AP Psychology: Biological Bases of Behavior (Unit 1) Diagram | Quizlet
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
heredity
The transmission of physical traits or predispositions from one generation to the next.
nature versus nurture
A debate surrounding the relative importance of heredity (nature) and environment (nurture) in determining behavior.
Charles Darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection ("survival of the fittest").
evolutionary psychology
The study of the roots of behavior and mental processes using the principles of natural selection. Usually involves the study of heredity and genetics on human behavior.
maladaptive behaviors
Behaviors that impair a person's ability to function socially, academically, or professionally.
endocrine system
The organ system that consists of glands that control many of the body's activities by producing hormones.
hormones
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another.
nervous system
A conglomeration of billions of cells specifically designed to provide a communication network within the human body.
central nervous system
The division that consists of the brain and spinal cord.
peripheral nervous system
A division of the nervous system consisting of all nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord.
sensory (afferent) division
Division of the nervous system that contains sensory nerve fibers, conducting impulses from receptors to the CNS.
motor (efferent) division
Division of the nervous system that carries motor (movement) commands from the central nervous system to muscles and glands.
autonomic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary activity of visceral muscles and internal organs and glands.
somatic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system that enables voluntary actions to be undertaken due to its control of skeletal muscles.
sympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations (i.e. fight-or-flight).
parasympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy (i.e. rest-and-digest).
neuron
A nerve cell forming the basic building block of the nervous system.
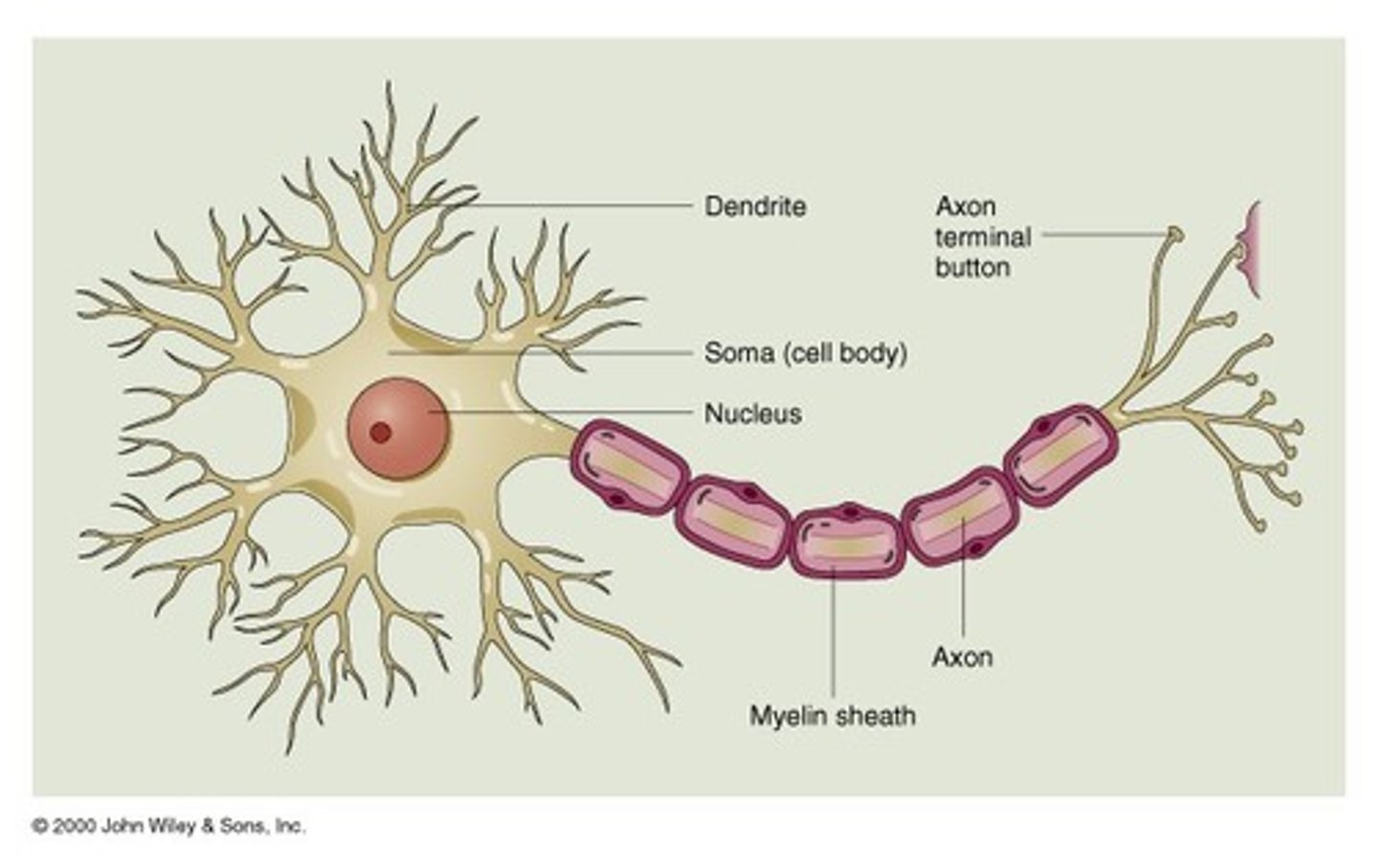
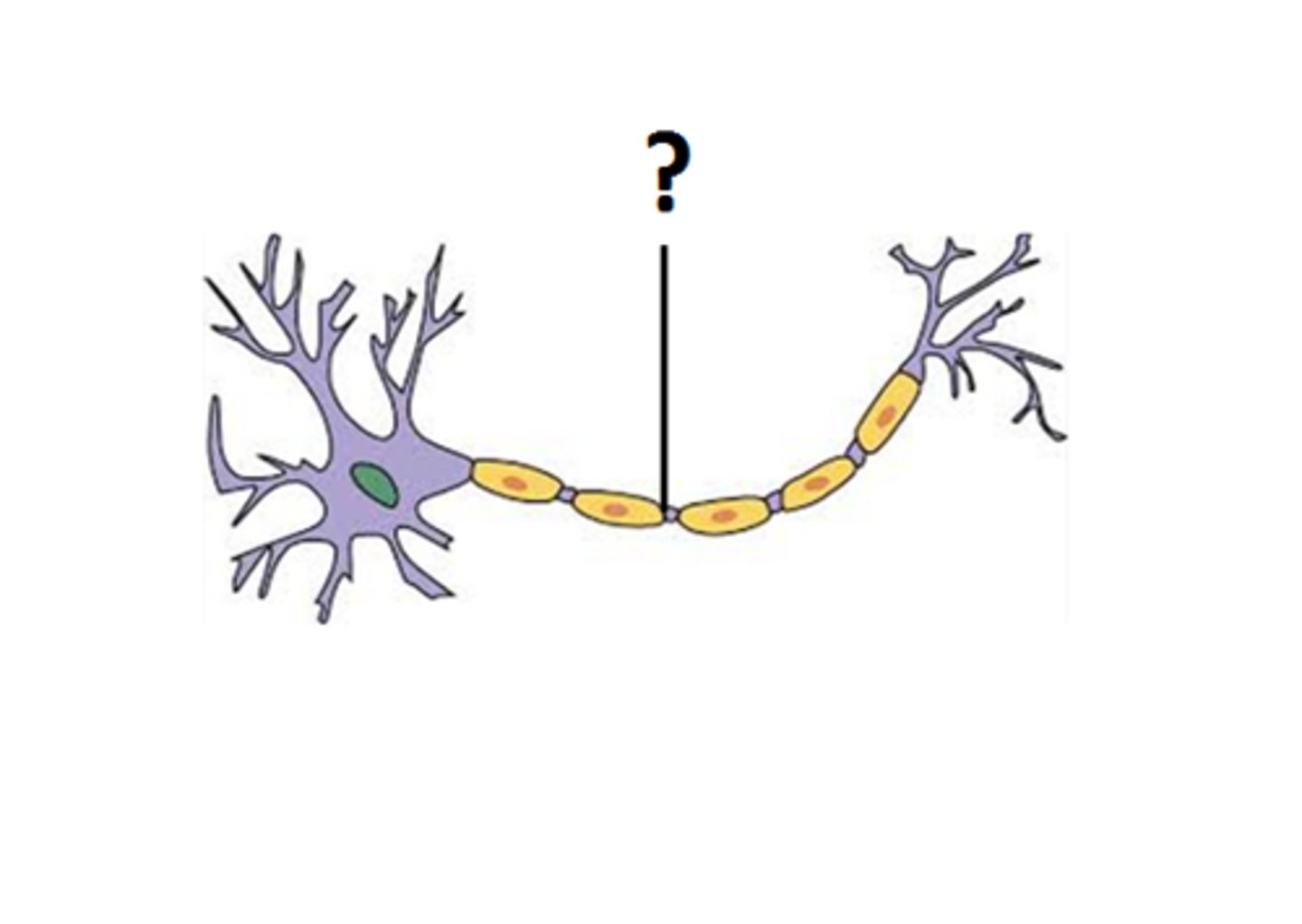
axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
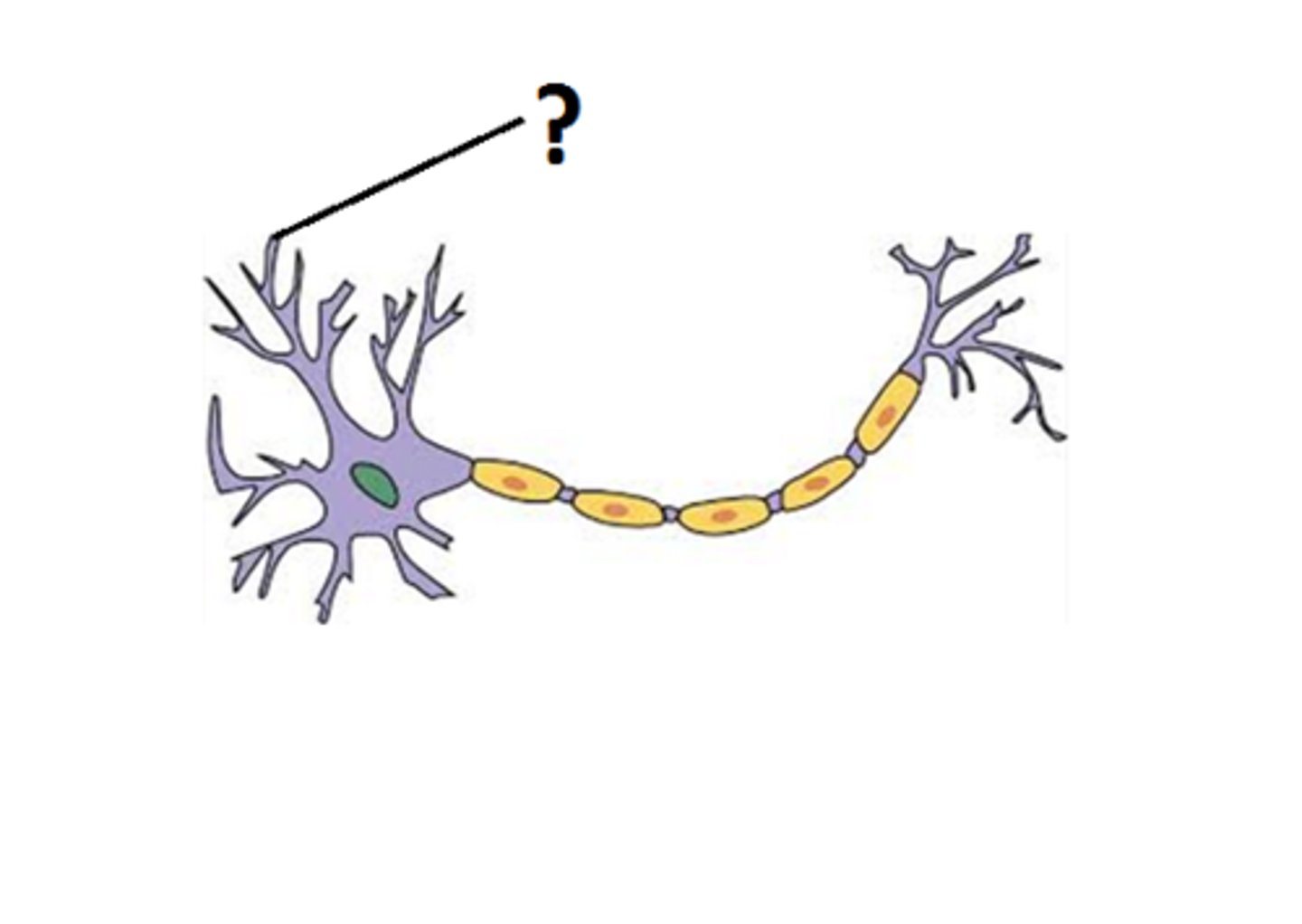
dendrite
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
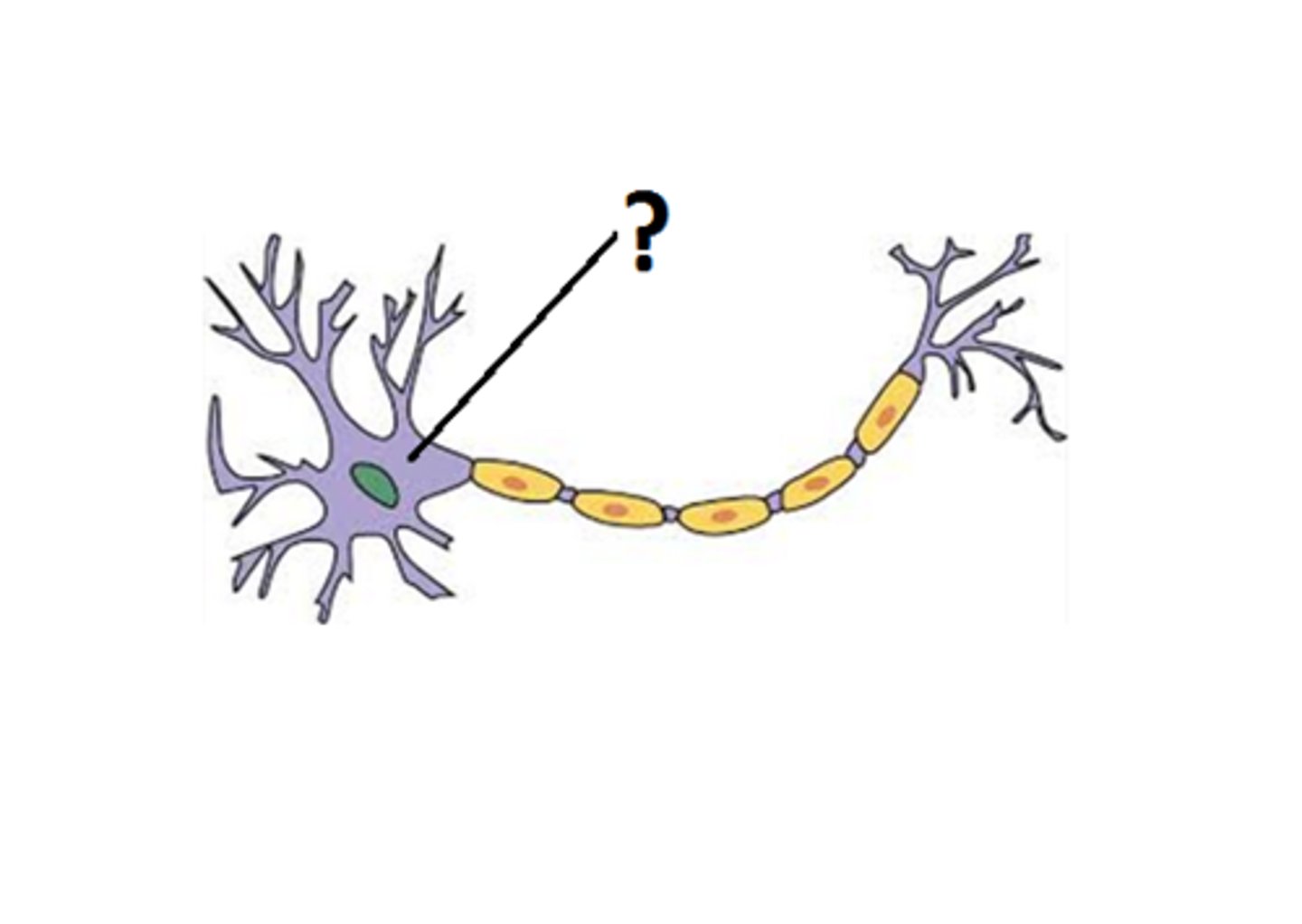
soma
The cell body of a neuron.
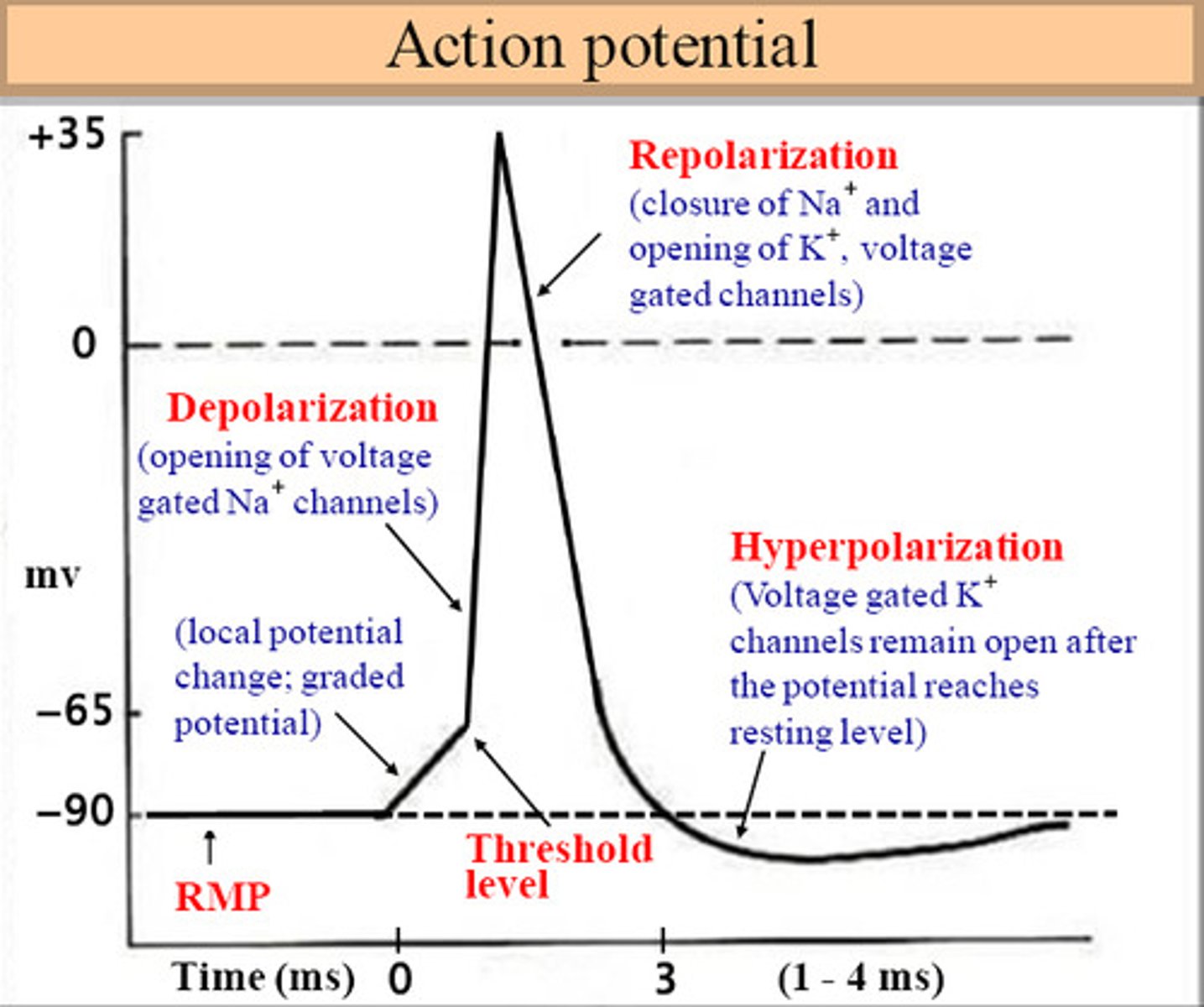
action potential
The change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell.
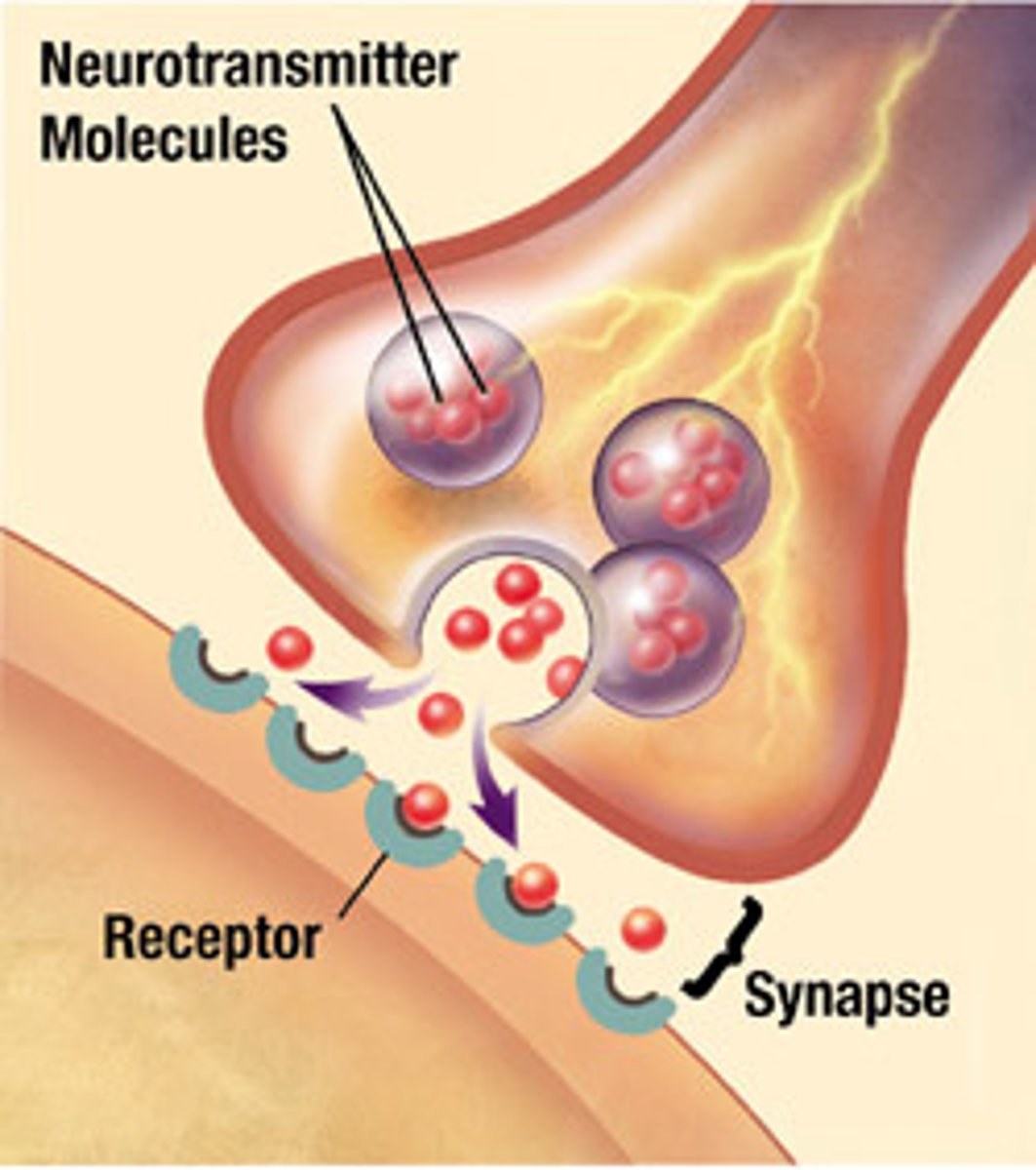
synapse
The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron.
reuptake mechanisms
The chemical process that allows neurotransmitters to be reabsorbed into the sending neuron.
agonists
Chemical substances that mimic or enhance the effects of a neurotransmitter on the receptor sites of the next cell, increasing or decreasing the activity of that cell.
dopamine
A neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system.
norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter involved in arousal, as well as in learning and mood regulation. Works to increase alertness, blood pressure, heart rate, and works with epinephrine to regulate flight-or-flight.
epinephrine
A neurotransmitter secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to stress (connected to the fight-or-flight response); also known as adrenaline.
serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger, sleep, arousal and sexual desire, and mood.
acetylcholine (ACh)
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction.
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
A neurotransmitter that reduces activity across the synaptic cleft and thus inhibits a range of behaviors and emotions, especially generalized anxiety.
excitatory neurotransmitters
Chemicals released from the terminal buttons of a neuron that excite the next neuron into firing.
inhibitory neurotransmitters
Chemicals released from the terminal buttons of a neuron that inhibit the next neuron from firing.
glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in strengthening long-term memory and learning (repeated tasks).
antagonists
Chemical substances that block or reduce a cell's response to the action of other chemicals or neurotransmitters.
cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body.
TERM
cerebellum
DEFINITION
Known as the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance.
brain stem
Connects the brain to the spinal cord, filtering information flow between peripheral nervous system and the rest of the brain.
thalamus
The brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem. Directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla.
TERM
pons
DEFINITION
A brain structure involved in the control of breathing, communication between different parts of the brain, and sensations such as hearing, taste, and balance.
TERM
medulla oblongata
DEFINITION
Part of the brain stem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus. Directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
brain lobe
A subdivision in the brain that often specializes in a type of brain activity.
TERM
frontal lobe
DEFINITION
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement.
TERM
temporal lobe
DEFINITION
An area on each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex near the temples which serves as the primary receiving area for auditory information, such as hearing and language.
TERM
parietal lobe
DEFINITION
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
TERM
occipital lobe
DEFINITION
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information by providing meaning and interpretation.
cerebral cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
visual cortex
The visual processing areas of cortex in the occipital and temporal lobes.
somatosensory cortex
A brain area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body sensations
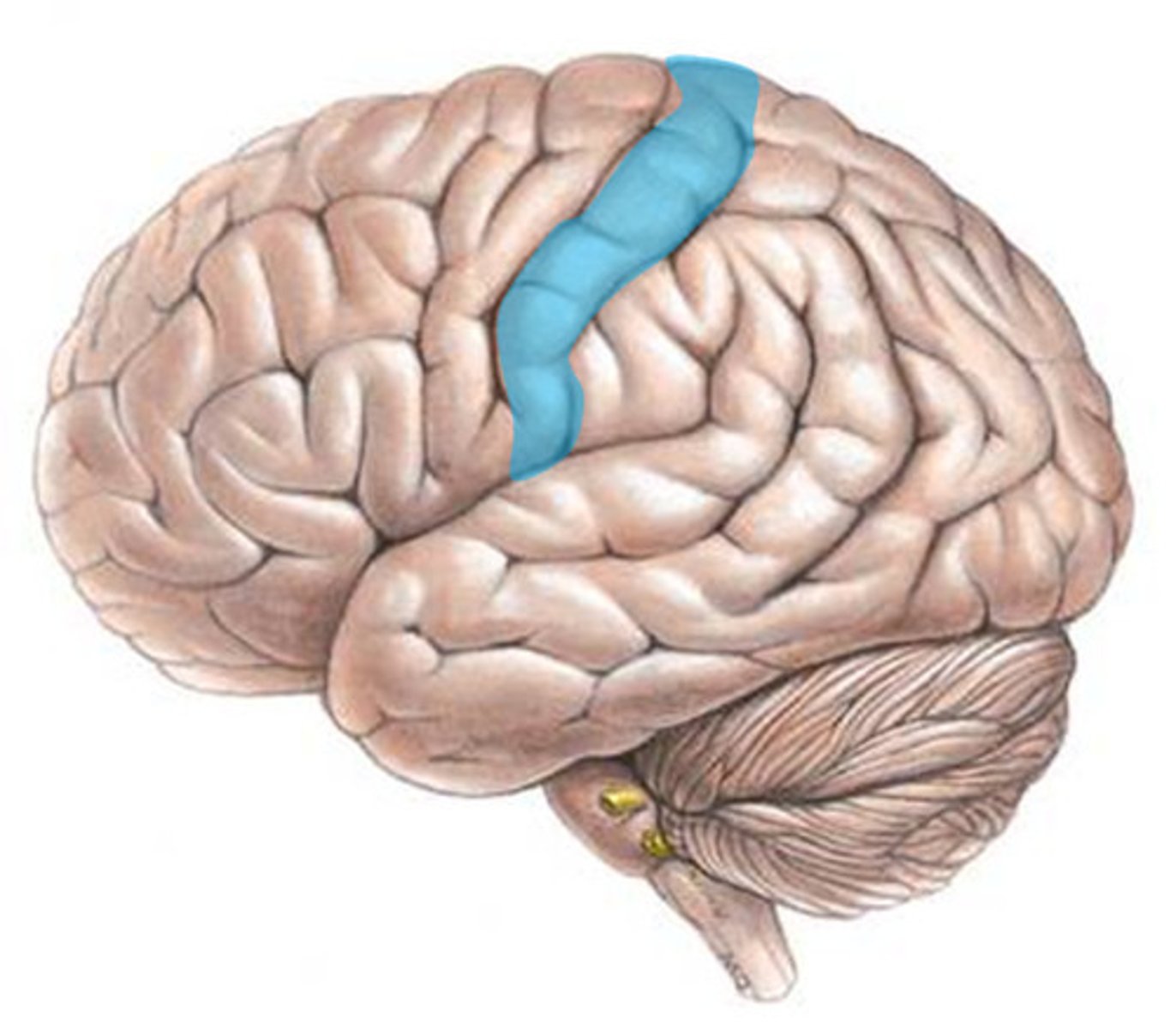
motor cortex
An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements.
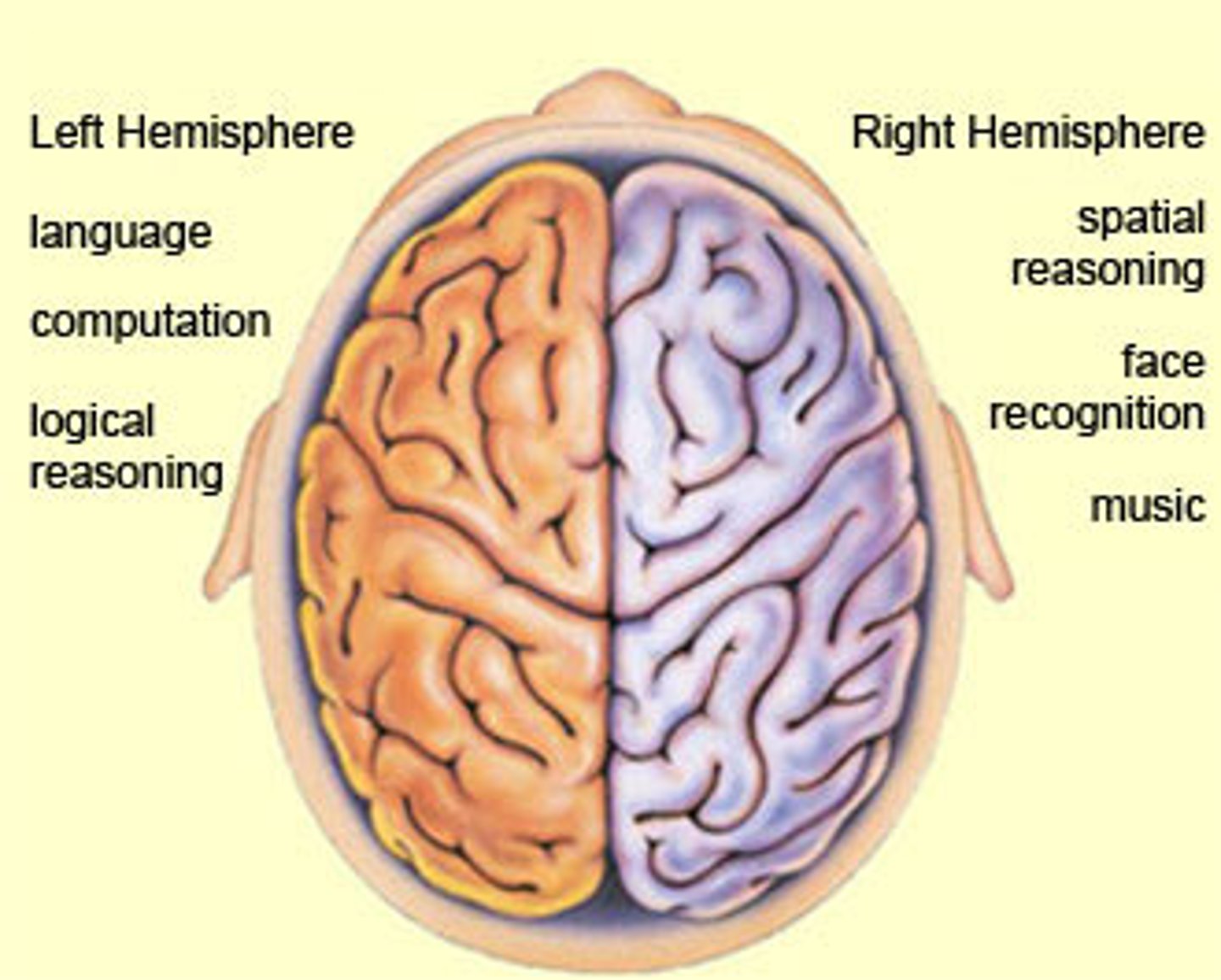
brain lateralization (hemispheric specialization)
Specialization of function in each brain hemisphere. The right hemisphere may be more active during spatial and creative tasks, while the left hemisphere may be more active during spoken language, logic, and sequential tasks.
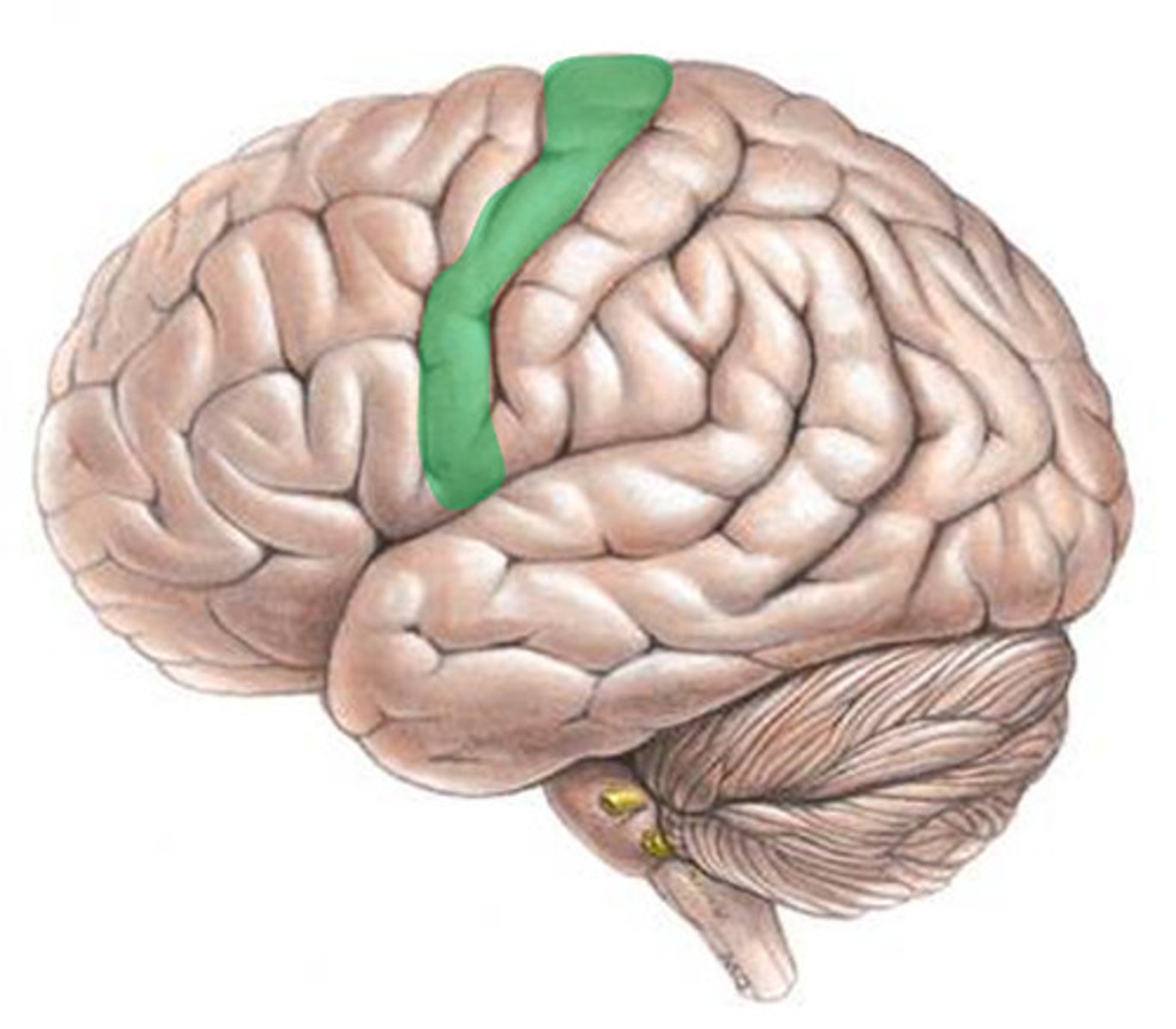
Broca's area (Paul Broca)
Controls language expression through an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
Wernicke's area (Carl Wernicke)
Controls language reception through a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe.
split-brain research
Surgical cutting of the corpus callosum to study the effects of disconnecting the right and left brain hemispheres, specifically, the independent functioning of the two hemispheres.
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
A technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain.
computerized tomography (CT) scanning
A computerized imaging technique that uses X-rays passed through the brain at various angles and then combined into an image.
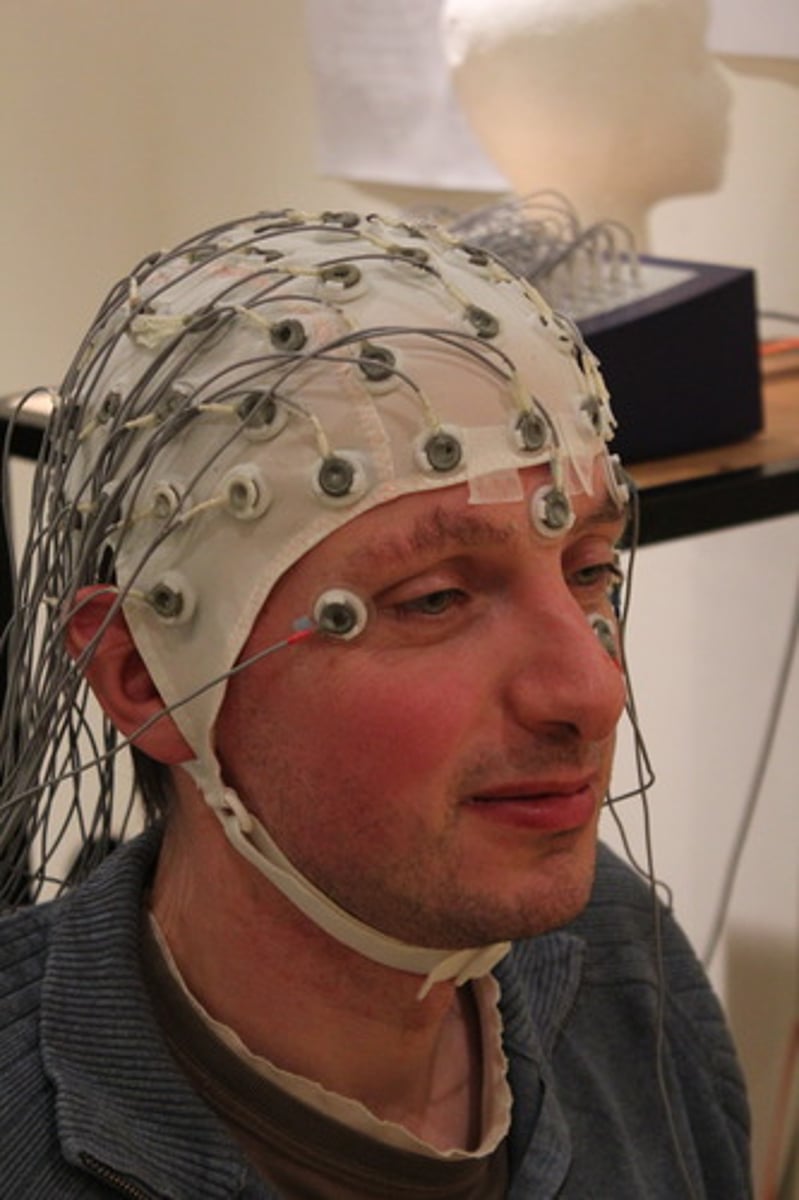
electroencephalography (EEG)
Recording the electrical activity of the brain via electrodes on the scalp.
brain lesioning
Abnormal disruption in the tissue of the brain resulting from injury or disease.
neuroplasticity
The ability within the brain to constantly change both the structure and function of many cells in response to experience or trauma.
Michael Gazzaniga
Pioneer in split-brain research. Developed our understanding of functional lateralization in the brain and how the cerebral hemispheres communicate.
psychoactive drugs
Chemicals that affect the nervous system and result in altered consciousness.
consciousness (Freud)
Belief that the conscious mind consists of everything inside of our awareness. This is the aspect of our mental processing that we can think and talk about in a rational way.
sleep cycle
A period of sleep lasting about 90 minutes and including one or more stages of NREM sleep, followed by REM sleep.
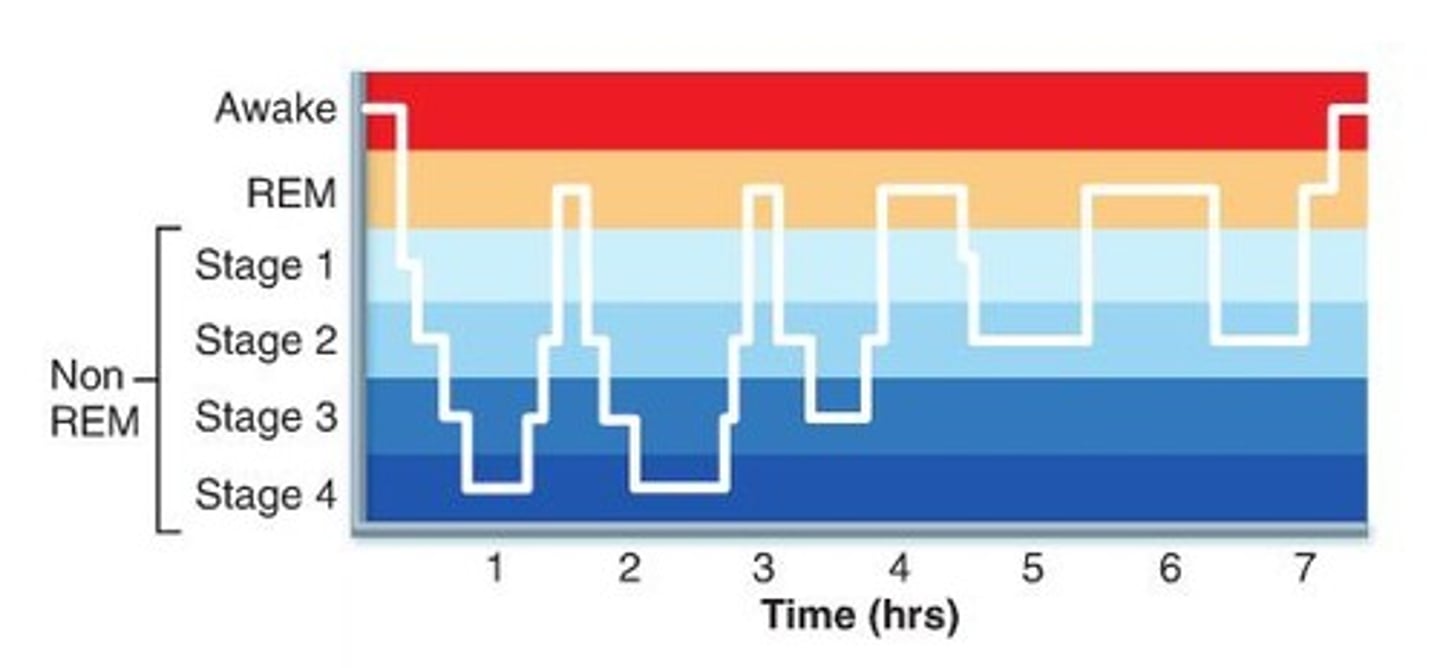
REM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep; a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because the muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches) but other body systems are active.
sleep disorder
Any sleep disturbance that regularly disrupts sleep, causing distress or impairment in important areas of everyday life during normal waking hours.
narcolepsy
A sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. The sufferer may lapse directly into REM sleep, often at inopportune times.