Particles and interactions AYr1
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Specific charge definition
the charge to mass ratio of a particle
Specific charge equation and units
charge/mass = Ckg^-1
nucleons definition
particles in the nucleus of an atom e.g. protons and neutrons
isotopes definition
an element with the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons
SNF range attractive
SNF range repulsive
0.5-3fm (femto metres)
0-0.5fm
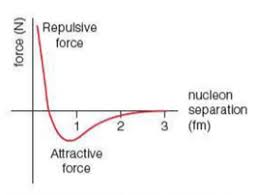
Strong nuclear force (SNF)
Fundamental force that binds nucleons together
counteracts electrostatic force of repulsion (between protons)
Strongest of the fundamental forces
Has both repulsive and attractive range to stop the nucleus collapsing in on itself
Strangeness completely conserved
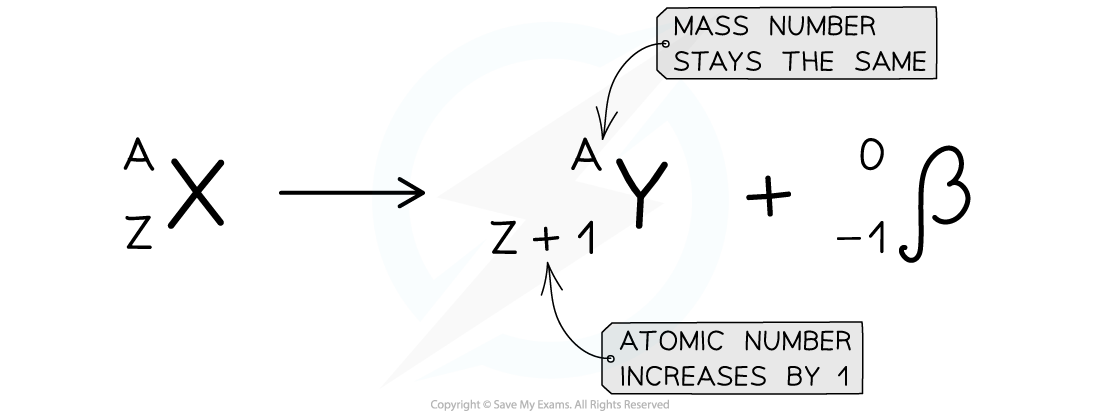
Beta minus decay equation
n → p + β− + νe/
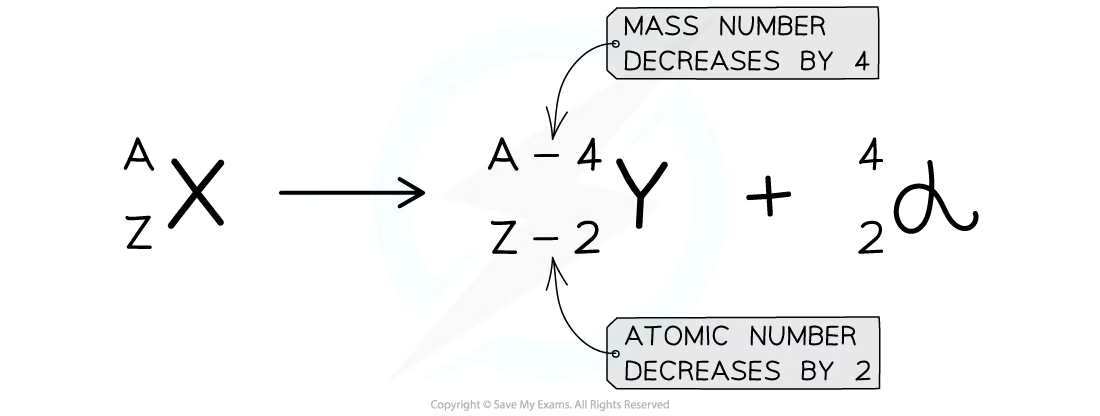
Alpha decay equation
Alpha particles are made of two protons and two neutrons. So 4 is nucleon number, 2 is proton number.
Antiparticle definition
A particle that has the same mass and rest energy of another particle, but all other properties are opposite (like charge) e.g:
proton and antiproton
electron and positron
neutron and antineutron
Photons
packets of electromagnetic energy
Annihilation
When a particle and antiparticle collide converting all of their mass into energy in the form of two photons
Equation for annihilation
E = mc² where c is the speed of light in vacuo
Pair production
Where a single photon is converted into an equal amount of matter and antimatter.
The energy of the photon has to be greater than the total rest energy of the particle and antiparticle
The excess energy is converted into kinetic energy
Fundamental forces (in order of strength)
Strong nuclear force
Weak nuclear force
Electromagnetic force
Gravity
Exchange particle
Also known as a virtual particle
Transmits the fundamental forces that hold nucleons, nuclei and atoms together
size of the exchange particles determines the range of the force
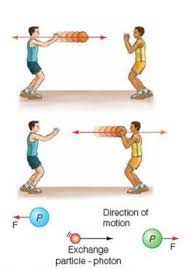
Exchange particle for (in spec only):
SNF
WNF
Electromagnetic (EMG)
Gravity
Pion (SNF)
W+ and W- (WNF)
Photon (EMG)
Graviton
Weak nuclear force (WNF)
Fundamental force that acts on all particles
Small range (10^-18)
Responsible for beta radiation (decay of neutrons into protons and electrons)
Responsible for nuclear fusion
strangeness conserved within +- 1
Electromagentic force
holds atoms together
Acts between all charged particles
Infinite range
Strength of interaction decreases with distance
Can be attractive or repulsive
Gravity
Weakest of the fundamental forces
Infinite range
Negligible on the atomic and nuclear scale
What are pions?
Exchange particles of the strong nuclear force
What is a kaon?
A particle decays into (only) pions
What is the quark structure of a K0 ?
K+?
K–?
down, anti-strange OR anti-down, strange
up, anti-strange
anti-up, strange
What is the quark structure of a π+?
π–?
π0?
up, anti-down
anti-up, down
up, anti-up OR down, anti-down
How are strange particles produced?
Produced through the strong interaction, they are always created in pairs
How do strange particles decay?
Weak interaction (e.g. kaons)
What is the only stable (free) baryon?
The proton is the only stable baryon into which other baryons eventually decay
What interactions do Hadrons decay by?
Strong, weak and electromagnetic. Leptons only decay by weak (and electromagnetic?).
Draw electron capture diagram and explain it.