AP Psych Unit 2 - Cognition
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
bottom-up processing
A cognitive process that begins with sensory input, where perception starts with the stimulus and builds up to a final interpretation.
top-down processing
A cognitive process that starts with higher-level cognitive functions, such as beliefs and expectations, which influence perception and interpretation of sensory information.
schema
a mental framework that helps organize and interpret information.
perceptual set
a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another, influenced by expectations and prior experiences.
Gestalt: closure
the tendency to perceive incomplete figures as complete by filling in gaps.
Gestalt: figure and ground
the organization of visual fields into objects (figures) that stand out from their surroundings (ground).
Gestalt: proximity
the tendency to group close objects together
Gestalt: similarity
the tendency to percieve similar objects as a group
change blindness
missing environmental changes because of limited attention capacity
cocktail party effect
the effect of percieving only specific words (like your name) out of a lot of sound
binocular depth cues
visual information from both eyes that helps perceive depth and distance.
retinal disparity
the difference in how your eyes can see the world - has to do with why you see 2 fingers when you place your finger far away from your eyes
convergence
the inward turning of the eyes when focusing on a close object, helping to perceive depth.
monocular depth cues
relative clarity, relative size, texture gradient, linear perspective, interposition
autokinetic effect
the optical illusion where a stationary point of light appears to move in a dark environment, often due to eye movements.
prototype
a mental expectation of what some kind of object or idea should look like
concept
a mental category used to group similar objects, events, or ideas, helping to organize knowledge and facilitate communication.
assimilation
associating new information with an existing schema
accommodation
changing an existing schema to fit new information
representativeness heuristic
interpreting an event in a particular way because of how similar it is to an existing prototype - leads to stereotypes
availability heuristic
interpreting an event in a particular way based on how quickly you remember a similar event
mental set
the tendency to operate using a framework that worked in the past
priming
the process by which exposure to a stimulus influences response to a subsequent stimulus, often unconsciously.
framing
influencing someone to believe something or behave a certain way by the language/stimulus used (Ads, etc)
gambler’s fallacy
believing the statistical likelihood for something changes based on how many times it’s happened (flipping a coin)
sunk-cost fallacy
the tendency to not abandon something after investing a large amount of time/effort/money into it, even if the losses will be greater than the rewards
executive functioning
The cognitive processes that enable goal-directed behavior, including planning, decision-making, and impulse control.
creativity
innovation (exploring new things), venturesome personalities, expertise in specific areas, collaboration
divergent thinking
the ability to think “outside of the box”
convergent thinking
thinking based on prior knowledge/experience
functional fixedness
not being open to trying things a different way/being unable to come up with alternative solutions because the typical way to solve a problem is unavailable.
explicit memory
clear memories of events, memorization
episodic memory
memory of personal experiences/events
semantic memory
facts/general knowledge
implicit memory
doesn’t require active recall
procedural memory
memory of skills, “muscle memory”
prospective memory
remembering to do something you planned or needed to do
long-term potentiation
the strengthening of synaptic signals over time to create and strengthen memory pathways
working memory model
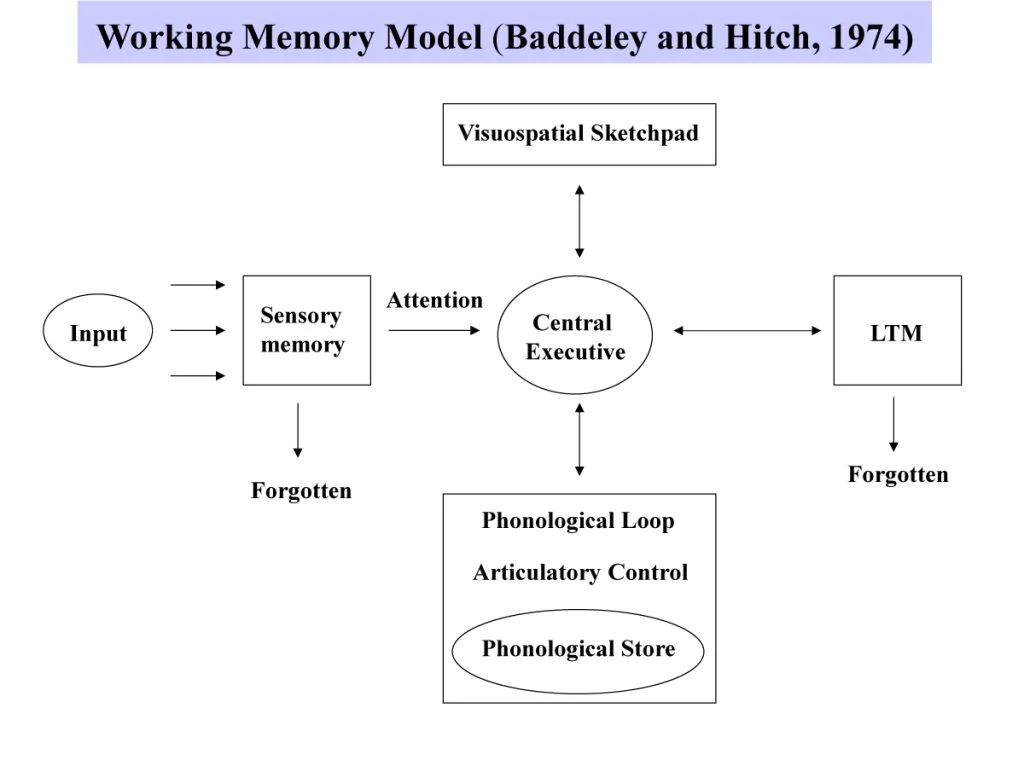
central executive
controls slave systems; part of working memory; in charge of processing sensory info
visuospacial sketchpad
slave system that holds images and sensory information
phonological loop
slave system that contains verbal content
multi-store memory model
sensory information → short-term memory → long-term memory (if important)
short-term memory
short-term, stays only when needed, then forgotten
long-term memory
encoded permanently, can be retrieved
sensory memory
short-term memory of sounds (echoic) or images (iconic)
consolidation
transformation of short-term memory into long-term memory
hippocampus
where explicit memories are stores
basal ganglia
skills like walking, writing, etc
cerebellum
forms associations - implicit memory
automatic processing
thinking that is fast and automatic
effortful processing
active interpretation
structural encoding
encoding based on form of words
semantic encoding
encoding based on meaning of words
phonemic encoding
encoding based off the sound of the words
spacing effect
reviewing things learned at intervals to increase recollection
serial position effect
remember things better that are at the beginning or end of a series
recency effect
remember the most recently learned information
primary effect
first items in a series remembered better because you rehearse them to yourself