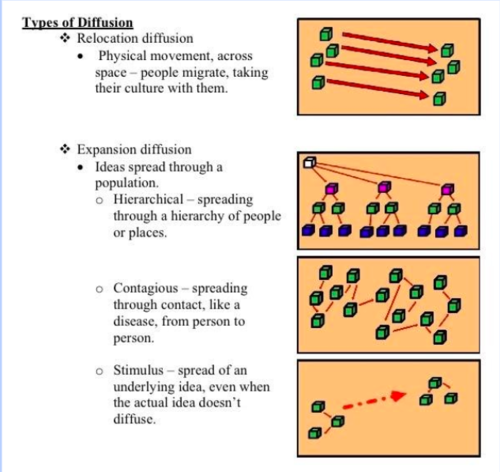
Types of Diffusion
1. Relocation
2. Expansion
2. Expansion
31
New cards
Relocation Diffusion
The spread of a cultural trait through the MIGRATION of people.
People migrate and take their cultures with them.
Ex: European migration to Americas led o spread of European languages and Christianity.
People migrate and take their cultures with them.
Ex: European migration to Americas led o spread of European languages and Christianity.

32
New cards
Expansion Diffusion
The spread of a cultural trait through the INTERACTION between people.

33
New cards
Types of Expansion Diffusion
1. Contagious Diffusion
2. Hierarchical Diffusion
3. Reverse Hierarchical Diffusion
4. Stimulus Diffusion
2. Hierarchical Diffusion
3. Reverse Hierarchical Diffusion
4. Stimulus Diffusion
34
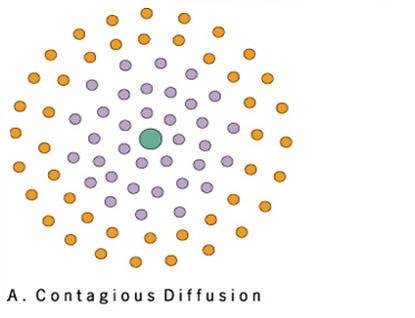
New cards
Contagious Diffusion
A cultural trait spreads continuously rapidly, and widely from its hearth through close CONTACT between people.
Ex: Viral Videos
Ex: Viral Videos
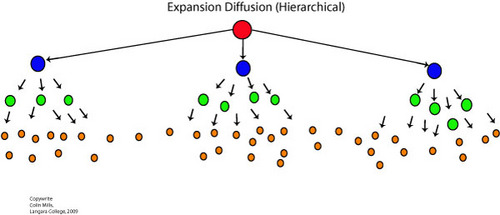
35
New cards
Hierarchical Diffusion
The spread of cultural traits from the MOST interconnected, powerful, wealthy people/places/organizations down to others.
Ex: Cell Phones, Cars, Music, Fashion, Popular culture trends, etc.
Ex: Cell Phones, Cars, Music, Fashion, Popular culture trends, etc.
36
New cards
Reverse Hierarchical Diffusion
The spread of cultural traits from the LEAST interconnected, wealthy, or powerful people/places/organizations outwards.
Ex: Hip Hop, Walmart, etc.
Ex: Hip Hop, Walmart, etc.

37
New cards
Stimulus Diffusion
The spread of an underlying principle or cultural trait but they are altered/modified due to cultural barriers, taboos, or differences.
Ex: McDonalds in India, Baseball in Japan, American Football, Noodles, etc.
Ex: McDonalds in India, Baseball in Japan, American Football, Noodles, etc.

38
New cards
Colonialism diffusing culture
Countries establish settlements in new areas and impose their religion, language, and cultures on the indigenous population.
Colonialism established modern borders.
Colonialism established modern borders.
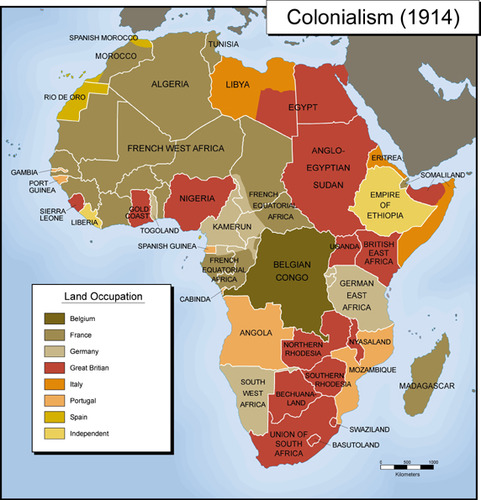
39
New cards
Neocolonialism diffusing culture
MDCs economically dominanting LDCs. LDCs send laborers to MDCs and they bring their culture.
40
New cards
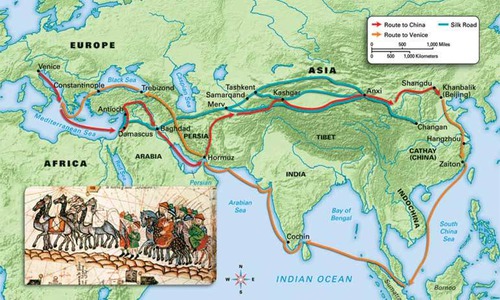
Trade diffusing culture
People interact to exchange goods. They exchange their cultures and people move to places.
41
New cards
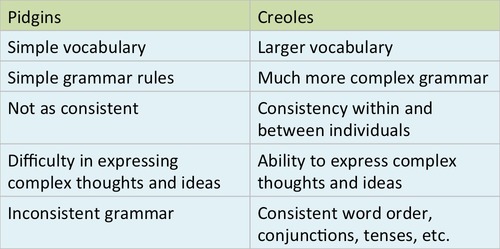
Pidgin Language
An extremely simplified, limited non-native language used by two people that speak two different languages.
Ex: Spanglish, Franglish, etc.
Ex: Spanglish, Franglish, etc.

42
New cards
Creole Language
A pidgin language that develops into a new combined language with native speakers. Frequently developed through settings of colonization or slavery.
Ex: Haitan, Cajun/Louisiana Creole.
Ex: Haitan, Cajun/Louisiana Creole.
43
New cards
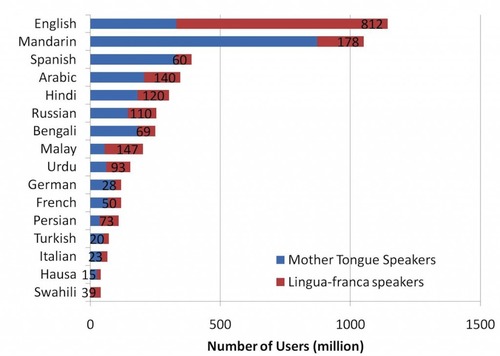
Lingua Franca
A language commonly used by speakers of two different languages for communication. Usually for business, trade, commerce, or in popular culture.
World Lingua Franca: English
China: Mandarian
Africa: Swahili
Eastern Europe/Russia: Russian
World Lingua Franca: English
China: Mandarian
Africa: Swahili
Eastern Europe/Russia: Russian
44
New cards
Dialects
Variations in accent, grammar, usage and spelling and develop out of geographic distance or isolation.
Ex: US and UK
Ex: US and UK

45
New cards
Official Language
Language used by the government of a country for laws, reports, signs, public objects, money, stamps, etc.

46
New cards
Friction of Distance
As a cultural trait diffuses, the people who adopt it might alter it.
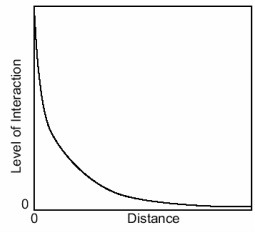
47
New cards
Contemporary methods of cultural diffusion
1. Internet & Tech
2. Social Media & Relationships
3. Media
4. Politics
5. The Economy
6. Urbanization.
Increased cultural and economic connectedness between people.
2. Social Media & Relationships
3. Media
4. Politics
5. The Economy
6. Urbanization.
Increased cultural and economic connectedness between people.
48
New cards
Cultural Convergence
The process of two or more cultures coming into contact with each other and adopting each other's traits to become more alike.
Ex: World Sports, Kpop, McDonald's, Language, etc.
Ex: World Sports, Kpop, McDonald's, Language, etc.

49
New cards
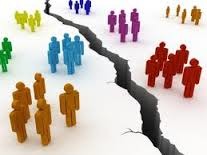
Cultural Divergence
Cultures become LESS alike from cultural and physical barriers.
The process of a culture restricting contact with other cultures in an attempt to retain its originality.
Separating/distinguishing from mainstream.
Ex: Amish
The process of a culture restricting contact with other cultures in an attempt to retain its originality.
Separating/distinguishing from mainstream.
Ex: Amish
50
New cards
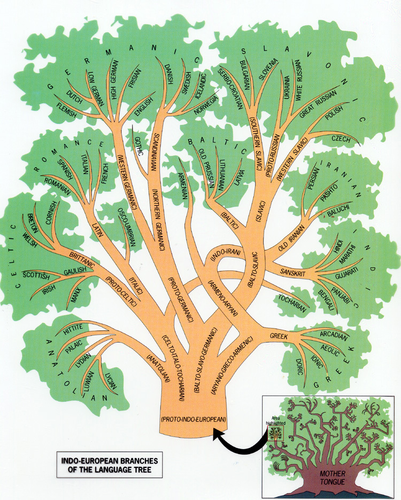
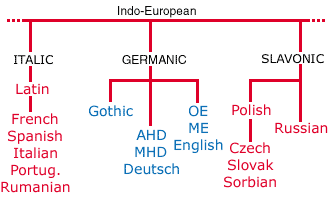
Language Family
Largest group of related languages which are connected through a common, ancient ancestry and trace back to a common origin.
Tree Trunk
Ex: Indo-European (3.2 billion speakers), Sino-Tibetan (1.4 billion speakers)
Tree Trunk
Ex: Indo-European (3.2 billion speakers), Sino-Tibetan (1.4 billion speakers)
51
New cards
Language Branch
A collection of languages that share a common origin from thousands of years ago.
They were separated from other languages in their family and now are distinctive although related.
Tree Branch.
Romance Branch, Germanic Branch, etc.
They were separated from other languages in their family and now are distinctive although related.
Tree Branch.
Romance Branch, Germanic Branch, etc.
52
New cards
Language Group
A collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in a more recent past with similar vocabularies and some overlap.
Tree Twig.
Ex: West Germanic, North Germanic, Indo-Arayan
Tree Twig.
Ex: West Germanic, North Germanic, Indo-Arayan

53
New cards
Languages
A means of communication.
Leaves.
Ex: English, Italian, Hindi
Leaves.
Ex: English, Italian, Hindi

54
New cards
Dialects
Variations of a language.
Ex: Difference in vocabulary, pronunciation, and spelling, British English and American English.
Ex: Difference in vocabulary, pronunciation, and spelling, British English and American English.

55
New cards
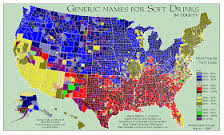
Isogloss
A geographic boundary within which a particular linguistic feature occurs.
Lines that divide dialects.
Ex: Sneakers in New England states vs. Tennis Shoes every where else.
Lines that divide dialects.
Ex: Sneakers in New England states vs. Tennis Shoes every where else.
56
New cards
Spatial Distribution of Religion
1. Hearths
2. Diffusion
3. Distribution
2. Diffusion
3. Distribution
57
New cards
Impact of Cultural Landscape of Religion
1. Architecture
2. Symbols
3. Pilgrimages & Holy Sites
4. Burial Practices
2. Symbols
3. Pilgrimages & Holy Sites
4. Burial Practices

58
New cards
The big four religions
77% of the World's Population
1. Christianity - 2.4 Billion
2. Islam - 1.9 Billion
3. Hinduism - 1 Billion
4. Buddhism - 500 Million
Other religions:
Judaism - 14 Million
Sikhism - 24 Million
Largest: Christianity
Fastest Growing: Islam
1. Christianity - 2.4 Billion
2. Islam - 1.9 Billion
3. Hinduism - 1 Billion
4. Buddhism - 500 Million
Other religions:
Judaism - 14 Million
Sikhism - 24 Million
Largest: Christianity
Fastest Growing: Islam

59
New cards
Universalizing Religions
1. Widely diffused from the Hearth
2. BOTH Expansion AND relocation diffusion
3. Not confined to a specific location
4. Missionary - Attempts to convert people to join
Ex: Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism, etc.
2. BOTH Expansion AND relocation diffusion
3. Not confined to a specific location
4. Missionary - Attempts to convert people to join
Ex: Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism, etc.

60
New cards
Ethnic Religion
1. Smaller diffusion and overall distribution from hearth
2. Restricted to relocation diffusion ONLY
3. Tied to specific location and/or ethnic group
4. Does NOT recruit new adherents
Ex: Hinduism, Judaism, Shintoism, Daoism, Confucianism, traditional religions, etc.
2. Restricted to relocation diffusion ONLY
3. Tied to specific location and/or ethnic group
4. Does NOT recruit new adherents
Ex: Hinduism, Judaism, Shintoism, Daoism, Confucianism, traditional religions, etc.

61
New cards
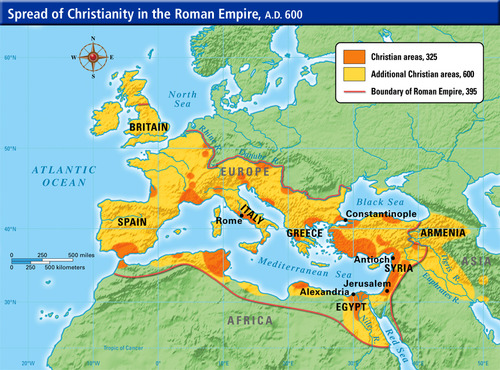
Diffusion of Christianity
Universalizing
Hearth: Israel
Contagious - Jesus' followers traveled through the Mediterranean & spread Christianity, Missionaries
Hierarchical - Emperor Theodosius made Christianity Roman Empire religion, the Crusades, Spanish Inquisition
Relocation - Colonization and Imperialism
Hearth: Israel
Contagious - Jesus' followers traveled through the Mediterranean & spread Christianity, Missionaries
Hierarchical - Emperor Theodosius made Christianity Roman Empire religion, the Crusades, Spanish Inquisition
Relocation - Colonization and Imperialism
62
New cards
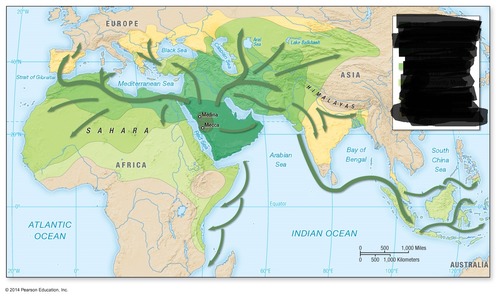
Diffusion of Islam
Universalizing
Hearth - Mecca and Medina, Saudi Arabia
Contagious - Muhammad taught people and spread Islam, Muslim traders brought Islam to India and Indonesia
Hierarchical - Muslim Empires throughout history, military conquest in North Africa, Islamic intellectuals in cities
Hearth - Mecca and Medina, Saudi Arabia
Contagious - Muhammad taught people and spread Islam, Muslim traders brought Islam to India and Indonesia
Hierarchical - Muslim Empires throughout history, military conquest in North Africa, Islamic intellectuals in cities
63
New cards
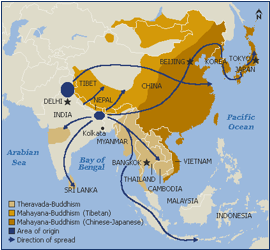
Diffusion of Buddhism
Universalizing
Hearth - Northern India/Nepal
Contagious - Buddha and missionaries traveled throughout Asia and spread Buddhism, Buddhist traders
Hierarchical - Emperor Ashoka of South Asia, converted to Buddhism and spread it through his empire
Hearth - Northern India/Nepal
Contagious - Buddha and missionaries traveled throughout Asia and spread Buddhism, Buddhist traders
Hierarchical - Emperor Ashoka of South Asia, converted to Buddhism and spread it through his empire
64
New cards
Diffusion of Hinduism
Ethnic
Hearth - India
Relocation - Hindu migrants brought Hinduism throughout the world
Hearth - India
Relocation - Hindu migrants brought Hinduism throughout the world
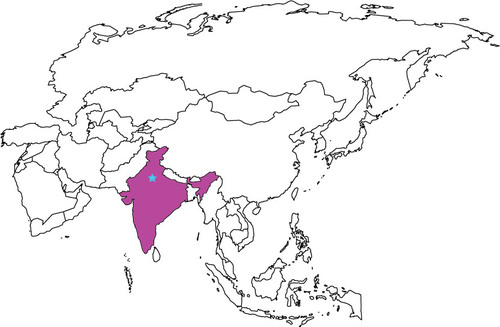
65
New cards
Diffusion of Judaism
Ethnic
Hearth - Israel/Lebanon
Relocation - Forced out of Israel during Roman Empire into South and East Europe, persecuted in Russia so fled, left Europe during Holocaust
Hearth - Israel/Lebanon
Relocation - Forced out of Israel during Roman Empire into South and East Europe, persecuted in Russia so fled, left Europe during Holocaust
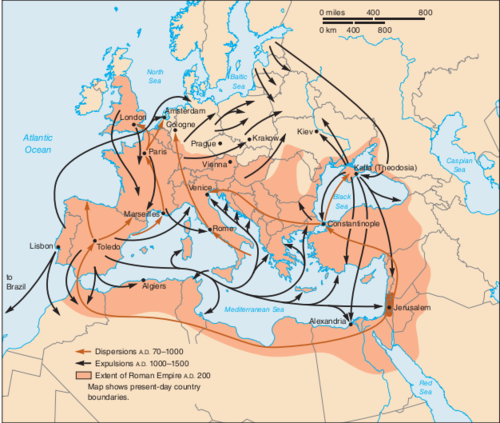
66
New cards
Diffusion of Sikhism
Universalizing
Hearth - Punjab, India
Relocation - Migration to surrounding areas during British Empire, missionaries
Hearth - Punjab, India
Relocation - Migration to surrounding areas during British Empire, missionaries
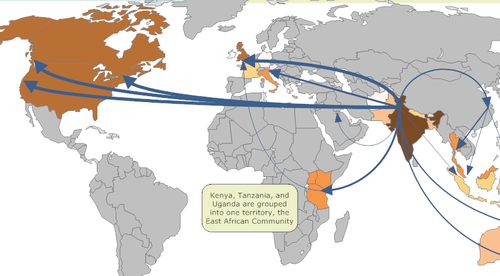
67
New cards
Acculturation
When people within one culture adopt some traits from another culture.
Ex: Guatemalan immigrant continue speaking Spanish at home but English in public.
Ex: Guatemalan immigrant continue speaking Spanish at home but English in public.
68
New cards
Assimilation
One culture forced or voluntary chose to abandon their original culture and adopts another culture.
Ex: Native Americans forced to learn English, cut their hair, change their clothing, given new names, and forced to become more "American" in Native American Boarding Schools.
Ex: Native Americans forced to learn English, cut their hair, change their clothing, given new names, and forced to become more "American" in Native American Boarding Schools.

69
New cards
Multiculturalism
The acceptance and tolerance of many different cultures which exist in close proximity to one another.
Ex: In 1971, the Canadian government established multiculturalism is a basic right of citizens.
Ex: In 1971, the Canadian government established multiculturalism is a basic right of citizens.
70
New cards
Syncretism
When two culture's traits blend together and form a new cultural trait.
Ex: Sikhism is a mix of Islam and Hinduism.
Ex: Sikhism is a mix of Islam and Hinduism.
