Organic - Chapter 6: Amines & Amides
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:30 PM on 8/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
nitrogen
Amines and amides contain _______.
2
New cards
medicines
The effectiveness of a wide variety of important __________ depends on the presence of the nitrogen-containing group.
3
New cards
amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids
Both amines and amides are abundant in nature and play crucial roles in the biochemistry of life (__________, ________, __________)
4
New cards
Amines
Organic derivatives of ammonia in which one or more of the hydrogens are replaced by an organic group.
5
New cards
NH3
Formula of Ammonia
6
New cards
Primary Amines
The N atom is bonded to one R group.
7
New cards
Secondary Amines
The N atom is bonded to two R groups.
8
New cards
Tertiary Amines
The N atom is bonded to three R groups.
9
New cards
common names
In amine nomenclature, _____________ are used extensively for compounds with low molecular weights.
10
New cards
False
T or F: Amines are the top priority when naming organic compounds.
11
New cards
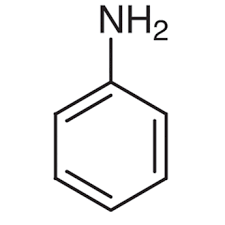
Aniline
Simplest Aromatic Amine
12
New cards
gases
Low molecular weight animes are _______ at room temperature. Heavier (more complex) amines are liquids or solids.
13
New cards
True
T or F: The N-H bond is not quite as polar as the O-H bond.
14
New cards
hydrogen bonds
Primary and Secondary amines can form _____________ between molecules (like alcohol).
15
New cards
lower
The hydrogen bonds formed between amine molecules are not as strong as those of alcohols, so amine boiling points are somewhat ______ than those of alcohols.
16
New cards
Tertiary
________ amines cannot form hydrogen bonds with themselves because the nitrogen has no attached H atom.
17
New cards
True
T or F: Tertiary amines have a similar boiling point to alkanes that have about the same molecular weight.
18
New cards
water soluble
Amines can hydrogen bond with water, making smaller amine molecules (less than six carbons) _____________.
19
New cards
ammonia
Low molecular weight amines have a sharp and penetrating odor similar to _________.
20
New cards
decaying fish
Larger amines smell like __________.
21
New cards
Putrescine
(1,4-diaminobutane) Larger amine molecule that smells like decaying fish.
22
New cards
Cadaverine
(1,5-diaminopentane) Larger amine molecule that smells like decaying fish.
23
New cards
organic bases
Amines are the most common _____________.
24
New cards
weak bases
All amines behave as _________ in water (similar ro NH3).
25
New cards
Bronsted bases
When _________ like ammonia reacts with water, they liberate OH- ions.
26
New cards
Ammonium ion + OH-
Results of adding amines with H2O.
27
New cards
Salt
Results of amines and HCl.
28
New cards
Amide + HCl
Results amines and acid chloride.
29
New cards
Amide + Carboxylic Acid
Results of amine and acid anhydride.
30
New cards
True
T or F: The same amines that react with hydrochloric acid, also reacts with other acids such as sulfuric, nitric, phosphoric, and carboxylic acids.
31
New cards
Amine Salts
___________ are named by changing "amine" to "ammonium" and adding the anion name (from the acid).
32
New cards
ionic compounds
Amine salts have physical properties of other ________________.
33
New cards
crystalline solids
Amine salts are white ____________ with high melting points.
34
New cards
parent amine
Because amine salts are ionic, they are more water soluble than their _____________.
35
New cards
strong base
Amine salts are easily converted back to amines by adding a __________.
36
New cards
pH dependent
The form in which amines occur in solutions is _____________.
37
New cards
Low pH
High H+ (_______) favors the amine salt.
38
New cards
High pH
High OH- (______) favors the amine.
39
New cards
amine cations
The _____________ in salts can have one, two, or three R groups attached to the Nitrogen.
40
New cards
False
T or F: It is not possible to have amine cations in which four R groups are attached.
41
New cards
Quaternary Ammonium Salts
Amine cations in which four R groups are attached, and contain no hydrogen that can be removed by a base.
42
New cards
pH independent
Since no hydrogen can be removed from quaternary ammonium salts, they only have one form so they are _____________.
43
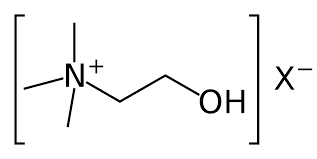
New cards
Choline Cation
Important quaternary ammonium ion in biochemistry.
44
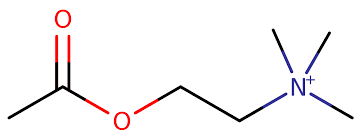
New cards
Acetylcholine Cation
Important quaternary ammonium ion in biochemistry.
45
New cards
disinfectant
Some quaternary ammonium salts have __________ properties.
46
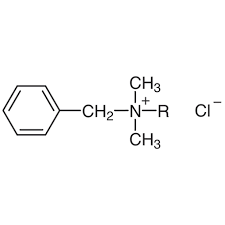
New cards
Benzalkonium Chloride
(Zephiran) Well known antiseptic. Its detergent action destroys the membranes that coat/protect microorganisms (it is used prior to surgery to disinfect hands/instruments).
47
New cards
Amides
Organic compounds that contain a functional group with a carbonyl attached to a nitrogen.
48
New cards
Amide Linkage
The single bond linking the carbonyl carbon and nitrogen atoms in the group.
49
New cards
carboxylic acid
Amides may be thought of as containing an ammonia or amine portion and a portion derived from a ________________.
50
New cards
reactive
The reaction of an amine with a carboxylic acid usually produces a salt and not an amide. Therefore, the preparation of amides requires the more _______ acid chlorides and anhydrides.
51
New cards
True
T or F: While both primary and secondary amines can form amides, but tertiary amines do not react to form amides.
52
New cards
Polyamides
Condensation polymers, produced by the reaction of diacid chlorides with diamines. The repeating units are held together by amide linkages (i.e. formation of nylon).
53
New cards
3 Billion
_________ of nylon and related polyamides are produced annually.
54
New cards
60%
About ____ of that is used in home furnishings such as carpet. The rest is used to make clothing and tire cords.
55
New cards
tubing, sutures
In medicine, nylon is used in specialized ________ and _________.
56
New cards
Proteins
Polymers (polyamides) made up of monomers of amino acids (amine group with a carboxylic acid group).
57
New cards
protein chains
Amide linkages are characteristics of ___________.
58
New cards
Neurotransmitters
The chemical messengers of the nervous system which carry nerve impulses from one nerve cell (neuron) to another.
59
New cards
synapse
Neurons (dendrite, soma, axon, synaptic terminals) are separated by a small gap called the _______.
60
New cards
axon
Molecules of a neurotransmitter are stored in small pockets in the _____ near the synapse.
61
New cards
synaptic terminal
The pockets release neurotransmitter molecules into the synapse when an electrical current flows from the soma, along the axon to the _____________.
62
New cards
electrical current
The _____________ is generated by the exchange of positive and negative ions across membranes.
63
New cards
dendrites
The released molecules diffuse across the synapse and bind to receptors on the ________ of the next neuron. Once the message has been delivered, the receiving cell sends it on to the next nerve cell.
64
New cards
Central Nervous System
In the _______________ (brain & spinal cord) the most important molecules are amines.
65
New cards
moods
Neurotransmitters are not only chemical messengers, they are also partly responsible for our _______.
66
New cards
norepinephrine, serotonin
A simplified biochemical theory of mental illness is based on two amines found in the brain: ______________ and ________.
67
New cards
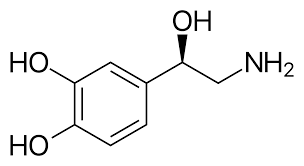
Norepinephrine
Synthesized from tyrosine (which converts to dopa and then dopamine), associated with depression and manic states.
68
New cards
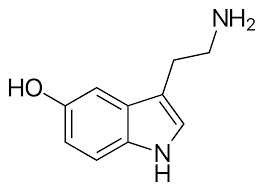
Serotonin
Synthesized from tryptophan, found to influence sleeping, the regulation of body temperature, and sensory perception.
69
New cards
Drugs
_______ that mimic serotonin are often used to treat depression, anxiety, and OCD.
70
New cards
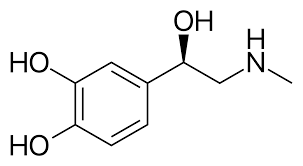
Epinephrine
(Adrenaline, Fight-or-Flight hormone) has a molecular structure or norepinephrine plus an N-methyl group, more important as a hormone than a neurotransmitter.
71
New cards
adrenal gland
Epinephrine is synthesized in the ____________ and acts to increase the blood level of glucose for energy. Also provides a sudden burst of energy released in response to pain, anger, or fear.
72
New cards
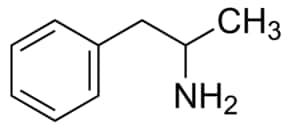
Amphetamine
(STP, speed, mescaline, meth, etc.) Powerful nervous system stimulant with an amine structure similar to epinephrine. Has severe detrimental effects on the body and mind.
73
New cards
Methamphetamine
Used legally and illegally to elevate mood or reduce fatigue.
74
New cards
Alkaloids
Class of nitrogen-containing organic compounds obtained from plants.
75
New cards
True
T or F: Plants are the sources of some of the most powerful drugs known.
76
New cards
Nicotine
Found in tobacco and used a stimulant in cigarettes, cigars, and chewing tobacco. It is not harmful but it is very addicting.
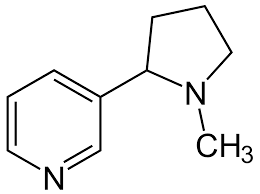
77
New cards
Caffeine
Found in coffee, soft drinks, chocolate, and tea. I used as a central nervous system stimulant. Not harmful but very addicting.
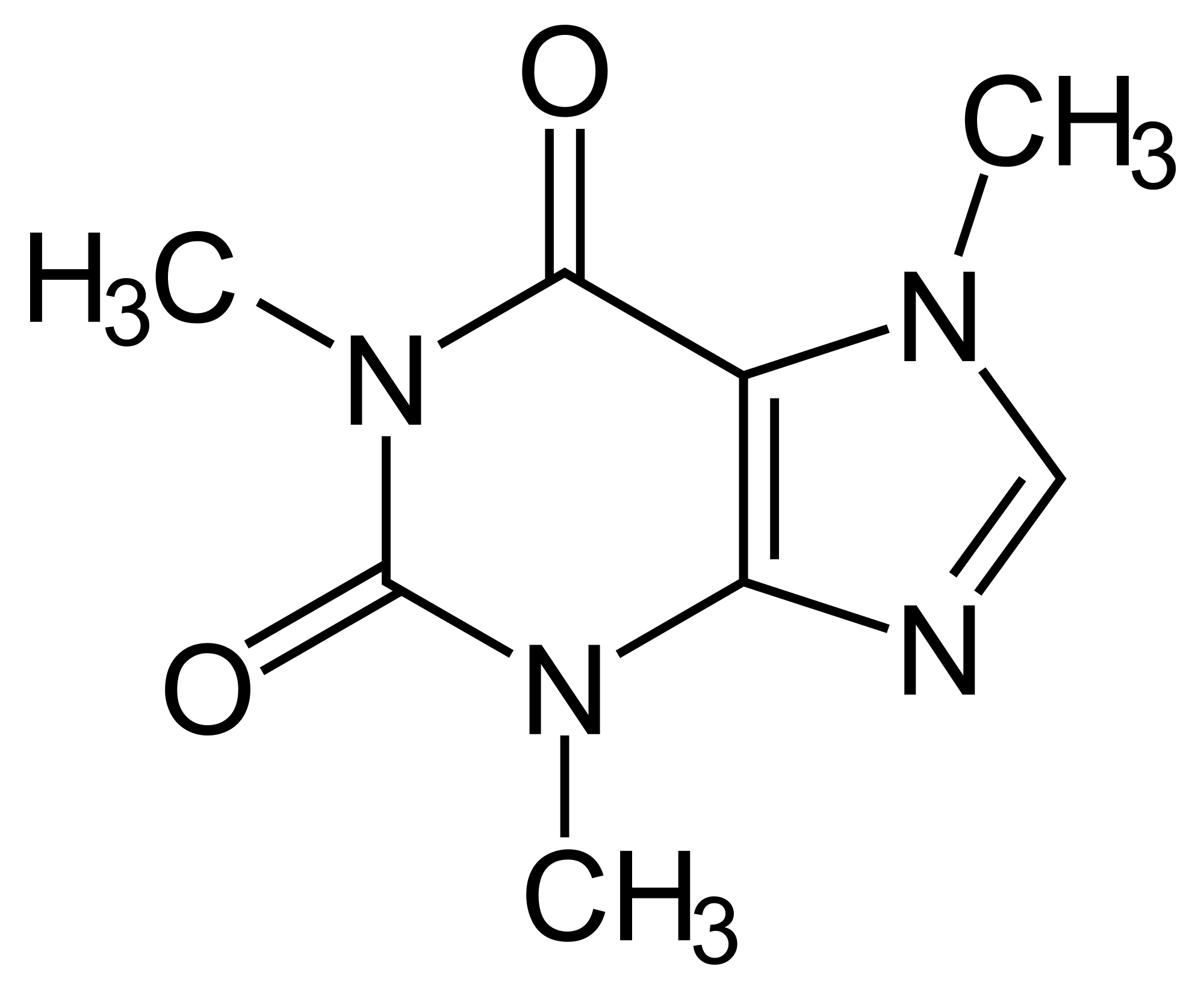
78
New cards
Quinine
Used to treat malaria.
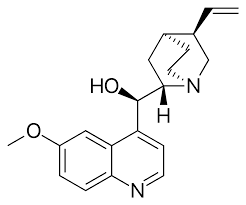
79
New cards
Atropine
Used as a preoperative drug to relax muscles and reduce saliva secretions (can also be used by eye doctors to dilate pupils).
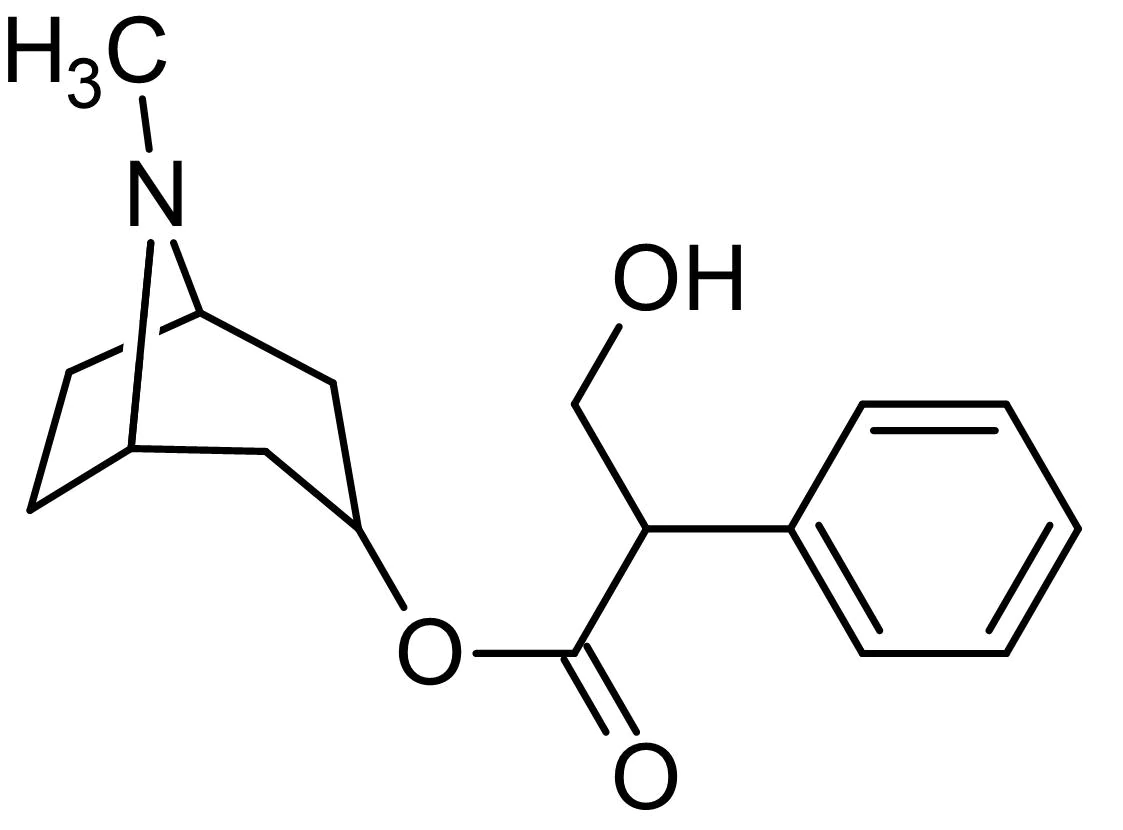
80
New cards
Opium
Used to make codeine (in cough medicines), morphine (pain killer), and heroin.
81
New cards
Formamide
The only unsubstituted amide that is a liquid, all others are solids with high melting points.
82
New cards
Unsubstituted Amides
________________ can form a complex network of intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
83
New cards
reduces, decreases
The substitution of a R group on the nitrogen ________ the number of intermolecular hydrogen bonds that can form thus causing melting points to __________.
84
New cards
shape
The hydrogen bonding of amides is important in maintaining the _______ of protein molecules.
85
New cards
six
Amides with fewer than _____ carbon atoms are soluble in water due to their ability to hydrogen bond.
86
New cards
carbonyl oxygen
Even substituted amides are soluble because the _________________ can hydrogen bond.
87
New cards
Amide Neutrality
Amides are neither acidic nor basic. The carbonyl group bonded to the nitrogen destroys the basicity of the original amine, and the nitrogen of the amine replaces the acidic -OH of the carboxylic acid.
88
New cards
Amide Hydrolysis
The reverse of the amide formation reaction where an amide is cleaved to produce a carboxylic acid and an amine or ammonia.
89
New cards
ester hydrolysis
As with ______________, amide hydrolysis requires a strong acid or a strong base.
90
New cards
catalyst
The _______ used determines the final product.
91
New cards
acidic conditions
Under _______________ the amine salt is produced along with the carboxylic acid.
92
New cards
basic conditions
Under ________________ the carboxylate salt is produced along with the amine.
93
New cards
salt
The form in which carboxylic acids and amines occur in solution depends on pH, one of the hydrolysis products must always be in the form of a ______.
94
New cards
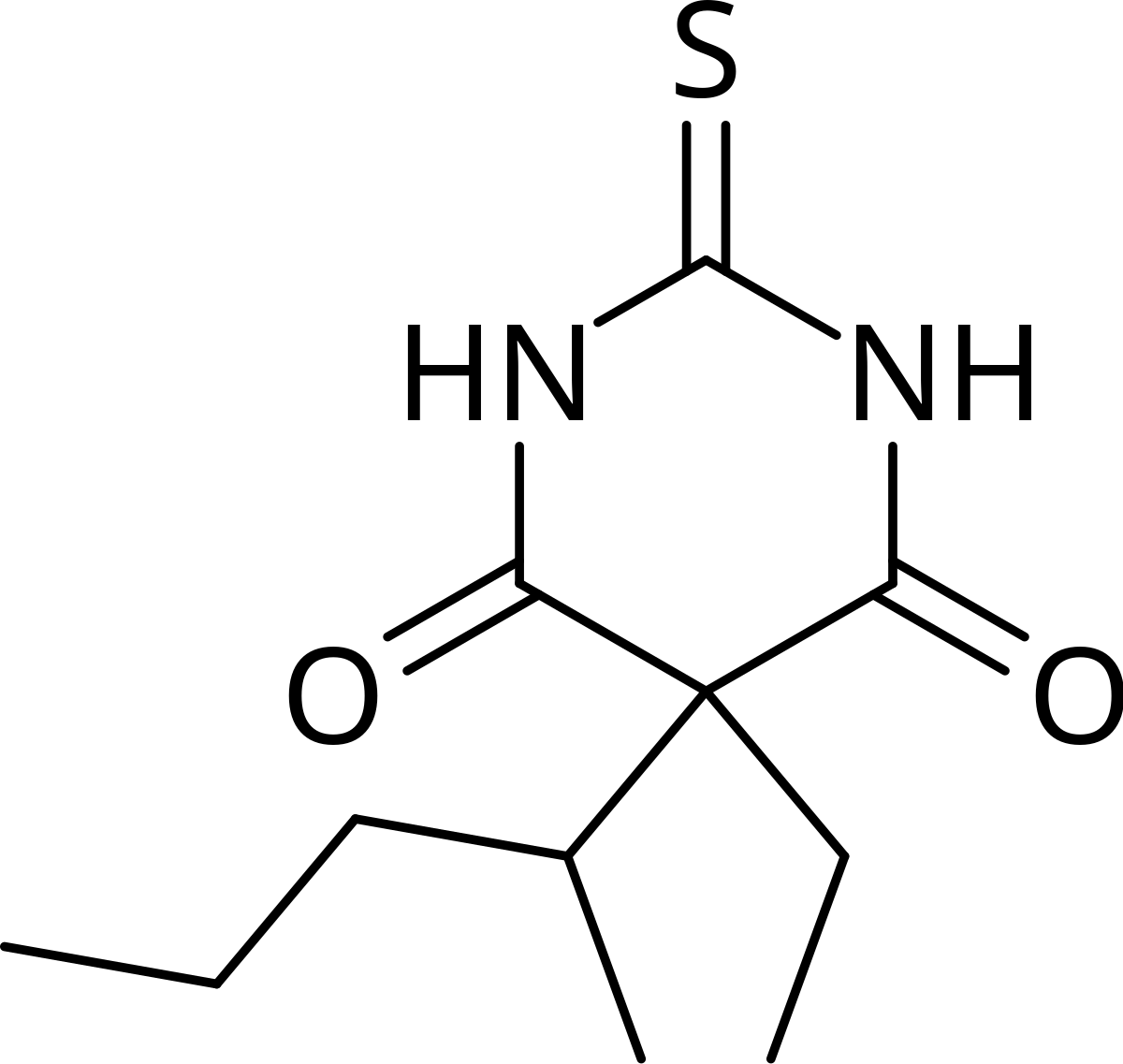
Thiopental
(Pentothal) Intravenous Anesthesia
95
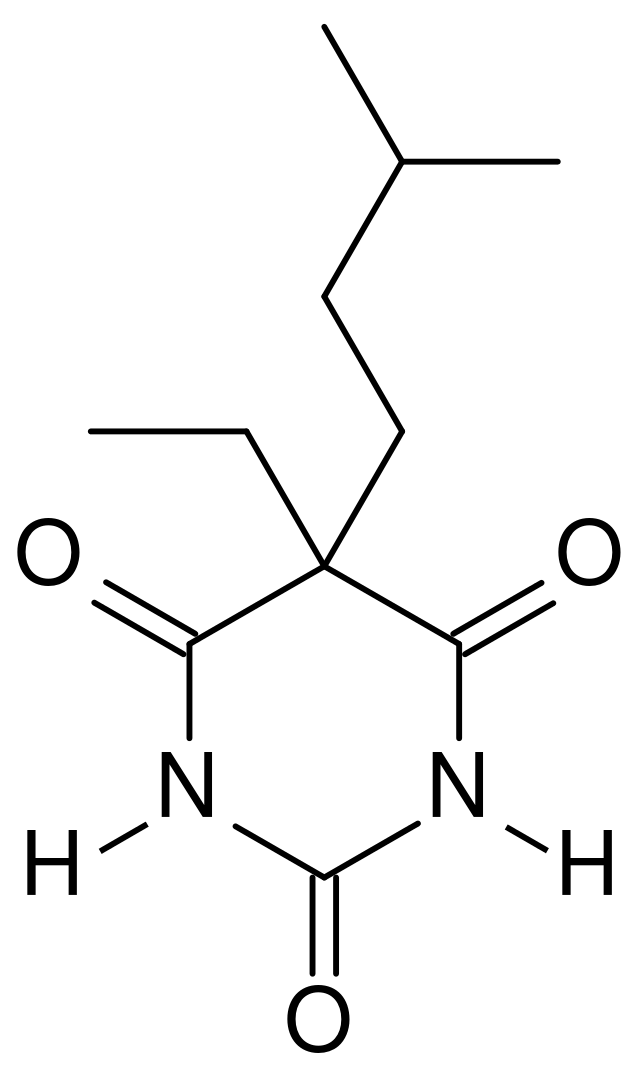
New cards
Amobarbital
(Amytal) Treatment of insomnia.
96
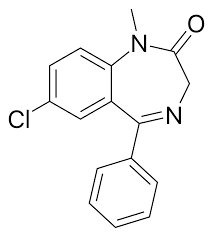
New cards
Diazepam
(Valium) Tranquilizer
97
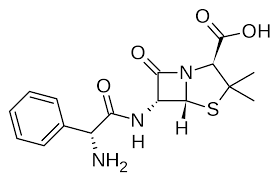
New cards
Ampicillin
(Polycillin) Antibiotic
98
New cards
Acetaminophen
Drug for minor pain.
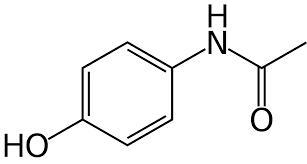
99
New cards
Ibuprofen
Drug for minor pain.
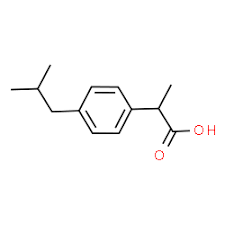
100
New cards
True
T or F: Jaedyn is awesome for making all of these study sets.