biodiversity
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
what is meant by biodiversity
the number of different habitats in an area, the number of species within those habitats and the genetic variation within each species
what are some examples of high biodiversity
amazon rainforest, woodland
why is biodiversity important
maintaining a balanced ecosystem
all species are interconnected, meaning we all rely on each other
what are the three different studies of biodiversity
habitat biodiversity
species biodiversity
genetic biodiversity
what is meant by habitat biodiversity
number of different habitats found within an area. Each species can support other species, so the greater the habitiat biodiversity, the greater the species biodiversity
what is meant by species richness
-the number of different species living in a particular area
what is meant by species evenness
a comparison of the number of individuals of each species living in a community
what does genetic biodiversity mean
the variety of genes within a species that make up a species
what does sampling mean ?
taking measurments of a limited number of individual organisms present in a particular area
can be used to estimate the number of organisms in an area
random sampling
selecting individuals by chance, each organism has an equal chance of being selected. Quadrant practical
non random sampling
sample is not chose at random
what does opportunistic mean
weakest form of sampling, as it may not be representative of the population. Uses organisms that are conveniently available, based of prior knowledge
what is stratified sampling
strata ( sub groups) bases on characteristics. Like popuplation being sperated into males and females. Then a random sample is taken from these stratas
what is systematic sampling
different areas within an overall habitat are identified, which are then sampled seperatley. A line transect can be used
what are the pros and cons of random sampling
pros- not biased
cons- may not cover areas equally, species may be missed leading to an underestimate
what are the pros and cons if opportumistic sampling
pros - easier and quicker then random
cons- over estiate of its importance
what are the pros and cons of stratified sampling
pros- all different areas of a habitat are sampled
cons- over represntation of some areas
what are the pros and cons of systematic samoking
pros- useful when a clear gradient in some environmental facors
cons- other species may be missed, leafding to an underestimate
quadrant
to study non mobile species , random sampling, use a ranodm number generator for coordinates
What exmpales are there of ways to sample animals
pooter ( sucking insects up with a straw )
Sweep nets ( insects in long grass)
Pitfall traps ( hole is dug and an insect falls into it )
Tree beating
Koch sampling
What ways are there of sampling plants
quadrant/ farm quadrant ( sometimes to use slow moving animals)
Point quadrant
What does species density mean
How many of a species is present, measured using a frame quadrant. This is an absolute measure not an estimate
What does frequency mean
This is used where individual members of a species are hard to count.
Explain how capture- recapture works
a sample of animals is trapped and marked (c1) and then realised
Later a second sample is collected and the number of marked individuals (c3) out of the total number captured is counted (C2)
C1 x c2/ C3 = total Population
What is assumed during capture recapture
Animals are mobile
There were no births or deaths
There was no immigration
The population is large
What doeas abiotic factors mean
Are non living conditions in a bit ist that have a direct effect in the living organism
What are some examples of abiotic factors
wind speed
Light intensity
Re;active humidity
PH
Temperature
Oxygen content in water
What does species richness mean
Number of different species in an area
What does species evenness mean
Number of individuals of each species in an ares
What is the equation for Simpsons index of diversity , and what do they mean
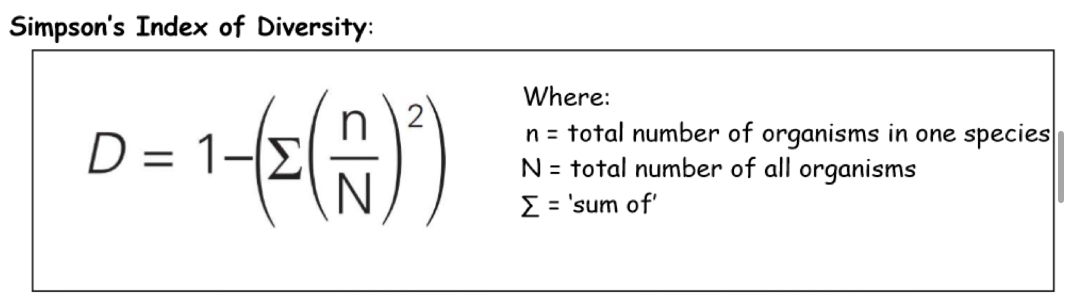
What does a low biodiversity tell us
low number of successful species
Stressful environment
Low number of species in the environment
Simple food webs
If environment changes it will effect the whole ecosystem
What does having a high biodiversity value tell us about a habitat
large number of successful species
Low stress environment
Food webs are complex
If there is a change on the environment it has a small effect on the whole ecosystem
Define allele
A different version or variant of the same gene, arising from differences in the base sequence, blue eye allele and brown eye allele are both eye genes
What is a genotype
An underlying genetic makeup of an organism, specifically referring to the combination of alleles it possesses for a particular gene or set of genes
What is a phenotype
An observable feature
What is a polymorphic gene
A gene that have more than 1 allele
What is a monomorphic gene
When there is only one variant of the gene
What factors could increase genetic biodiversity
mutations in the DNA of an organism, creating a new allele
Interbreeding between different populations, this is known as gene flow
Which factors decrease genetic diversity
selective breeding
Captive breeding programmes
Artificial cloning
Natural selection
Genetic drift
Genetic bottlenecks
The founder effect
Explain genetic bottlenecks
Where few individuals within a population survive an event or change, thus reducing the gene pool
What is the founder effect
When a small number of individuals create a new colony, geographically isolated from the original. The gene pool of this new population is small
What is genetic drift
Because of random Nature of alleles being passed from parent to their offspring, the frequency of occurrence of an allele will vary. In some cases the excistnece of a particular allele can disappear from population altogether. Genetic drift is more pronounced in populations with low genetic biodiversity
What is the equation for measuring genetic biodiversity
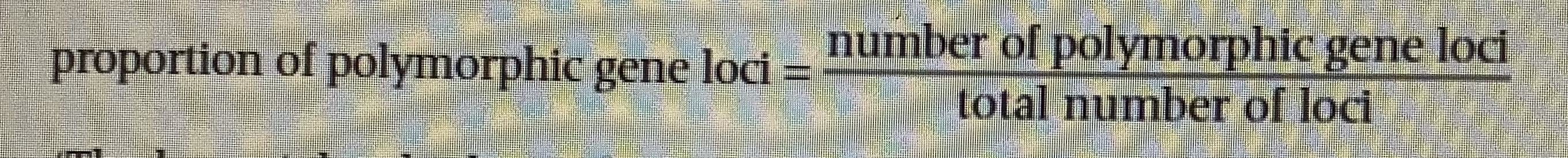
What are the 3 main factors effecting biodiversity
human population growth
Agriculture
Climate change
How does deforestation affect biodiversity
reduces the number of trees
Destroying habitat, food source and shelter for animals species
Forcing animals to migrate to other areas
How does climate change affect biodiversity
loss of habitat due to melting of polar ice caps
Loss of habitat due to rising sea
Change is abiotic factors
Altering the timing of life cycles, especially on species that are dependent on temperature
What are the main 3 reasons for maintains biodiversity
ecological ( maintains health )
Economic ( financial values)
Aesthetic
What is a keystone species
A species that influence many other species in an ecosystem. For example beavers and wolves
What are the names of the two main ways of maintaining biodiversity
In situ
Ex situ
What does In situ conservation mean
Protecting species in their natural habitat
What does ex situ conservation mean
This involves protecting a species by removing part of the population from a threatened habitat and placing it in a new location.
What are some examples of in situ conservation
National parks and marine conservation zones
Giving legal protection to endangered species
Controlling the introduction of species that threaten local biodiversity
Protecting habitats
What are some advantaged of in situ conservation
both habitat and species are conserved
Larger population can be protected
Maintains genetic diversity of species
Less disruptive
Chances of population recovery is greater then ex situ
What are some disadvantages of in situ conservation
difficult to control some factors: poachers, predators and disease
It needs large areas
May conflict with humans in the ares
What are some examples of ex situ conservation
seed banks
Botanic garden
Zoos
What are some advantages of ex situ conservation
easier to check health of individuals that in situ conservation
Organisms are in a controlled environment
Can be used to reintroduce species
Breeding can be regulated to maintain or even increase genetic diversity
What are some disadvantages of ex situ conservation
impossible to recreate the complete natural habitat
Expensive and hard to sustain
Only small numbers of individuals can be cared for
Many species can’t breed in captivity to dont adapt to their new location
Doesn’t address the underlying problem that the species was facing
What are the 3 international agreements
CBD
CITES
IUCN
What does CBD stand for
Rio Convention on Biological Diversity
What does CITES stand for
Convention on international trade in endangered species
What does IUCN stand for
International Union for the conservation of Nature
What is CBD
Develop international cooperation for strategies on:
Use of organisms, habitats and ecosystems
Sharing genetic resources
Sharing of access to knowledge and tech
Promoting ex situ conservation methods
What does CITES do
regulating trade in selected, endangered species o their products
Trade doesn’t endanger species or their population
Prohibiting commercial trade in wild plants
Basically all trade stuff
What does the IUCN do
It complies and puplished the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species which asses the conservation status of species world wide
it supports countries to work together to protect endangered species
What is the local conservation agreement
CSS
What does CSS stand for
Countryside Stewardship Scheme
What does the CSS do
It aimed to make conservation a part of normal farming and lang management practice
-sustaining beauty and diversity
improving wildlife habitats
Restoring neglected land
Improving opportunities