AP Environmental 4.1 - 4.3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:18 PM on 11/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
zones of the earth
- core
- mantle & asthenosphere
- crust (continental and oceanic)
- mantle & asthenosphere
- crust (continental and oceanic)
2
New cards
what is the earth's crust broken into?
tectonic plates
3
New cards
what to tectonic plates float on?
the asthenosphere
4
New cards
who discovered continental drift?
Alfred Wegener
5
New cards
continental drift
the gradual movement of the continents across the earth's surface through geological time
6
New cards
why does continental drift occur?
b/c of plate tectonics, which move because the interior of the earth isn't heated equally (convection currents)
7
New cards
what drives the movement of tectonic plates?
convection currents
8
New cards
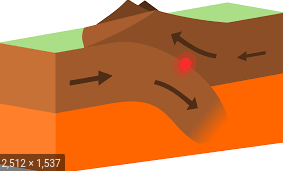
convergent plate boundary
can result in the creation of mountains, island arcs, earthquakes, tsunamis, deep sea trenches, and volcanoes
9
New cards
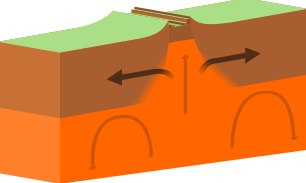
divergent plate boundaries
can result in seafloor spreading, rift valleys, and earthquakes
10
New cards
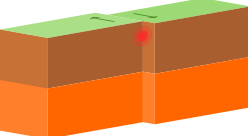
transform plate boundaries
can result in earthquakes
11
New cards
p (earthquakes)
moving across
12
New cards
s wave (earthquakes)
up and down
- more dangerous
- more dangerous
13
New cards
weathering
the process of wearing or being worn by long exposure to the atmosphere
14
New cards
mass wasting
the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity
15
New cards
erosion
the geological process in which earthen materials are worn away and transported by natural forces such as wind or water
16
New cards
physical weathering
mechanical breakdown of rocks and minerals
17
New cards
chemical weathering
chemical breakdown of rocks and minerals
- release essential nutrients from rocks
- release essential nutrients from rocks
18
New cards
types of chemical weathering
- dissolution
- oxidation
- hydrolysis
- anthropogenic
- oxidation
- hydrolysis
- anthropogenic
19
New cards
types of physical weathering
- frost wedging
- unloading
- thermal expansion
- biological activity
- plant root wedging
- unloading
- thermal expansion
- biological activity
- plant root wedging
20
New cards
frost wedging
a form of physical weathering that breaks down rocks through the freezing and thawing process
ex. boulders and mountains in cold climates with large cracks
ex. boulders and mountains in cold climates with large cracks
21
New cards
unloading
the removal of great weights of rock or ice that lie on the surface
ex. the domes in Yosemite
ex. the domes in Yosemite
22
New cards
thermal expansion
the tendency of matter to change in shape, volume, and area in response to a change in temperature
ex. railway tracks in the summer
ex. railway tracks in the summer
23
New cards
biological activity
when plants break up rocks with roots
ex. tree roots breaking up rocks
ex. tree roots breaking up rocks
24
New cards
plant root wedging
fractures in rocks are enlarged by the growth of plant roots
ex. tree roots making cracks in rocks larger
ex. tree roots making cracks in rocks larger
25
New cards
dissolution
when water comes into contact with rocks and dissolves the minerals that make up that rock into individual elements
ex. dissolving a teaspoon of salt into water
ex. dissolving a teaspoon of salt into water
26
New cards
oxidation
when oxygen reacts with other elements and electrons are transferred between two elements
ex. the reaction between magnesium and oxygen that forms magnesium oxide
ex. the reaction between magnesium and oxygen that forms magnesium oxide
27
New cards
hydrolysis
a new solution is formed as chemicals in rock interact with water
ex. sodium minerals react with water to form a saltwater solution
ex. sodium minerals react with water to form a saltwater solution
28
New cards
anthropogenic
weathering as a result of human action
ex. burning of fossil fuels
ex. burning of fossil fuels
29
New cards
why is surface area so important to the weathering process?
smaller pieces have more surface area for water and gasses to react with the rock. therefore, smaller rocks undergo chemical weathering faster than large rocks
30
New cards
joints
a type of extension fracture formed by movement of the rock in a direction perpendicular to the plane of fracture
31
New cards
why are joints so important to the process of weathering?
they effectively cut large blocks of rock into smaller one thus increasing the surface area where chemical reactions can take place
32
New cards
how do caves and sinkholes form?
water dissolves minerals in the rock, leaving residue and open spaces within the rock
33
New cards
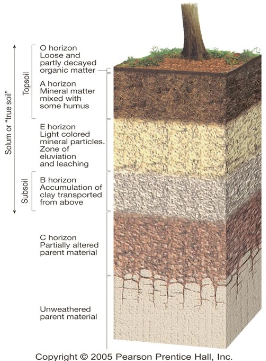
layers of soil horizons
34
New cards
humus
organic component of soil
35
New cards
eluviation
the transportation of dissolved or suspended materials by the movement of water (rain)
36
New cards
leaching
draining a soluble chemical from the soil
37
New cards
solum
layers that have gone through soil formation
38
New cards
o horizon (organic)
- decomposed organic material
- also called humus
- most pronounced in forests
- also called humus
- most pronounced in forests
39
New cards
a horizon (topsoil)
- surface soil/topsoil
- organic mixed with mineral material
- most biological activity
- organic mixed with mineral material
- most biological activity
40
New cards
e horizion
minerals
- zone of leeching
- zone of leeching
41
New cards
b horizon (subsoil)
mineral material - zone of accumulation of metals and nutrients
42
New cards
c horizon
- least weathered
- similar to parent material
- similar to parent material
43
New cards
soil layer acronym
Only After Eating is Beall Cheerful
44
New cards
what make up the components of soil?
sand, silt, clay
45
New cards
describe how to use a soil texture chart
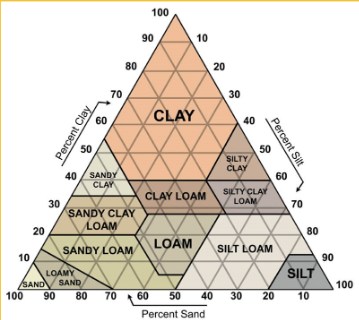
46
New cards
physical properties of soil
permeability
47
New cards
permeability
the rate at which water can flow through a substance
48
New cards
porosity
the pore space in soil between mineral particles filled with either air or water
49
New cards
chemical properties of soil
- CEC
- base saturation
- base saturation
50
New cards
base saturation
proportion of bases to acids in soil expressed as a percentage
51
New cards
CEC
*Cation Exchange Capacity*
- nutrient holding capacity
- clay, acidic pH, organic material
- nutrient holding capacity
- clay, acidic pH, organic material
52
New cards
biological properties of soil
- fungi, bacteria, protozoans = 80-90%
- rodents, earthworms, snails, slugs (detritivores) - mixing, breakdown of material
- nitrogen fixing bacteria
- rodents, earthworms, snails, slugs (detritivores) - mixing, breakdown of material
- nitrogen fixing bacteria
53
New cards
why is the biological part of soil so important for soil health?
because biologically active soils increase organic mater which causes their capacity to hold water to increase