Intro to Urinary System
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Upper Urinary System
Kidneys and ureters
Lower urinary system
Urethra and bladder
Where are the kidneys located?
Retroperitoneal cavity
Anterior to the right kidney
R adrenal gland, liver, Morison’s pouch, C loop of duodenum and right colic flexure
Anterior to the left kidney
Left adrenal gland, spleen, stomach, pancreas, left colic flexure and coils of jejenum
Posterior to right kidney
Back muscles, 12th rib, and diaphragm
Posterior to left kidney
Diaphragm, 11-12th ribs, back muscles
Which kidney lies slightly lower than the other and why?
The right kidney lies slightly lower than the left due to the liver's pushing it inferiorly.
Kidneys move how with respiration?
About 1 inch down
Length of kidney should be
9-12cm
Width of kidney should be?
5cm
AP of kidney should be?
2.5cm
Which kidney is slightly longer, but how many cm in length should they be to each other?
Left, 2cm
2 parts of kidneys
Renal parenchyma and renal sinus
2 parts of renal parenchyma
Renal medulla and renal cortex
Functioning renal tissue
Renal parenchyma
What part of the renal parenchyma is outermost and responsible for filtration of blood?
Renal cortex
What part of the renal parenchyma is innermost and responsible for absorption?
Renal medulla
Renal sinus includes
Collecting system, renal vessels, fat, nerves and lymphatics
The collecting system is compromised of what?
Minor and major calyces and renal pelvis
Hilar structures A to P
Vein, artery, ureter
Hilar structures P to A
Ureter, Artery, Vein
Pathway of Urine
Parenchyma, minor calyces, major calyces, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder, urethra
Inner to Outer parts of kidneys (4)
Renal capsule, perirenal fat, Gerota’s fascia, pararenal fat
Renal capsule purpose
Surrounds kidney itself
Perirenal fat
Covers renal capsule
Gerota’s fascia
surrounds kidney and adrenal gland
Pararenal fat
surrounding fat
Functional unit of the kidney
Nephron
Two main structures of a nephron
Corpuscle and tubule
Where are nephrons located?
In the cortex and medulla
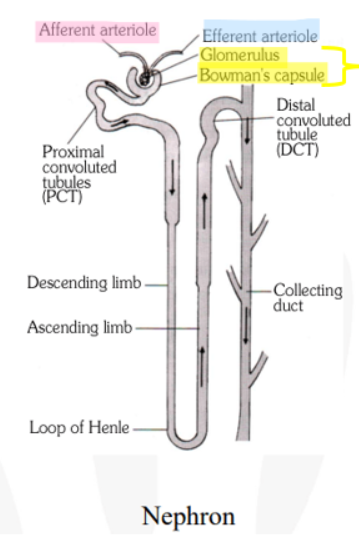
Renal corpuscle
Network of capillaries (glomerulus) surrounded by a cuplike structure (Bowmans capsule)
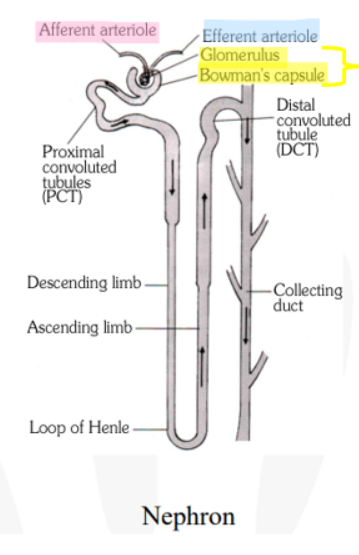
Afferent arteriole
Blood flow into the glomerulus
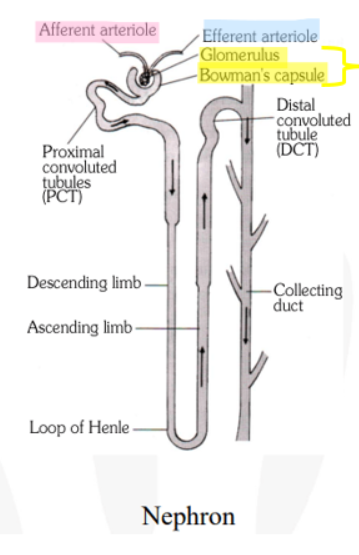
Efferent arteriole
Blood flow from glomerulus
Flow from renal proximal convoluted tubule to distal convoluted tubule
Proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule
Urine from the distal convoluted tubules of several nephrons does what next?
Drains into a collecting duct
What is the relationship between kidneys and BP?
Kidneys play a large part in BP regulation
Where do ureters enter the urinary bladder?
Posterolaterally via the trigone
Two urinary structures not typically seen on US?
Ureter and urethra
Vascular supply of kidneys
Aorta, renal artery, anterior and posterior branches, segmental, interlobar, arcuate, interlobular, afferent arterioles
Where does the renal artery become the larger anterior and small posterior artery?
At hilum
Where do the segmental arteries divide?
In sinus
Where do interlobar arteries divide?
Between pyramids
Where do the arcuate arteries divide?
At base of pyramids
Where do the interlobular arteries divide?
in cortex
Where do the afferent arterioles divide?
to nephron
What is special about the RRA?
It is the longest vessel and only vessel to run posterior to the IVC
Renal veins drain into where?
IVC
Renin
enzyme that controls BP
Physiology of kidneys
Filter blood, excrete waste via urine, absorption and regulate BP
Formation of urine involves what three processes within the nephron?
Glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion
What organs have excretion functions?
Skin, lungs, liver, large intestines and kidneys
Main metabolic waste products include
Water, carbon dioxide, and nitrogenous wastes (Urea, uric acid and creatinine)
Blood tests for renal disease
BUN, GFR, Serum creatinine and WBC count
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) will be affected by kidney dysfunction how
Will increase
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) will be affected by kidney dysfunction how
Will decrease
Serum creatinine will be affected by kidney dysfunction how?
Will increase
WBC count will be affected by kidney infection how
Will increase
Urine tests for renal disease
Urinalysis, Urine pH, Specific gravity, blood, protein, creatinine clearance and urine culture
Hydronephrosis
Fluid in collecting system
Normal cortex thickness shoudl be
Greater than or equal to 1cm
Medullary pyramids appear how on US?
Hypoechoic
How should the renal cortex appear relative to the liver parenchyma?
Isoechoic or slightly hyperechoic
Renal detail may be obscured if the patient has
Hepatocellular disease, gallstones, rib interference or other abnormal collection between liver and kidney
Prominent columns of Bertin may be confused with
avascular renal neoplasms
Dromedary Hump
bulge of cortical tissue that can occur on the mid/lateral border of the kidney
Dromedary humps primarily occur on which kidney?
Left
What is the echogenicity of the dromedary hump compared to the rest of the renal cortex?
Isoechoic
Junctional Parenchymal Defect
triangular, echogenic area typically located anteriorly adn superiorly
Where does a Junctional Parenchymal Defect affect, and does it affect function?
Cortex and no
Fetal Lobulation may persist in up to what percent of adults?
51%
Fetal Lobulation
surfaces of kidneys are generally indented in between calyces
Sinus Lipomatosis
Deposition of moderate amount of fat in renal sinus, with parenchymal atrophy
Extrarenal Pelvis
Tends to be larger than normal renal pelvis and located outside of the sinus medial to the hilum
Unilateral Renal Agenesis will result in
compensatory hypertrophy
Renal hypoplasia
Underdeveloped, small kidney
Horseshoe Kidney
Kidneys are fused at inferior poles, connecting isthmus is seen anterior to aorta
Double/Duplicated Collecting System
Division of renal sinus, results in an upper and a lower collecting system
Which collecting system is more likely to develop hydronephrosis and back up if there is a duplicated collecting system?
Upper
What is the most common congenital anomaly of the urinary tract?
Double collecting system
Ectopic kidney
Kidney is not where it is supposed to be but still functions normally
What is the most common location for an ectopic kidney?
Pelvis
Cake Kidney
Fused kidneys in renal pelvis, not very common
What should the texture of the bladder wall be?
Smooth
What should the bladder wall measure?
3-6 mm
What is used to examine the bladder due to being the best type of detection for early neoplasms?
Cytoscopy
Transabdominal sonography will allow visualization of most lesions greater than what?
5 mm
Stricture
Narrowing
Ureteral strictures may result from
Inflammatory disease, TB, impacted urogenital stone, localized periureteral fibrosis, schistosomiasis, iatrogenic ureteral injury or radiation therapy
Ureterocele
Cyst-like enlargement of the lower end of the ureter, typically congenital