Lecture 15 | Environmental Economics
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cap & Trade, Economics, Money & Persuasion, Policy Instruments, Carrot & Stick, Tangible & Intangible Factors, Valuing Environment, & Damaging Environment | Key Concepts & Ideas
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Environmental Economics
control pollutions, promote sustainability in capitalistic/democratic society
How is environmental economics concerned with both capitalism and democracy?
businesses and laws
Environmental economics is about _____ and ______
money, persuasion
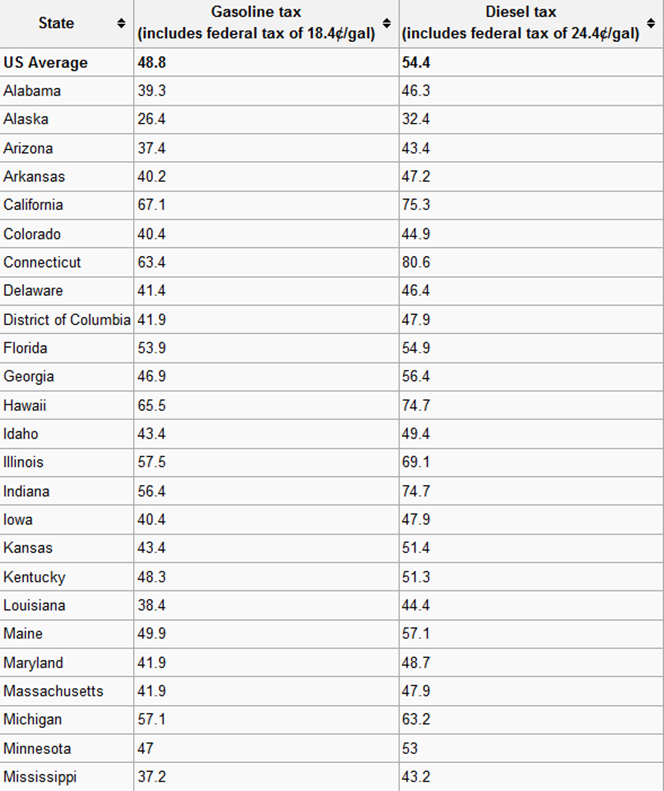
What is a gas tax intended to do? Consider the definition of environmental economics
raise money for government, persuade people not to drive as much
How does a gas tax encourage people to behave how we want?
incentive not to drive, less driving is less pollution/traffic/wear & tear
What is the principal idea behind environmental economics?
use tools to encourage behavior from people & businesses
Policy Instruments
tools used to change behaviors
What are 4 examples of policy instruments?
laws, regulations, taxes, & subsidies
Why do we want to change the behaviors of businesses and people?
there’s something we want to protect

Tangible Factors
a physical thing you can see/touch, house, wetland, stream
What are examples of policy instruments used to protect tangible factors?
laws, wetland protection act, clean water act (rivers & streams)

Intangible Factor
not physical, still has value, sunset, clean water, fun

Explain why clean water is both a tangible and intangible factor:
water is tangible, but sense of safety to drink it intangible
Why do we want to discourage certain behaviors?
they remove/reduce the value of tangible/intangible factors
What should businesses be discouraged from? What policy instruments can we use to do so?
polluting, environmental regulations (fines for polluting/exceeding limits)
What should people be discouraged from? What policy instruments can we use to do so?
damaging public property, fines for littering, trespassing, & damaging
What principle should be respected always? How can we use policy instruments to ensure it is upheld?
precautionary principle, criminal penalties for killing endangered species

What are some ways we can use policy instruments to encourage behaviors we want?
subsidies to install solar panels, HOV lanes for carpooling, subsidies for farmers to grow less profitable crop, getting a nickel back for recycling
What are the most effective/best policy instruments?
include BOTH carrot/encouragement and stick/discouragement
How does the gas tax employ both the carrot and the stick?
stick = cost of gas going up, carrot = incentives to buy hybrid/electric
How does the Cap & Trade model employ both the carrot and the stick for CO2 emissions?
stick = new taxes on emitting, carrot = ability to profit trading unused credits

Consider a company that is dumping waste into a river. What is key to remember about making environmental economic decisions?
complex decisions, balance rights & costs

Describe how valuing environmental damage can be easy:
when you can assign monetary value to the damage

Describe how valuing environmental damage can be difficult:
difficult to associate monetary value with damage to experiences
Which of the following is NOT an example of valuing environmental damage that is easy?
agricultural runoff leads to a nearby pond becoming a scummy mess
Which of the following is NOT an example of valuing environmental damage that is difficult?
you buy a property and build an evaporation pond that ruins the soil and leads to $1.5 million loss in value
How do those damaging the environment have the upper hand in defending the damage they caused?
easy to value their profits, hard to value the damage
Commons
resource openly available to all, provides benefits, environment

What are 5 common benefits the environment provides?
cfrrp: clean air & water, food, raw resources, recreation, pollution processing
What is the effect of a private entity damaging the environment?
lose access to benefits worth $33 trillion

Factory A and Factory B both use the river to produce their goods. Factory A dumps their waste into the river upstream of Factory B. How does this affect Factory B?
spend money to clean water, charge customers more, outcompeted by A
What are the two perspectives of recreation?
common good to enjoy, too much traffic causes damage
What is a policy instrument that can be used to balance enjoyment and protection of recreational sites?
admission/entrance fees
Describe how using entrance fees for recreational sites applies to the principles of environmental economics:
generates money to fix damage, discourages too many people from visiting
What are 4 reasons why people damage the environment?
sibr: short term, individual profit, believe benefits end, resources grow slowly
Describe how people thinking short term harms the environment:
lag time, no one wants to give up benefits today to prevent losses in future
Describe how individual profit being more valued than aggregate loss harms the environment:
more concerned with personal gain than how the benefits cost the entire group
Describe how no one believing environmental benefits will end harms the environment:
minimize our effect on environment, nimby, no one thinks their impact harms environment
Describe how environmental resources growing slowly actually causes people to harm the environment more
get the resource before someone else does