regeneration
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
define regeneration
long term upgrading of existing places
define rebranding
creating a new look or reputation for an area
often relying on an areas industrial past
altering the attitudes people have towards an area
centres on place marketing
define reimaging
making a place more attractive + desirable for people to invest in, live in or visit
what are the key features of regeneration
aims to attract economic investment
sustainable
benefits everyone
long term/ lasting improvements
social, economic + environmental
needs of an area must be understood
what are the sectors of economic activity
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
quinary
describe the primary sector of economic activity
extraction of raw materials (e.g. mining + farming)
typically in rural areas
describe the secondary sector of economic activity
processing raw materials + manufacturing (e.g. iron + steel + car manufacturing)
typically in conurbations
describe the tertiary sector of economic activity
service sector, tourism + banking (e.g. teachers. doctors + tour guides)
found throughout the UK
describe the quaternary sector of economic activity
high-tech research + design (e.g. web designers + research scientists)
typically found in large cities
describe the quinary sector of economic activity
knowledge management, business consultancy + leadership (e.g. CEOs + business consultants)
London + other large cities (e.g. Manchester)
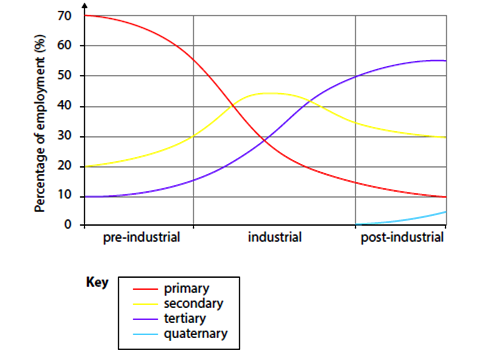
how have economic sectors changed over time
why is there a link between income deprivation + educational deprivation
deprivation leads to educational deprivation:
cannot afford private education
cannot afford to spend time helping to educate their children
educational deprivation leads to deprivation:
lack the skills to access higher paying jobs
what is meant by the function of an area
the role it plays for the community + the surroundings
commercial, administrative, retail or industrial
some places have regional, national or global functions
what are high order functions
banks, department stores, doctors surgeries
located in larger settlements
what are low order functions
grocery stores, post offices + pubs
found in smaller villages
why are functions of places changing
internet + broadband service
changing customer habits (i.e. online shopping)
large rise in small businesses nationally
how may the function of urban areas change
industrial revolution: factories (e.g. cotton in Manchester)
deindustrialisation: cheaper foreign imports lead to unemployment + deprivation
post-industrialisation: reurbanisation- factories converted into flats + many jobs in tertiary sector
how may the function of rural areas change
primary industry (agriculture)
agricultural decline due to cheaper foreign imports + mechanisation means less workers are needed
post-production countryside: diversification
how might age structure change
natural change
migration
rural areas have a higher elderly population + lower unemployment rates than urban areas
how might ethnic composition change over time
in-migration + out-migration:
post war migration from former colonies of British empire to assist with post-war rebuilding (e.g. Jamaican migrants came to London on Windrush in 1948)
eastern European migration to UK when EU expanded in 2004
what is the median age of people in rural areas
45
what is the median age of people in urban areas
37
in the 2011 census, what percentage of people in England + Wales were white
86%
what does filtering down mean
the changes made to an area when lower income groups (e.g. lower paid immigrants or students) move there
what is gentrification
process of renewal when affluent people move into an area
results in change in social structure of the area + increased property values
can lead to displacement of lower income families + small businesses
why might people have differing views on gentrification
higher income people support it because the area is improved
lower income may be against it because they may be displaced as house prices rise so are too high for them to afford
council supports it because higher income people pay higher taxes
property developers support it because house prices rise
define studentification
process of social, environmental + economic change to an area due to large numbers of students
potential conflict with residents due to anti-social behaviour
students unlikely to carry out improvements to an area
2/3 of 10,000 residents in Headingly, Leeds are students concentrated in 73 streets of terraced houses
what are the physical factors affecting the changing characteristics of places
location: proximity to large cities + core economic zones
environment/ attractiveness
technology: lifts allow high rise buildings, vehicles facilitate urban sprawl, Wi-Fi allows people to work from home
how does the accessibility + connectedness of a place change its characteristics
access to other places by road, rail + air allows investment
how does planning by governments + other stakeholders change the characteristics of a place
national government policies on restructuring UK economy, trying to equalise benefits + reduce negative externalities of change
green belts
expanded towns developed to relieve population pressure from larger cities
conservation areas to limit new developments + encourage conversions
large schemes must have an Environmental Impact Assessment
how can the changing characteristics of a place be measured
to measure change, data over time is needed
employment trends: census data
demographic changes: census data
land use changes: maps + photos
levels of deprivation: Index of Multiple Deprivation
how does historical development affect the changing characteristics of a place
post-production era: end of primary production (i.e. agriculture) + manufacturing
competition for land for commercial, retail, residential + infrastructure functions (highest value land in CBD)
changes in consumer trends:
corner shop to supermarket to online
increased demand for single homes due to demographic + cultural trends
big businesses + TNCs shape consumer demand, + therefore the character of places (e.g. cloned shopping centres)
increased affluence has increased leisure + tourism functions + people may have second homes
historical buildings can be an asset or a deterrent (legacy of toxic waste from manufacturing)
describe the changes in Manchester between the 1930s + today
centre of industrial revolution, wool + cotton, thousands of jobs
1894- Manchester ship canal opened:
75,000 employed at Salford Quays
Manchester Docks were 3rd busiest port in Britain
deindustrialisation due to expansion of secondary industry in emerging economies (e.g. Japan + Taiwan)
factories struggled to compete with lower wages + less regulation in workplace, leading to closing of businesses
widespread unemployment + deprivation
1971-81: Manchester lost 50,000 full time jobs + 17.5% of its population
present function: UK’s second largest city, many museums, theatres, bars + restaurants, Manchester Piccadilly is busiest train station in England outside of London
when was Manchester ship canal opened
1894
how many people were employed at Salford Quays in 1894
75,000
by how much did Manchester’s population decrease from 1971-81
by 17.5%
how many full time jobs were lost in Manchester from 1971-81
50,000
how can places be represented formally
tourist board websites
local council press release
national government data
how can places be represented informally
social media
online forums + comments
vlogs + blogs
what was the historical function of Manchester
centre of industrial revolution, wool + cotton, thousands of jobs
1894- Manchester ship canal opened:
75,000 employed at Salford Quays
Manchester Docks were 3rd busiest port in Britain
what was the historical function of Scarborough
castle built in 12th century
developed into a spa town in the 18th century- attracted tourists
flourished as a spa town, a seaside resort, a fishing port + had a prosperous shipbuilding industry
what were the key processes resulting in changes of the function of Manchester
deindustrialisation due to expansion of secondary industry in emerging economies (e.g. Japan + Taiwan)
factories struggled to compete with lower wages + less regulation in workplace, leading to closing of businesses
widespread unemployment + deprivation
1971-81: Manchester lost 50,000 full time jobs + 17.5% of its population
1998-2015: 84% increase in city centre jobs (reurbanisation)
what were the key processes resulting in changes of the function of Scarborough
1845: Scarborough York Railway increased visitors
19th century: decline of shipbuilding industry due to foreign competition
cheaper flights abroad in the 2000s were detrimental to Britain’s tourism industry
what is Manchester’s present function
UK’s second largest city- capital of the north
many museums, theatres, bars + restaurants
Manchester Piccadilly is the busiest English train station outside of London
population of 586,100 (in 2021)
what is Scarborough’s present function
aims to attract tourists (e.g. through Alpamere Waterpark)
large fishing + services industry
many factories (e.g. McCains)
largest industry is accommodation + services
due to specialised industry, a major event could lead to the collapse of Scarborough’s economy
population of 108,700 (2021)
what are the reasons for changes in Manchester’s function
physical factors:
flat land is good for agriculture + constructing infrastructure, making Manchester more accessible
cotton mills + factories converted into flats + offices
accessibility:
close to Leeds, Liverpool + Sheffield
Manchester airport
many TNCs with head offices in Manchester (e.g. Etihad + Adidas)
M60 + M6
historical development:
one of fastest growing city centre populations (grew by 149% from 2002-15)
first council homes built in early 20th century
metrolink built in 1992
world’s first industrial city
main industry changed from cotton to entertainment industry
local + national planning:
urban entrepreneurialism in 1987- focus on increasing city’s competitiveness within global market
tried to maintain historical buildings, as it attracts people to the area
increased demand for space from residents + businesses, so may have to reduce size of greenbelts
in 1970s planning officials said nothing higher than historic buildings should be built, but this was overturned in 1990s to usher investment
how did local + national planning contribute to the change in function of Manchester
urban entrepreneurialism in 1987- focus on increasing city’s competitiveness within global market
tried to maintain historical buildings, as it attracts people to the area
increased demand for space from residents + businesses, so may have to reduce size of greenbelts
in 1970s planning officials said nothing higher than historic buildings should be built, but this was overturned in 1990s to usher investment
by what percentage did Manchester’s population increase by from 2002-15
149%
what physical factors led to a change in Manchester’s function
flat land is good for agriculture + constructing infrastructure, making Manchester more accessible
cotton mills + factories converted into flats + offices
how has historical development contributed to a change in Manchester’s function
one of fastest growing city centre populations (grew by 149% from 2002-15)
first council homes built in early 20th century
metrolink built in 1992
world’s first industrial city
main industry changed from cotton to entertainment industry
what are the reasons for changes in Scarborough’s function
physical factors:
seaside which allows for fishing + beach to attract tourists
no major motorways
peripheral region
accessibility:
not very accessible
railway opened in 1845 + links Scarborough to York, Leeds, Manchester + Liverpool
historical development:
market hall opened in 1852
identity as a seaside resort was born in 1960s due to wealthy middle class + cars enabling transport to the town
local + national planning:
20,000 new affordable homes backed by European Investment Bank built for whole of UK
McCain foods will invest £100m in expanding Scarborough plant, which will increase employment opportunities
could receive £20m of funding to invest in local peoples priorities by 2034 as part of a plan to revive high streets
by 2035, Scarborough’s economy will be refocused with an emphasis on digital + creative industries
how did Manchester’s population change from 2011-21
increased by 10%
how did Scarborough’s population change from 2011-21
decreased by 0.1%
what is the median age in Manchester
31
what is the median age in Scarborough
50
what percentage of people in Manchester are white as of 2021
57%
what percentage of people in Scarborough are white as of 2021
97%
how has Manchester’s ethnic composition changed from 2011-21
increased by 52%
what percentage of homes in Manchester are socially rented
30%
what percentage of homes in Scarborough are socially rented
14%
where is Manchester ranked on the rank of most deprived local authorities in the IMD
6th out of 326
where is Scarborough ranked on the rank of most deprived local authorities in the IMD
90th out of 326
what are the reasons for deprivation in Manchester
lack of employment
deindustrialisation led to job losses
new investment offers employment in skilled jobs, but people in deprived areas cannot benefit from high skilled jobs
older buildings no longer suitable for new industry
what are the reasons for deprivation in Scarborough
lack of employment opportunities due to poor connectedness + lack of investment