LIFESCI 3K03 Topic 6 Part I: Brain Control - Prefrontal Cortex
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:23 AM on 12/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
1
New cards
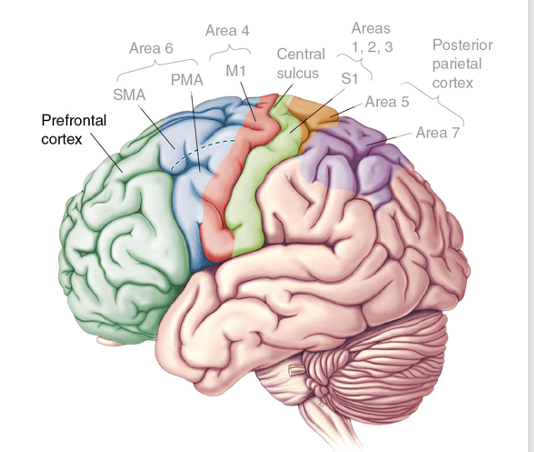
explain prefrontal cortex and what executive function is
- Highest in the chain of command and greatest complexity
- Identifies a goal and determines what needs to be done to accomplish this
“What you need to do”
- Highly connected with sensory cortex
Executive Function (EF):
- Higher cognitive processes for planning, organizing, and controlling thoughts, speech, and behaviors
- Involves a wide-range of skills
- Identifies a goal and determines what needs to be done to accomplish this
“What you need to do”
- Highly connected with sensory cortex
Executive Function (EF):
- Higher cognitive processes for planning, organizing, and controlling thoughts, speech, and behaviors
- Involves a wide-range of skills
2
New cards
executive function and movement: describe goal-directed actions and attention
1. Goal-directed actions
Organizing
- What is the goal and how does this relate to the current sensory state?
Planning
- What will need to be done to accomplish the goal?
Directing
- Sending this information to the next processing station (i.e., motor cortex)
2. Attention
Multitasking
- Allocating attention among tasks performed simultaneously
Response inhibition
- Respond effectively with distractions/irrelevant information
- Similar to a second level of “sensory gating” (i.e., thalamus filtering)
Organizing
- What is the goal and how does this relate to the current sensory state?
Planning
- What will need to be done to accomplish the goal?
Directing
- Sending this information to the next processing station (i.e., motor cortex)
2. Attention
Multitasking
- Allocating attention among tasks performed simultaneously
Response inhibition
- Respond effectively with distractions/irrelevant information
- Similar to a second level of “sensory gating” (i.e., thalamus filtering)
3
New cards
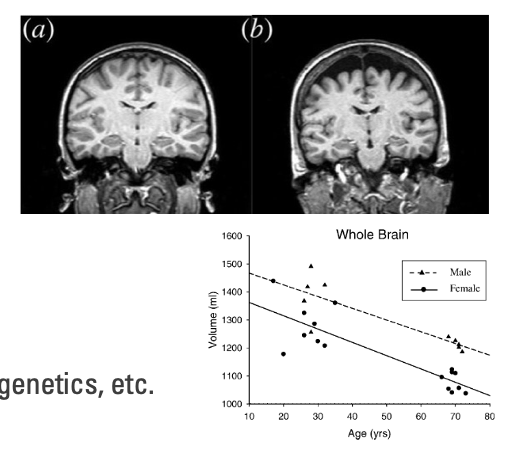
explain executive function and aging
Executive function declines with age
- Lesions in white matter
- Loss of gray matter
- Loss of dendritic branching
Changes are highly variable
- Decline can be minimal in healthy aging
- Influenced by things like lifestyle, education, genetics, etc.
- Lesions in white matter
- Loss of gray matter
- Loss of dendritic branching
Changes are highly variable
- Decline can be minimal in healthy aging
- Influenced by things like lifestyle, education, genetics, etc.
4
New cards
what are some aging related declines?
Overall processing speed
Problem solving ability
- Organizing, planning, directing
Controlling attentional resources
- Multitasking and response inhibition
Declines are not to a level of dysfunction in healthy aging
Problem solving ability
- Organizing, planning, directing
Controlling attentional resources
- Multitasking and response inhibition
Declines are not to a level of dysfunction in healthy aging
5
New cards
changes in gait parameters with age
decrease in gait speed
decrease in step length
increase in step time
increase in variability in these parameters
- however, healthy older adults may have little to no change
- reduced EF may be an important driver of these changes
decrease in step length
increase in step time
increase in variability in these parameters
- however, healthy older adults may have little to no change
- reduced EF may be an important driver of these changes
6
New cards
executive function and gait
Gait is a complex motor task that uses executive function
- Not fully managed by CPGs (especially in humans)
- EF needed to plan, organize, and direct of movements
- Often must also divide attention to other tasks
EF allows effective division of attention between gait and other tasks
- Dual-task or Multi-tasking (e.g., Walk and talk/text)
- Not fully managed by CPGs (especially in humans)
- EF needed to plan, organize, and direct of movements
- Often must also divide attention to other tasks
EF allows effective division of attention between gait and other tasks
- Dual-task or Multi-tasking (e.g., Walk and talk/text)