Unit 0 - Intro to Psychological Science Practices
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
psychology
scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of humans and other animals
behavior
any observable and measurable action taken by a person or other animal (anything a person/animal does)
mental processes
internal, subjective experiences inferred from behavior (sensation, perceptions, dreams, thoughts, beliefs, and feelings)
theory
explanation using an integrated set of principles that organize observations and predicts behavior and events
hypothesis
a testable prediction, often implied by a theory
case study
one individual or group studied in hopes of revealing universal principles
meta-analysis
type of research that analyzes data from multiple previous studies
naturalistic observation
observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate or control the situation
experiment
only research method that forms cause and effect relationships
independent variable
variable being manipulated
dependent variable
outcome being measured
experimental group
subjects receiving the treatment
control/placebo group
subjects not receiving treatment
random assignment
assignment of participants to experimental and control groups by chance, minimizing preexisting differences between the groups
random sample
each person in a population has equal chances of being chosen for the study
representative sample
group being studied reflects the larger population
The Placebo Effect
change in dependent variable due to belief in independent variable
correlation
measure of extent to which 2 factors may vary together and how well they predict one another
positive correlation
2 sets of data tend to rise and fall together
negative correlation
1 set of data rises while the other falls
correlation coefficient
statistical index of relationship between 2 variables
scatterplot
graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of 2 variables
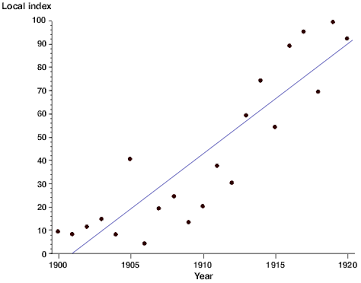
illusory correlation
perceiving a relationship where none exists/perceiving a stronger-than-actual relationship
operational definition
carefully worded statements of exact procedures (operations) used in a research study
confounding variables
factor other than the factor being studied that might influence a study’s results
sampling bias
flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample
participant bias
(un)consciously behaving in a way to ensure research outcome fits expectations that the subject perceives the researcher wants to find
experimenter bias
(un)consciously conducts research to ensure outcome fits expectations
quantitative data
numbers
qualitative data
categorical results
descriptive statistics
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups
inferential statistics
numerical data that allows one to generalize/infer from sample data the probability of something being true of a population
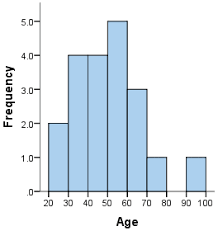
histogram
pie chart
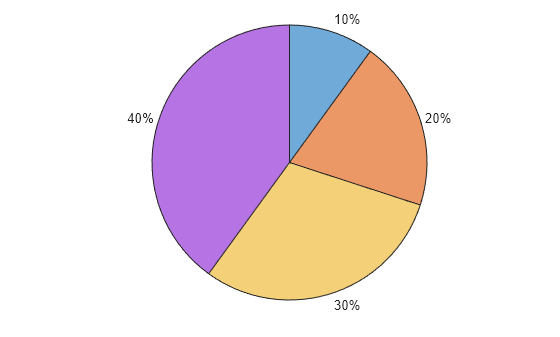
mean
average of a data set
median
score found at the exact middle of a data set
mode
most occurring value in a data set
range
difference between the highest and lowest values of a data set
standard deviation
measurement of the amount of variation in a data set
distribution
shape of the graph when all values are plotted
positive distribution
when data is skewed to the left
negative distribution
when data is skewed to the right
normal curve
when the graph has a symmetrical distribution
statistical significance
how likely it is that the resulting data occurred by chance
p-value
measure of statistical significance
institutional review
ensures ratified involving human and/or animal participants are conducted ethically and responsibly
informed consent
voluntary agreement given by a competent adult to participate in a study
informed assent
agreement to participate given by individuals not able to give informed consent (IC from a legal guardian also needed)
protection from harm
participants must not be exposed to unnecessary physical or psychological risk
confidentiality/anonymity
no personal information relating to the participants is shared
necessary deception
intentionally misleading or withholding information when research demands it
proper debriefing
researchers must explain the true purpose of the study and reveal any deception that was used and why it was necessary
structuralism
early perspective focused on identifying elements of thought and the mind
functionalism
early perspective focused on the purpose of elements
behavioral approach
focus on what can be measured, counted, and recorded (reflexes and behaviors)
cognitive approach
focus on thoughts
psychodynamic approach
focus on the unconscious
biological approach
the mind is what the brain and body do
humanistic approach
optimistic focus on each person reaching their full potential
sociocultural approach
society and culture influence our behavior
evolutionary approach
focus on purpose and aspects of humanity that benefit reproduction and the continuation of the human species