IB Chemistry HL - CHAPTER 7
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards
Conditions of dynamic equilibrium
1. the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
2. happen in a closed system.
3. the concentrations of the reactants and products is constant.
4. there are no changes in macroscopic properties.
2
New cards
Reaction constant

3
New cards
Kc > 1
Greatest concentration of products.
4
New cards
Kc < 1
Greatest concentration of reactants.
5
New cards
New reaction constant by doubling coefficients

6
New cards
New reaction constant by reversing the reaction
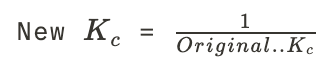
7
New cards
The reaction quotient,Q
The reaction quotient, Q, is the ratio of products and reactants for a reaction that has not yet reached equilibrium.
8
New cards
Q = Kc
The reaction is at equilibrium
9
New cards
Q < Kc
The reaction proceeds to the right
10
New cards
Q > Kc
The reaction proceeds to the left
11
New cards
Increase in concentration of reactants
Reaction proceeds to the right.
No change in Kc.
No change in Kc.
12
New cards
Decrease in concentration of reactants
Reaction proceeds to the left.
No change in Kc.
No change in Kc.
13
New cards
Increase in concentration of products
Reaction proceeds to the left.
No change in Kc.
No change in Kc.
14
New cards
Decrease in concentration of products
Reaction proceeds to the right.
No change in Kc.
No change in Kc.
15
New cards
Increase in temperature
Reaction proceeds to the endothermic side (+T = +∆H).
Kc changes.
Kc changes.
16
New cards
Decrease in temperature
Reaction proceeds to the exothermic side (-T = -∆H).
Kc changes.
Kc changes.
17
New cards
Increase in pressure
Reaction proceeds to the side with the least gaseous molecules.
No change in Kc.
No change in Kc.
18
New cards
Increase in pressure
Reaction proceeds to the side with the most gaseous molecules.
No change in Kc.
No change in Kc.
19
New cards
Effect of a catalyst
No change.