FDA Final Exam
1/265
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
266 Terms
This authorized FDA to order device product recalls:
1990 Safe Medical Devices Act
This was the first major US law to regulate the safety of food and drugs:
1906 Pure Food and Drugs Act
This addressed the gaps in the Pure Food and Drugs Act of 1906:
1912 Sherley Amendment
This is when FDA gained responsibility for regulating biological products (vaccines & blood products):
1944 Public Health Service Act
This was the streamlined premarket approval for certain low-risk devices:
1997 FDA Modernization Act
This requires medical device companies to pay fees to FDA when submitting a premarket submission, registering establishment and listing devices with agency:
2002 Medical Device User Fees Amendment
This expanded the FDA’s authority over to medical devices:
2007 FDA Amendments Act
This made it so all new drugs must prove safety before marketing:
1938 Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act
This made it so safety and efficacy before marketing became a requirement:
1962 Kefauver-Harris Amendments
In addition to the FDA, name 2 departments that fall under the Department of Health and Human Services:
NIH, CDC
What does CDRH stand for?
Center for Devices and Radiological Health
What does CDER stand for?
Center for Drug Evaluation and Research
What does OCP stand for?
Office of Combination Products
What does ORA stand for?
Office of Regulatory Affairs
What does CBER stand for?
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research
This act is responsible for the regulation of medical devices:
Food and Drug Cosmetic Act
Classification relates directly to the _____ and _____.
Intended use, indications for use
Define intended use:
General purpose of the medical device or its function
What you claim the medical device does/EXACTLY what your product is used for
Define indications for use:
Describes the disease or condition the medical device will diagnose, treat, prevent, cure, or mitigate, including a description of the target patient population
Define risk:
The potential harm that a device could cause to the patients, environment, or end users
Define controls:
Set of quality practices and procedures that ensure a product is designed an developed to meet user needs and intended uses
Provide an example of a Class I device:
Low risk (Bandages)
Provide an example of a Class II device:
Moderate risk (Pregnancy test)
Provide an example of a Class III device:
High risk (Pacemaker)
What is used to determine regulation?
21 CFR, the Code of Federal Regulations, which governs food and drugs in the US
What is the information from the classification of the device used to find?
The proper pathway to get your product registered with FDA
What is used to determine product code?
FDA product code classification database
What two elements are needed to determine classification of a device?
Applicable regulation and product code
What makes a device eligible for Self-Registration?
It is Class I
What makes a device eligible for 510(k)?
A device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device
What makes a device eligible for PMA?
Class III devices or devices for which no predicate device exists
What is the traditional 510(k)?
Standard pathway for demonstrating substantial equivalence
What is the special 510(k)?
Device modification where changes do not affect the intended use or raise questions on safety/efficacy
What is the abbreviated 510(k)?
Used when FDA-recognized consensus standards, special controls, or guidance documents are available
What makes a device eligible for De Novo Classification?
Class III device without a predicate may use the De Novo classification process to reclassify it as a Class I or II if it presents low to moderate risk
What makes a device eligible for a Humanitarian Use Device (HUD)?
Devices intended to treat rare conditions affecting fewer than 8,000 patients per year may qualify, significantly reduces the data requirements
What is a Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE)?
Marketing application for a HUD and is exempt from the effectiveness requirements
What is the purpose of the investigation device exemption (IDE)?
Allows the investigational/unapproved medical device to be used in a clinical study to collect safety and effectiveness data (typically to support a PMA, very occasionally a 510(k))
Must have approved IDE before the study starts
A device with this type of risk requires both FDA and IRB approval prior to being used in a clinical trial.
Significant risk device
A device with this type of risk requires only IRB approval prior to being used in a clinical trial.
Nonsignificant risk device
Provide one difference between the development and approval pathways for drugs vs. biologics.
Drugs are approved through the New Drug Application (NDA)
Biologics are approved through the Biologics License Application (BLA)
What is the difference between the centers for drugs vs. biologics?
Drugs: CDER
Biologics: CBER
Which medical device pathway does not require clinical trials?
510(k) or ANDA
This answers questions about safety:
Preclinical Research
What is In vitro?
Conducted outside of living organism
What is In vivo?
Conducted in a living organism
Explain when an ANDA would be used.
Contains data submitted to FDA for the review and potential approval of a generic drug (not required to provide preclinical or clinical data)
When in the development cycle is an IND submitted?
Before conducting clinical trials or research
Who is part of the FDA IND review team?
Group of scientists and specialists in different fields
How long does the FDA review team have to review IND submission?
30 days
What is the purpose of the following steps of a clinical trial for Phase I:
Safety and dosage
What is the purpose of the following steps of a clinical trial for Phase II:
Efficacy and side effects
What is the purpose of the following steps of a clinical trial for Phase III:
Efficacy and monitoring of adverse reactions
Name the two special review programs for medical devices:
Breakthrough device program and STeP
What is Fast Track?
Filed by the manufacturer and expedites the review of drugs to treat an unmet medical need
Providing therapy where none exists or which may be potentially better than available therapy
What is Breakthrough Therapy?
Expedites the development and review of drugs that are intended to treat a serous condition
Preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement over available therapy on a clinically significant endpoint
What is Breakthrough Devices Program?
For medical devices and device-led combination of products
What is Accelerated Approval?
Allows drugs for serious conditions that filled an unmet need to be approved based on surrogate endpoint
What is the clinical benefit of accelerated approval?
A positive therapeutic effect that is clinically meaningful in the context of a given disease
What is Priority Review?
FDA’s goal is to act on an application within 6 months
Focus on drugs that offer significant improvements in the safety or effectiveness when compared to standard applications
Define surrogate endpoint:
A measure or biomarker used in clinical trials as a substitute for a clinical endpoint that directly measures how a patient feels, functions, or survives. Essentially, it’s a substitute measure that is believed to predict the effect of a treatment on the real clinical outcome.
When is Orphan Drug Designation used?
Drugs used to prevent, diagnose, or treat a rare disease or condition. Used for disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people in the US.
Name one special program for drugs that allows manufacturers to use surrogate endpoints.
Accelerated approval
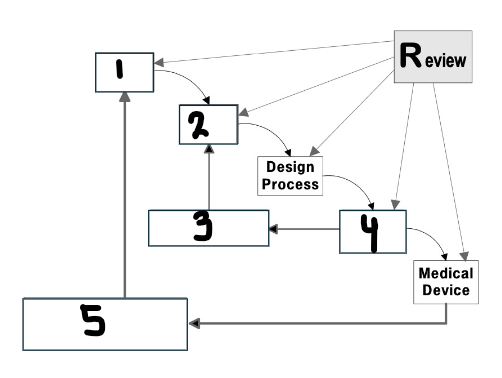
What goes in the first box?
User needs
What are user needs?
Intended use
Indications for use
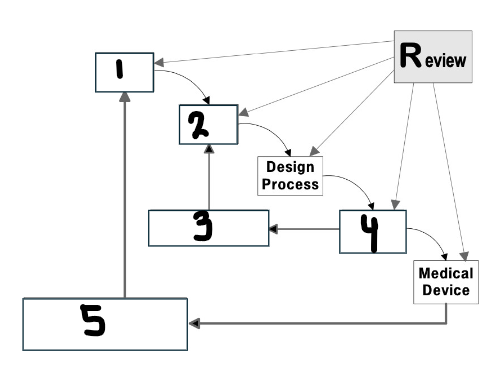
What goes in the second box?
Design input
What are design inputs?
Performance criteria, requirements, and features of the medical device
Measurable and objective inputs
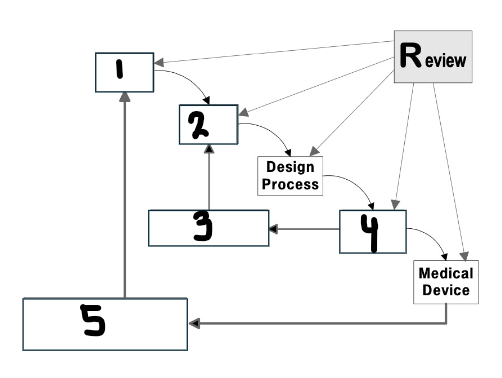
What goes in the third box?
Verification
What is design verification?
Confirmation by objective evidence that the design output meets design input (I made the product correctly)
Define how you will verify that your design has met the specification
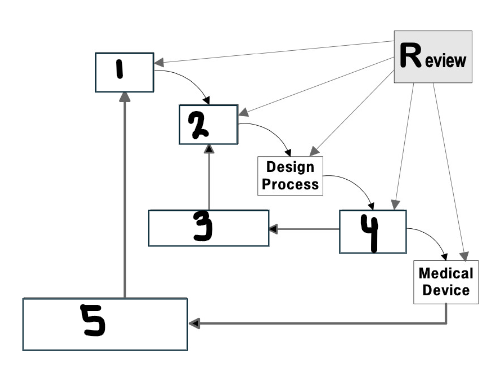
What goes in the fourth box?
Design output
What are design outputs?
Results of a design effort at each design phase and at the end of the total design effort
Must be measurable and testable
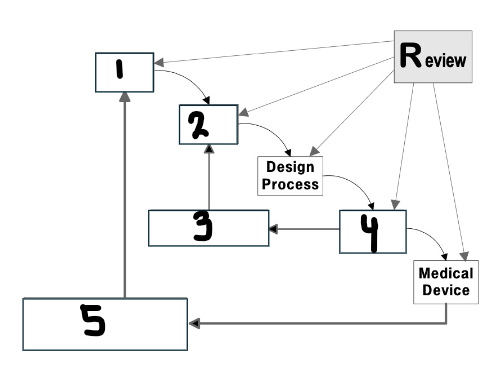
What goes in the fifth box?
Validation
What is design validation?
Establishing by objective evidence that specification conforms with user needs and intended uses (I made the correct product)
What are design reviews?
Formal review and agreement on design controls conducted at various stages of the medical device design process
Define design transfer:
Translate device into product specifications
Define design changes:
Review design changes before you implement
Define design history file:
Shows you designed a compliant device according to your plans
Which standard states risk management processes must be defined for all medical device products?
ISO 14971
Which standard states electrical standards for medical devices?
IEC 60601
Which standard states usability of medical devices as it relates to safety?
IEC 62366
Which standard states biocompatibility?
ISO 10993
What is a hazardous situation?
Circumstances in which people, property, or environment is/are exposed to one or more hazards
What is a hazard?
Potential source of harm
What is harm?
Injury or damage to health of people or damage to property or environment
What is risk management plan?
Describes risk management activities throughout product lifecycle
What is risk assessment analysis?
Systemic use of available information to identify hazards and eliminate the risk (ISO 14971:2019)
Which two documents identify which zones of risk are acceptable and which require risk reduction?
Risk Management Procedure and Risk Management Plan
What is risk control?
Risk controls reduce risks identified in risk evaluation to acceptable levels
What is risk acceptability?
After identifying all risk control measures and implementing them, evaluate residual risks
What is risk management review?
Risk management report summarizes all your risk management activities and include any benefit-risk analysis
What is production and post-production information?
Risk management is a total product lifecycle process
Define probability of occurrence:
Chance that a given event will occur, the likelihood something will happen
Define severity:
Measure of possible consequences of a hazard
Good design controls are intended to:
Reduce risk
What is the proactive risk management tool (full name) used in the design, development, and manufacturing stages and what does it specifically relate to?
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Proactive risk management tool used in design, development, and manufacturing stages
Risk is a calculated combination of what two elements?
Probability of occurrence of harm and severity of harm
According to ISO, what is the definition of benefit?
Positive impact or desirable outcome of the use of a medical device on the health of an individual or positive impact on patient management or public health
21 CFR 58 establishes which regulations?
The Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) regulations for nonclinical laboratory studies that support applications for research or marketing of medical products regulated by the FDA.
What are the objectives of 21 CFR 58?
Ensure data integrity & reliability
Standardizes lab practices
Protects human & environmental health
What is covered under 21 CFR 58?
In vitro studies
Animal studies
Environmental safety tests