CP Bio Honors Chapter 6 (and 7)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
To help in oxidation and reduction reactions.
grab electron, bring to the ETC
Anaerobic conditions
refers to an environment lacking oxygen, where organisms rely on fermentation or anaerobic respiration for energy production.
aerobic reactions
Reactions that require oxygen to efficiently produce ATP through cellular respiration, primarily in the mitochondria.
What goes into lactic fermentation?
Glucose, which is broken down
what does lactic fermentation produce?
it produces ATP and lactic acid.
Alcoholic fermentation
A metabolic process that converts pyruvic acid into alcohol and carbon dioxide in the absence of oxygen, commonly used by yeast and some bacteria.
what goes into alcoholic fermentation?
pyruvic acid and NADH
what does alcohol fermentation produce?
It produces ATP, ethanol/ethyl alcohol, and carbon dioxide. it also regenerates NAD+
How can you prevent lactic acid buildup?
I can eat more ready-carbs a day before a physical activity. You can also build endurance and work out so your body grows used to it.
While light independent reactions don’t rely on the light, they do rely on the light- dependent reactions why?
the ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions are needed to convert carbon dioxide into glucose in the Calvin cycle.
How many times does the Calvin cycle need to make G3P a full sugar?
The Calvin cycle must go around six times to produce enough G3P to form one full sugar molecule.
light dependent- reactions
occur during photosynthesis
require light to convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
H2O + Light —> O2 + a little ATP + some NADPH
Light independent reactions
occurs during photosynthesis
do not require light to produce glucose, instead they use ATP and NADPH generated from light-dependent reactions.
ATP+NADPH+CO2 —> C6H12O6+ ADP + NADP
This is the Calvin Cycle
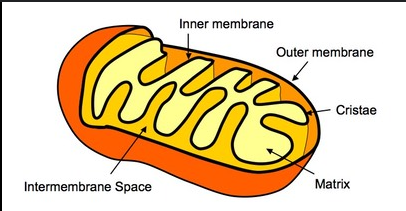
Describe how the ETC creates a H+ gradient across the inner membrane
High H+ in there Intermembrane space
Low H+ in the matric
Hydrogen wants to go to matrix but in order to do this, they need to go through a protein called ATP Synthase.
In product, 30-38 ATP is made
The bigger the concentration gradient and bigger difference, the more energy
QUIZ QUESTION
Things you HAVE to mention in order
How do plants get their energy they need to survive starting from the sun.
Sun+CO2+ Water (H2O), photosynthesis, Light reactions, chlorophyll, chloroplast, Photosystem II, ETC, Photosystem I, ATP, NADPH, CO2 —>Light Independent reaction, Calvin Cycle (6 times to make G3P a glucose molecule) Then, into Cellular respiration Glucose broken down by glycolysis (takes 2 ATP) to produce 4 ATP and 2 pyruvate then in the Mitochondria, they will be oxidized( pyruvate oxidation) by removing Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and adding Coenzyme A, this creates Acetyl CoA, which in the Krebs cycle mixes with a compound and produces many electron carriers, which then get transported to the ETC, There, they electrons get dropped off and sent through the ETC while hydrogens are getting pumped into the inner membrane space. Electrons will combine with O2 and Hydrogen ions and create H2O then the extra hydrogens in the inner membrane space will be pumped through the ATP Synthase and 30-38 ATP will be made.
In the cellular respiration equation, what molecules are part of the light dependent reactions? 6CO2+6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
6 H2O, light, and 6 O2 ( Water, light, and oxygen)
In the cellular respiration equation, what molecules are part of the light independent reactions? 6CO2+6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
6 CO2, C6H12O6 (Carbon dioxide and glucose)
Where is the most acidic region of mitochondria?
inner membrane space
Where does the carbon come from for plants to make structures like leaves, stems, root, tree trunks, etc?
Carbon dioxide
what has to be removed from pyruvate to prep it for the Krebs cycle?
carbon dioxide
what reactant of photosynthesis is the source of oxygen product?
H2O
What “Ancient Enzyme” is sometime tricked into grabbing O2 instead of CO2
Rubiscu
what is the chemical that comes out of the Calvin cycle
G3P
what compound is added to pyruvate to prep for Krebs cycle?
Coenzyme A (it becomes Acetyl CoA)
Is production of ATP an endergonic or exergonic reaction?
endergonic reaction
where does pyruvate oxidation occur?
Mitochondrial matrix
What does glycolysis translate to?
Sugar breaking
Another name for Krebs Cycle
Citric Acid Cycle
Reactants of Cellular Respiration
O2+ C6H12O6 (glucose and oxygen)
anaerobic step of cellular respiration
glycolysis
what structure allows gas exchange for a plant?
Stomata
what electron carriers is used during photosynthesis?
NADPH and NADP+
What pigment reflects greenlight?
Chlorophyll
what is the name given to organisms that cannot photosynthesize and consume their food
heterotrophs
what is the source of electrons that photosystems II and I excite?
H2O
The mitochondria likes to…
breath
Reactants of photosynthesis
CO2, H2O, sunlight
from photosynthetic equation, CO2 is the oxidized form of…
glucose (C6H12O6)
Where is G3P produced?
Stroma in chloroplast
what “calms” the electron between photosystem I and II
ETC
What is the name of the experiment that sealed candles, mice, and plants in jars?
Priestley’s experiment
Which type of plant will do light- dependent reactions at night?
CAM plants