CIS 125 Ch.1 Quiz
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Information Technology
hardware, software and media used to store, organize, retrieve and communicate information
Information systems
organized combination of hardware, software, infrastructure, data and people used to accomplish a specified organizational or personal objective
What do technologies have in common?
they deal with information
What are the three emerging technologies that will have a great impact on the future?
5G, IoT, and AI
What is 5G?
Fifth-generation cellular networking which can handle information better than prior generations.
IoT
Internet of Things; refers to an infinite network of connected sensors embedded in physical objects
Examples of IoT
smart homes, sensors in automated cars, and fitness trackers
IoT Percentage in security and surveillance
40%
IoT percentage in industrial automation & manufacturing
39%
IoT percentage in Process automation
also 39%
IoT percentage in Environmental, social, & corporate governance
33%
IoT percentage in Advanced measurement infrastructure & smart meters
32%
IoT Percentage in connected consumer electronics
29%
What is AI?
Artificial Intelligence; a family of technology that is close to the human cognitive abilities; used in many tools such as machine learning, natural language processing, and expert systems
Generative AI
tools that create content such as text, images, videos, & audio; includes ChatGPT, Gemini, Copilot, etc.; can supplement human activity like brainstorming and critiquing
How to use AI responsibly?
Encourage learning (not bypass it); collaboration (not substitution); avoid plagiarism; be transparent; be critical; keep data privacy; check to see if it is approved by professor
What is VR?
Virtual Reality; fully immersive experience in which the tech makes you sense that you are in a different environment
What is AR?
Augmented Reality; systems overlay information on top of elements of the real world
Mixed Reality
combines elements of real and virtual worlds allowing users to interact with both physical and virtual worlds
DIK Hierarch
Data—→Information——>Knowledge——>Wisdom
Data
raw, unorganized facts, observations, and symbols with no inherent meaning on their own
Information
Data that has been organized, processed, and structured to provide context and meaning, often answering "Who," "What," "When," and "Where" questions.
Knowledge
A deeper comprehension of information, including concepts, principles, and axioms, derived from processed information and experience
Wisdom
The ability to apply knowledge, often with ethical consideration and foresight, to make sound decisions and predictions.
Connectedness
information requires connecting data elements to give them context and meaning
Usefulness
information that is interpreted and applied is useful, leading to knowledge
What does poor information literacy lead to?
information asymmetries
Good quality information in business improves
productivity, regulatory compliance, high-quality decision making
Bad information can cause
Legal issues, harmed reputations, missed opportunities, lost revenue
Intrinsic Quality
important dimensions of quality regardless of the context or how the information is represented.
Contextual Quality
dimensions that may be viewed differently depending on the task at hand.
Representational quality
how the information is provided to the user.
Accessibility Quality
whether authorized users can easily access the information.
Information Quality Dimensions
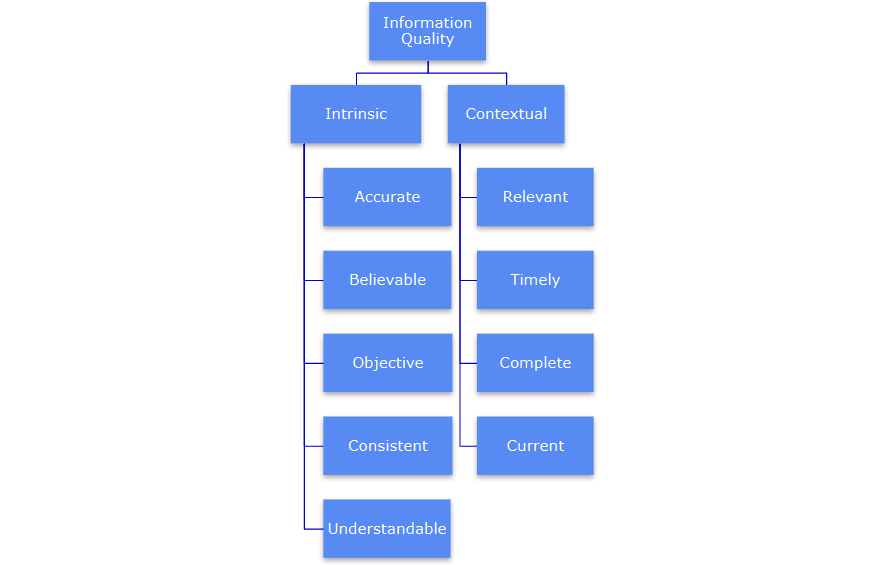
Accurate Info.
correct; free from error and is reliable
Believable
regarded as credible and true
Objective
free from bias
Understandable
easily comprehend
Consistent
compatible with previous info.
Relevant
applicable and useful for task at hand
timely
available in time to perform the task at hand
complete
of sufficient depth and breadth for task at hand
current
sufficiently up-to-date for task at hand
Business uses of info.
communication, support processes, decision making
Business process
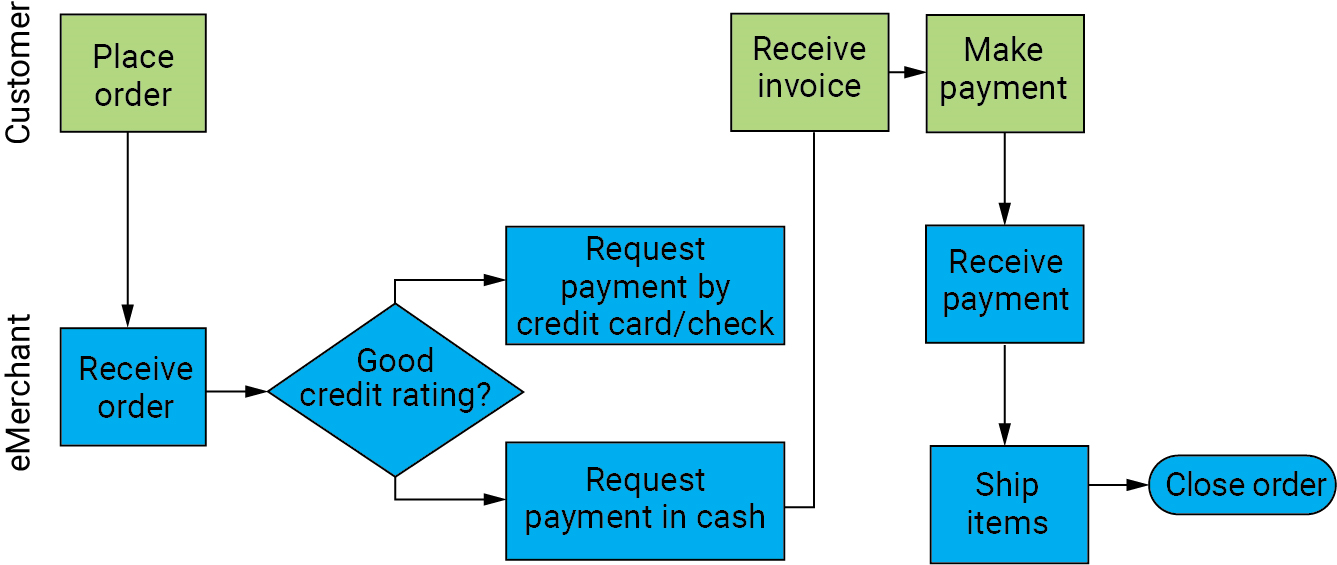
What do information systems careers focus on?
designing, building, supporting, or managing information systems
Information analysis careers do what?
they make use of systems to retrieve, report, and analyze information contained in the systems