CS 215 Before Midterm
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What are the core technologies that enable the Internet to work?
While there are a wide variety of protocols that make ups the Internet, the ones that are necessary for minimal operation are:
Internet Protocol (IP),
transmission control protocol (TCP),
and user datagram protocol (UDP).
What are some examples of applications that need reliable communication (TCP)? What would be better server with low latency communication (UDP)?
reliable: online banking, web content delivery
low-latency: video streaming, audio, game score updates
Why are IP addresses and domain names necessary? What is the mechanism for translating between them?
IP addresses are for computers. Domain names are for humans.
The mechanism for translating between them is called DNS.
What is the difference between the Internet and the Web
The Internet consists of all of the computers connected to one another using the Internet Protocol (IP). There are a wide variety of other protocols and supporting applications built upon the Internet.
The web is one such example, using HTTP as the protocol, along with web servers and web browsers as applications that "speak" this protocol.
What are the roles of the web browser and web server within the client-server architecture of the web?
The web browser is what is used by the human. Based on the user interaction (entering a URL, clicking on a link, etc.), it requests information from the web server.
The web server does not initiate any requests; it only responds to requests from the web browser, providing the necessary content. Otherwise, it remains idle.
What is the purpose of :// in a URL?
The colon (:) is the divider between the scheme and the object-address.
The double slashes (//) specify that what follows will be the name of the computer to send the request to. As a result, the // should be thought of as going with the domain name (e.g., //www.cs.uregina.ca), rather than thinking of it as part of the separator.
Why is the host header necessary when requesting a page from www.cs.uregina.ca using HTTP?
When your browser turns www.cs.uregina.ca into an IP number using DNS (in this case 142.3.150.53), the response also specifies that the canonical name for the computer is actually hermes.cs.uregina.ca.
It is possible for a single computer to have many different domain names mapped to its one IP address. This is the basis for virtual web hosting (where many different websites are hosted by the same server). Since your browser now knows that 142.3.150.53 has more than one domain name, it also knows that it needs to specify which host it wanted to talk to in the first place. This is why is sends the host header as part of the HTTP request.
What is the key difference between HTTP/1.0 and HTTP/1.1?
HTTP/1.0 closes the TCP connection to the server after the response have been received.
HTTP/1.1 specifies that the TCP connection be kept open for a short period of time after the response is received, giving the browser a small window of opportunity to request the supporting documents (if necessary).
Since hypertext documents may contain links to content that is hosted on the same server as the page itself, keeping the connection open for a short period of time can allow this content to be retrieved more quickly. This is because the overhead of creating a new TCP connection can be saved.
Why is the user interface so important in websites?
Most web applications are designed to be used by people with little or no training on the software. As a result, the interface is fundamentally important; it is the gateway to the functionality of the site.
What is the main purpose of documenting the usability requirements separate from the functional requirements?
The usability requirements allow us to match the required functionality to the design of the interface. It allows us to consider what the core user tasks are, as well as the necessary but less common tasks.
The core user tasks should be easily and readily identified in the interface. The less common tasks should be easy for the user to find and remember how to use.
What are the key features of the four design principles discussed in this course?
Grid-based design: line things up; put the important things where people look.
Hierarchical navigation: organize content in a hierarchy; consider carefully whether it is better to be broad & shallow vs. narrow & deep.
Consistency: be consistent in the writing, fonts, layout, and style; any deviation from the "design language" will make users wonder why things are now different.
Subtlety when drawing attention: when you need to draw the user's attention to something, do so with subtle changes to the page; drawing attention to too many things draws attention to nothing.
What are the Five E’s of Usability?
Effective, efficient, engaging, error-tolerant, and easy to learn. We can use this as a checklist when designing the user interface to ensure that we are supporting the users appropriately as they perform their tasks.
Effective - can they easily do a task correctly?
Efficient - can the user complete a task quickly?
Engaging - positive experience, going to different pages, different components, interactions on the page
Error-Tolerant - if a user makes a mistake, it is easy to recover
Easy to Learn - user can quickly understand how to use the interface
What is the purpose of sketching?
The purpose of sketching (in many different disciplines) is to think and reason about potential designs, evaluate and refine the designs, and shape new ideas. It is meant to be an active process that results in many different sketches, rather than documenting some final design.
What is the relationship between prototypes and sketching?
Sketching is a design process of thinking, reasoning, evaluating, and refining design ideas. A sketch itself can be considered a low-fidelity prototype of the interface. As a result, it can be evaluated in consideration of the tasks the user needs to perform, adherence to design principles, and whether it is usable.
What is the difference between sketching and storyboarding?
Sketching a single interface screen is a method for creating a low-fidelity prototype. It shows a single page view of the website. For tasks that are complex and require the user to visit multiple pages in the site, storyboards are used to illustrate the steps in the task and the pages that are viewed. Both allow you to think and reason about whether the interface design is usable (efficient, effective, engaging, error-tolerant, and easy to learn).
Why is the hyperlink tag called an anchor tag?
The anchor tag specifies a particular element on the page to serve as the anchor for a hyperlink. The content of the <a> tag is called the anchor. The location specified in the href attribute is the destination. Here, "href" refers to the "hypertext reference".
Why is it good practice to continue to follow the XHTML syntax rules, even when writing HTML5 documents?
XHTML enforces rules that make an HTML document precise and unambiguous. Following these rules continues to make valid HTML documents, and ensures that we are telling the browser exactly what we mean.
Which tags are necessary to build a minimal webpage?
Note that HTML5 says that the <html>, <head>, and <body> tags are optional, you should assume that they are mandatory in order to build a precise and complete document.
What is the difference between the GET and POST methods for a form tag?
The GET method sends the form data embedded in the URL, using the question mark to separate the file name from the data, and [variable]=[value] pairs for the data separated by the ampersand. The POST method embeds the data within the body of the HTTP request.
Before using any of the new tags specified in HTML5, what should we do?
Since not all browsers yet support all of the new features of HTML5, we should check that the feature or new tag that we want to use is supported in our target web browser.
Of the three ways to add CSS to HTML documents, which is the preferred way and why?
CSS can be added inline within an HTML tag, at the document-level, and via external files. External CSS is preferred since it allows one CSS to be applied to multiple HTML documents, and enables efficient debugging and modification (only one file needs to be updated).
Given that there are so many different types of selectors, how do you know which to use when applying a style to an element?
Your general goal is to keep things as simple as possible. Start with a generic style that can be added using the universal selector (e.g., fonts applied to all elements). For styling that is applied to every instance of an element, use the simple selector (e.g., style applied to alltags). For any further styling, use the class or generic selectors, depending on whether the style should be applied to a single tag (class) or different types of tags (generic). Use the other selectors only in very special cases where the style cannot be applied using these simple rules.
Because of the high degree of flexibility of CSS, it is possible for multiple rules to be applied to the same HTML element. How are conflicts resolved?
The conflict resolution in CSS is based on a sorting process, which is called "the cascade". The general rule is that more specific specifications take precedence over more general ones. The general order is id, class/generic, contextual, simple, and universal. If there is still a tie, precedence is given to the most recently loaded specification (last specification in the last CSS file loaded).
What is the value of using CSS Grid Layout instead of tables or CSS positioning to align elements?
The old way of producing a grid-based design in a web page was to use tables. The problem with this is that the layout of the page is specified in the HTML code, where it should be in the CSS specification. An early solution to this was to use position and float to align parts of the page, but this was sometimes fragile. The new solution is to use CSS Grid Layout. It allows for the grid structure to be specified, along with styles for the individual elements, all written in CSS. The HTML code can then simply specify the content to go into the grids.
What happens with parseInt and parseFloat functions if the string does not start with a number?
Any leading and trailing spaces are ignored. If the first character after spaces are removed cannot be converted to a number, the function returns NaN.
What happens if you try to multiply an integer by a “abc” string?
(let x = "abc"; let y = 3 * x;)
The result will be NaN since abc can’t be coerced into an integer
How is “===” different from “==”
“===” no coercions are performed, compares both the value and the type of the variable
“==” only compares the value using coercions
What is the output of:
var x = [3, 5, 2, 1, 4, 10, 12];
x.sort();
document.write("sorted order: " + x.toString() + "<br/>");
sorted order: 1,10,12,2,3,4,5
What is the output of:
var x = [3, 5, 2, 1, 4, 10, 12];
function num_order(a, b) {
return (a - b); }
x.sort(num_order);
document.write("sorted numerically using a sort function: " + x.toString() + "<br/>");
sorted numerically using a sort function: 1,2,3,4,5,10,12
What are the three elements of the JavaScript Language?
Core JavaScript provides the core programming constructs (variables, operators, expressions, statements, functions, etc.).
Client-Side JavaScript provides objects that support interaction with the browser.
Server-Side JavaScript provides objects that support interaction with the web server.
Why should you prefer to use implicit embedding of JavaScript in HTML, rather than explicit embedding?
Implicit embedding places the JavaScript code in a separate file, which can then be linked to as many different HTML files as needed. As a result, this method supports the reusability of code. In addition, by linking to an external file, bug fixes in the code only need to be done in one place, supporting the maintainability of the code.
What is the difference between the undefined and null data types? What is an example of encountering an undefined variable?
Null is the data type assigned when no memory allocation has been made. This happens when a variable is used before it is declared. For example, suppose the variable 'a' has not yet been declared. When it is used in the following statement, it is null: var x = a + 3;.
An undefined variable is one that has been declared, but has not been assigned a value. In the example, above, if you issued the statement 'var a;' first, the variable is declared but has not been given a value (and by extension a data type). As a result, it is of type undefined.
The + operator provides both number and addition and string concatenation. If there is a string as either operand, it defaults to concatenation. What can you do to ensure that you get number addition?
In order to ensure that you get number addition when using the + operator, you must ensure that any variables that may contain string formatted numbers are explicitly converted to the Number data type. That is, you cannot rely on implicit coercions, and must instead perform explicit coercions. The most flexible of these are the parseInt and parseFloat methods, as they default to NaN when they fail.
Why is it that arrays can hold data of many different types?
Since JavaScript is a dynamically typed language, variables can change their data type as values are assigned. As a result, an array can hold any data type in each of its array elements.
What happens if you provide too few parameters in a function call? What about too many parameters?
If too few parameters are provided in a function call, the remaining variables from the function signature are undefined. If too many parameters are provided, the extras are ignored. In both cases, the function executes since this is not an error.
What are the three methods for creating objects in JavaScript?
The first method is to create a blank object using the Object constructor, and then dynamically assign properties and methods.
The second is to create a constructor function, and use this to create the object.
The third is to create a class that contains the constructor and methods, and use this to create the object.
Why are regular expressions so important in JavaScript programming
Regular expressions allow string patterns to be specified, which can then be used to perform search, replacement, and other string operations. Because much of what we need to do in web applications is verify string data, regular expressions are common.
What is DOM?
Complex data structure that represents everything that is in the webpage and programming.
An abstract model that defines the interface between HTML documents and application programs. It serves as an API (application programming interface) for accessing and manipulating the web page that is loaded in the browser.
What two objects are created as a web page is being loaded by a browser?
Window object:
represents the browser window that displays the document
properties and methods are visible to all JavaScript (implicit or explicit) within the document
treated as global variables and methods
all new variables and methods are added to the Window object
Document object
represents the displayed HTML document
a property of the Window object
What is an event in JavaScript?
notification that something specific has occurred
in JavaScript, an object is implicitly created by the browser in response to something having happened
What is an event handler in JavaScript?
a script (function) that is implicitly executed in response to the appearance of an event
What is an event registration in JavaScript?
the process of connecting an event handler to an event
assign the handler function to a DOM object property
Why is it important to define the event handler function before the event registration code is executed?
The name of the event handler function is passed as the second argument when we register the event listener. If we do not follow this order, the browser will not be able to register the event, and an error will be reported in the browser console indicating that it could not find the event handler function.
What is the difference between Core JavaScript and Client-Side JavaScript?
Core JavaScript provides the fundamental constructs of the programming language. Client-Side JavaScript adds a collection of objects and their associated methods and properties that enable programmatic interaction with the web browser and the HTML document it is showing.
How can we access the Document Object Model (DOM) using JavaScript?
The document variable is automatically created by the browser, and it holds the DOM. Using methods like document.getElementByID("abc") allows us to access elements from within the DOM (in this case, the one with id="abc").
What is the difference between DOM0 and DOM2 event registration?
In DOM0 event registration, the events are specified within the HTML tag (e.g.,). With DOM2, the events are explicitly registered on the elements using the method addEventListener(). The DOM2 method is preferred since it supports the separation of JavaScript from HTML.
What is the mechanism that allows events that occur on a child element to be passed to the parent element to deal with? What can be done to stop this from happening?
This is called "event propagation". If a user clicks on a <p> tag that is embedded within a <div> tag, it allows the event to reach the underlying <div> tag. This is called the "bubbling phase". If you are listening for the event on the child element and wish to stop the bubbling of the event up to the parent, execute the stopPropagation method of the event object.
If we register an event using the DOM2 method, what object is passed to the event handler?
The event handler function will receive an instance of the Event object. This object contains important properties and methods associated with the event itself. A critical property is "target", which is a reference to the element upon which the event occurred. We can use this property rather than document.getElementById to find the element that the event listener was added to.
Why is performing client-side form validation important?
By validating form data on the client side, we do not need to waste the limited server resources on processing data that is not correct. In addition, we can save on network resources. By validating on the client-side, the feedback is given more quickly, and we can do so even before the user has submitted the form by checking things as the user moves through the form (change, blur, and focus events).
What information should we provide back to a user when validating data in the form?
We should let the user know where the error occurred (which field), what the error is, and what the user can do to fix it. This supports the interface in being error tolerant, one of the Five E's of Usability.
What is the difference between change, blur, and focus events
The focus event fires when an element has received focus. The focus event is not cancelable.
The blur event fires when an element has lost focus.
A change event is an event that occurs when the value of an HTML element is modified
Give an example code:
In an event handler on a form element, if you find that the value is not the correct format, traverse the DOM from that element (event.target) up to its parent <div> tag (.parentNode), and then change its style to put a red border on the element to signify an error.
function validateAndHighlightError(event) {
const inputElement = event.target;
const inputValue = inputElement.value;
const isValidFormat = /^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/.test(inputValue);
if (!isValidFormat) {
let parentDiv = inputElement.parentNode;
// Traverse up until a <div> parent is found
while (parentDiv && parentDiv.tagName !== 'DIV') {
parentDiv = parentDiv.parentNode;
}
if (parentDiv) {
inputElement.style.border = '2px solid red';
}
} else {
inputElement.style.border = '';
}
}
What is Dynamic HTML?
Collection of technologies that enable an HTML document to be dynamically manipulated after it has been loaded in the browser. The primary components are JavaScript and browser-support for making changes in the DOM.
Why is it better to use JavaScript to change an element’s class, rather than change the CSS specification directly?
Changing the CSS specification directly in the object (the properties in the style object) can make debugging a little difficult since you have to interact with the interface to see the outcome. By specifying the different alternatives in CSS, you can test how they look simply by editing the class properties in the HTML code. With things sufficiently tested, changing the class is simply a matter of changing the className or editing the classList properties in JavaScript.
What can we do to change the class without affecting the existing classes that might be assigned to the element?
The classList property of an element is a list of the classes associated with the element. With that object, you can use the add method to add a new class to the list, or the remove method to remove a class. Such changed do not affect the other classes. This is in contrast to the className property, where changing it overwrites any existing classes that may have been assigned.
DO you have to do anything special after changing the DOM to force the browser to refresh what is show?
No. Any changed in the DOM (document object) are automatically reflected in the browser.
Suppose we wish to insert a new HTML element as a sibling of a particular element. What steps do we need to take?
First, you should create the new element using the document.createElement method. Then you should access the parent of the target node using the parentNode property. With that node, the appendChild method will add the new node as a child of the parent of the target (i.e., as a sibling).
Suppose we wish to insert a new HTML element as a sibling of a particular element. What steps do we need to take?
First, you should create the new element using the document.createElement method. Then you should access the parent of the target node using the parentNode property. With that node, the appendChild method will add the new node as a child of the parent of the target (i.e., as a sibling).
If we want an element to be moved to a specific location using JavaScript code, what do we need to specify in the CSS to allow this to happen?
In order for an element to be dynamcially positioned, the position must be set to either absolute or relative in the CSS. The difference is in what serves as the frame of reference. Then, setting the style.top and style.left properties of the element will move it to the desired location.
What additional properties are provided in the Event object when the event is a mouse event (click, mousemove, mouseover, etc.)?
The Event object will include properties that tell you where the mouse is in the browser window (clientX, clientY), where the mouse is in the display window (screenX, screenY), which button was pressed (button), and whether any of the control keys were held down during the event (altKey, ctrlKey, shiftKey, metaKey).
For a web-based client-server architecture, what is the communication mechanism between the client and the server?
HTTP
What is the purpose of sketching?
To document the final design
Why is HTTP/1.1 more efficient than HTTP/1.0 for retrieving hypertext documents?
because it keeps the connection open for a short period of time rathen then closing it and then having to request it again.
What is a trait of an 'efficient' interface?
The user can perform all tasks quickly
What makes a web design consistent?
Always use standardize abbreviations.
Present data values only when knowledge of these values is needed.
etc
Suppose you have an HTML element that is receiving CSS specifications due to a simple selector, an id selector, and a class selector. What is the order of precedence?
id first, then class, then simple selector
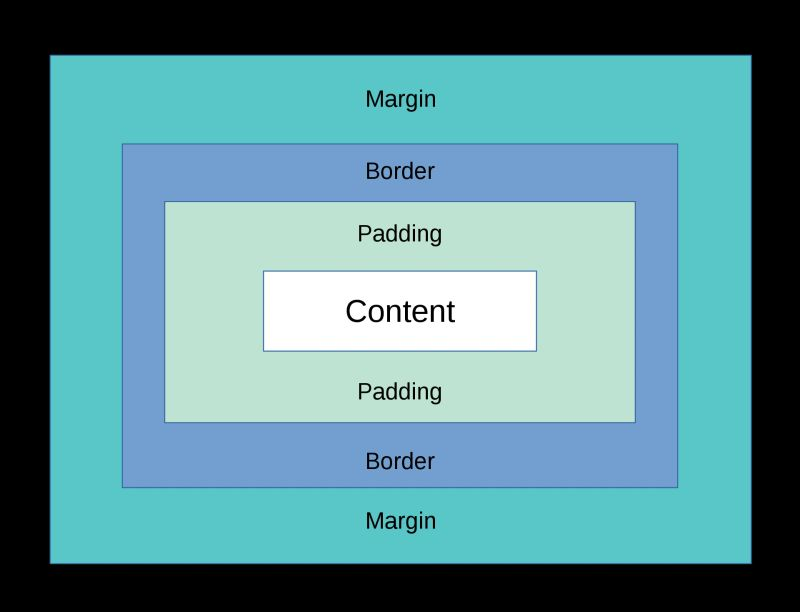
According to the box model, which CSS specifications adds more space between the border and the content of an element?
Padding
How do you add two class styles to the same paragraph?
<p class="a b">Hello World</p>
What are valid ways to create an array with the values 1, "two" and 3?
var a = new Array (1, "two", 3);
var a = new Array (3); a[0]=1; a[1]="two"; a[2]=3;
var a = [1, "two", 3];
How do you pass a function as a parameter assuming the function signature is "function order (a, b)"?
x.sort(order);
Which pieces of information are necessary for event registration?
the element on which the event is to be registered, the type of event and the name of the event handler function
When doing form validation, what property of a form element holds the data?
value
What happens if you try to call a function with fewer parameters than what it is specified to receive?
No errors - the missing parameters become undefined
What method for searching for elements in the DOM will return a single DOM element?
document.getElementById()
What is DOM?
tree structure
stands for "Document Object Model"
exists within the document variable