Calc 2 - Hyperbolic, Improper Integrals, Sequences, Monotone Sequences, Series of Constants, Series of Functions, & Power Series
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
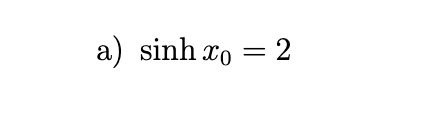
In each part, a value for one of the hyperbolic functions is given at an unspecified positive number x0. Use appropriate identities to find the exact values of the remaining five hyperbolic functions at x0.
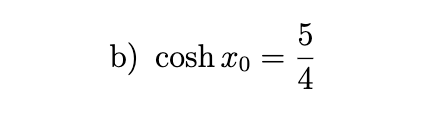
In each part, a value for one of the hyperbolic functions is given at an unspecified positive number x0. Use appropriate identities to find the exact values of the remaining five hyperbolic functions at x0.
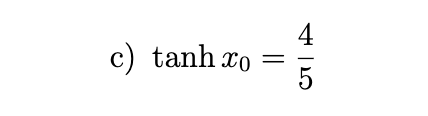
In each part, a value for one of the hyperbolic functions is given at an unspecified positive number x0. Use appropriate identities to find the exact values of the remaining five hyperbolic functions at x0.
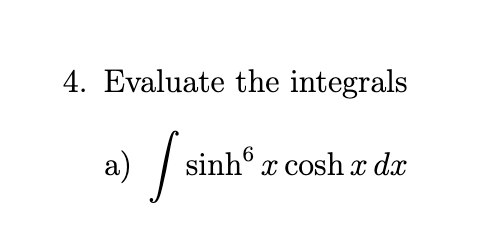
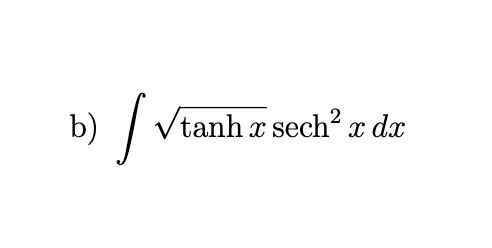
evaluate
2/3(tanh3/2 x) + C
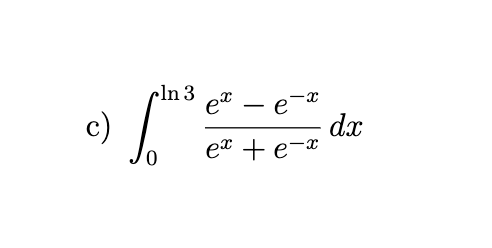
evaluate
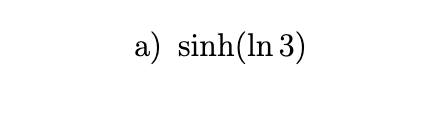
Find the exact numerical value of each expression.
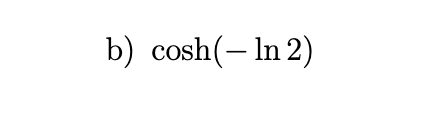
Find the exact numerical value of each expression.
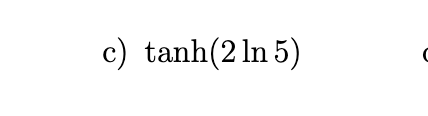
Find the exact numerical value of each expression.
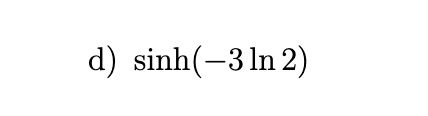
Find the exact numerical value of each expression.
-63/16
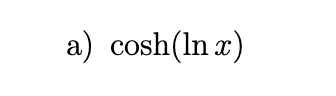
In each part, rewrite the expression as a ratio of polynomials
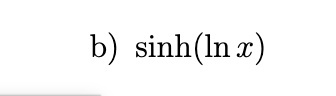
In each part, rewrite the expression as a ratio of polynomials
(x² - 1)/2x
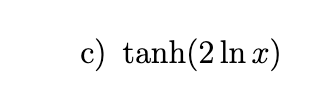
In each part, rewrite the expression as a ratio of polynomials
(x4 -1)/(x4 +1)
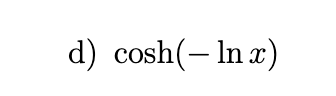
In each part, rewrite the expression as a ratio of polynomials
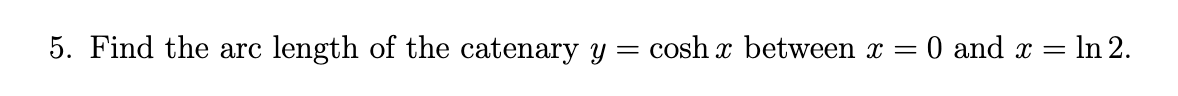
3/4
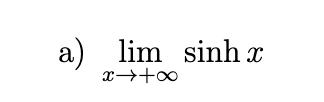
Find the following limits, and confirm that they are consistent with the graphs of the functions involved in each case.
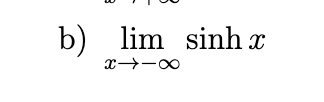
Find the following limits, and confirm that they are consistent with the graphs of the functions involved in each case.
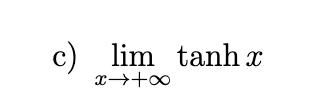
Find the following limits, and confirm that they are consistent with the graphs of the functions involved in each case.
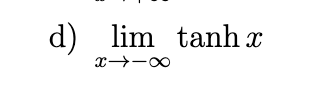
Find the following limits, and confirm that they are consistent with the graphs of the functions involved in each case.
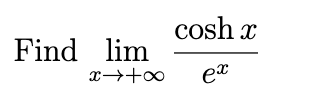
1/2
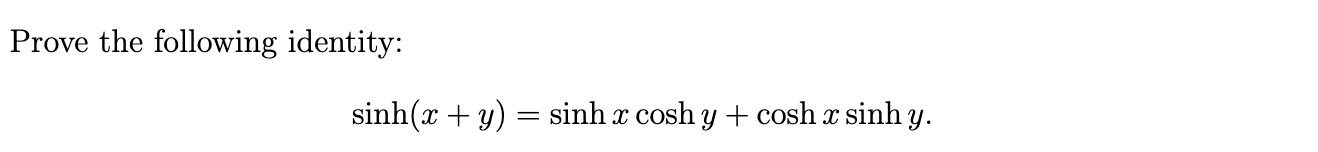

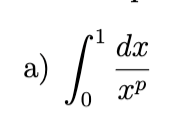
In each part, determine all values of p for which the integral is improper
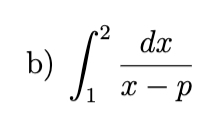
In each part, determine all values of p for which the integral is improper
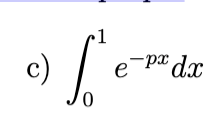
In each part, determine all values of p for which the integral is improper
never improper
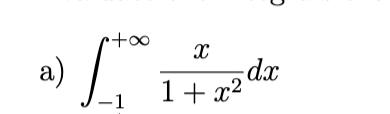
diverges
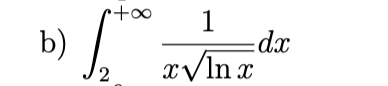
divergent
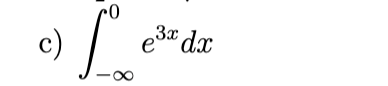
convergent to 1/3
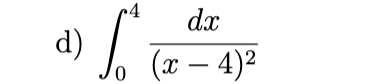
Divergent
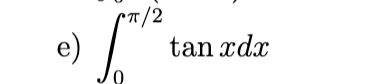
Divergent
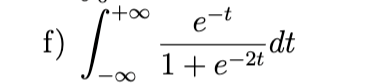
Convergent to pi/2
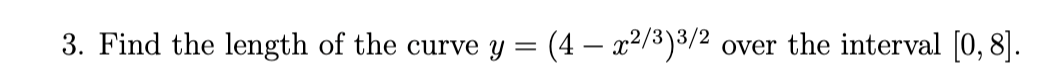
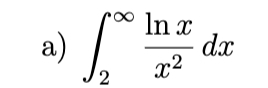
convergent
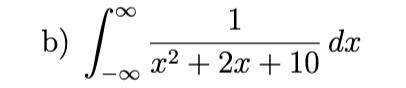
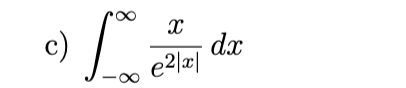
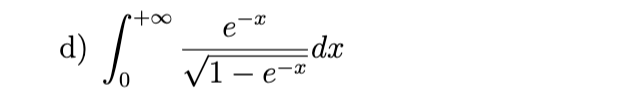
hint:
Use the substitution u = 1 − e(-x)
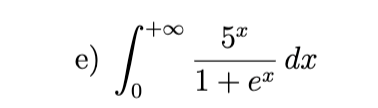
5ln(2) (hint: use substitution)
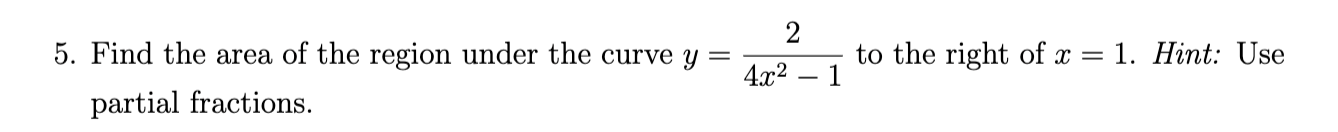
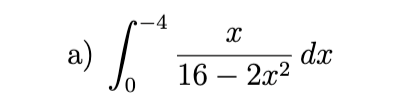
Divergent
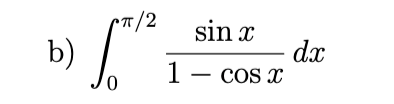
-inf, divergent
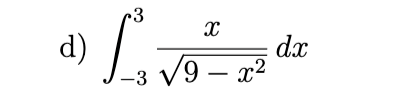
converges to 0
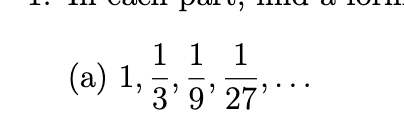
In each part, find a formula for the general term of the sequence, starting with n = 1
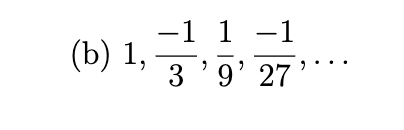
In each part, find a formula for the general term of the sequence, starting with n = 1
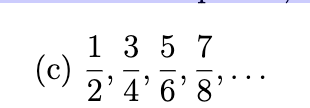
In each part, find a formula for the general term of the sequence, starting with n = 1
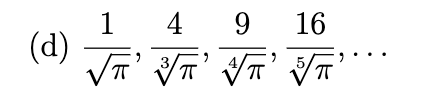
In each part, find a formula for the general term of the sequence, starting with n = 1
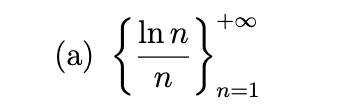
Write out the first five terms of the sequence, determine whether the sequence converges, and if so find its limit.
Convergent (limit = 0)
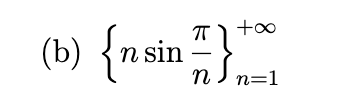
Write out the first five terms of the sequence, determine whether the sequence converges, and if so find its limit.
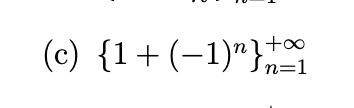
Write out the first five terms of the sequence, determine whether the sequence converges, and if so find its limit.
diverges
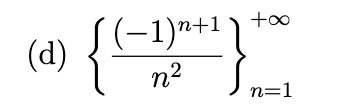
Write out the first five terms of the sequence, determine whether the sequence converges, and if so find its limit.
Convergent
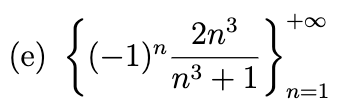
Write out the first five terms of the sequence, determine whether the sequence converges, and if so find its limit.
divergent (oscillating between 2 and -2)
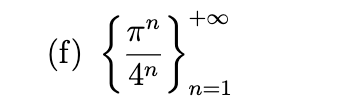
Write out the first five terms of the sequence, determine whether the sequence converges, and if so find its limit.
Converges to 0
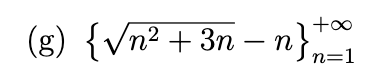
Write out the first five terms of the sequence, determine whether the sequence converges, and if so find its limit.
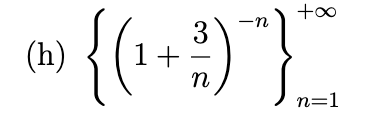
Write out the first five terms of the sequence, determine whether the sequence converges, and if so find its limit.
convergent (1/e³)
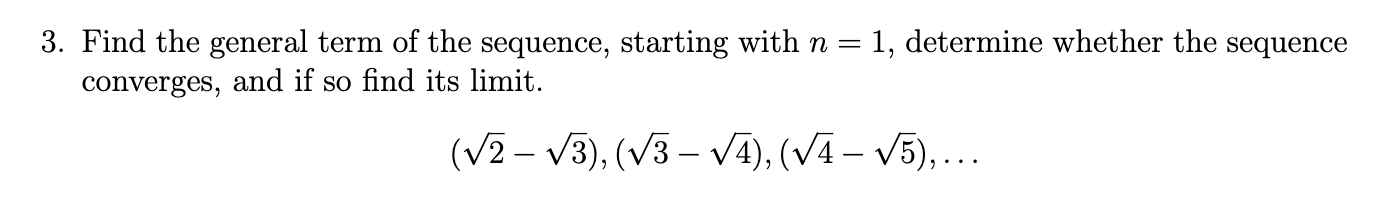
converges, limit =0

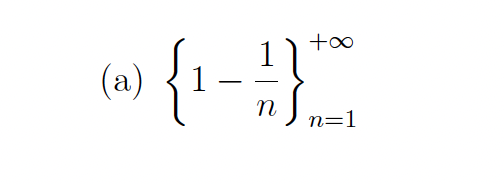
Use the difference a(n+1) − an to show that the given sequence {an} is strictly increasing or
strictly decreasing.
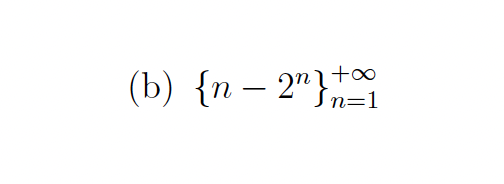
Use the difference a(n+1) − an to show that the given sequence {an} is strictly increasing or
strictly decreasing.
strictly decreasing
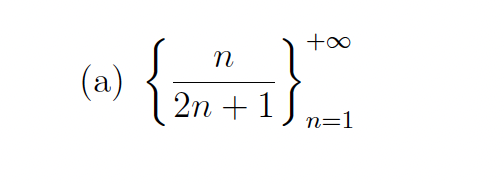
Use the ratio an+1/an to show that the given sequence {an} is strictly increasing or strictly
decreasing.
strictly increasing
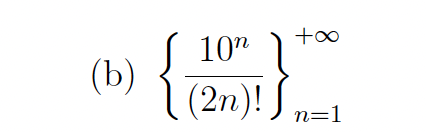
Use the ratio an+1/an to show that the given sequence {an} is strictly increasing or strictly
decreasing.
strictly decreasing
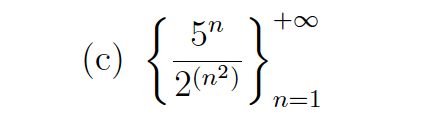
Use the ratio an+1/an to show that the given sequence {an} is strictly increasing or strictly
decreasing.
strictly decreasing
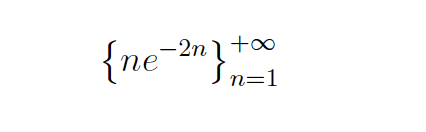
ignore

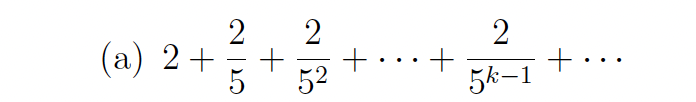
In each part, find exact values for the first three partial sums, find a closed form for the nth
partial sum, and determine whether the series converges by calculating the limit of the nth
partial sum. If the series converges, then state its sum.
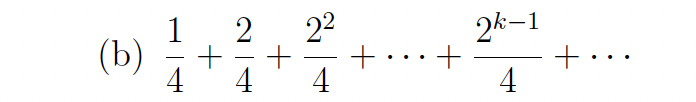
In each part, find exact values for the first three partial sums, find a closed form for the nth
partial sum, and determine whether the series converges by calculating the limit of the nth
partial sum. If the series converges, then state its sum.
Divergent
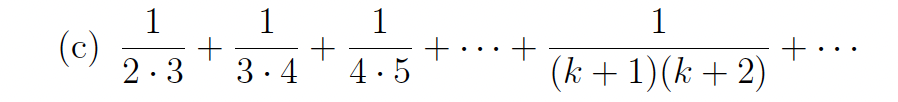
In each part, find exact values for the first three partial sums, find a closed form for the nth
partial sum, and determine whether the series converges by calculating the limit of the nth
partial sum. If the series converges, then state its sum.
Convergent to 1/2
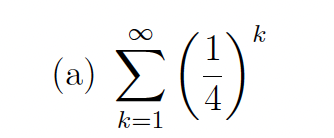
In each part, determine whether the series converges or diverges. If the series converges,
then state its sum.
Convergent, sum = (1/4)/(1-1/4)
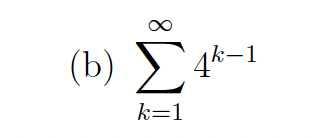
In each part, determine whether the series converges or diverges. If the series converges,
then state its sum.
divergent (ratio is greater than 1)
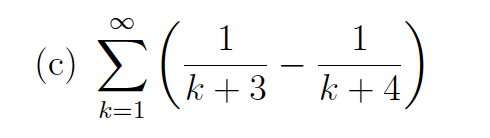
In each part, determine whether the series converges or diverges. If the series converges,
then state its sum.
converges and convergent to 1/4
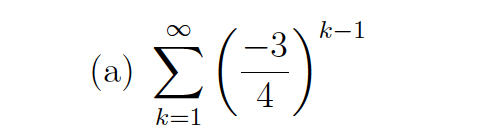
Determine whether the series converges, and if so find its sum
Convergent, sum = 4/7
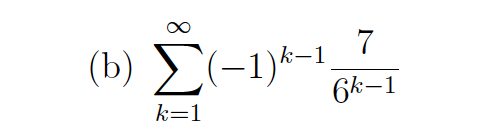
Determine whether the series converges, and if so find its sum
Convergent, sum = 6
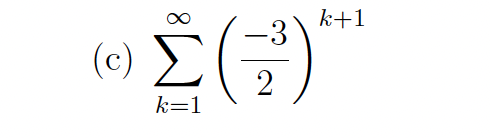
Determine whether the series converges, and if so find its sum
divergent
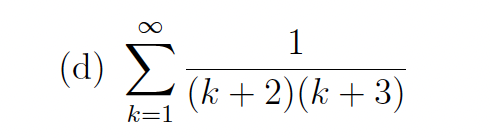
Determine whether the series converges, and if so find its sum
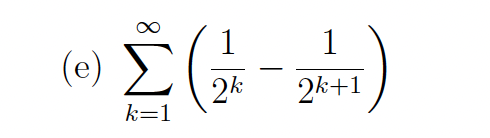
Determine whether the series converges, and if so find its sum
convergent (1/2)
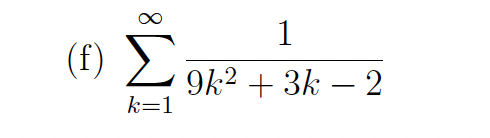
Determine whether the series converges, and if so find its sum
Convergent, sum =1/6
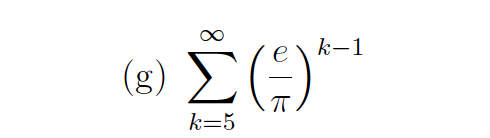
Determine whether the series converges, and if so find its sum
convergent
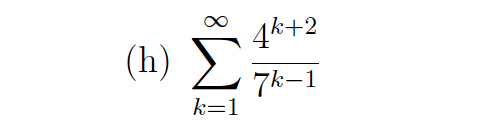
Determine whether the series converges, and if so find its sum
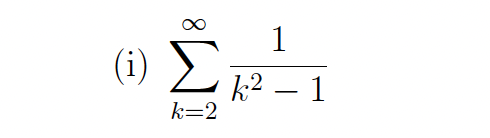
Determine whether the series converges, and if so find its sum
convergent and its sum is ¾ (PFD)
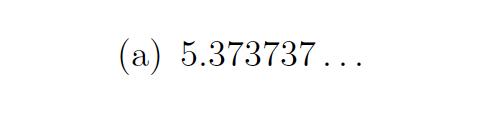
Express the repeating decimal as an irreducible fraction.
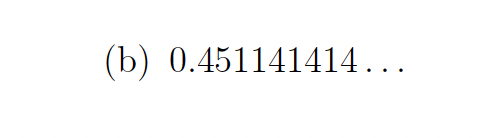
Express the repeating decimal as an irreducible fraction.
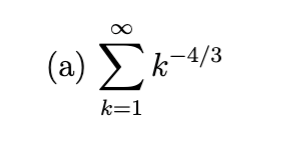
convergent

Divergent

convergent p series

covergent

divergent
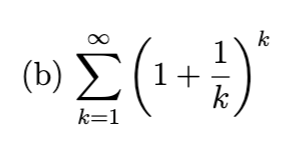
divergent (e)

Divergent (grandi’s series)
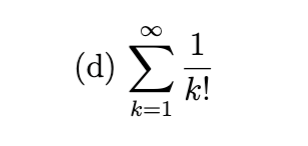
converges

Convergent
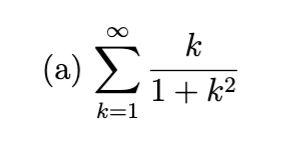
divergent (ordinary comp test)
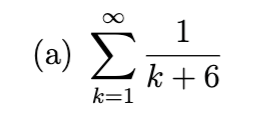
diverges
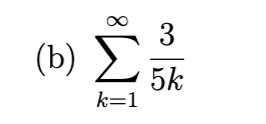
divergent
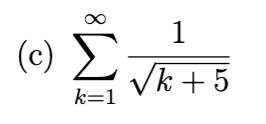
diverges
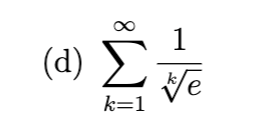
divergent
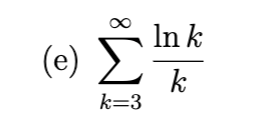
divergent
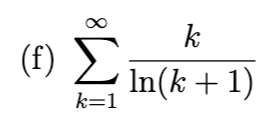
divergent

Convergent