homeostasis 🧠
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
what does the human nervous system consist of
central nervous system
peripheral nervous system
what is the central nervous system
the brain and spinal chord
what is the peripheral nervous system consist of
all the nerves in the body
what does the nervous system enable
humans to react to their surroundings and to coordinate their behaviours
what is a bundle of neurones known as
a nerve
adaptions of the nervous system
neurones have a cell body
some have axons over a metre
axons insulated by fatty myelin sheath with small uninsulated sections
what does the receptor detect
stimuli in the environment
what is the order of the pathway through the nervous system
stimulus - receptor - coordinator - effector - response
describe the nervous system
very fast
precise electrical impulses through nerves
responds quickly
faster
describe the endocrine system
relies on hormones
travel throughout entire body
only affects certain cells
longer lasting
more generalised
what is negative feedback
whenever the levels of something get too high they’re brought back down, and vice verse
what does an involuntary response not involve
the conscious part of the brain as the coordinator of the reaction
the process for reflexes
stimulus is detected by a receptor
sensory neurone sends electrical impulses to the spinal cord
passed to a relay neurone in the spinal chord
a relay neurone synapses with a motor neurone
a motor neurone carries an impulse to a muscle
muscle will contract
what are the three main types of neurones in a reflex arc
sensory
relay
motor
what do sensory neurons do
carry impulses from sense organs to the cns
what do relay neurones do
found inside the CNS and connect sensory and motor neurones
what do motor neurones do
carry impulses from the CNS to effectors
describe a sensory neurone
long
have a cell body branching off the middle of an axon

describe a relay neurone
short
have a small cell body at one end with many dendrites
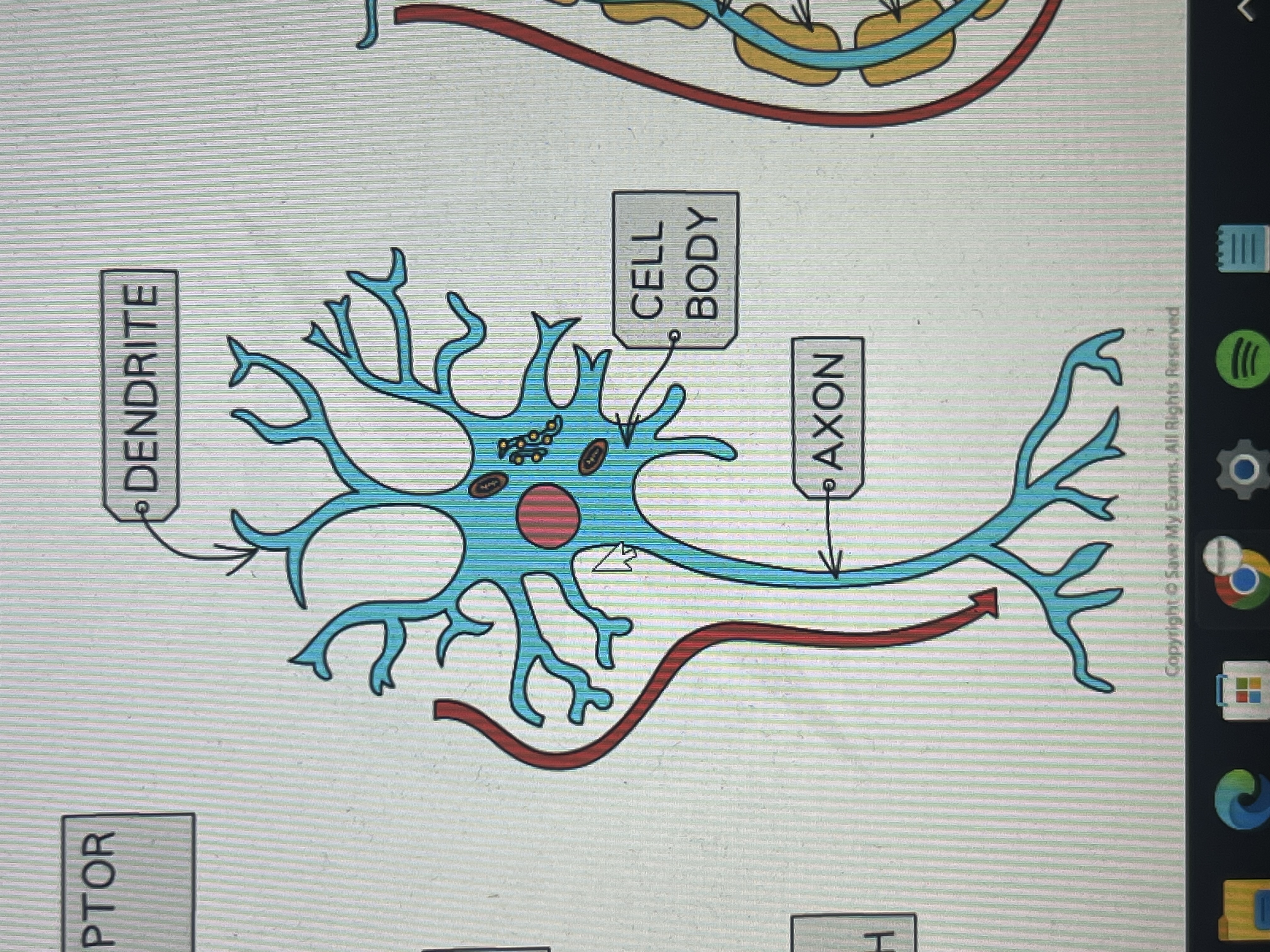
describe a motor neurone
long
have a large cell body at one end
long dendrites branching off it
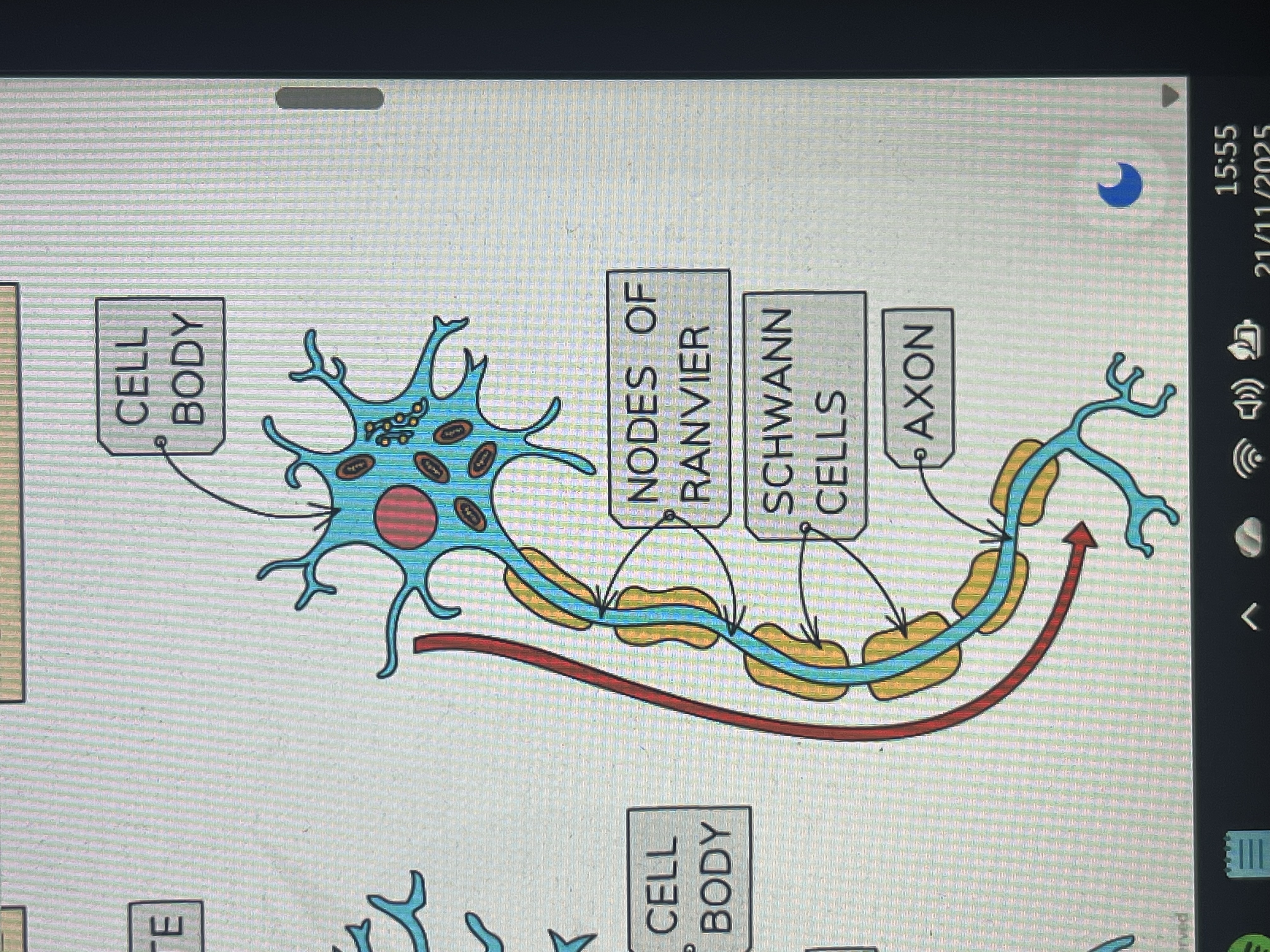
what are neurones separated by
synapses
how small are synaptic junctions
10nm in size
what chemicals are released into the synaptic cleft and diffuse across it
neurotransmitters
what is reaction time
time taken to respond to a stimulus
what can reaction time be affected by
age
stress
drugs
describe the cerebral cortex
the outer layer of the brain
divided into two hemispheres
highly folded
what is the cerebral cortex responsible for
intelligence
memory
consciousness
personality
describe the cerebellum
underneath the cerebral cortex
what is the cerebellum responsible for
balance, muscle coordination and movement
describe the medulla
region that controls unconscious activities such as heart rate and breathing
describe the eye
s a sense organ containing receptors
sensitive to light intensity and colour
purpose of the eye
receive light and focus it onto the retina
adaption to bright or dim light
accommodation to focus on objects
function of the retina
controls the light receptor cells that detect light intensity and colour of light
function of the optic nerve
sensory neurone that carries electrical impulses from the eye to the brain
function of the sclera
the white layer of the eye that covers the eyeball
function of the cornea
transparent covering of the front of the eye that refracts light
function of the iris
controls how much light enters the pupils
function of the ciliary muscles
ring of muscles around the lens which relaxes and contracts to change the shape of the lens
function of the suspensory ligaments
work with the ciliary muscles to change the shape of the lens
function of the lens
transparent disc that changes shape to focus light onto the retina
what does the eye do when dim light
pupil dilates so more light can enter
what does the eye do when bright light
pupil constricts so less light enters
what is accommodation
the process of changing the shape of the lens to focus on near or distant objects
what does changing the shape of the lens alter
how much light is refracted
describe the eye muscles when focusing on a near object
ciliary muscles contract
suspensory ligaments loosen
the lens is then thicker and refracts light rays more strongly
describe the eye muscles when focusing on distant objects
the ciliary muscles relax
the suspensory ligaments are pulled tight
the lens is then thin and only slightly refracts light rays
what is the other name for short sightedness
myopia
what is the other name for long sightedness
hyperopia
describe how laser surgery works and the risks
can be used to change the shape of the cornea
all surgical processes have a risk of unexpected change occurring during the procedure which could lead to worse vision or an infection
how is myopia fixed with laser eye surgery
the cornea is slimmed down, reducing the refractive power
how is hyperopia fixed with laser eye surgery
the cornea shape is changed so the refractive power is increased
ways of treating eye defects surgically
laser eye surgery
lens replacement surgery
describe how lens replacement works and the risks
completely replaces the lens of the eye with a plastic artificial lens
more invasive than laser surgery and carries a risk of damage occurring to the retina, leading to complete sight loss
what temperature do enzymes work best at
37 degress celcius
what is body temperature monitored and controlled by
the thermoregulatory centre in the brain
what happens if body temperature is too high
blood vessels dilate,the and sweat is produced from teh sweat glands
cause a transfer of energy from the skin to the environment, cooling the body down
what happens if body temperature is too low
blood vessels constrict and sweating stops and skeletal muscles contract to shiver
these mechanisms reduce heat loss to the surroundings
what is the endocrine system composed of
glands which secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream
describe the pituitary gland
master gland. makes hormones such as fsh and lh
describe the pancreas
produces insulin which regulates the blood glucose levels
describe the thyroid
produces thyroxine, which controls metabolic rate and affects growth
describe the adrenal glands
produces adrenaline
what do the ovaries produce
oestrogen
what do the testes produce
testosterone
what is TSH and what does it do
thyroid stimulating hormone which secrets the thyroid to release thyroxine
what is excess glucose turned into and where
in liver and muscle cells, excess glucose is converted into glycogen for storage
what happens if theres too much glucose
cells of the body losing water by osmosis
can be very dangerous
what does the pancreas do if blood glucose concentration is too high
secretes insulin to bring it back down
what is type 1 diabetes
a disorder in which the pancreas fails to produce a sufficient amount of insulin to control blood glucose levels
describe type 2 diabetes
the body cells no longer responding to insulin produced by the pancreas - the person still makes insulin but their cells are resistant to it and dont respond as well as they should
what hormone does the pancreas secrete if glucose is too high
glucagon that causes glycogen to be converted into glucose and released into the blood
when is insulin produced
when blood glucose rises and stimulates liver and muscle cells to convert excess glucose into glycogen to be stored – this reduces the blood glucose level
when is glucagon produced
when blood glucose falls too low and stimulates liver and muscle cells to convert stored glycogen into glucose to be released into the bloodstream – this increases the blood glucose level
what does too much water in the blood result in
cells swelling as water moves into them, this has a diluting effect and can lead to bursting
what does too little water in the blood result in
the cells lose water by osmosis, this has a dehydrating effect and can lead to cell death
what are the 2 sources of water in the body
produced by aerobic respiration
water in the diet
how is water lost
leaves the body via the lungs during exhalation
water, ions and urea are lost from the skin in sweat
what do the lungs mainly excrete and why
carbon dioxide as a product of aerobic respiration during exhalation
what do the kidneys mainly excrete and why
excess water, salt and urea by producing urine
what is digestion of proteins from the diet resulting in
excess amino acids which need to be excreted safely as they cant be stored in the body in the same way that glucose can
deamination definition
the process of breaking down excess protein
mostly happens in the liver
how does deamination occur
enzymes in the liver split up amino acid molecules, with the part containing carbon turned into glycogen and the other part containing nitrogen turned into ammonia
ammonia is toxic to our cells and is immediately converted to urea which can be transported around the body safely for excretion by the kidneys
what does the kidney help to control
the water content of the body and the concentrations of substances dissolved in the fluids of the body
what does the kidney contain
highly branched capillary network that form filters which contain pores with an average radium of 3 nano meters